MALE REPRO
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
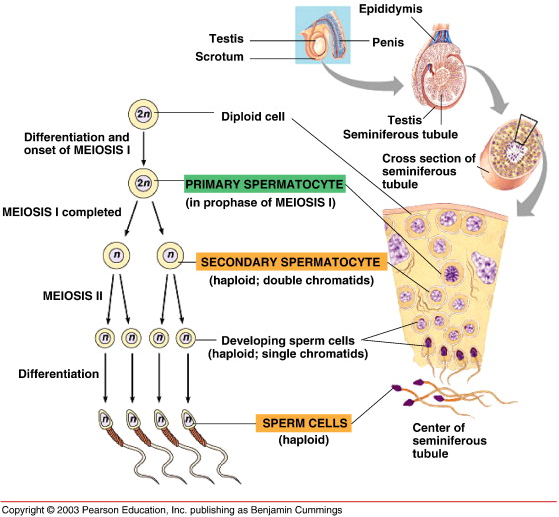
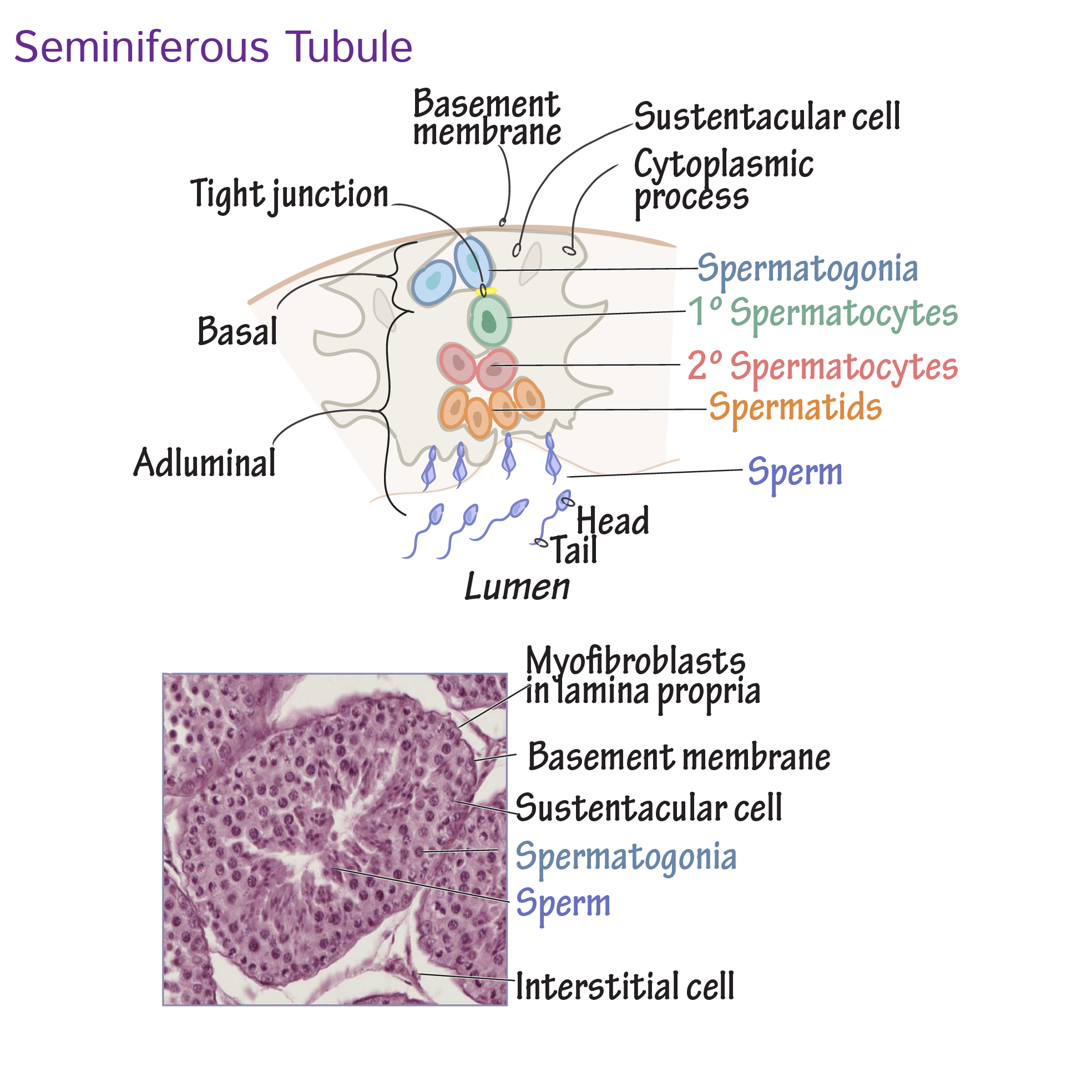
Spermatogonium
A male germ cell that is always in contact with the seminiferous tubule basement membrane.
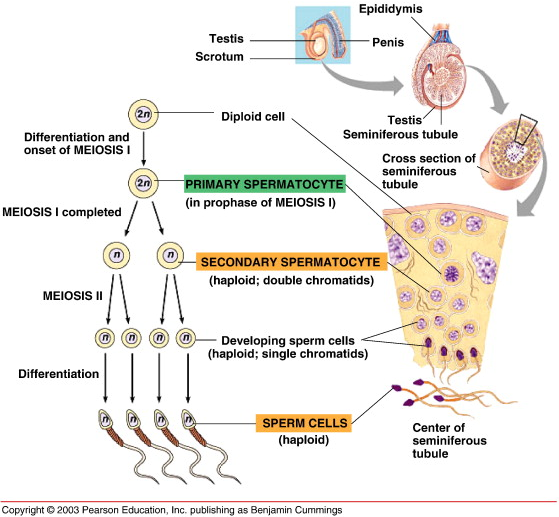
Primary spermatocyte
A diploid cell resulting from the mitotic division of spermatogonium, which divides via meiosis I.
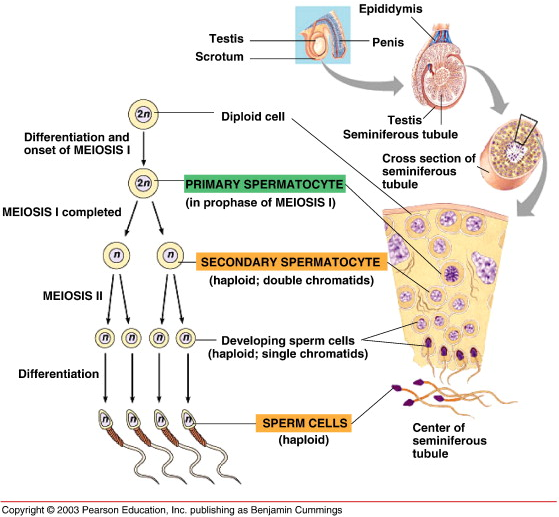
Secondary spermatocyte
A haploid cell that divides via meiosis II.
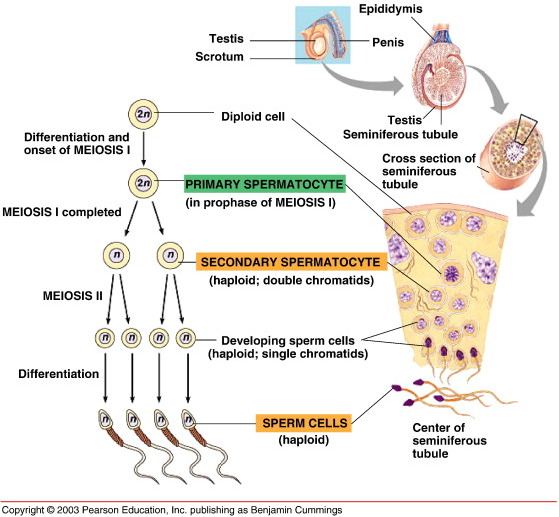
Spermatid
The cell formed after the second meiotic division that differentiates into sperm cells through spermiogenesis.
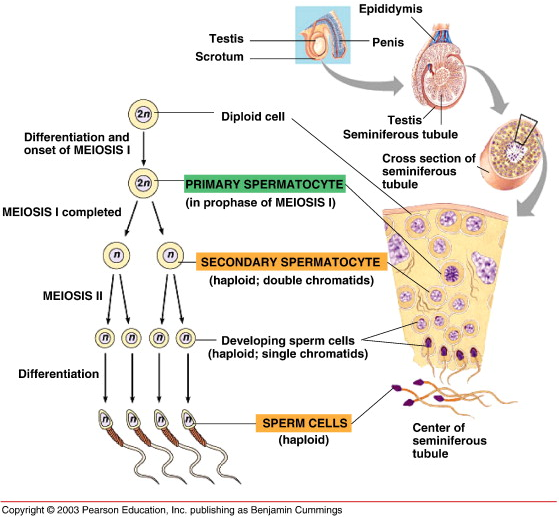
Spermatozoa
Mature sperm cells consisting of a head, midpiece, and tail.
Dartos muscle
A thin layer of muscle in connective tissue surrounding the scrotum responsible for wrinkling the skin.
Cremaster muscle
An extension of the abdominal muscles that raises or lowers the testes in response to temperature.
Erection
Result of parasympathetic activation causing vasodilation of penile arteries (smooth muscle relaxation in their tunica media)
Increased blood flow in the arteries results in an engorgement of the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum due to an increase in the blood volume within their sinusoids.
Corpora cavernosa
Two columns of erectile tissue in the penis that become engorged with blood during erection.
Pampiniform plexus
A network of veins surrounding the testicular artery that helps in thermoregulation of the testes.
counter-current heat exchange system
so that warm blood in arteries leaving the body heats cooler blood in the veins leaving the testes.
The arterial blood entering the testis is now less than 370C.
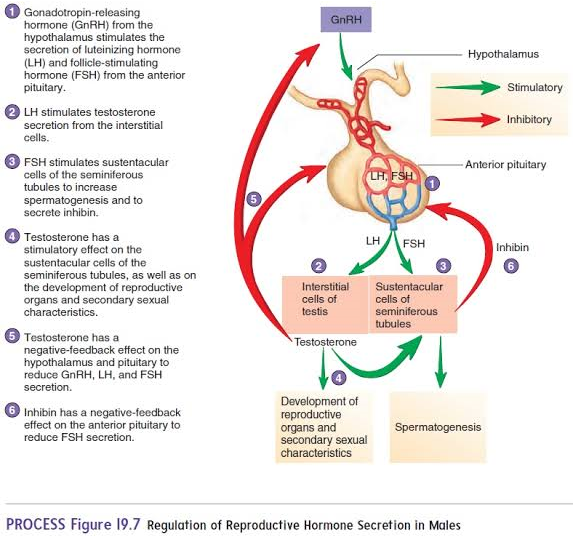
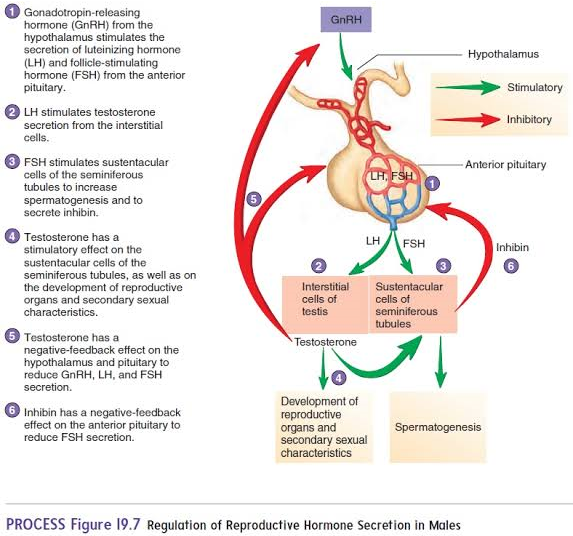
GnRH
Hormone originating in the hypothalamus that targets the anterior pituitary.
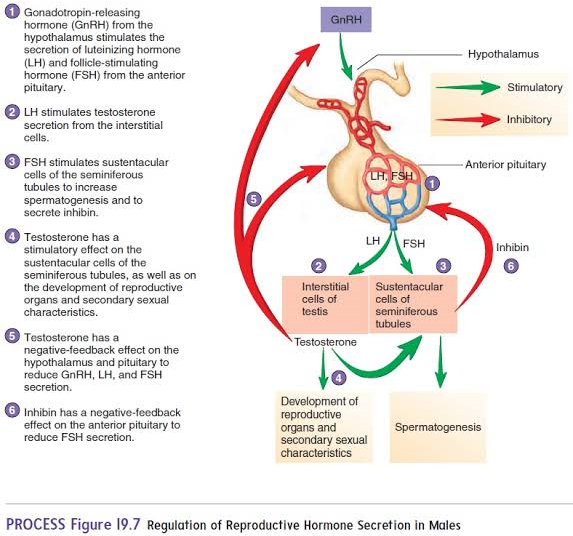
FSH
Hormone from the anterior pituitary that stimulates Sertoli cells to produce androgen-binding protein (ABP).
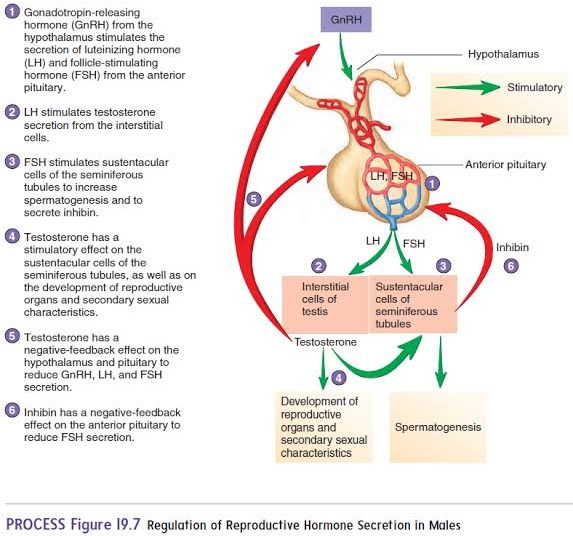
LH
Hormone from the anterior pituitary that stimulates interstitial cells to produce testosterone.
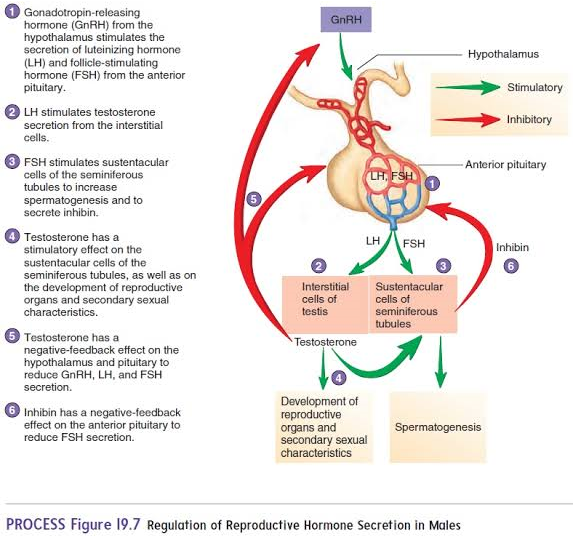
Testosterone
Hormone that stimulates spermatogenesis and regulates secondary sexual characteristics.
ABP (Androgen Binding Protein)
Binds to testosterone to increase its levels, made by Sertoli cells.
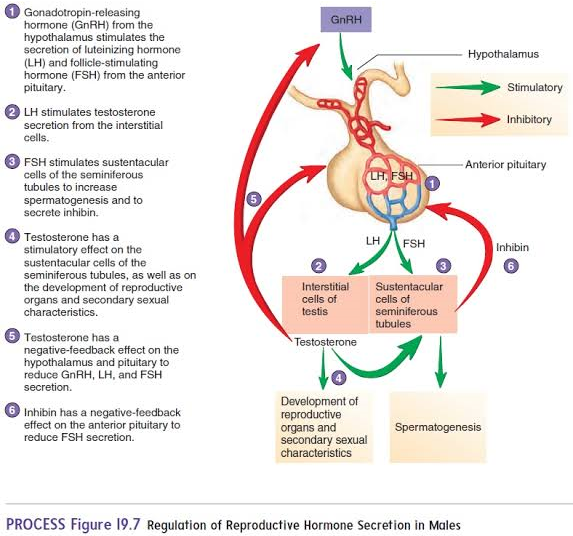
Inhibin
origin: Sertoli cells
inhibits GnRH and FSH when sperm count is high.
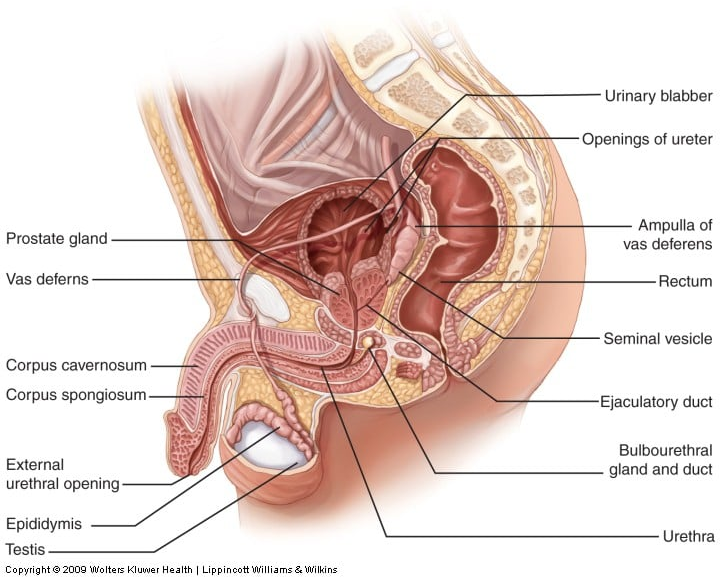
Bulbourethral gland (Cowper's)
5% of semen
Produces alkaline mucus that acts as lubricant and neutralises the urethra's pH during intercourse.
Seminal vesicles
60% of semen.
fructose, citric acid etc to nourish sperm
fibrinogen (fibrin) to coagulate semen
prostaglandins = uterine contractions to transport sperm
Prostate gland
Gland that produces 30% of semen
containing fibrinolysin that help dissolve coagulated sperm.
seminal plasmin = antimicrobial
Spermatogenesis
The entire process that forms spermatozoa.
Spermiogenesis
The differentiation of a spermatid into a mature spermatozoon.
Spongy urethra
The section of the urethra that travels through the penis.
Path of sperm to the vas deferens
Seminiferous tubules
Straight tubules (tubulus rectus)
Rete testis
Efferent ductules
Head of epididymis
Body of epididymis
Tail of epididymis
Vas deferens
A and B cells of spermatogonia
A replenishes stem cell pool, while B becomes primary spermatocyte.
Erection stimulation
parasympathetic nervous system.
Emission/ejaculation stimulation
sympathetic nervous system.
Tunica albuginea
Thickened layer of fibrous tissue surrounding the corpora cavernosa; allows for compression of veins during erection.
location of sperm cells
Spermatocytes are located closer to the middle as they mature; spermatogonium is always in contact with the basement membrane while sperm are within the lumen.
epithelium of epididymis
pseudostraified, columnar with stereocilia
stereocilia increases surface area
ejaculatory duct location
Duct which is located at the ampulla of the ductus deferens. This duct projects into the prostate gland and ends at the opening into the urethra.