Aerobic Bioenergetics and Metabolic Pathways in Cells
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the main hydrogen and electron carrier molecules involved in aerobic bioenergetics?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
What is the role of NADH in cellular respiration?
NADH is shuttled into mitochondria for ATP generation and must be converted back to NAD.
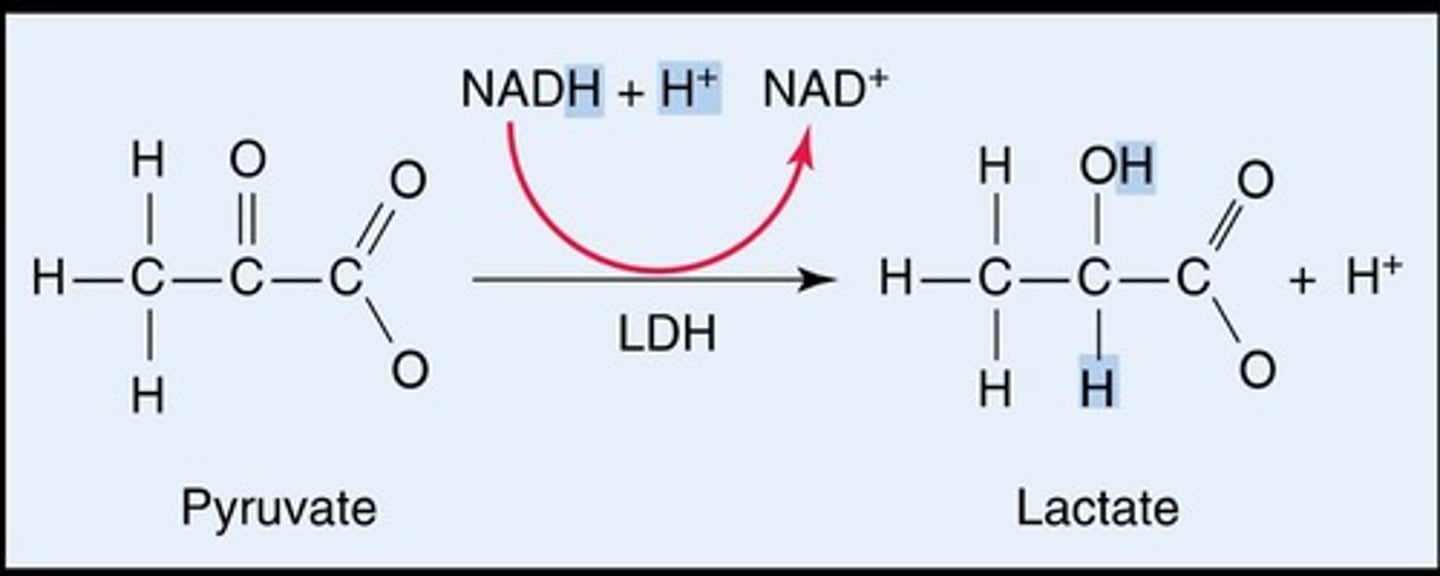
How is pyruvic acid converted to lactic acid?
Through anaerobic metabolism catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
What is the citric acid cycle also known as?
The Krebs Cycle
What is the ATP yield from one mole of glucose during aerobic metabolism?
32 moles of ATP
What is the overall efficiency of aerobic respiration?
34% of the energy from glucose is converted to ATP, with 66% released as heat.
What is the process of beta-oxidation?
The breakdown of triglycerides into fatty acids, which are then converted to acetyl-CoA for energy use.
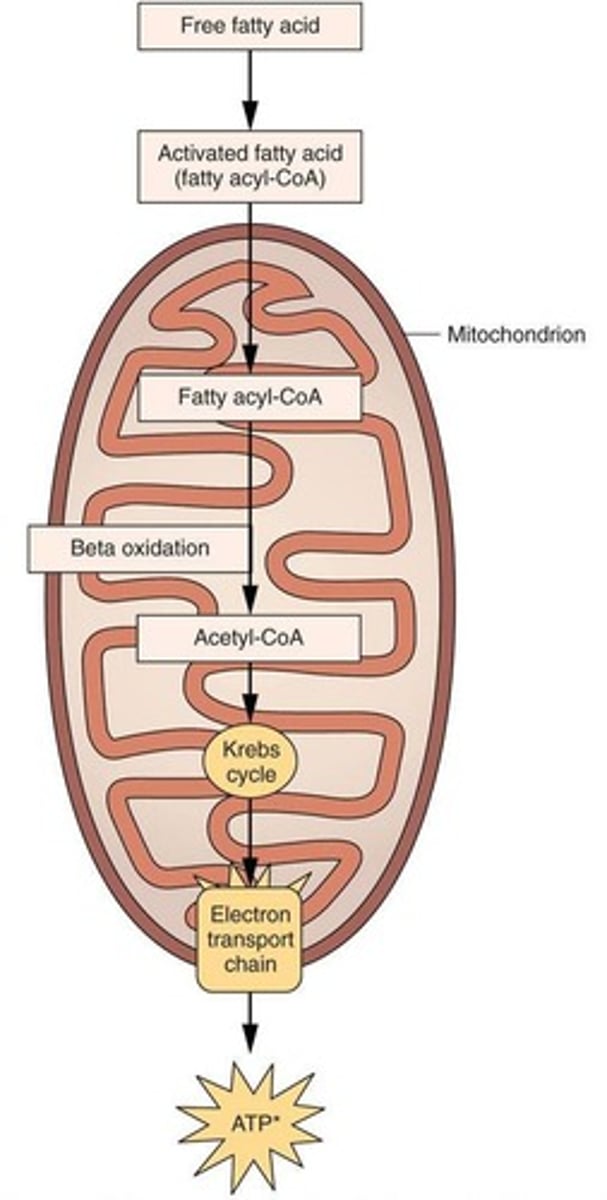
What happens to fatty acids during aerobic metabolism?
Fatty acids are converted to acetyl-CoA and enter the citric acid cycle for energy production.
What is the energy yield of one mole of ATP?
7.3 kcal
What regulates the rate of a metabolic pathway in bioenergetics?
Rate-limiting enzymes
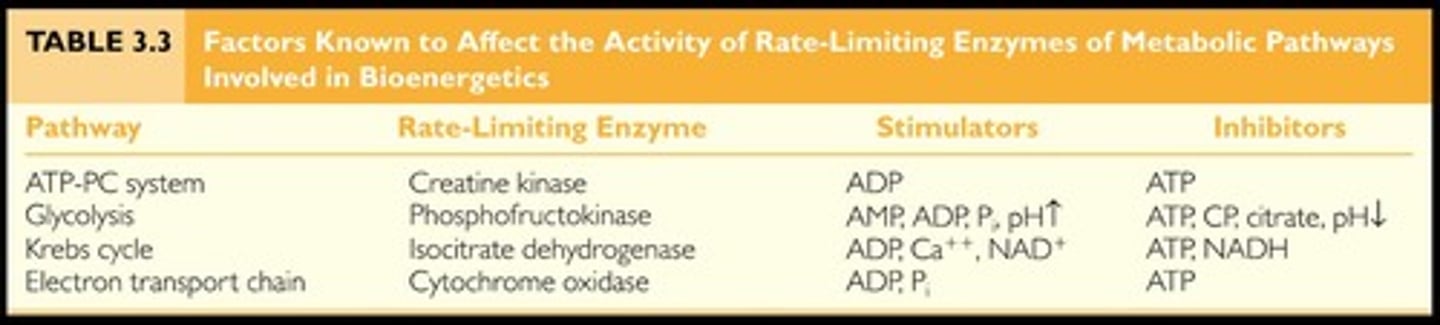
How do high levels of ATP affect ATP production?
High levels of ATP inhibit ATP production.
What stimulates aerobic ATP production?
Low levels of ATP and high levels of ADP+Pi, as well as calcium.
What role does the electron transport chain play in aerobic metabolism?
It facilitates oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria, producing ATP.
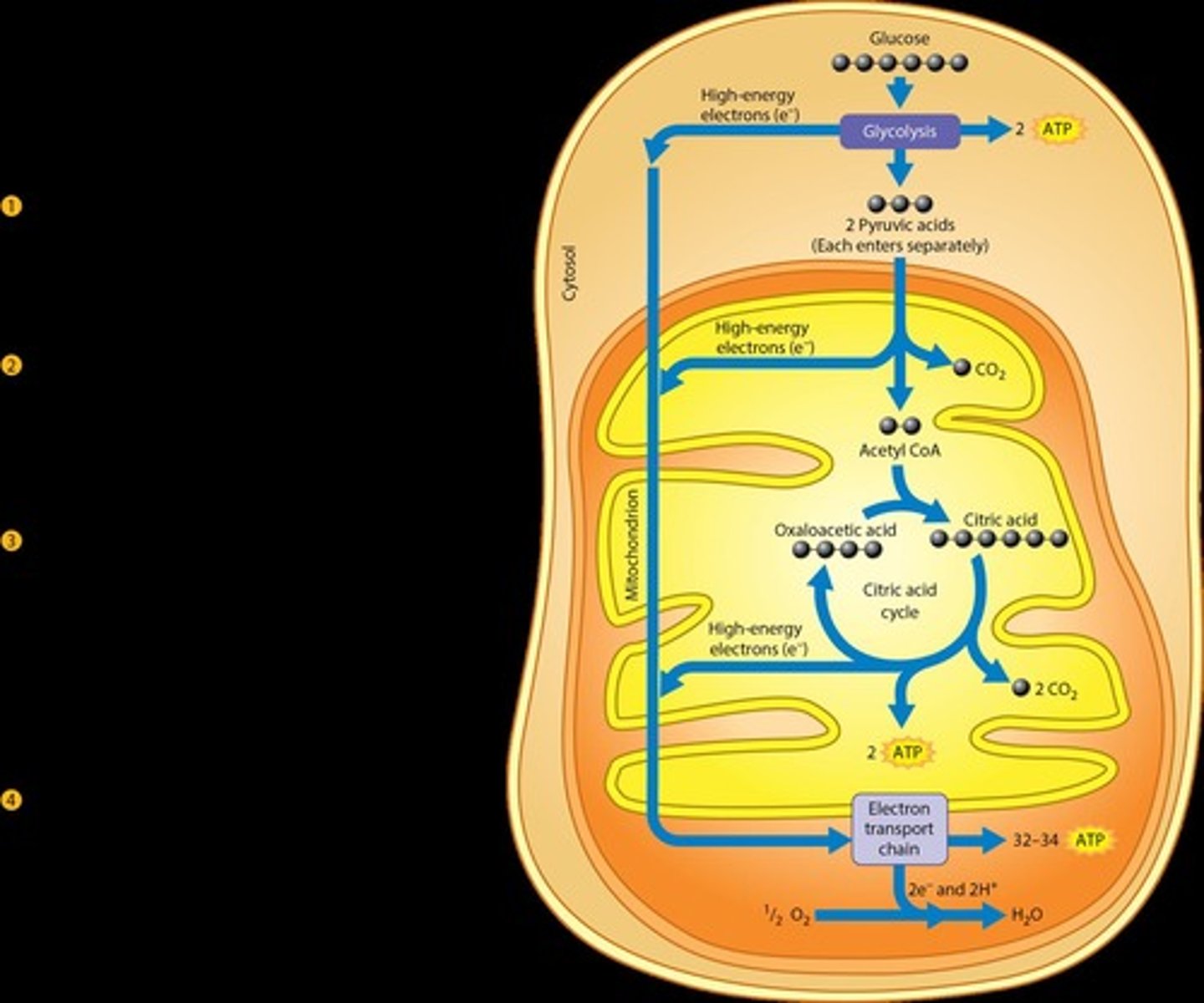
What is the fate of electrons removed from NADH and FADH during aerobic respiration?
They are passed along carriers to produce ATP and accepted by O2 to form water.
What happens to glycerol during fat metabolism?
Glycerol is broken down into glucose, pyruvic acid, acetyl-CoA, and Krebs cycle intermediates.
What is lipolysis?
The process of breaking down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids.
What is the significance of acetyl-CoA in metabolism?
Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle and is used for energy production.
What is the role of specific transport systems in mitochondria?
They shuttle H+ ions across the mitochondrial membrane.
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle?
To generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA.