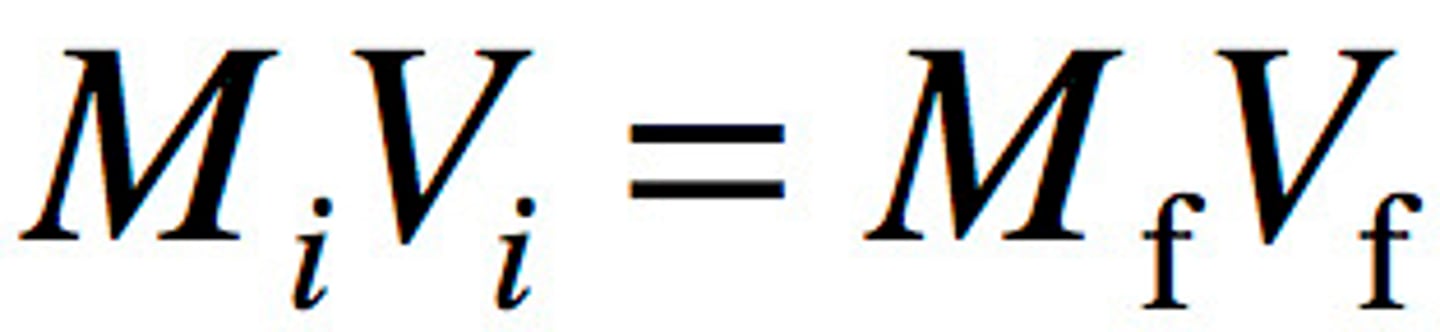6 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
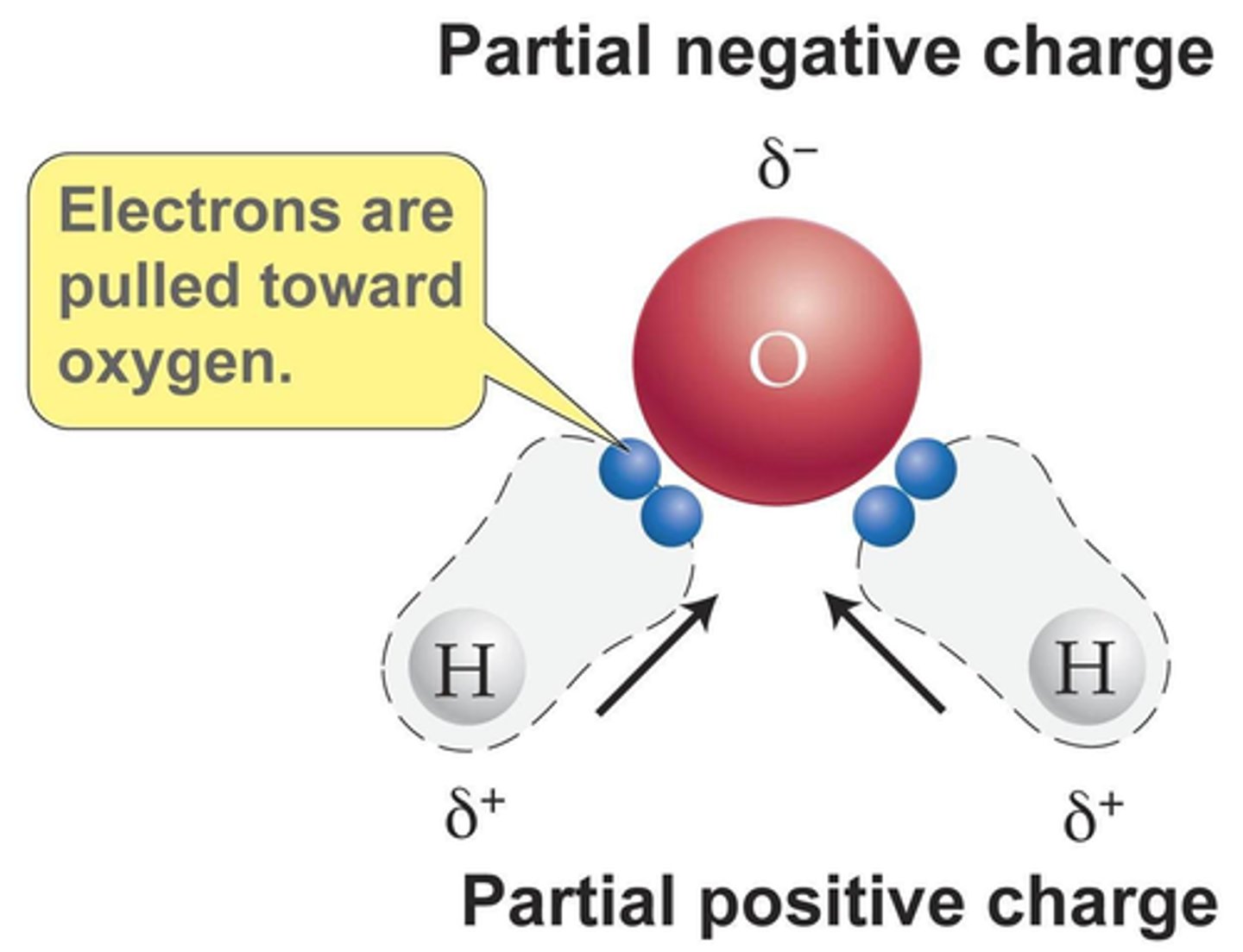
Polarity
water is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom negatively chargedwith one oxygen atom negatively charged and two hydrogen atoms positively charged. and two hydrogen atoms positively charged.
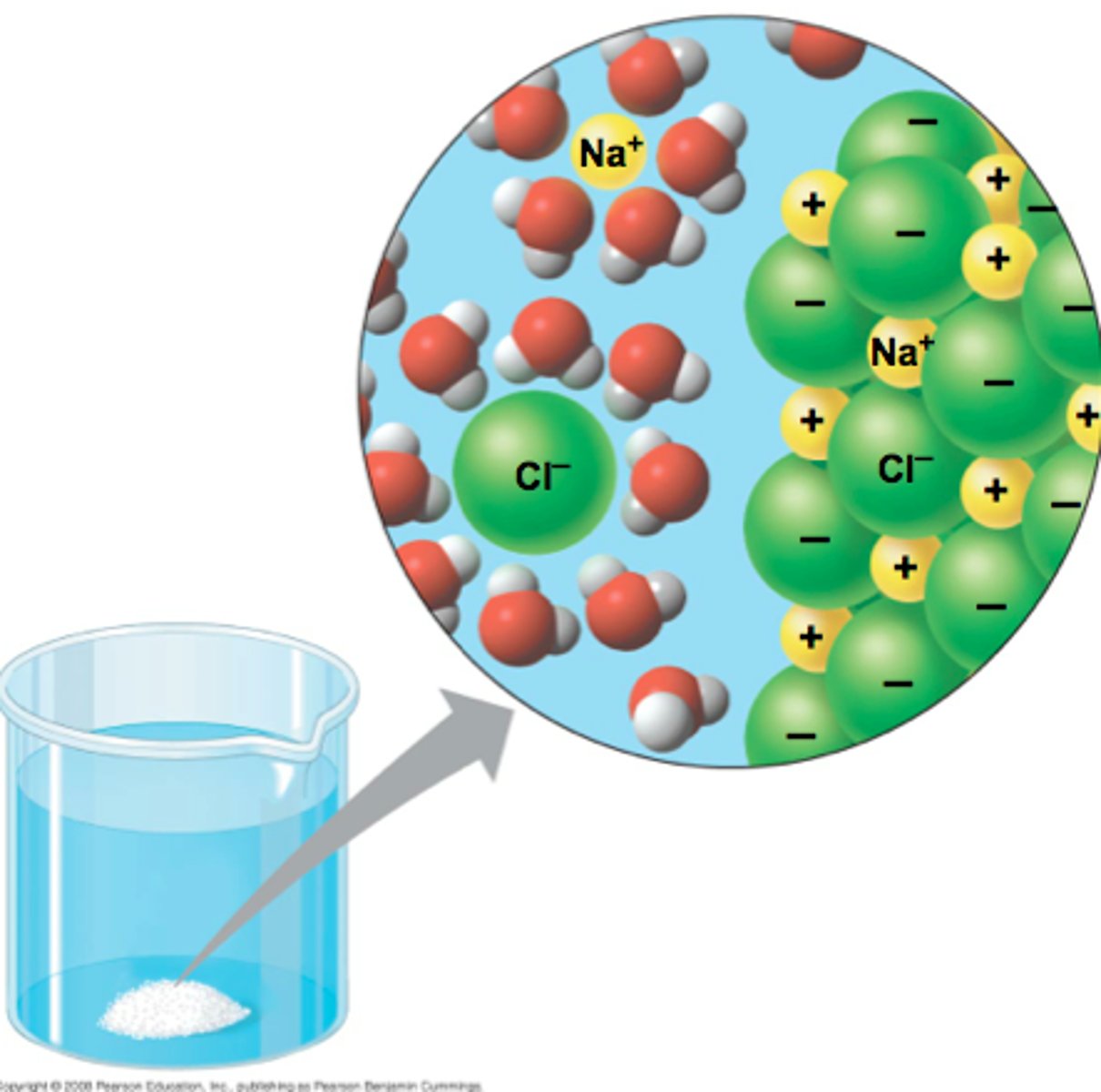
Universal solvent
Water - due to its polarity and ability to dissolve other polar molecules
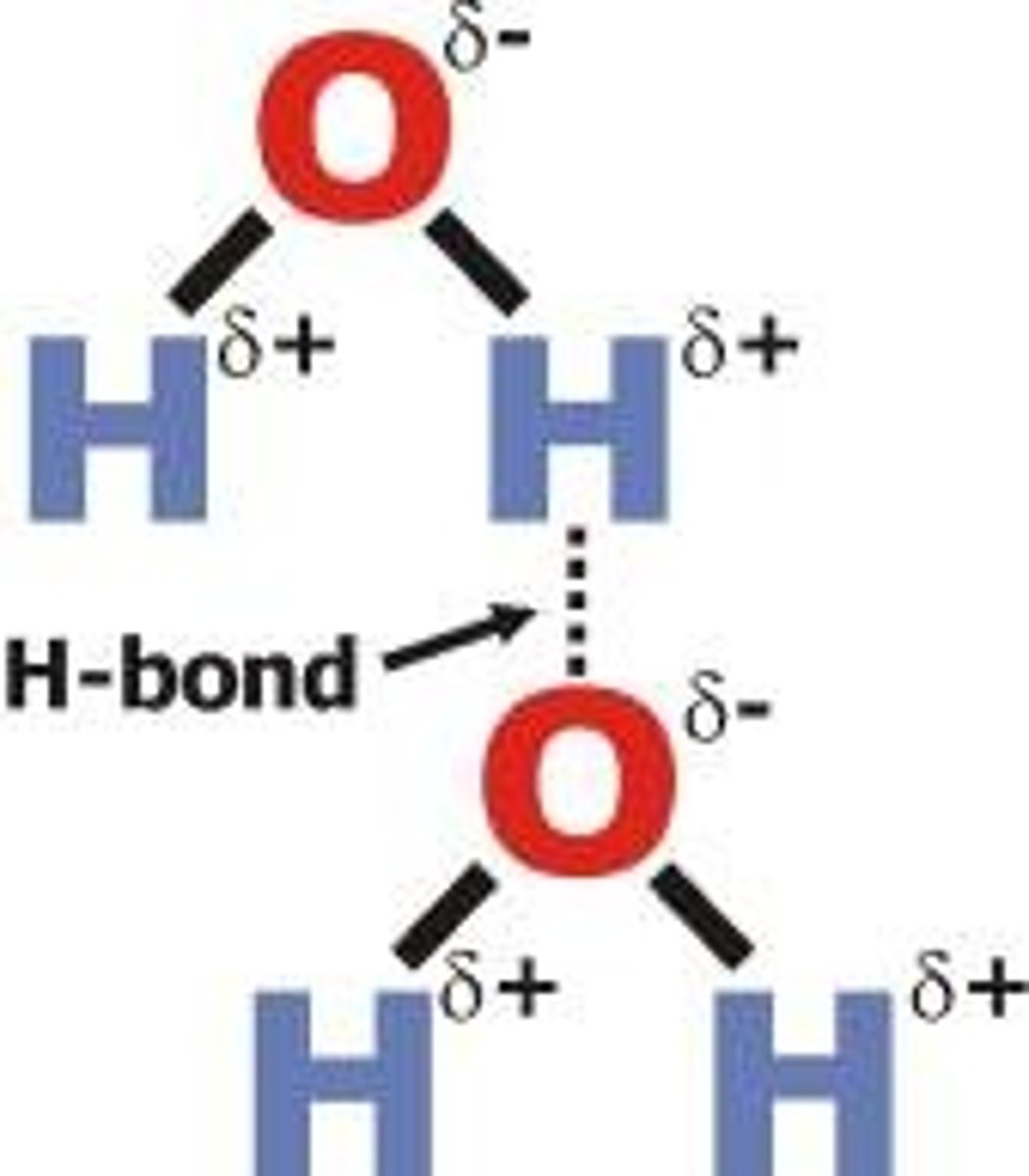
Hydrogen bonds
he weak intermolecular bonds that form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule.
Solute
substance being dissolved
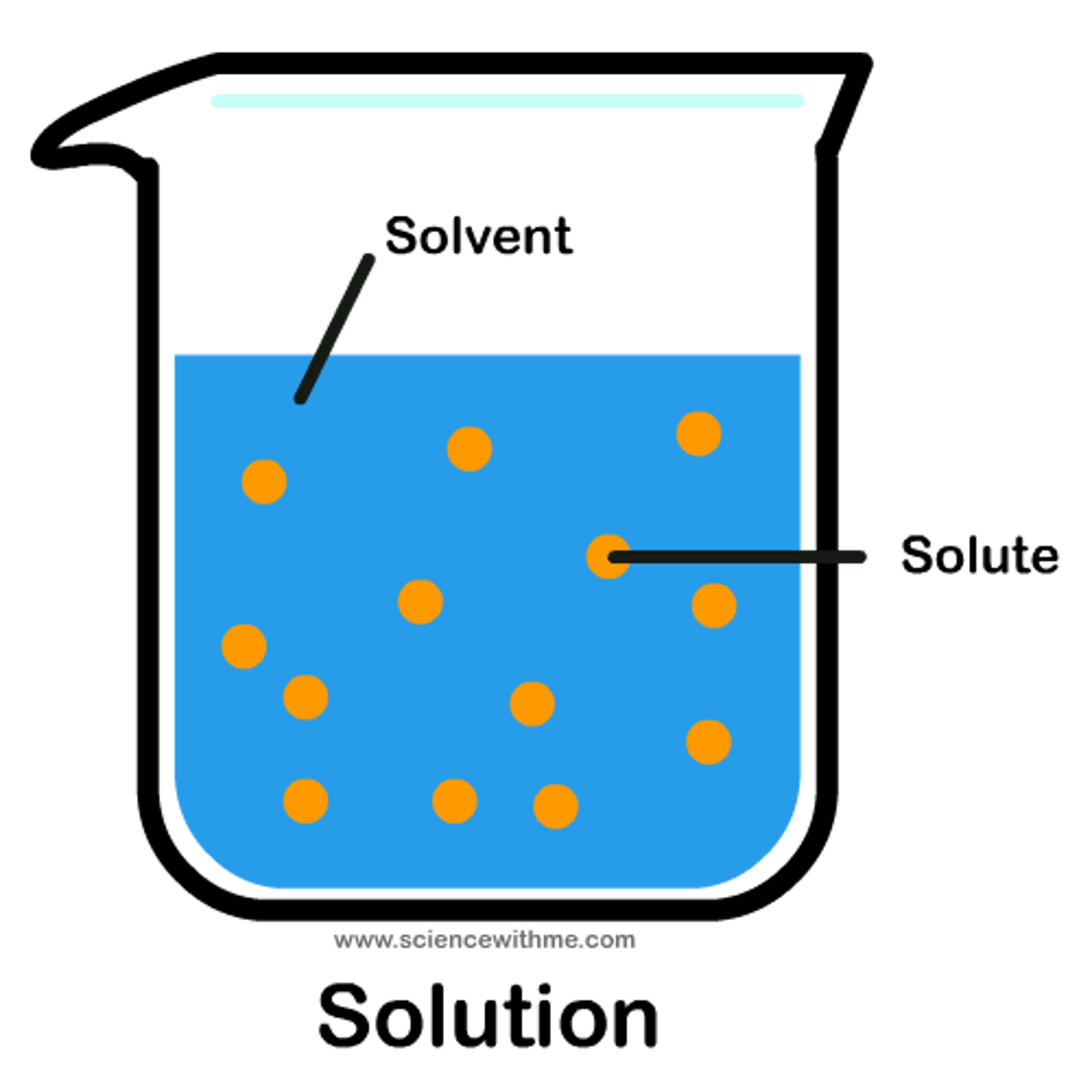
Solution
homogeneous mixture of two or more substances (solute + solvent)
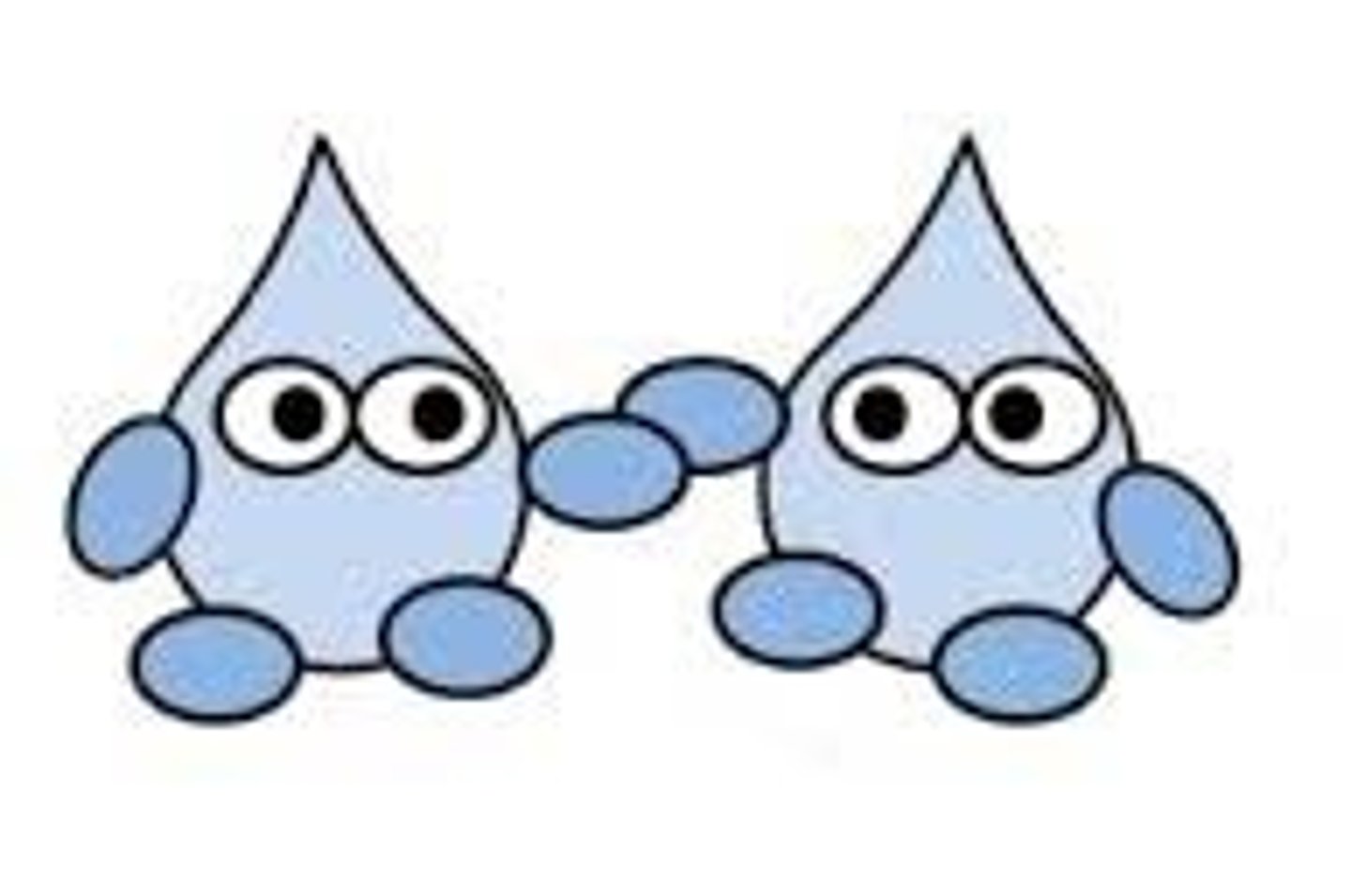
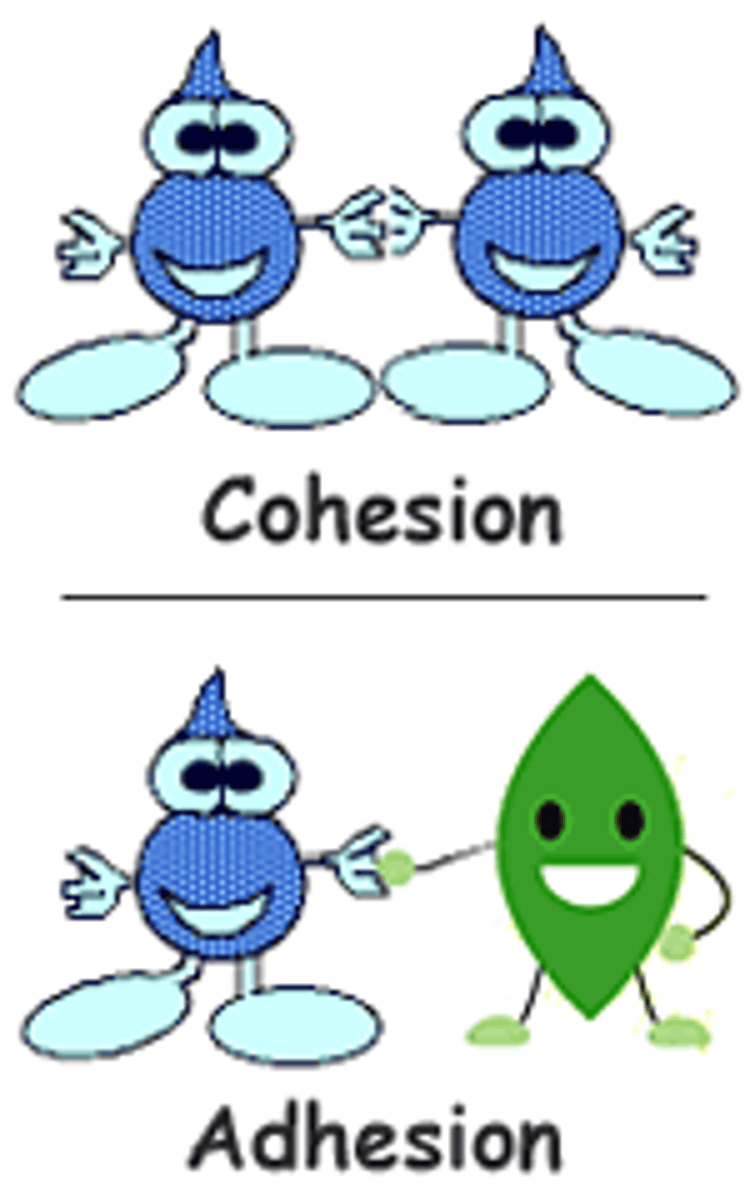
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances (water and another substance)
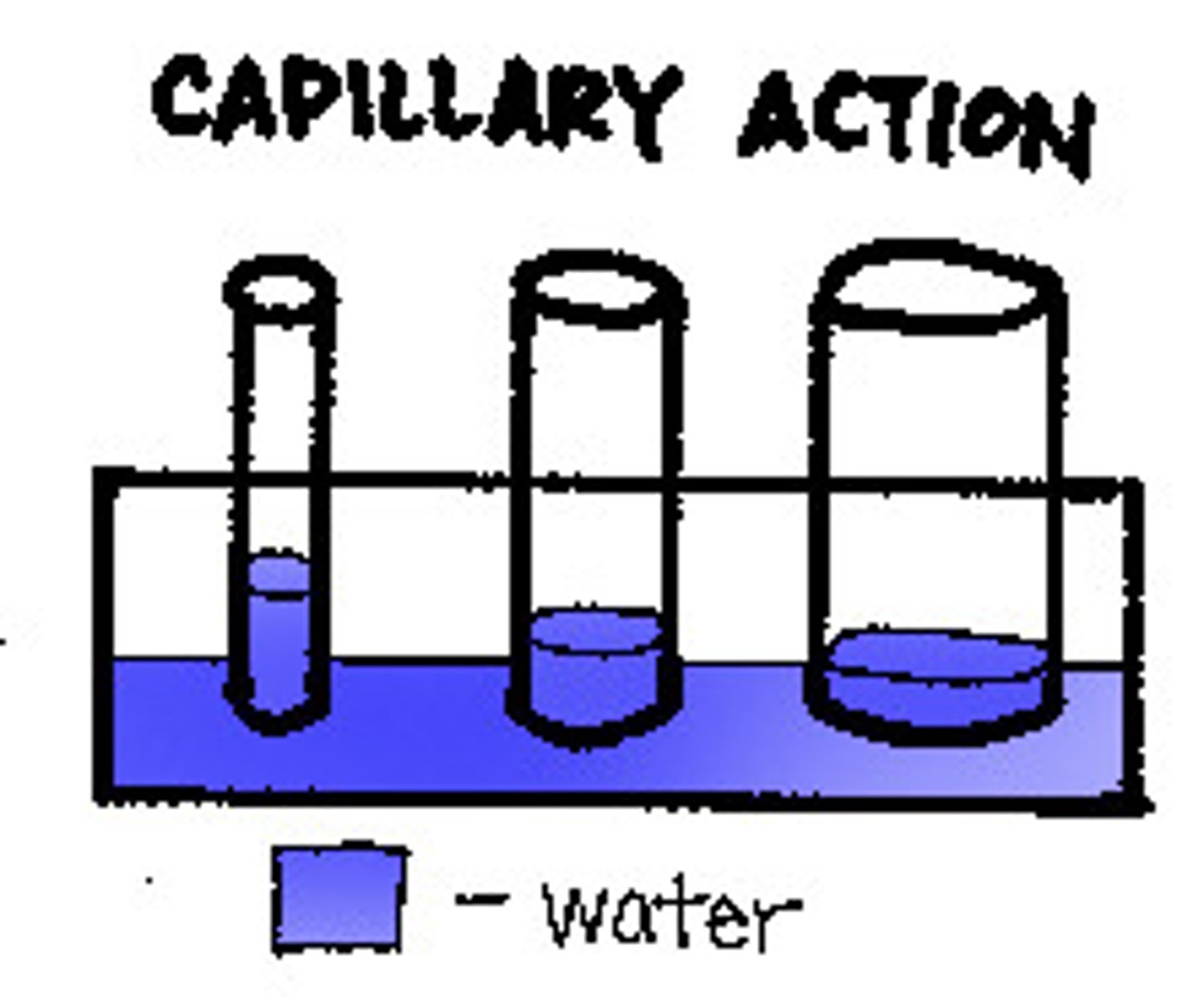
Capillary action
tendency of water to rise in a thin tube against the force of gravity, and due of the cohesion and adhesion forces of attraction.
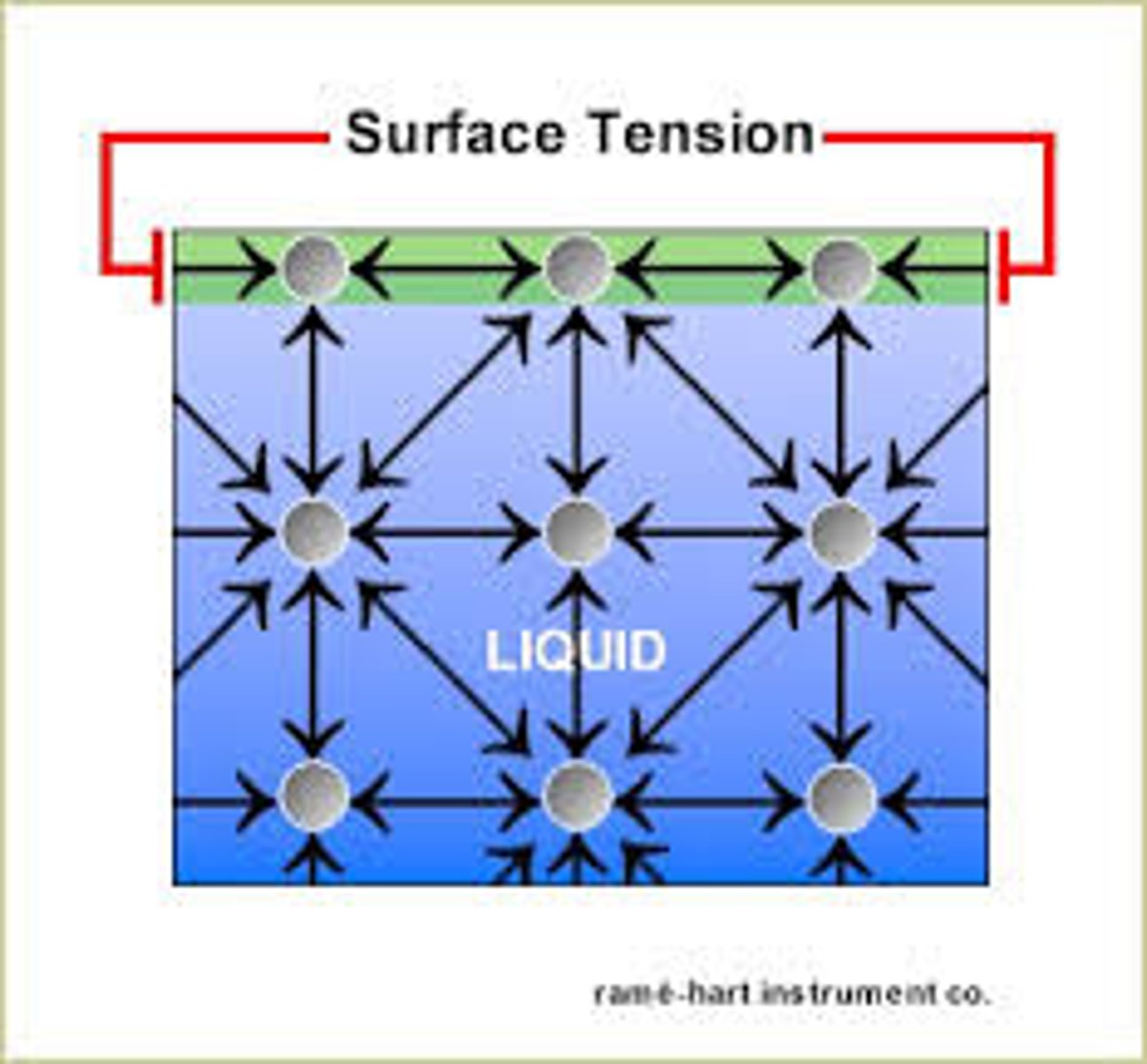
Surface tension
An invisible film at the surface of water that allows objects to walk. This is caused by the cohesive forces.
High specific heat capacity
Water has a high specific heat, meaning it takes more energy to increase the temperature of water compared to other substances.

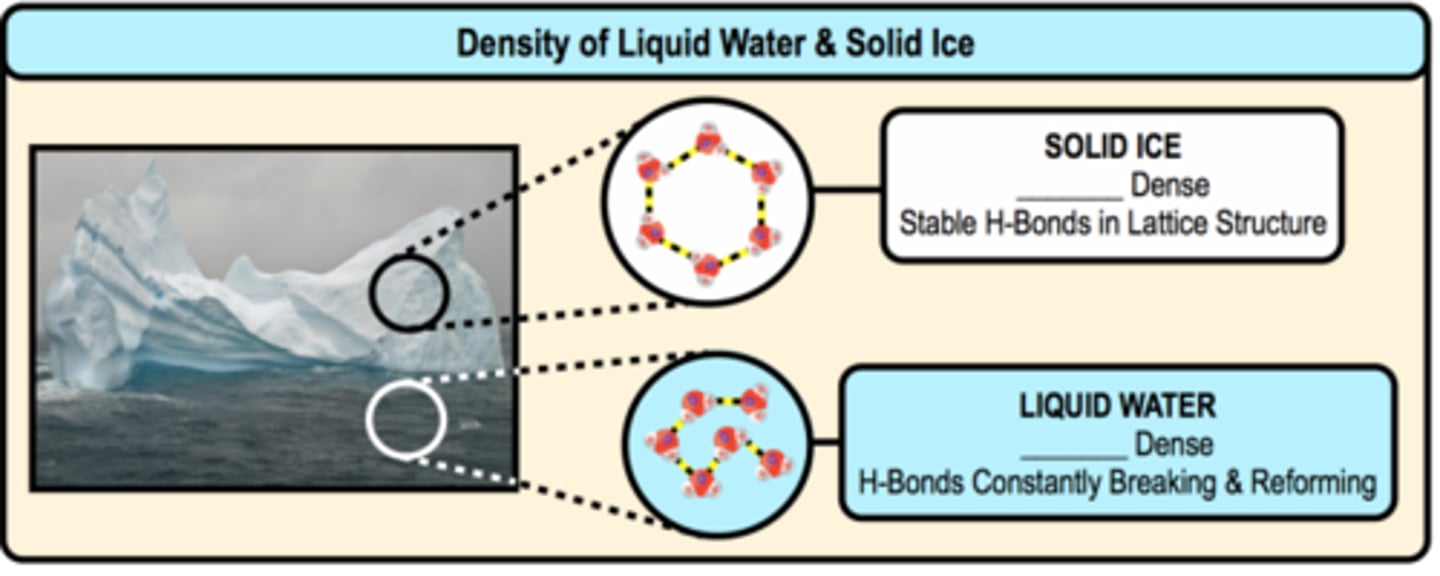
Low density as a solid (ice)
ice is less denser than water because in ice the molecules arrange themselves in a rigid tetrahedral structure due to which cage like spaces
What forces allow water droplets on leaves?
Water droplets stick to surface and seem to defy gravity because of form because the adhesive forces that bond them to the surface of the grass blade.
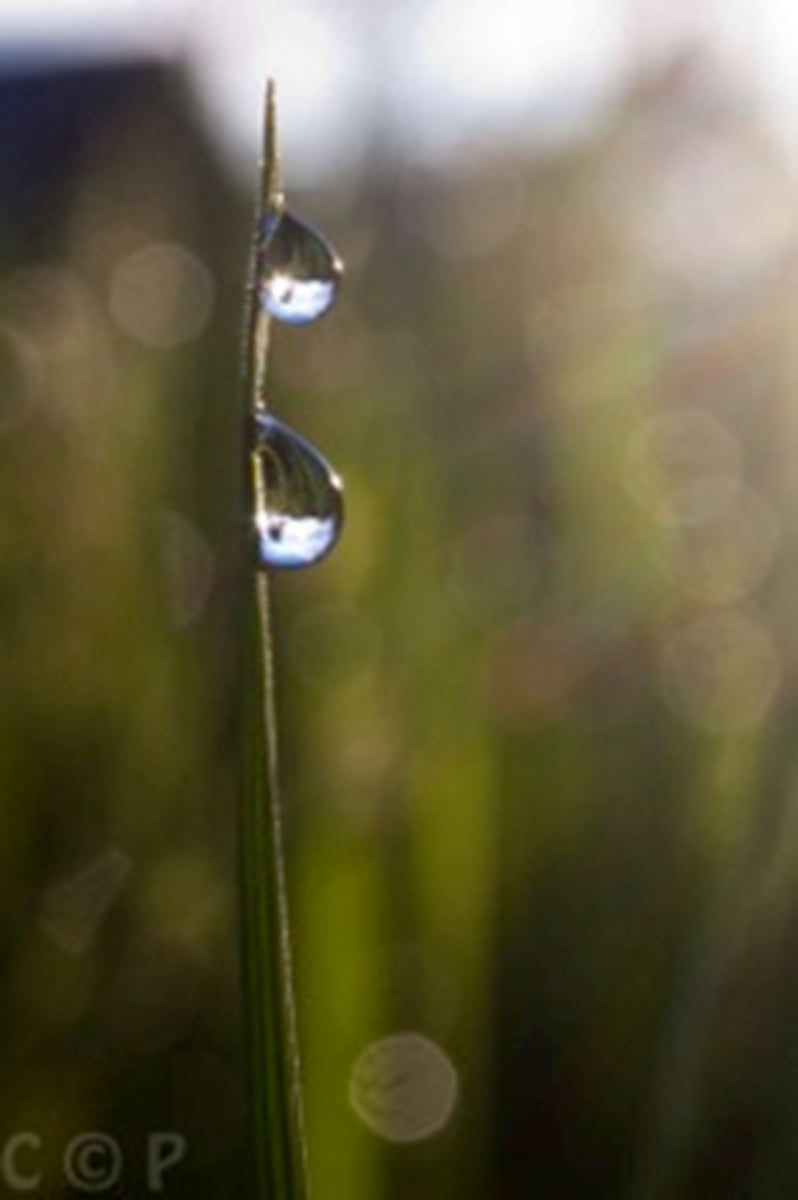

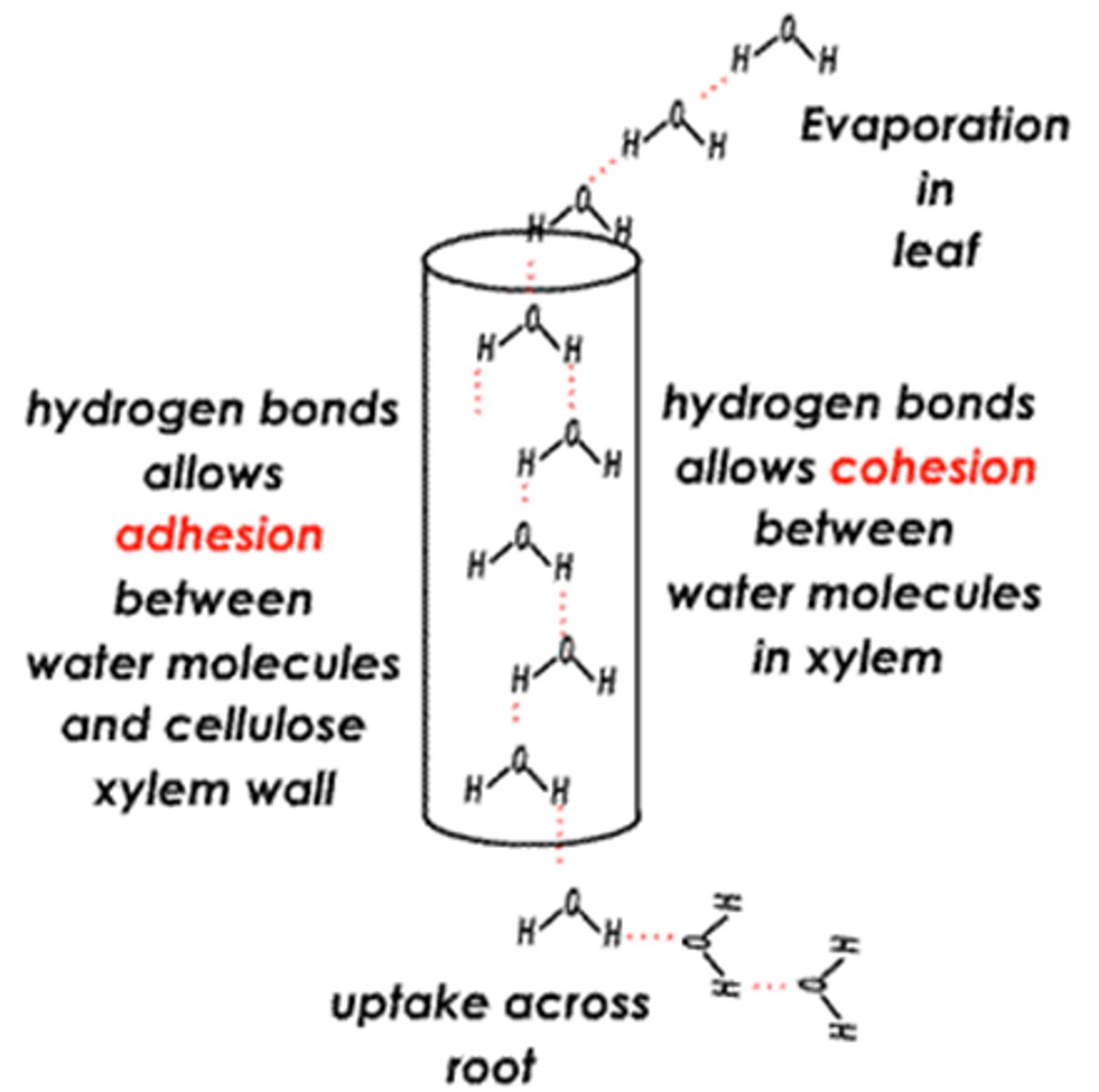
What forces allow water to rise against gravity in plants?
Capillary action is caused by the combination of adhesive forces causing water to bond to a surface, e.g. the sides of a xylem vessel and the cohesive forces bonding water molecules together. Capillary action is helpful in the movement of water during transpiration and also when you drink using a straw.
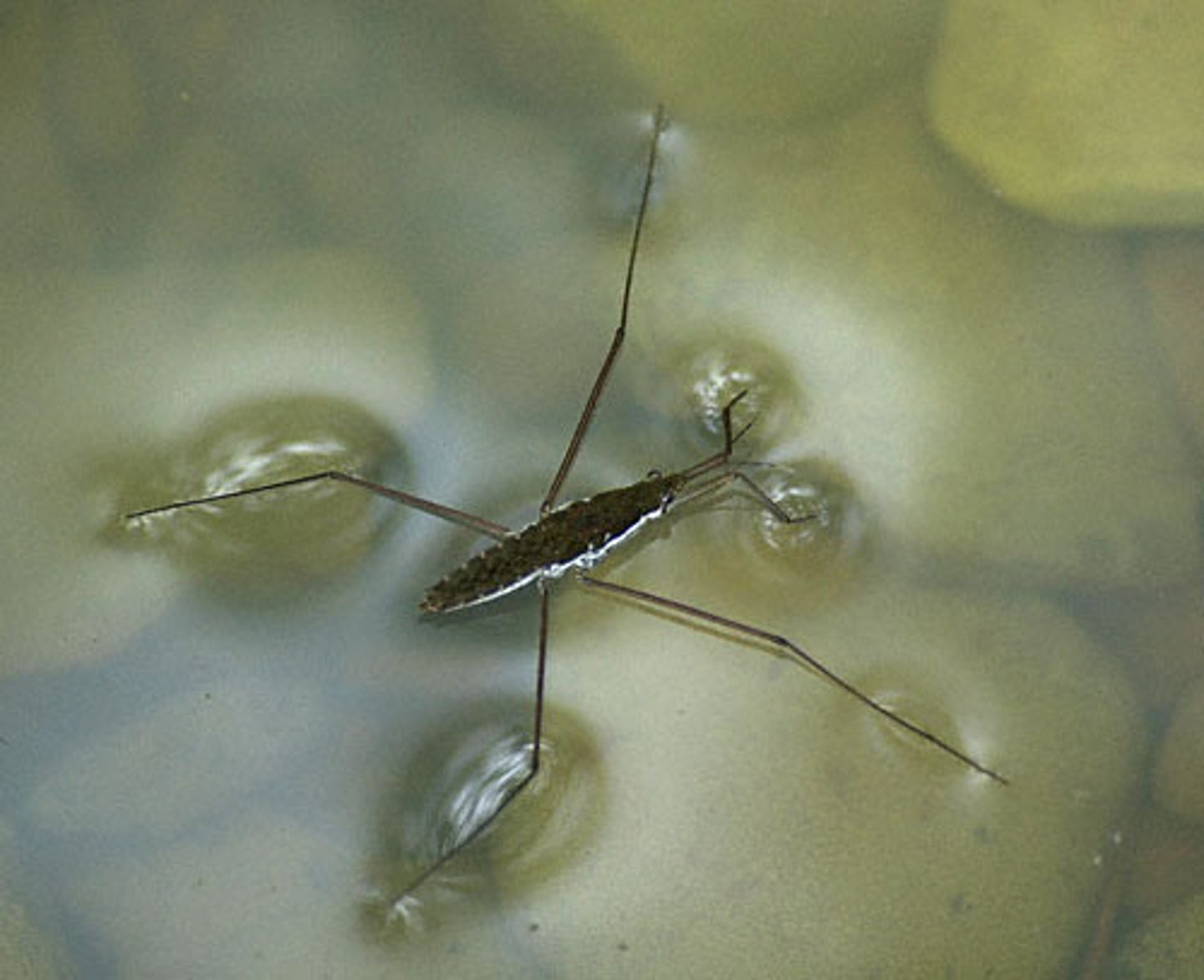
What forces allow a water strider to float on water?
Surface tension is caused by the cohesive hydrogen bonding resisting an object trying to penetrate the surface.

What allows nutrients to be transported in and out of cells?
Blood plasma consists of mainly of water (95%) plus dissolved substances which it transports. Polar molecules and ions are easily transported by water.
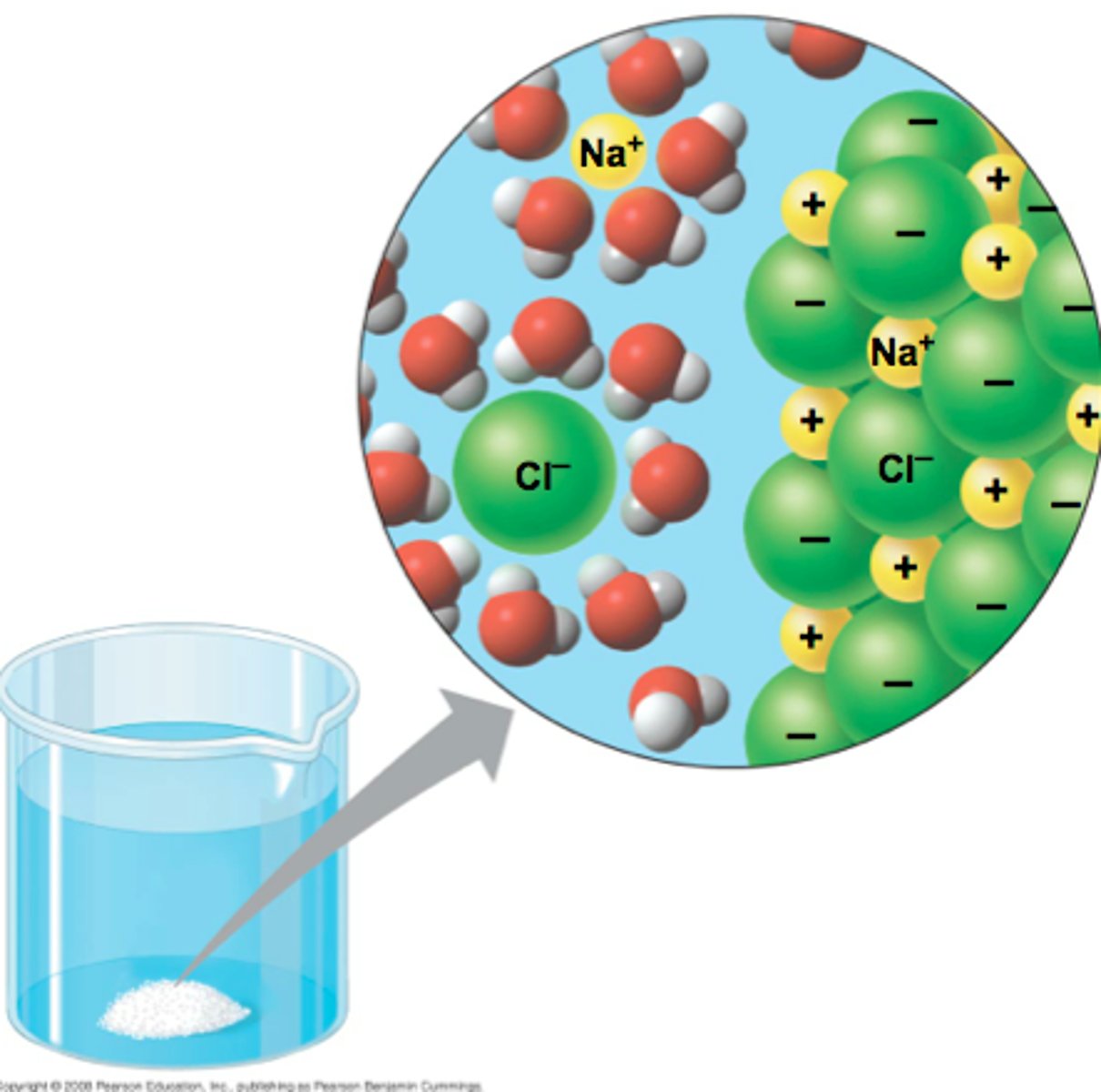
Why is the high specific heat of water important for life on earth?
Three-fourths of the earth is covered by water. The water serves as a large heat sink responsible for:
- Prevention of temperature fluctuations that are outside the range suitable for life.
- Coastal areas having a mild climate
- A stable marine environment

How does water help regulate the temperature of the human body?
The high specific heat capacity of water allows water to absorb the energy of cellular respiration and maintain a constant temperature.

How does water help regulate the body temperature when a person is sick?
With a high fever, you body sweats. Water molecules as they evaporate to carry energy away from your body.

How does the low density of ice help aquatic life in low temperature?
The ice layer that forms on the surface (and not at the bottom) of a lake insulates the water beneath and maintains a high enough temperature to sustain aquatic life

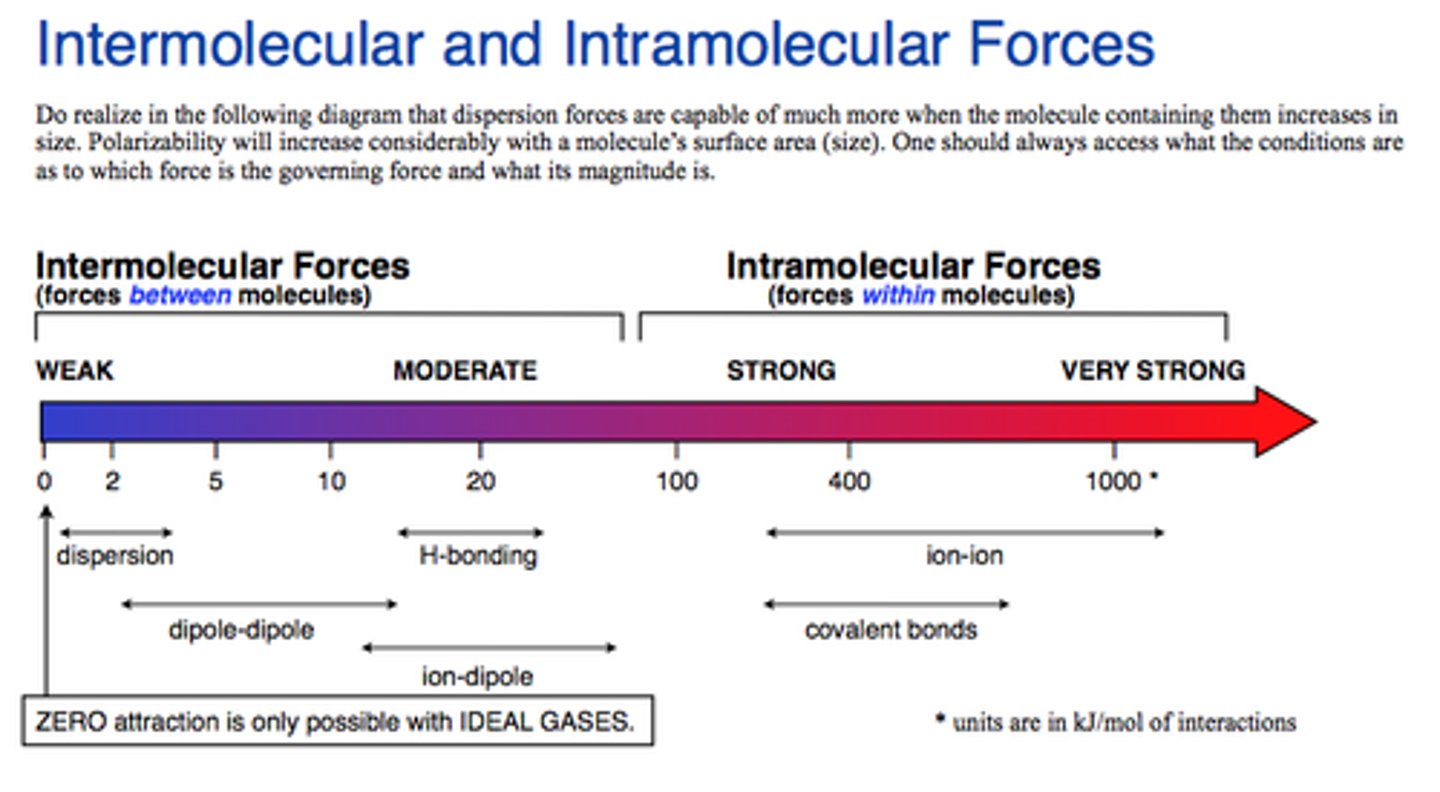
Intramolecular forces
These are the forces that hold chemical compounds together (bonds). There are three types of bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic
Intermolecular forces
These are the forces of attraction between different atoms or compounds. There are four types of intermolecular forces: ion - dipole, hydrogen bonding, dipole - dipole, and London dispersion forces.
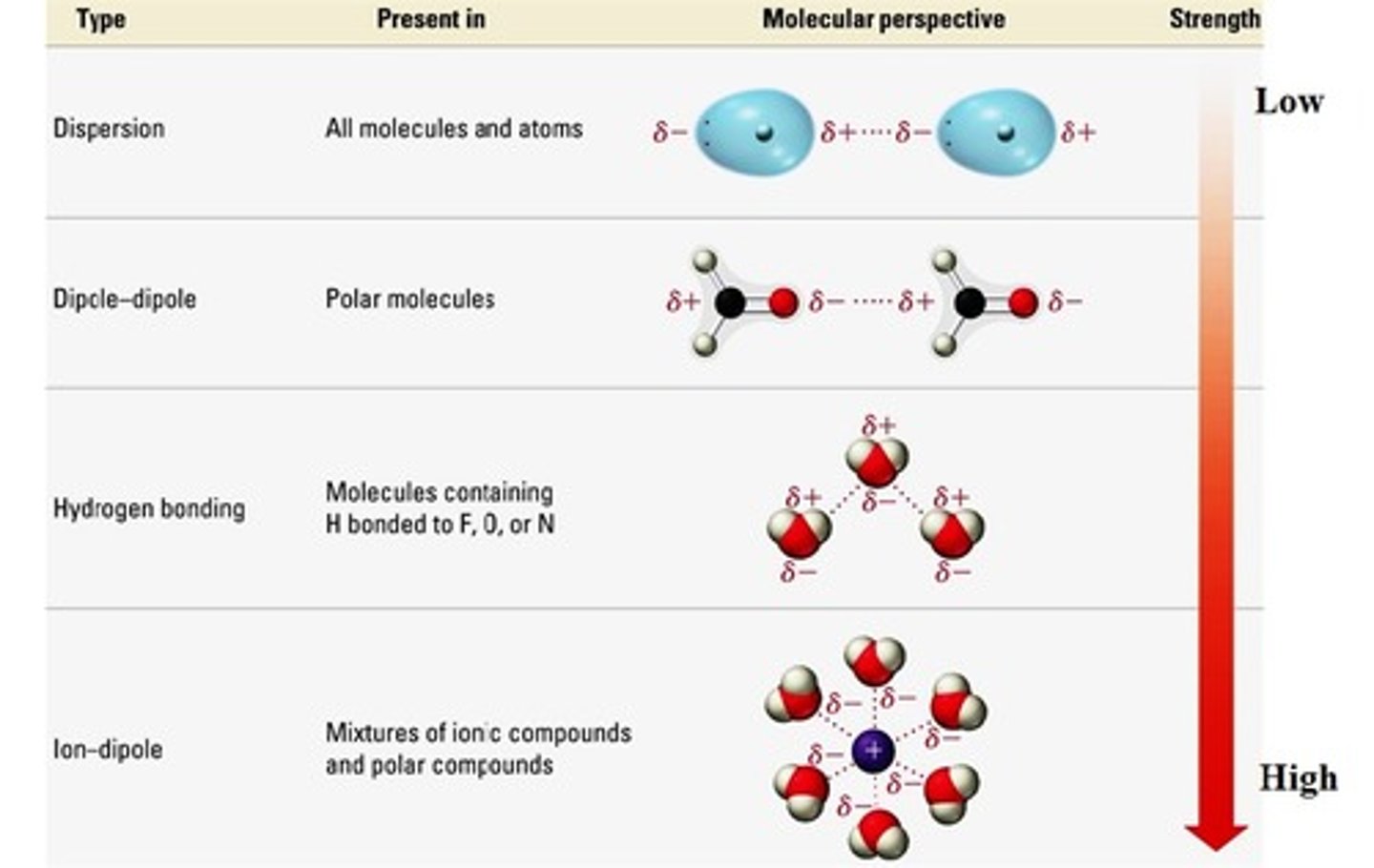
List the types of intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest.
London dispersion forces, dipole - dipole, hydrogen bonding, and ion - dipole
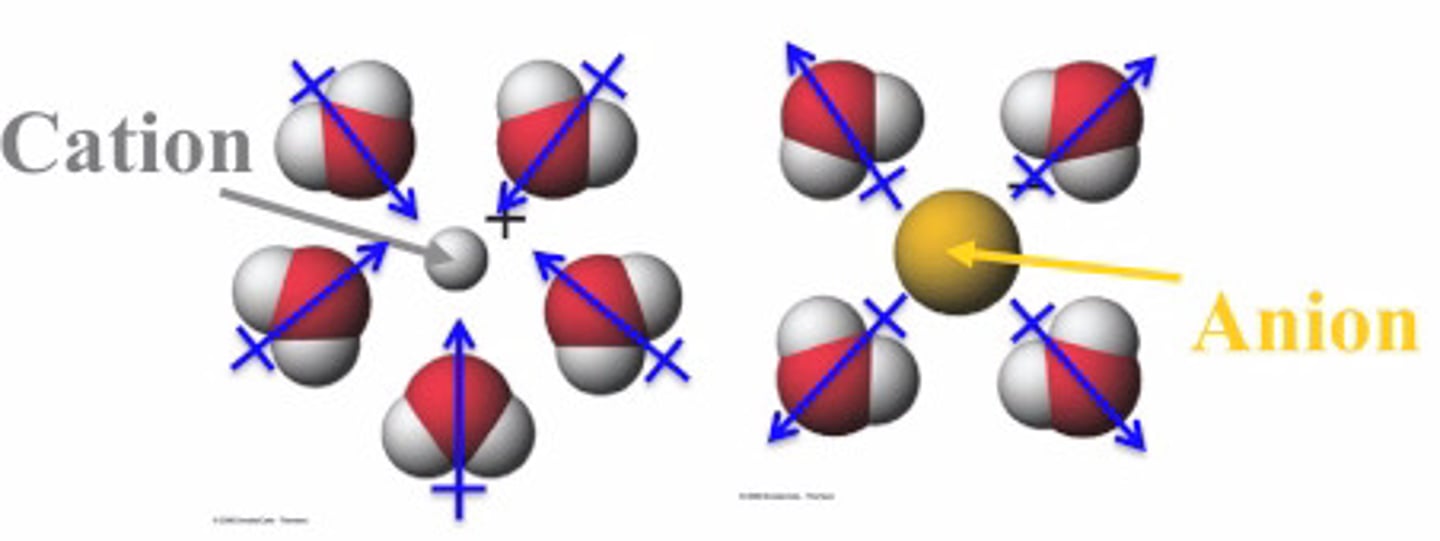
ion - dipole force
an intermolecular force between an ion and the oppositely charged end of a polar molecule
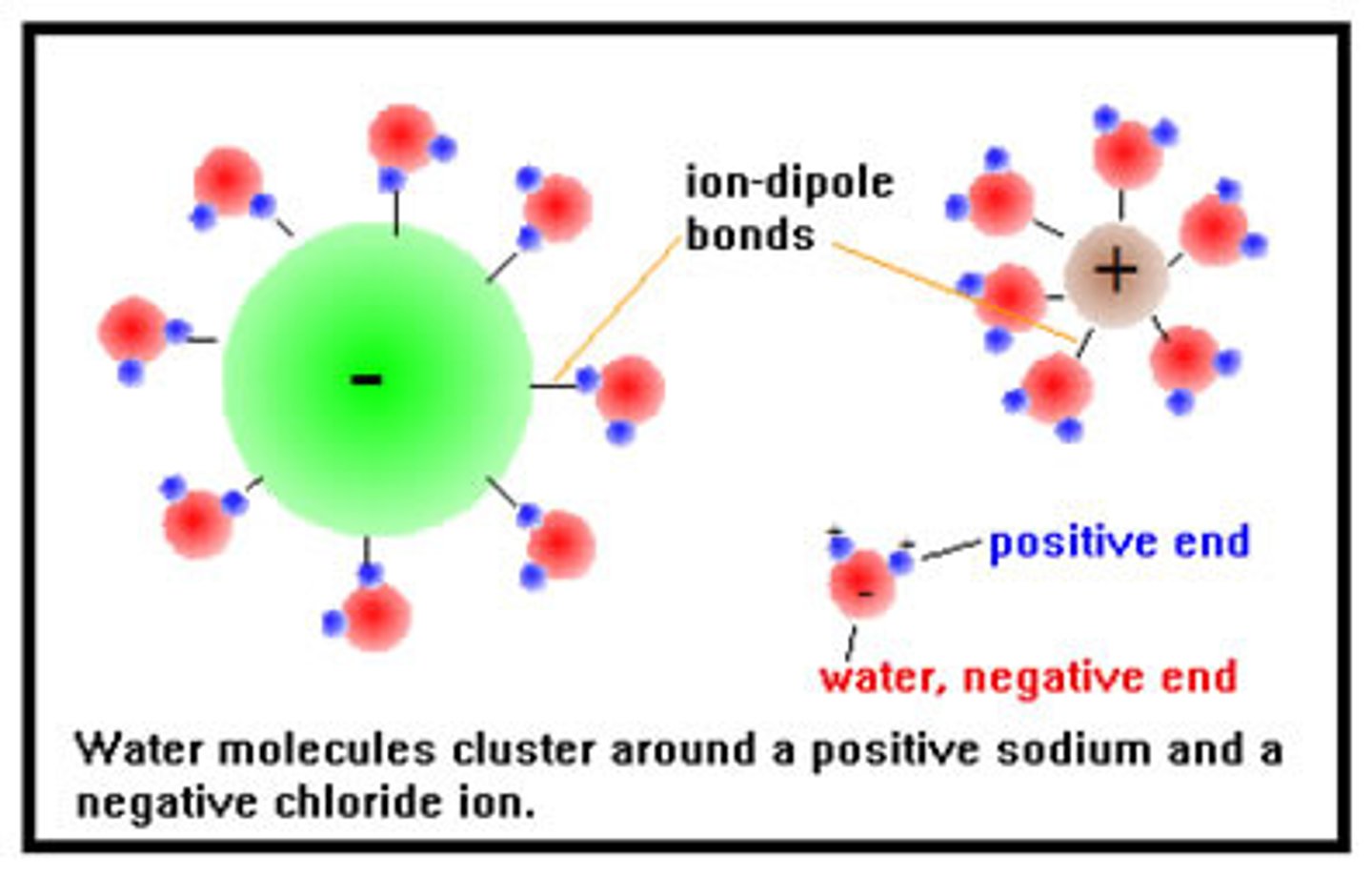
How would you draw a diagram of calcium chloride in water showing the ion - dipole force?
The positive calcium ion would be surrounded by the negative oxygen of water molecules. The negative chloride ion would be surrounded by the positive hydrogens of the water molecules.
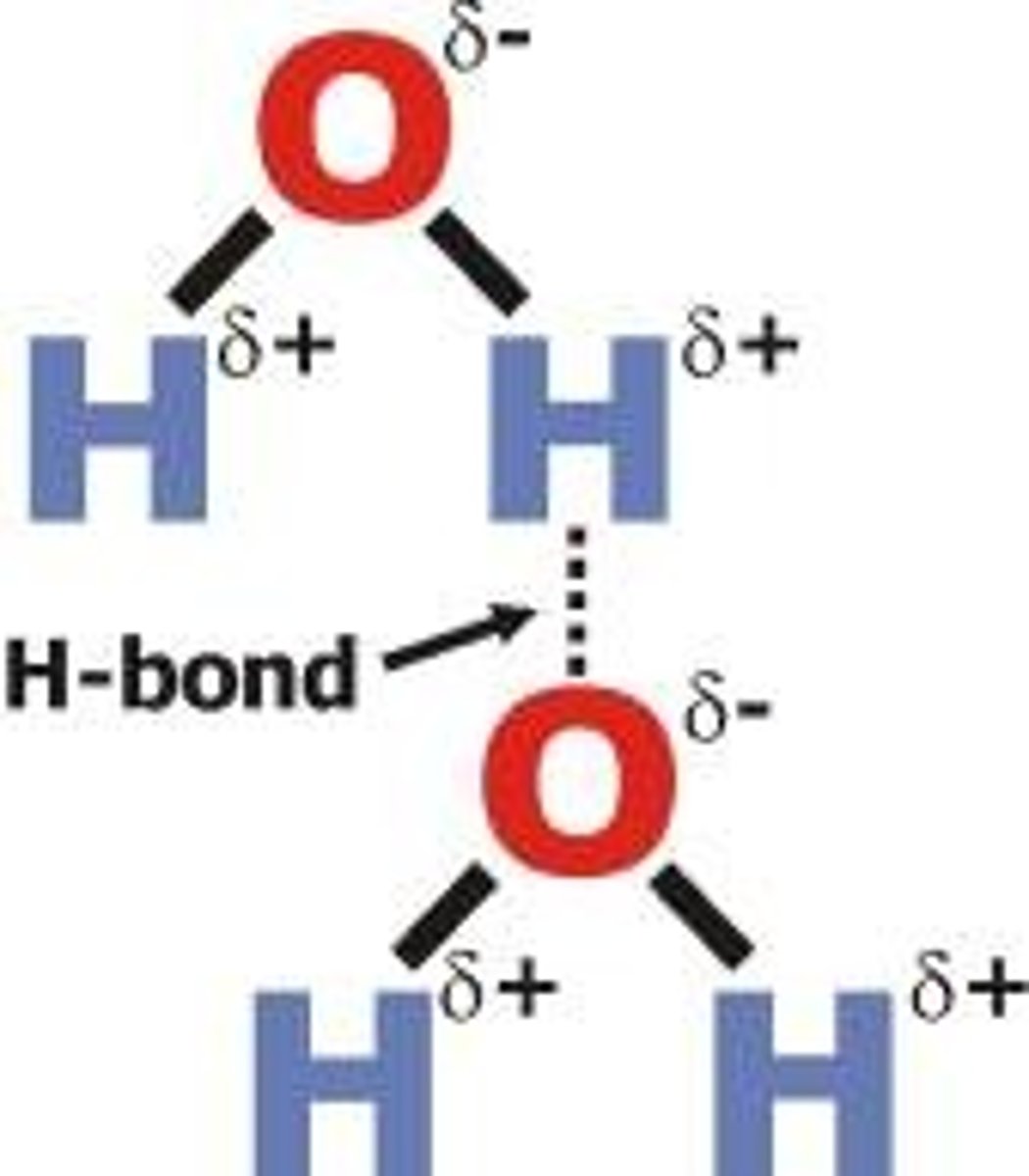
Hydrogen bonding
strong type of intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction. Occurs between hydrogen and F, O or N
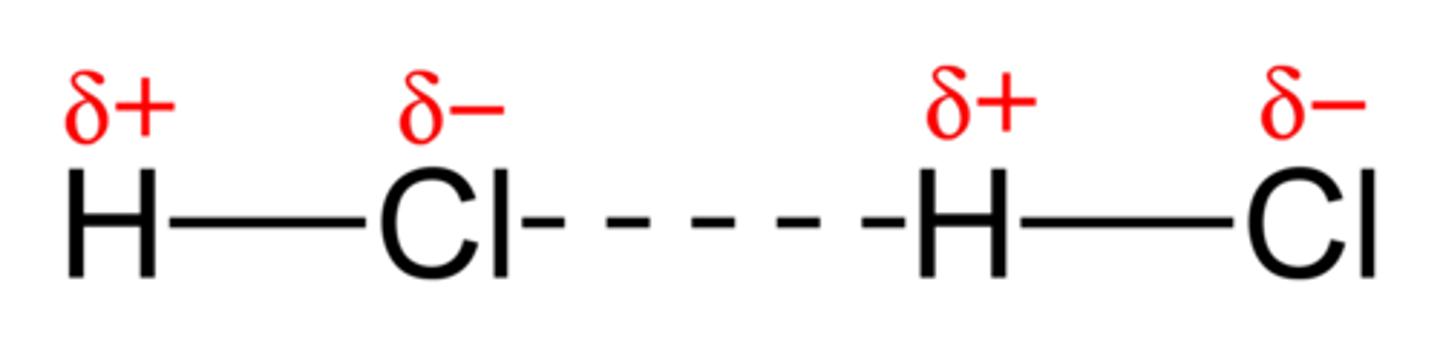
dipole - dipole forces
attractions between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules (do not include hydrogen bonding)
London dispersion forces
The intermolecular attractions resulting from the constant motion of electrons and the creation of instantaneous dipoles
What type of intermolecular forces are present in a solution of ammonia (NH3)?
hydrogen bonding and London dispersion forces
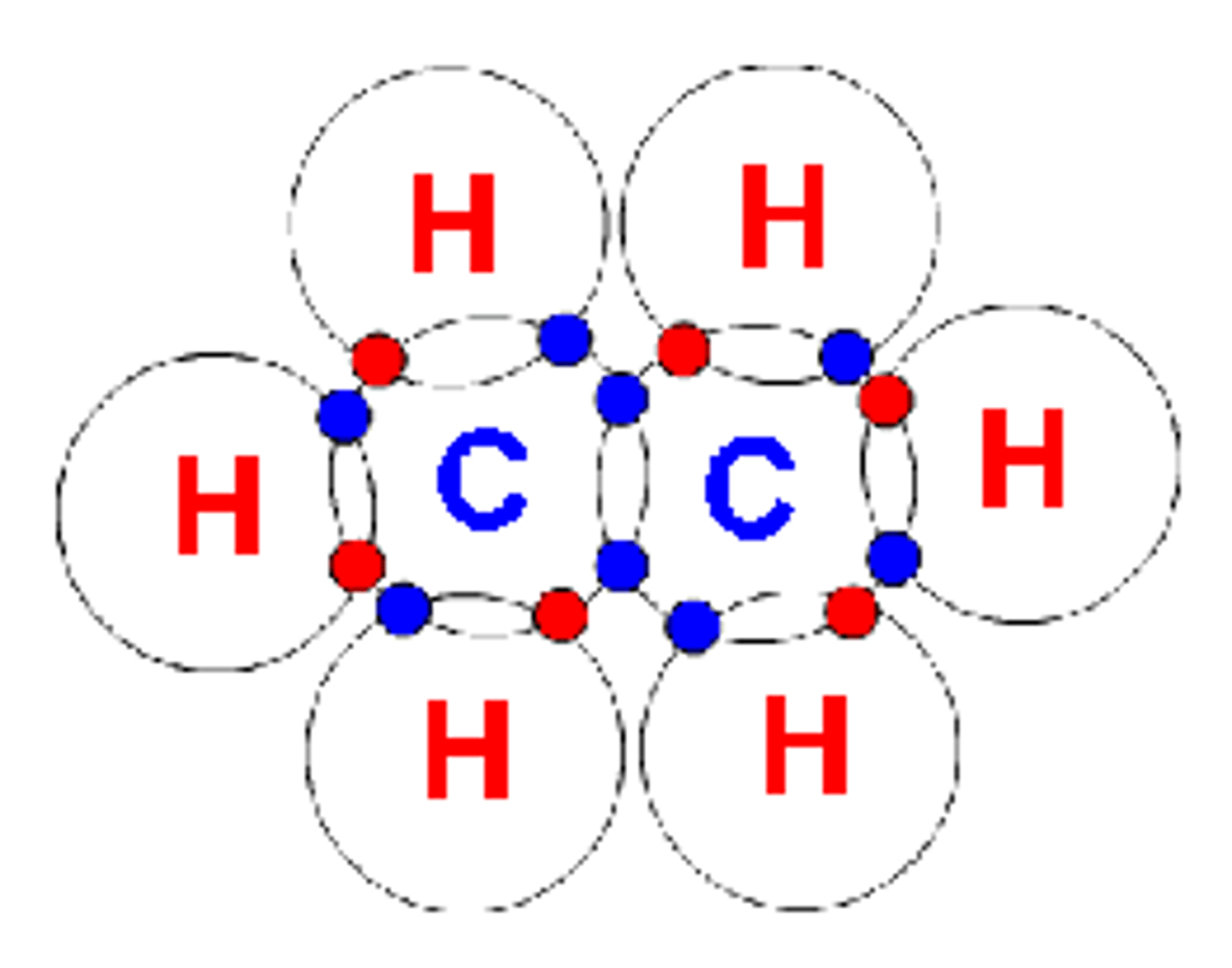
What type of intermolecular forces are present in ethane (C2H6)?
London dispersion forces (nonpolar molecule)
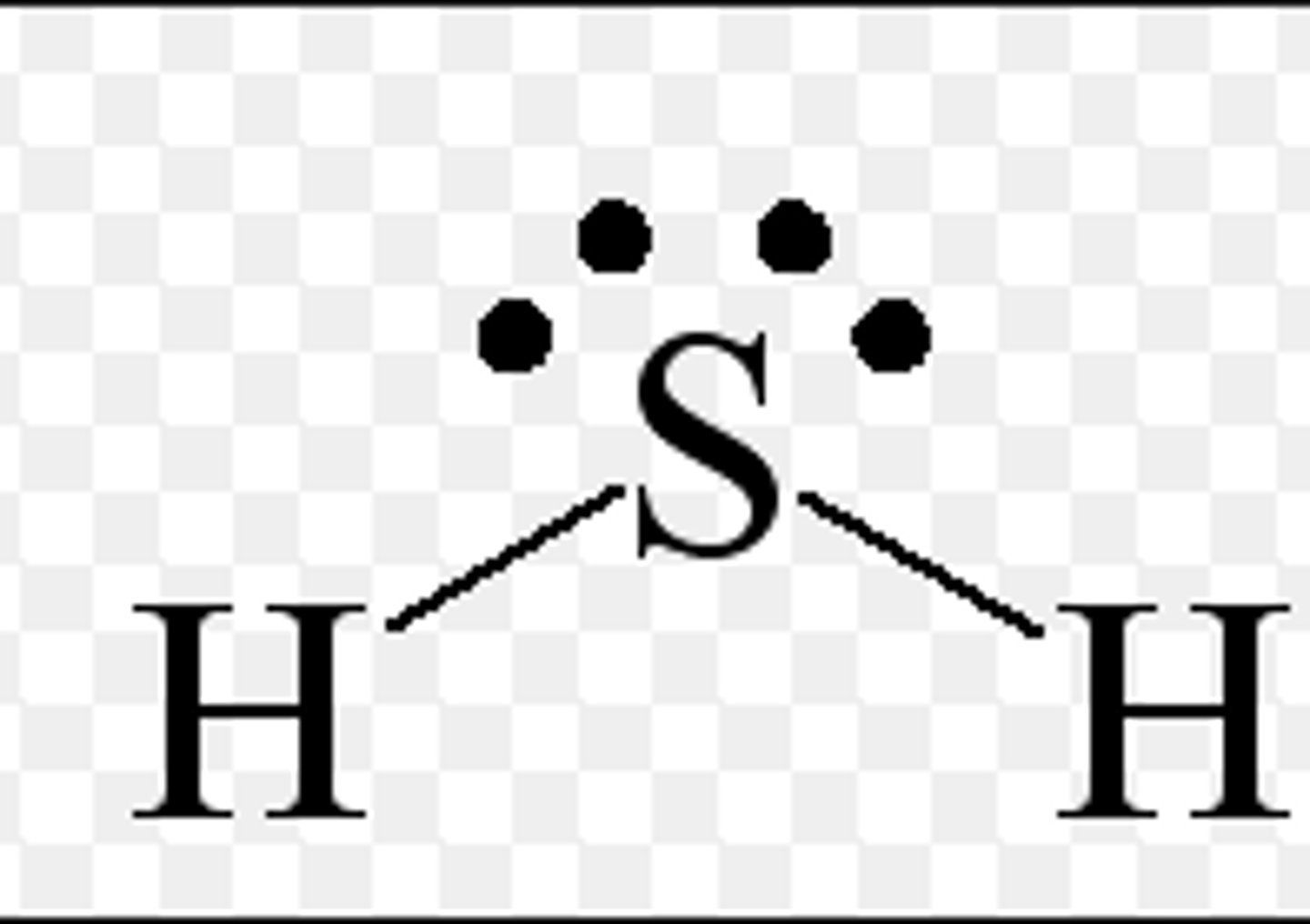
What type of intermolecular forces are present in dihydrogen sulfide?
dipole - dipole and London dispersion forces
What type of intermolecular forces are present in phosphorus trichloride?
dipole - dipole and London dispersion forces
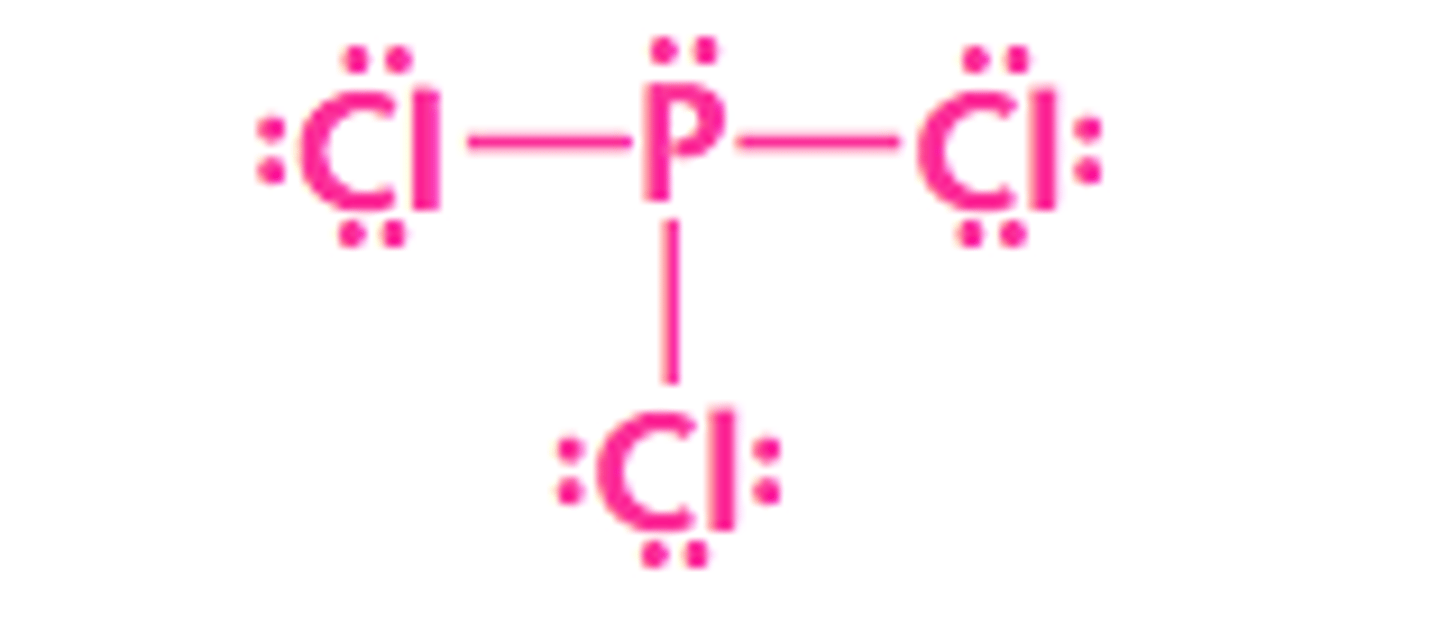
What type of intermolecular forces are present in an aqueous copper (II) sulfate solution.
ion - dipole forces between the copper ions, sulfate ions and water
hydrogen bonding between water molecules
London dispersion forces
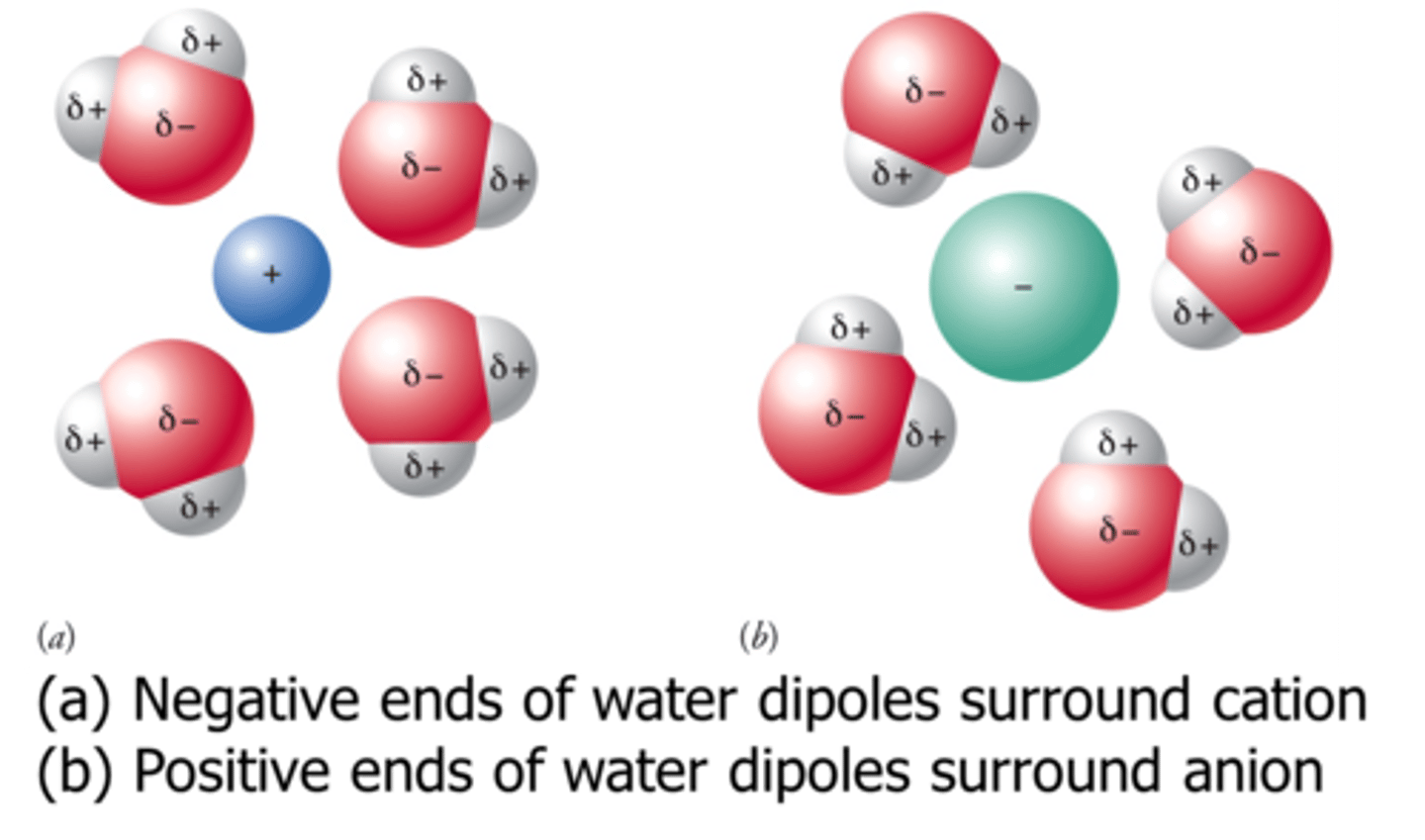
What is a precipitation reaction?
When two soluble substances react together to make a product which is insoluble (the precipitate)
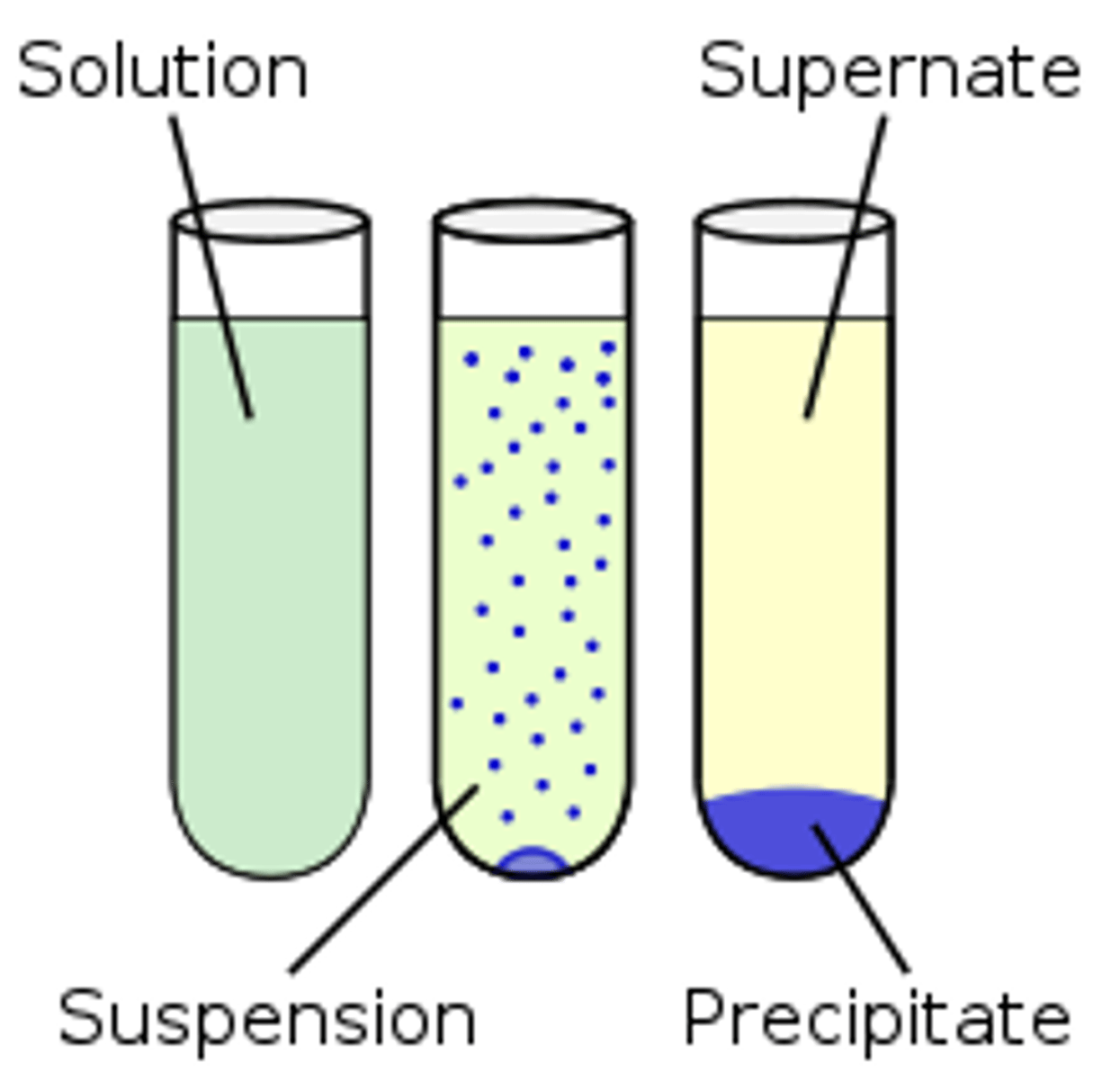
What is a precipitate?
a solid that forms and settles out of a liquid mixture

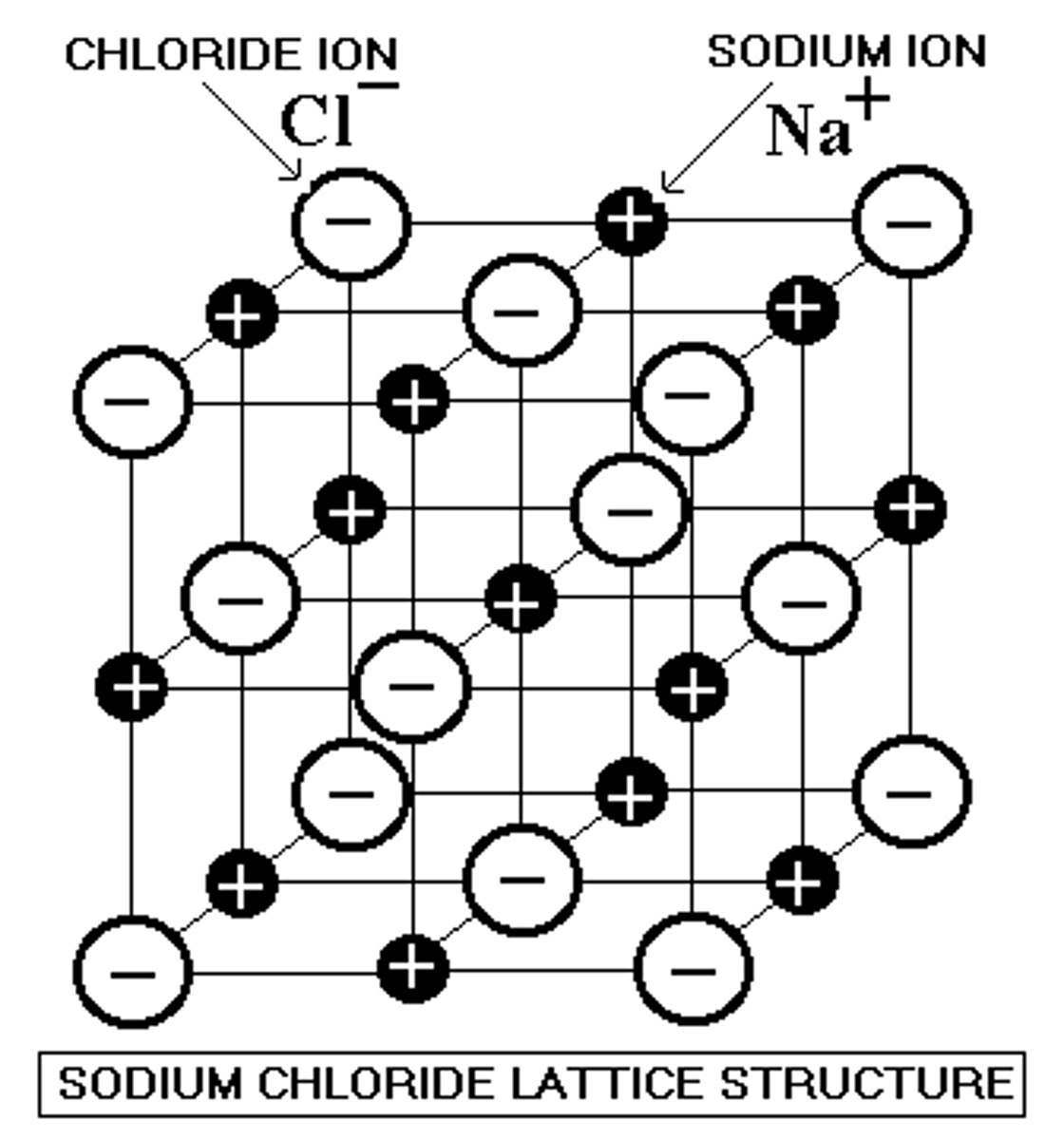
What forces hold ionic compounds together as solids?
The force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions forms a lattice structure
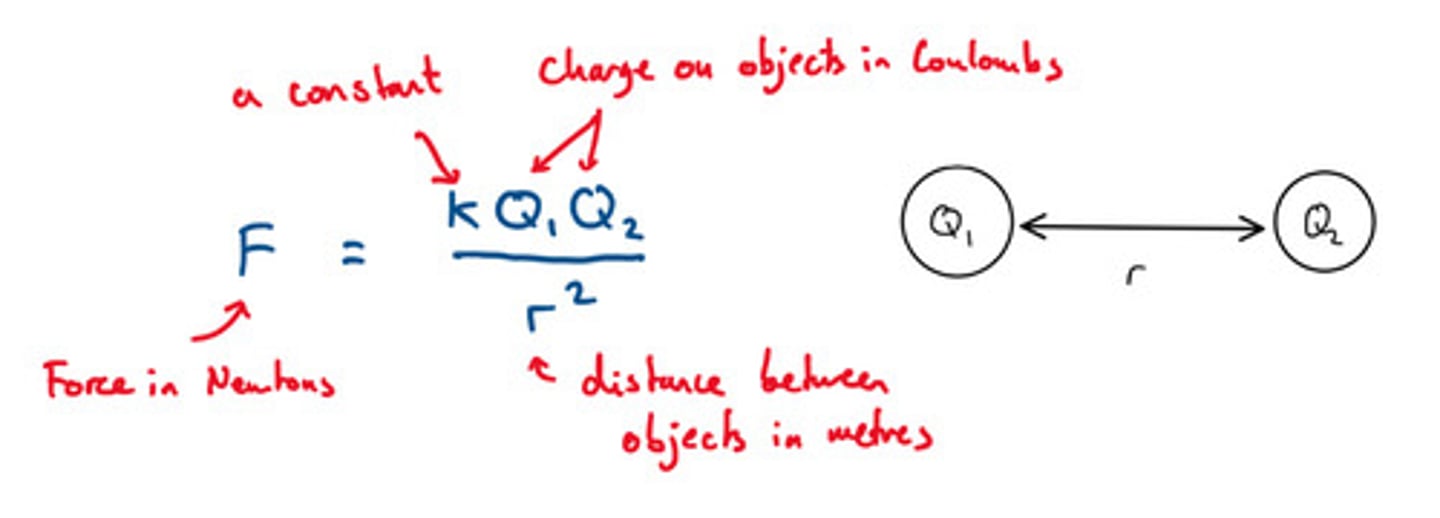
How can we determine the strength of an ionic bond?
ionic bond strength is determined by the charge and the size of the ions. Coulombs Law
- the greater the charges (multiply the charge of the anion and cation), the greater the strength
- if the product of the ion charges are the same, the compound with the smaller radius will have the greater strength
What is a spectator ion?
an ion that appears on both sides of an equation and is not directly involved in the reaction
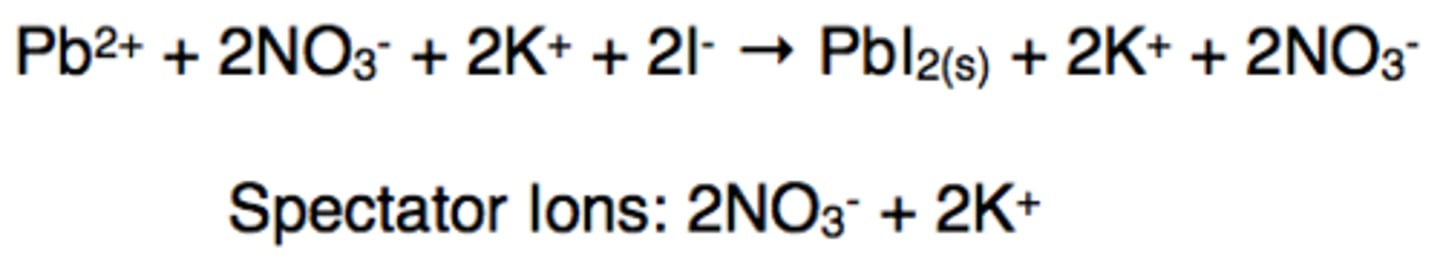
Write the molecular, complete ionic and net ionic equation for calcium chloride and sodium carbonate.
See diagram

Write the molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equation for lead (II)nitrate and potassium iodide.
See diagram
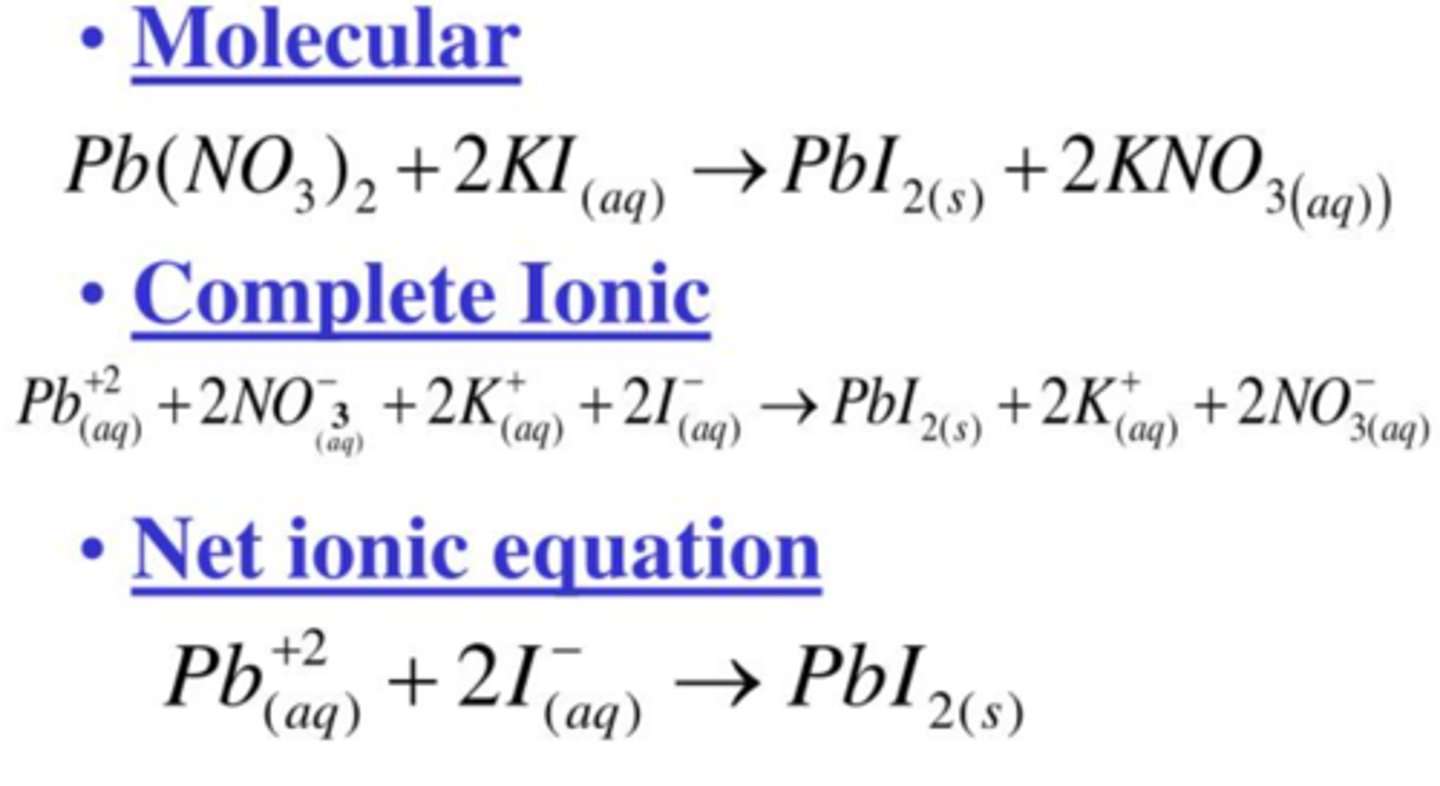
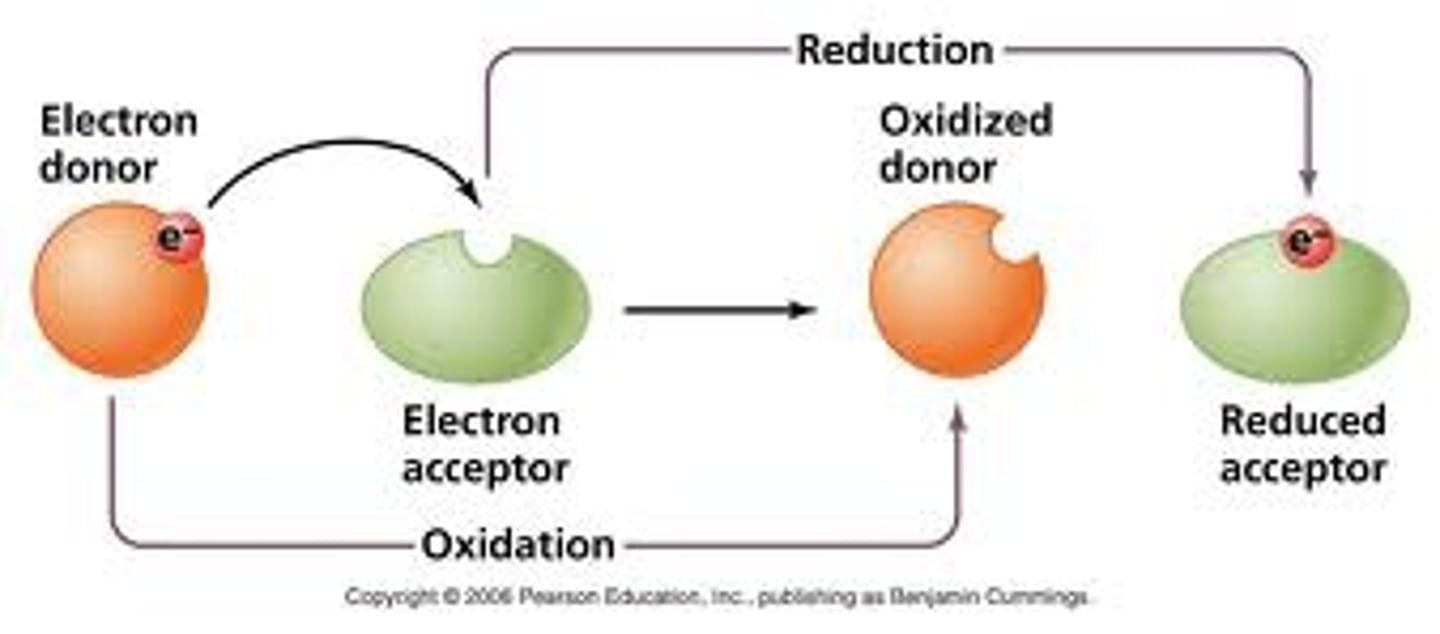
Oxidation Reduction Reactions
a reaction that involves the transfer of electrons between reactants
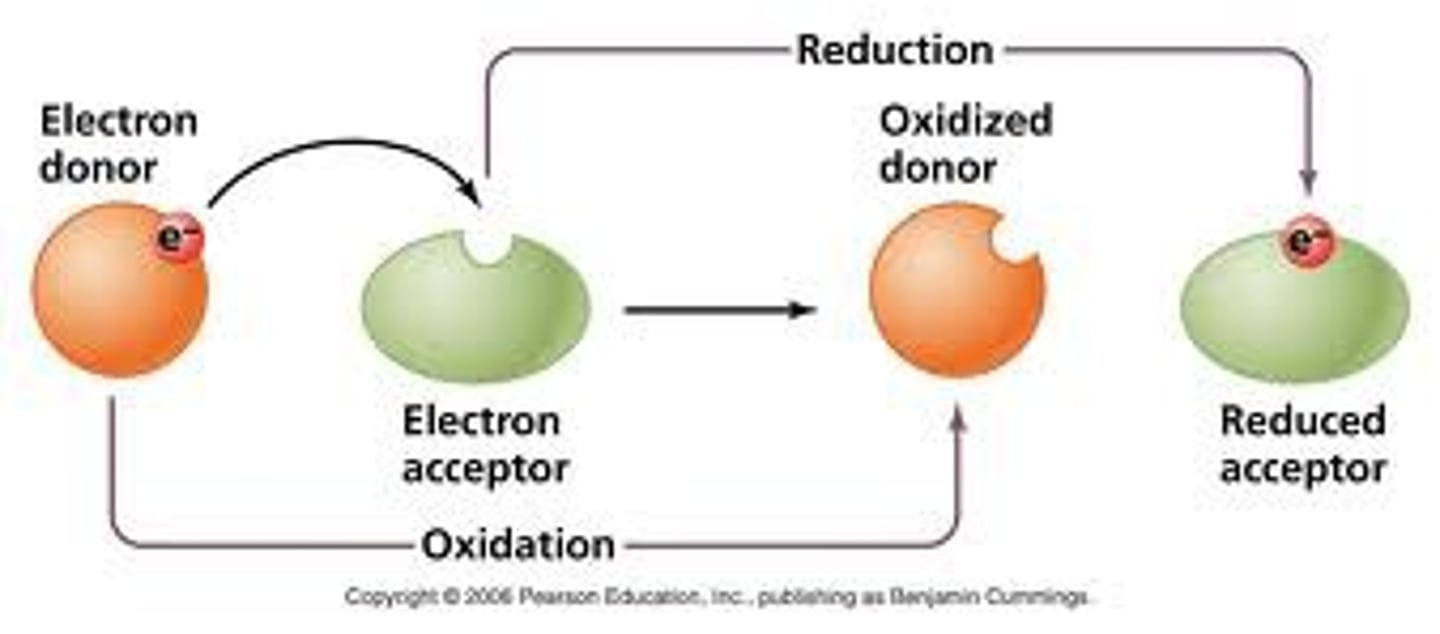
What are the 4 types of reactions that are always redox?
synthesis, decomposition, combustion, and single replacement reactions are always redox
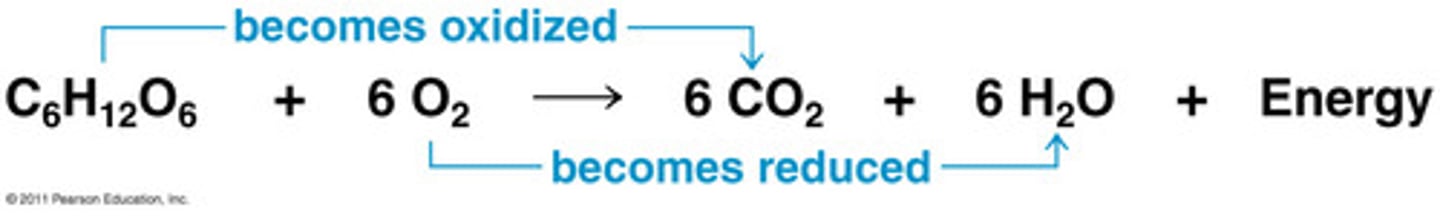
oxidation
loss of electrons
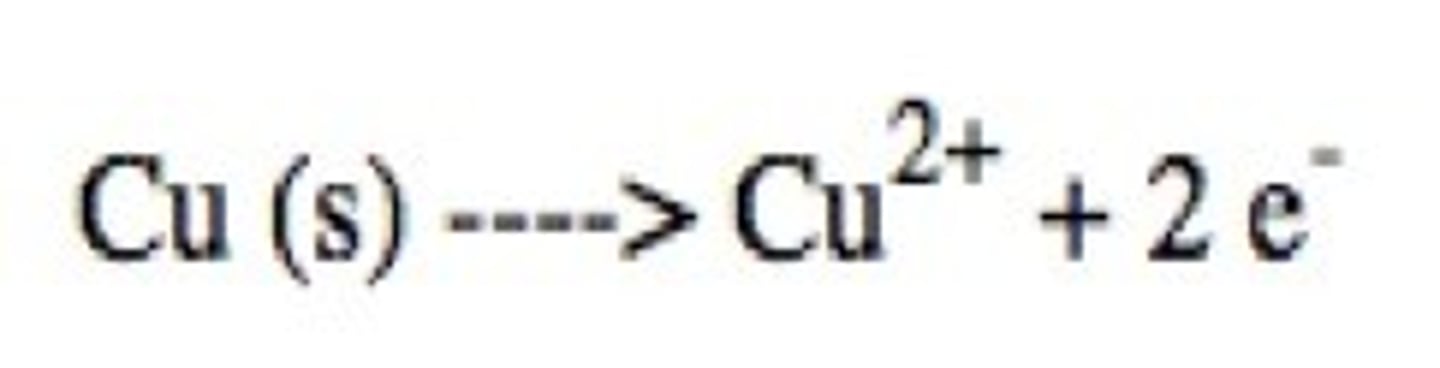
reduction
gain of electrons
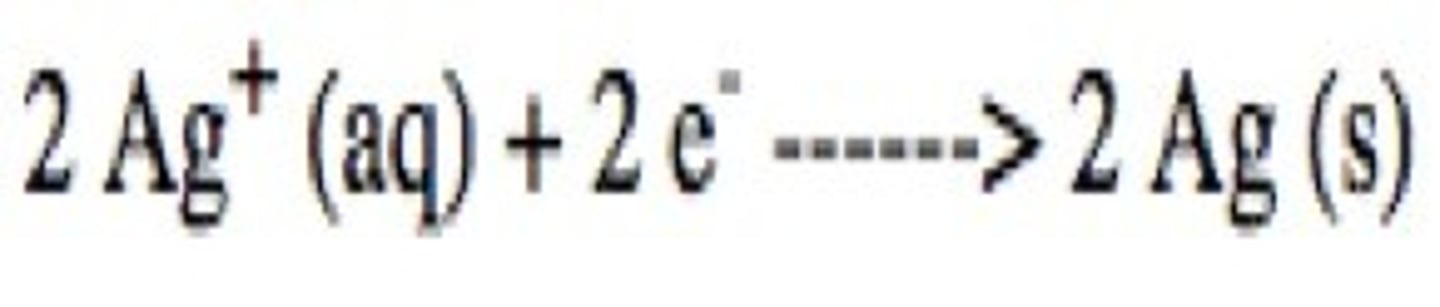
LEO GER
Lose Electrons Oxidation, Gain Electrons Reduction
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain

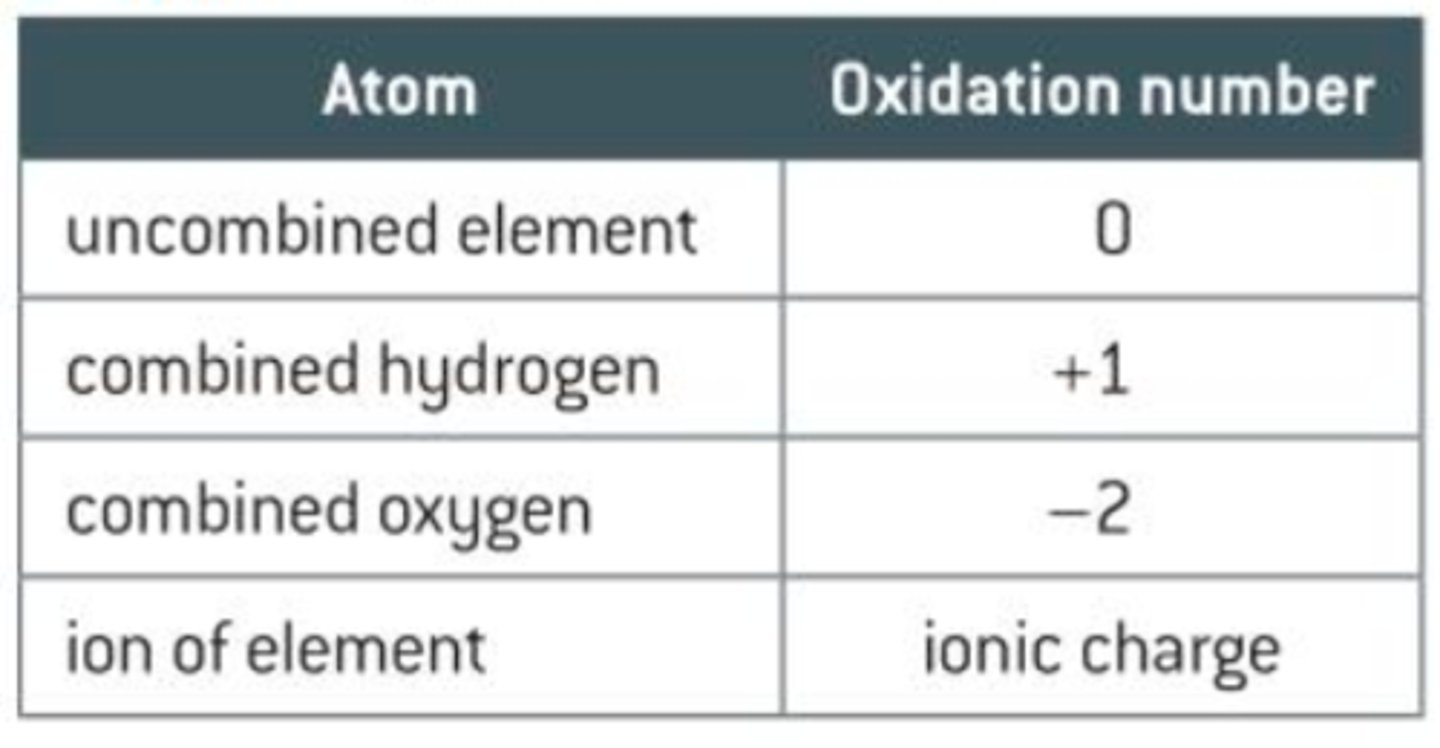
What is the oxidation number for oxygen?
-1 in peroxides
-2 in all other compounds (except with F)
Oxygen gas is 0.
What is the oxidation number for hydrogen?
+1 with non-metals
-1 with metals
hydrogen gas is 0.

What is the oxidation number for fluorine?
-1 (MOST IMPORTANT)
fluorine gas is ).

What are the oxidation numbers for the elements in calcium phosphate?
Calcium - + 2 (normal charge of alkaline earth metal)
Oxygen - -2 (normal oxidation number for oxygen)
Phosphorus - +5
3 (+2 Ca) + 2 (+5 P) + 2 (4 (-2 O) = 0

What are the oxidation numbers for the elements in aluminum acetate?
Al - +3 (normal ion charge)
C - + 0
H - +1
O - -2
(+3 Al) + 3 (2 (0 C)) + (3(3 (+1 H)) + (3 (2 (-2 O)) = 0
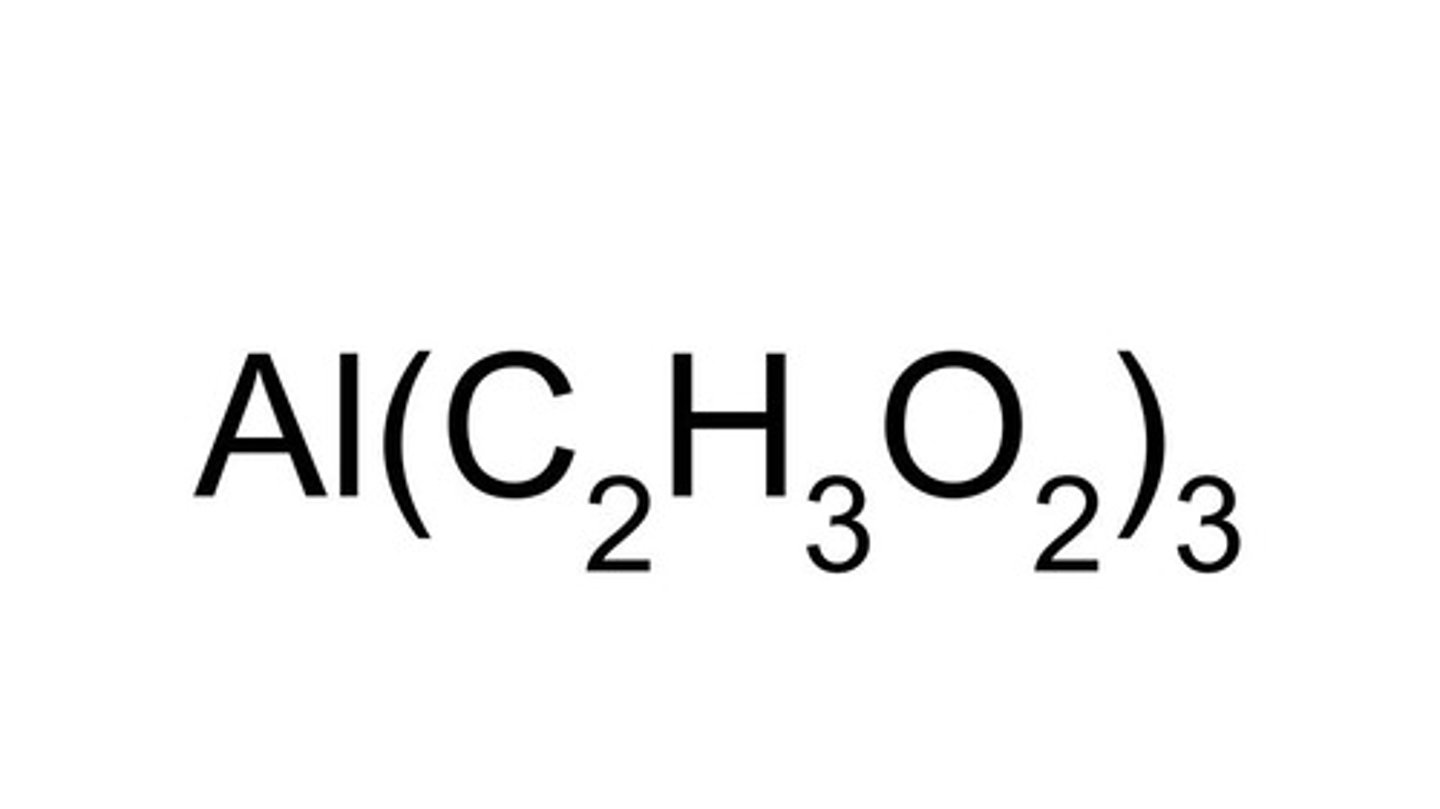
Write the synthesis reaction for solid sodium metal and chlorine gas. Identify what is oxidized and what is reduced.
Sodium is oxidized
Chlorine is reduced
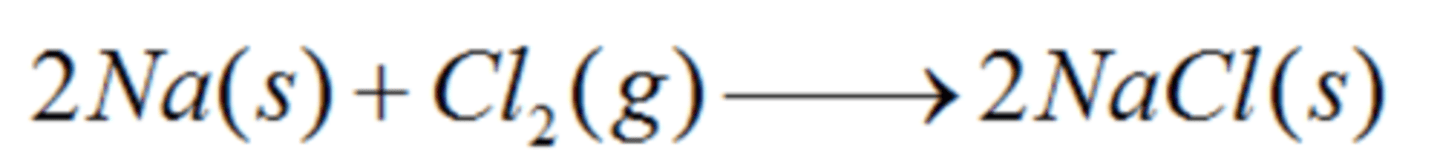
Write the synthesis reaction for solid zinc metal and iodine gas. Identify what is oxidized and what is reduced.
Zinc is oxidized
Chlorine is reduced
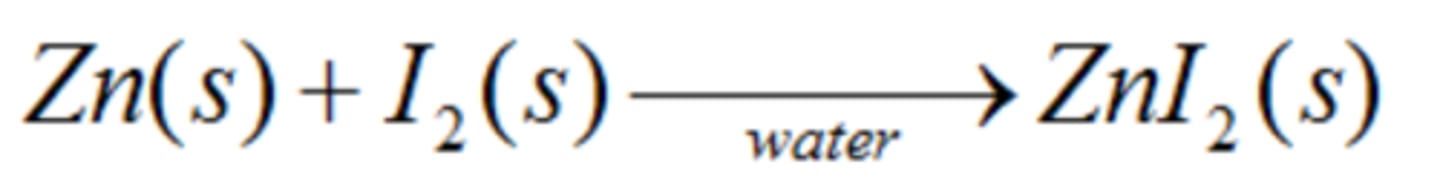
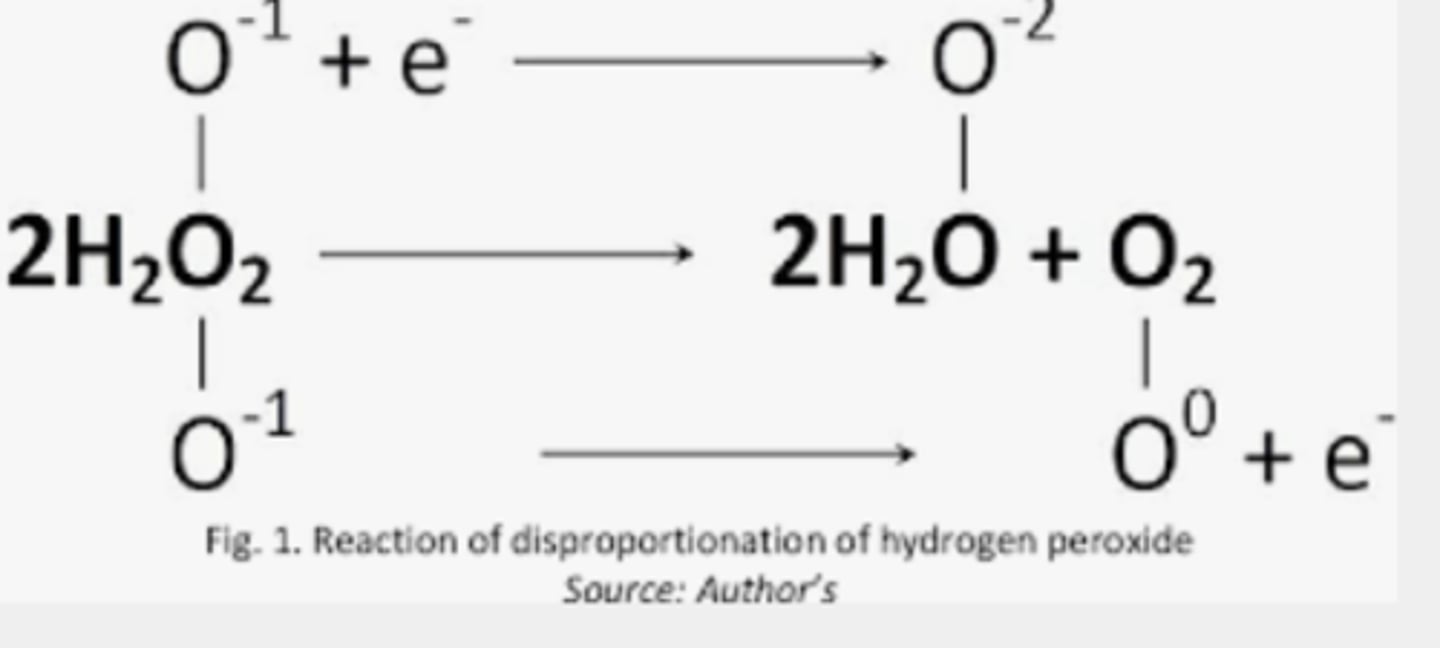
Write the decomposition reaction for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Identify what is oxidized and what is reduced.
Oxygen is oxidized
Chlorine is reduced
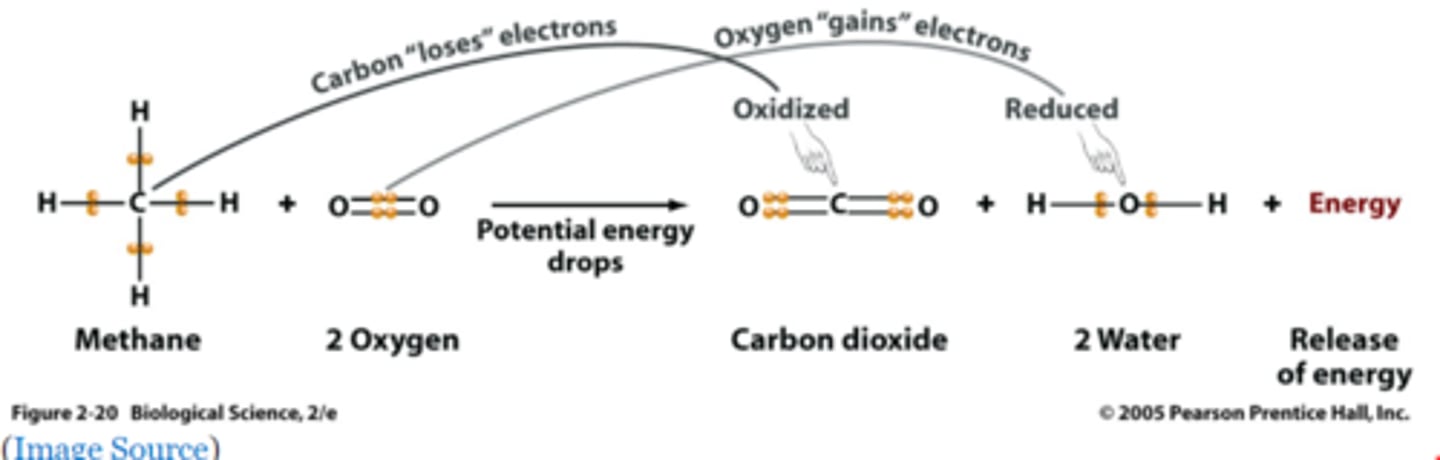
Write the combustion reaction for methane (CH4).
Identify what is oxidized and what is reduced.
Carbon is oxidized.
Oxygen is reduced.
Write the single replacement reaction for magnesium and hydrochloric acid.
Identify what is oxidized and what is reduced.
What is the spectator ion?
Magnesium is oxidized.
Hydrogen is reduced.
Chlorine is a spectator ion.
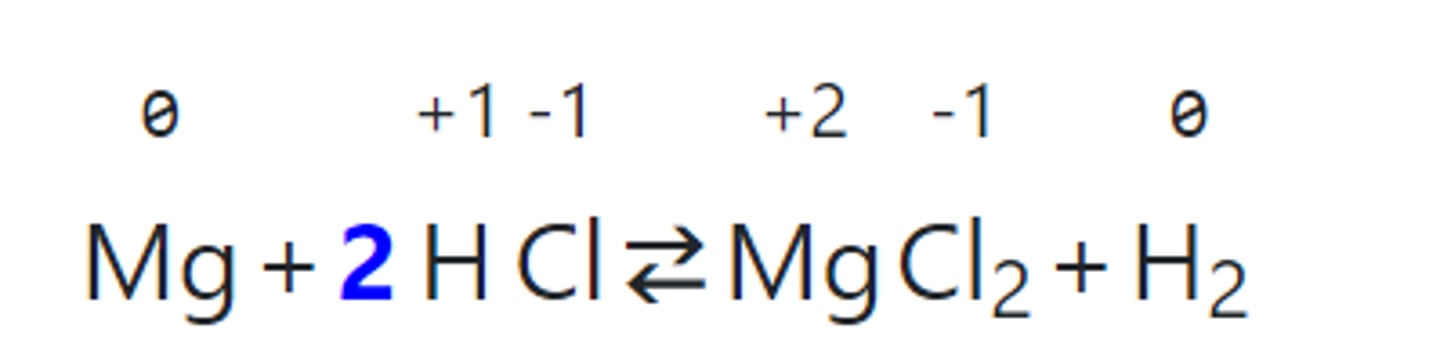
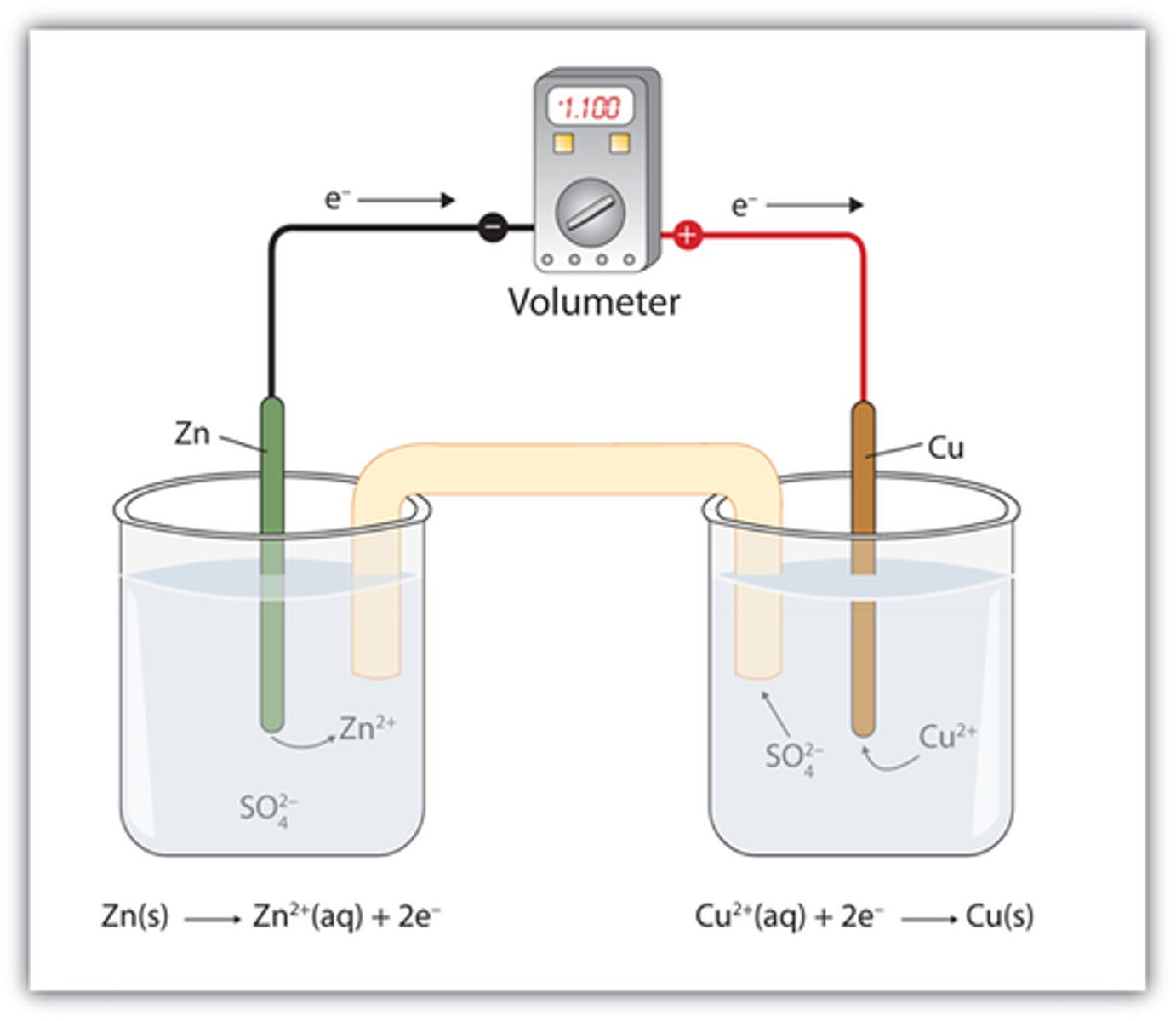
Write the single replacement reaction for solid zinc and copper sulfate.
What are the oxidizing and reducing agents?
What is the spectator ion?
Copper is the oxidizing agent.
Zinc is the reducing agent.
Sulfate is the spectator ion.
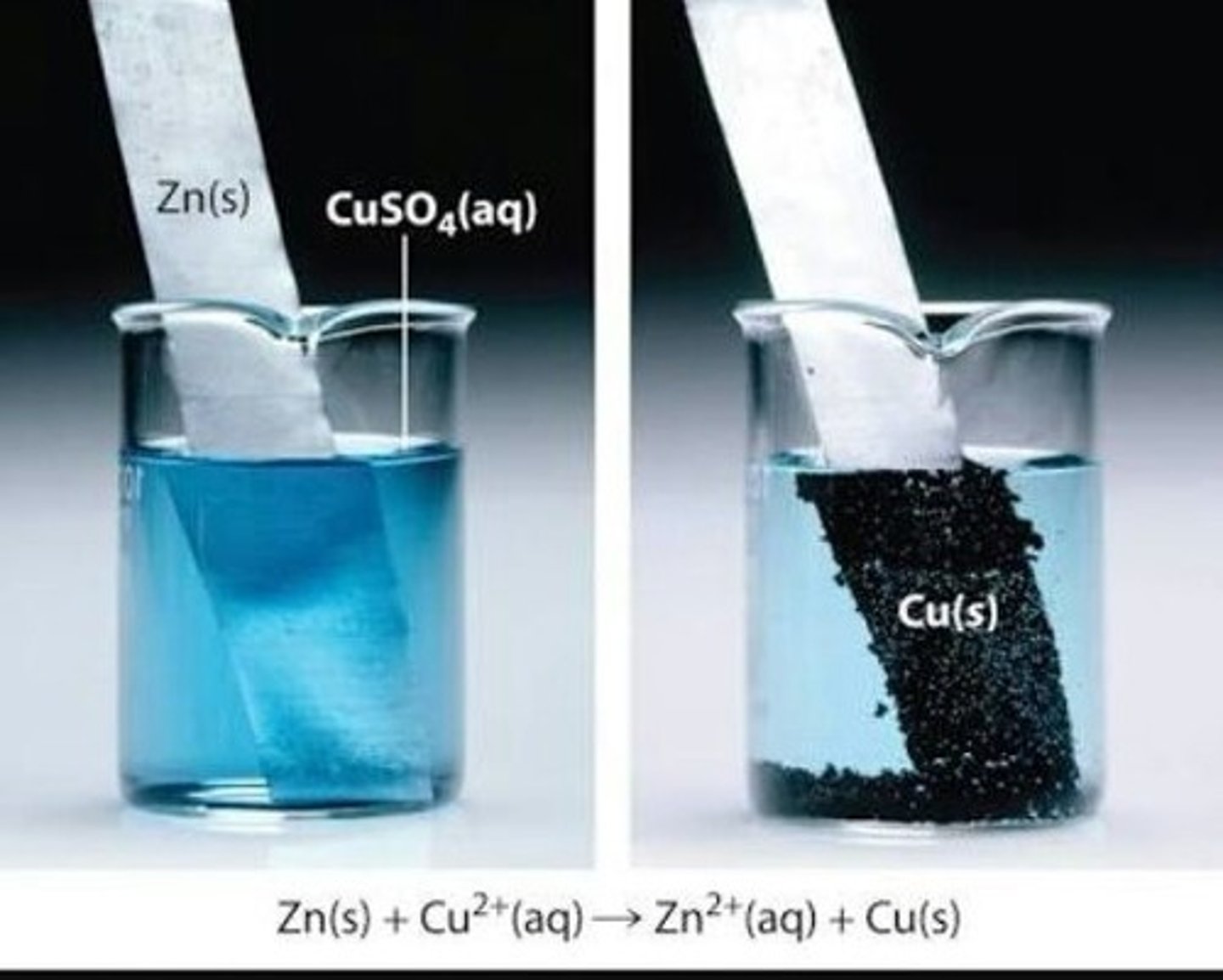

Write the single replacement reaction for solid zinc and copper sulfate.
What are the oxidizing and reducing agents?
What is the spectator ion?
Zn (s) ---> Zn2+ + 2 e-
Cu2+ + 2 e- ---> Cu (s)
How can I identify redox reactions?
1. Write the oxidation numbers. If the oxidation numbers change for products and reactants then you have a redox reaction (there must be an oxidizer and a reducer present)
2. Look for the key reactions that are always redox - synthesis, decomposition, combustion, and single replacement.
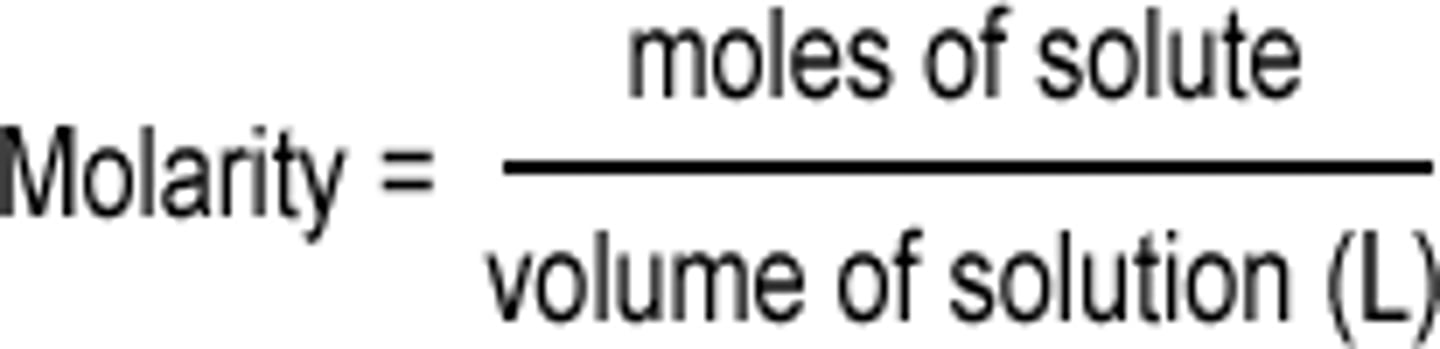
How do you calculate molarity?
moles of solute/liters of solution
How do you calculate the molarity of a solution that has been diluted?
initial molarity x initial volume = final molarity x final volume