AP Bio Unit 1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
polarity
When there are differences in atomic electronegativities
Water is polar due to the oxygen being negative and the hydrogen being positive
hydrogen bond
A weak bond interaction between the negative and positive regions of 2 separate molecules
Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules
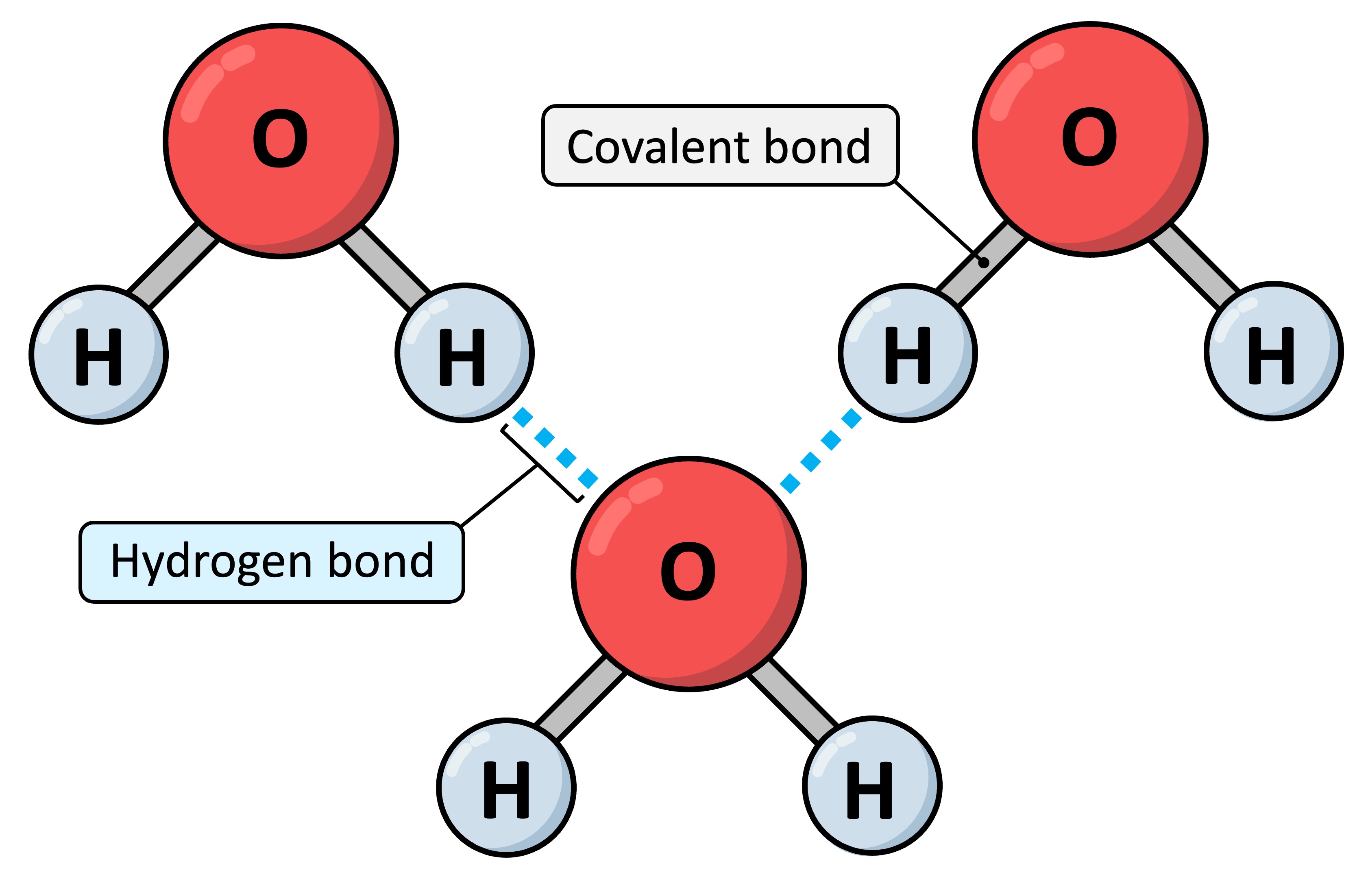
cohesion
When 2 of the same molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other

adhesion
When 2 different molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other

surface tension
When many water molecules are bonded tightly together near the surface of the water
Helps plants floating on the water with photosynthesis
solvency
When water molecules use adhesion to break apart other molecules
high heat capacity
Water’s cohesive property allows it to absorb a lot of thermal energy before changing chemical states, resisting sudden changes in temperature
capillary action
Water can go up a tube with its cohesive and adhesive abilities
Helps bring water up plant roots
carbon
Used to build Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
Stores energy
Builds basic cell structures
nitrogen
Used to build proteins and nucleic acids
phosphorous
Used to build certain lipids and nucleic acids
monomers
Chemical subunits used to create polymers
Connect to other monomers through covalent bonds
polymer
A macromolecule made of many monomers
dehydration synthesis
OH and H come off of 2 monomers, joining the monomers together with a covalent bond
H2O is the byproduct
hydrolysis
H2O splits apart a polymer
Opposite of dehydration synthesis
nucleic acids
3’ hydroxyl end and 5’ phosphate end
Antiparallel 5’-3’ direction
adenine-thymine bond
Held together by 2 hydrogen bonds
Destabilizes faster than guanine-cytosine
guanine-cytosine
Held together by 3 hydrogen bonds
Destabalizes slower than adenine-thymine
amino acids
Held together by covalent bonds from dehydration synthesis
primary structure of proteins
Determined by the sequence of amino acids held together by covalent bonds, called peptide bonds
secondary structure of proteins
Arises through local folding of the amino acid chain into elements such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets
tertiary structure of proteins
The overall 3D shape of the protein and often minimizes free energy
Various types of bonds and interactions stabilize the protein at this level
quaternary structure of proteins
Arises from the interactions between multiple polypeptide units
carbohydrates
Held together by covalent bonds from dehydration synthesis
DNA
Double-stranded
Contains thymine
Deoxyribose sugar
RNA
Single-stranded
Contains uracil
Ribose sugar