PAS407 - Oral cavity & Nasal cavity
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Function of nasal cavities
o olfaction – smelling
o respiration – breathing
o filtration of dust
o humidification of inspired air
o elimination of sinus, nasolacrimal duct secretions
o Divided by the nasal septum
respiratory area of nasal cavity: does what?
o inferior 2/3rds
o warms, moistens inspired air
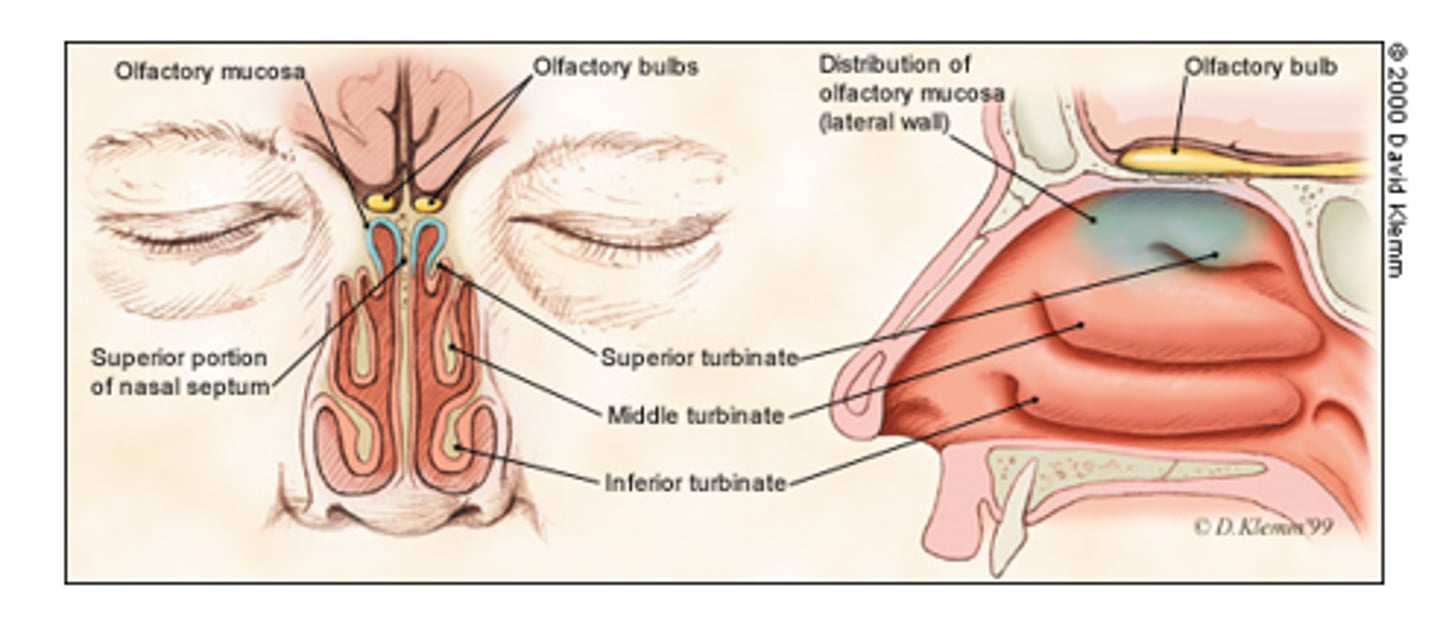
olfactory area of nasal cavity: does what?
o superior 1/3rd
o contains peripheral organ of smell
what are the nasal conchae?
o three conch-shaped plates that project inferiorly to assists in warming, moistening air; swell during irritation, infection, etc
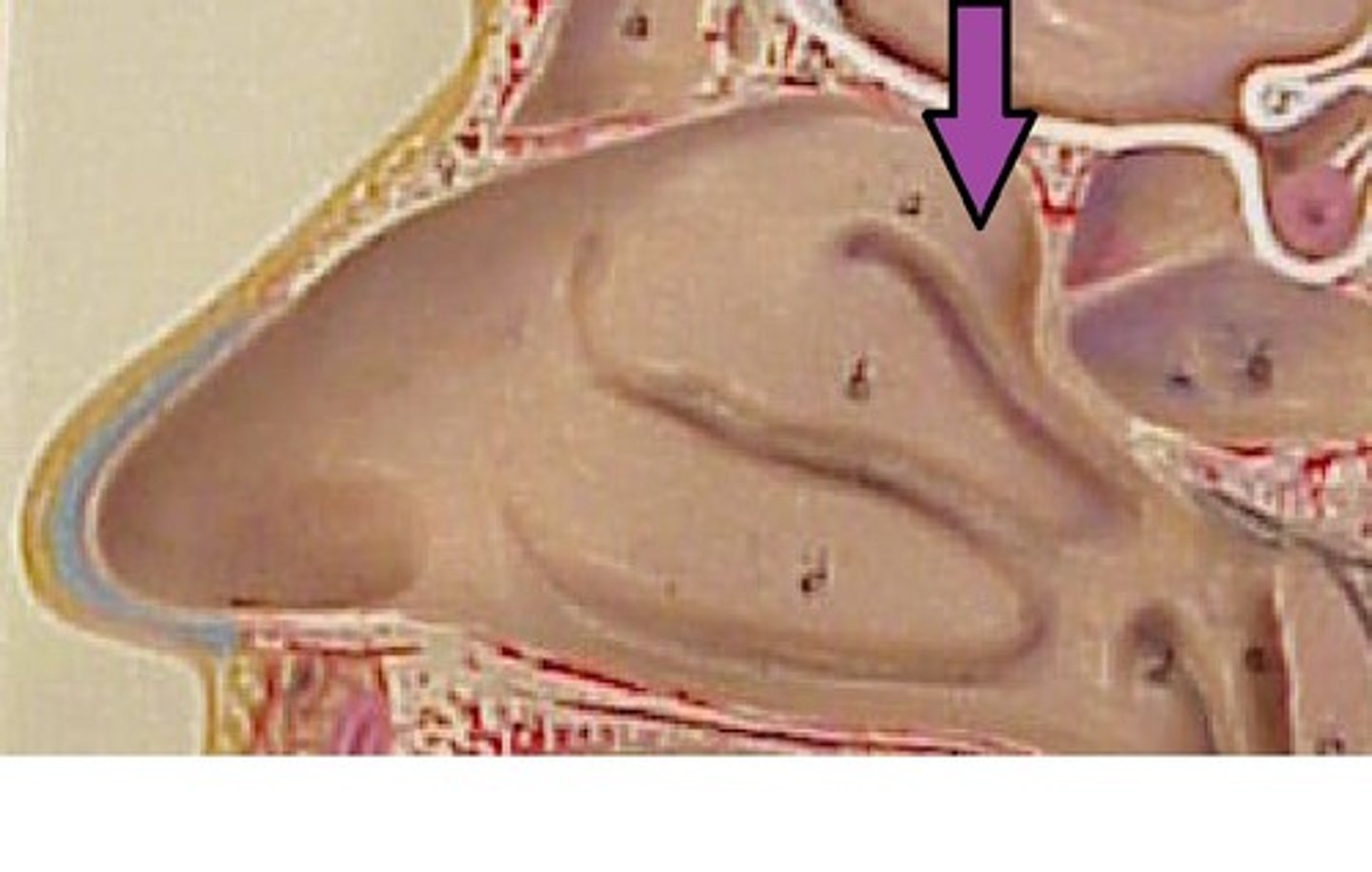
What is the spheno-ethmoidal recess?
location of opening of sphenoidal sinus
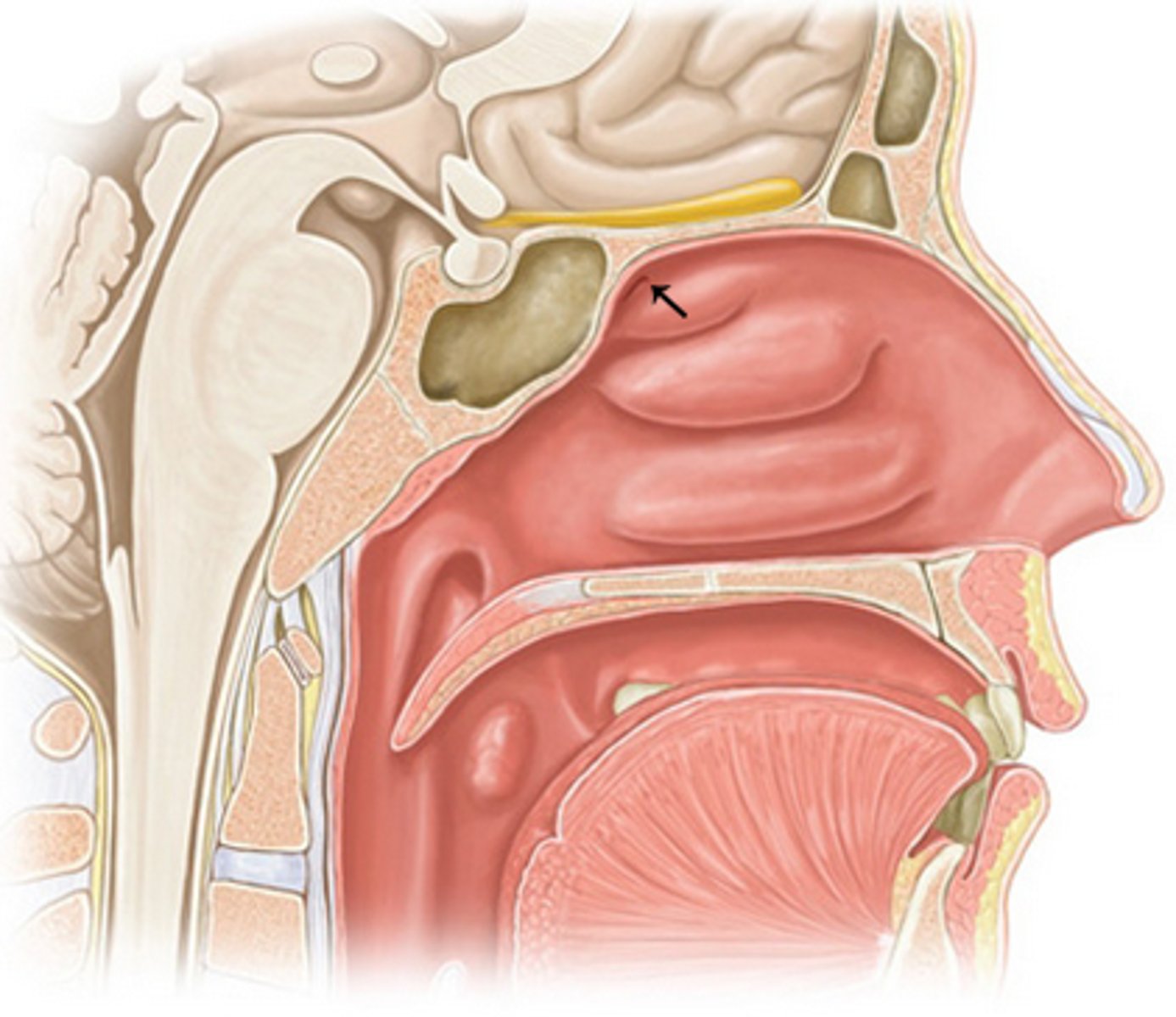
what is a nasal meatus?
small recess between conchae and lateral wall
superior nasal meatus between what and contains what?
narrow passage between superior, middle nasal conchae
opening of posterior ethmoidal sinuses
middle nasal meatus is between what? It contains what? (3)
between middle, inferior nasal conchae
· ethmoidal infundibulum
· semilunar hiatus
· ethmoidal bulla (bubble)
inferior nasal meatus is below what? contains what?
§ inferolateral to inferior nasal concha
§ contains opening for tears from nasolacrimal duct
roof of nasal cavity supplied by:
anterior/posterior ethmoidal arteries
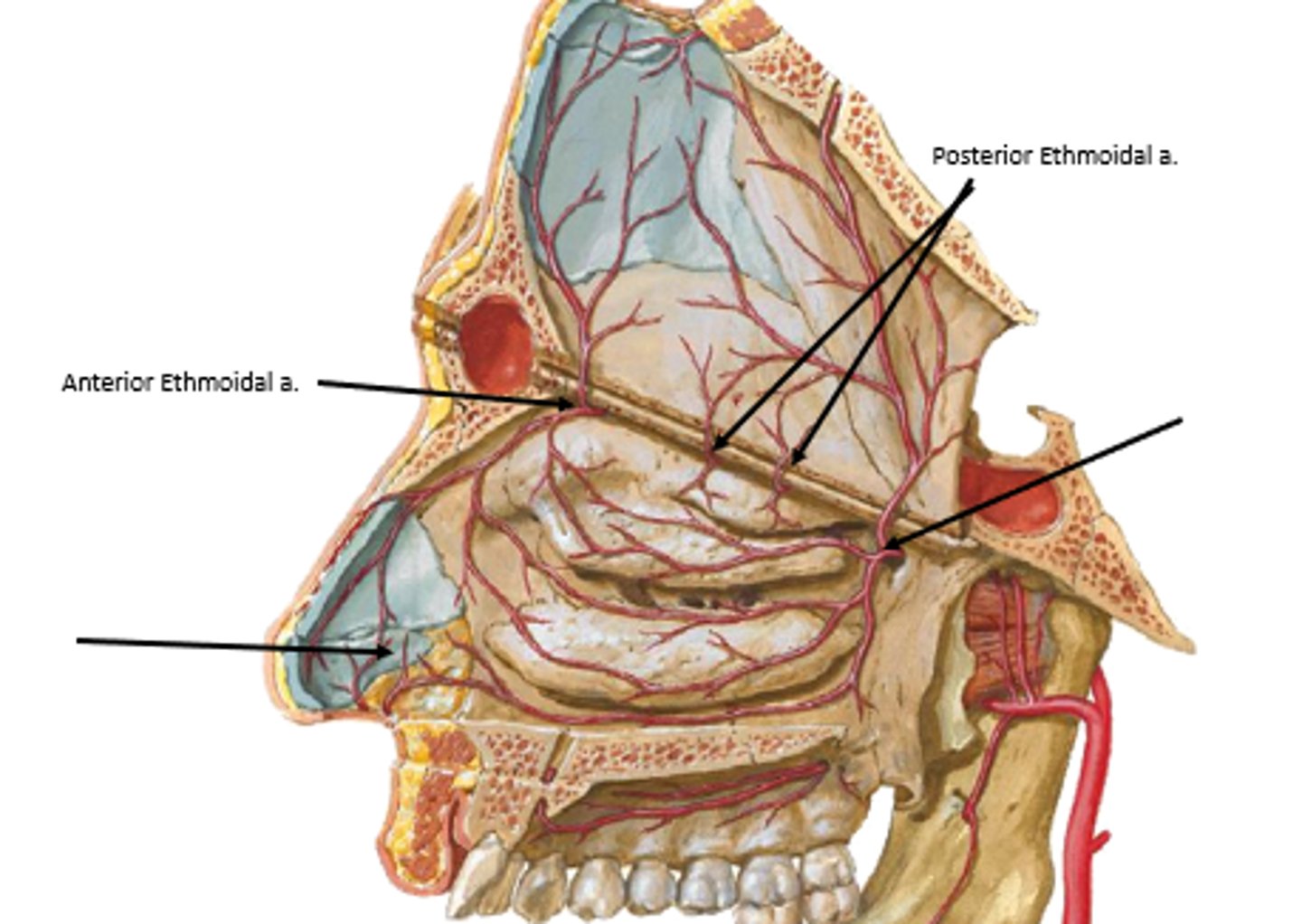
medial/lateral walls of nasal cavity supplied by:
sphenopalatine artery
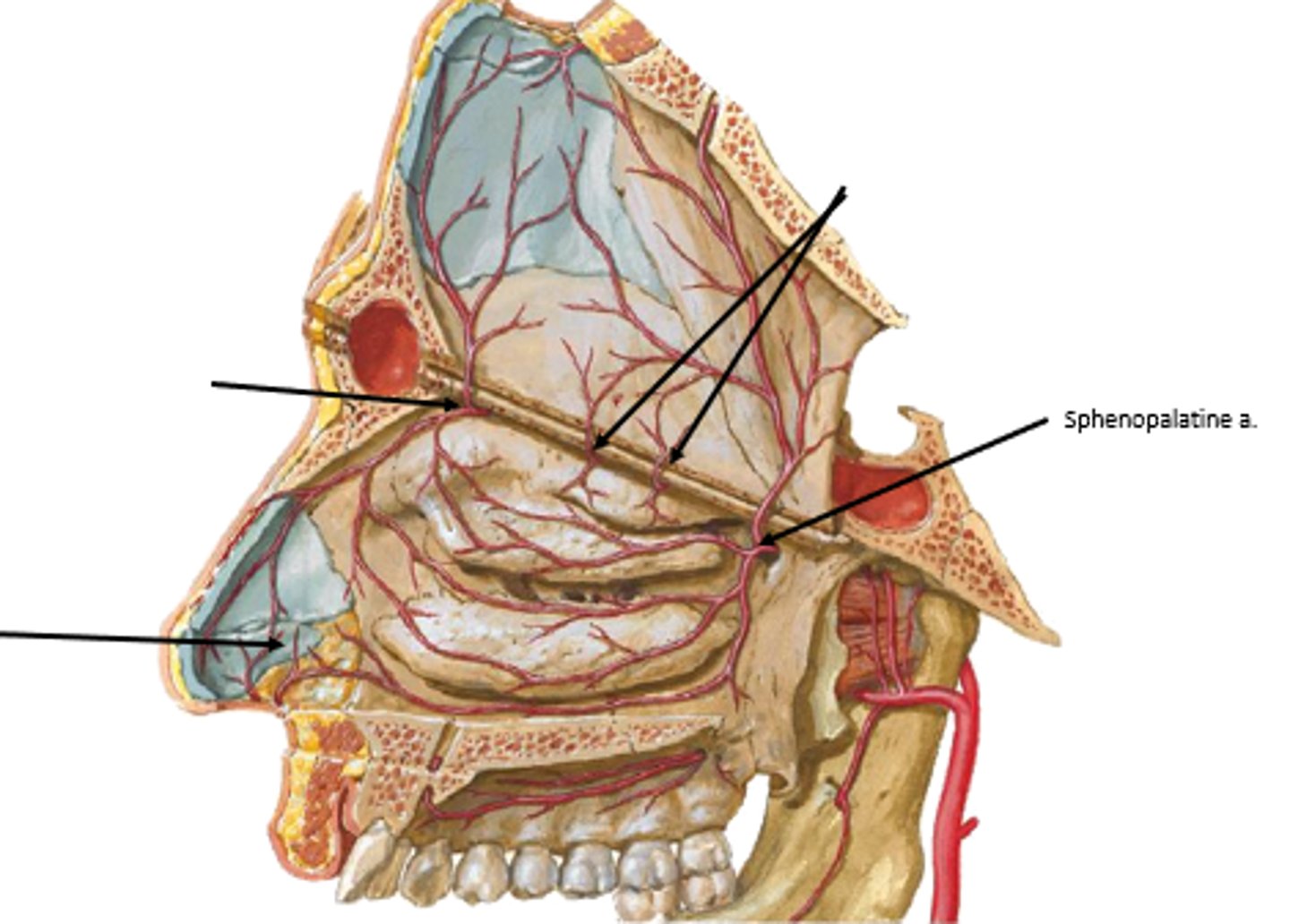
· floor of nasal cavity supplied by:
greater palatine artery
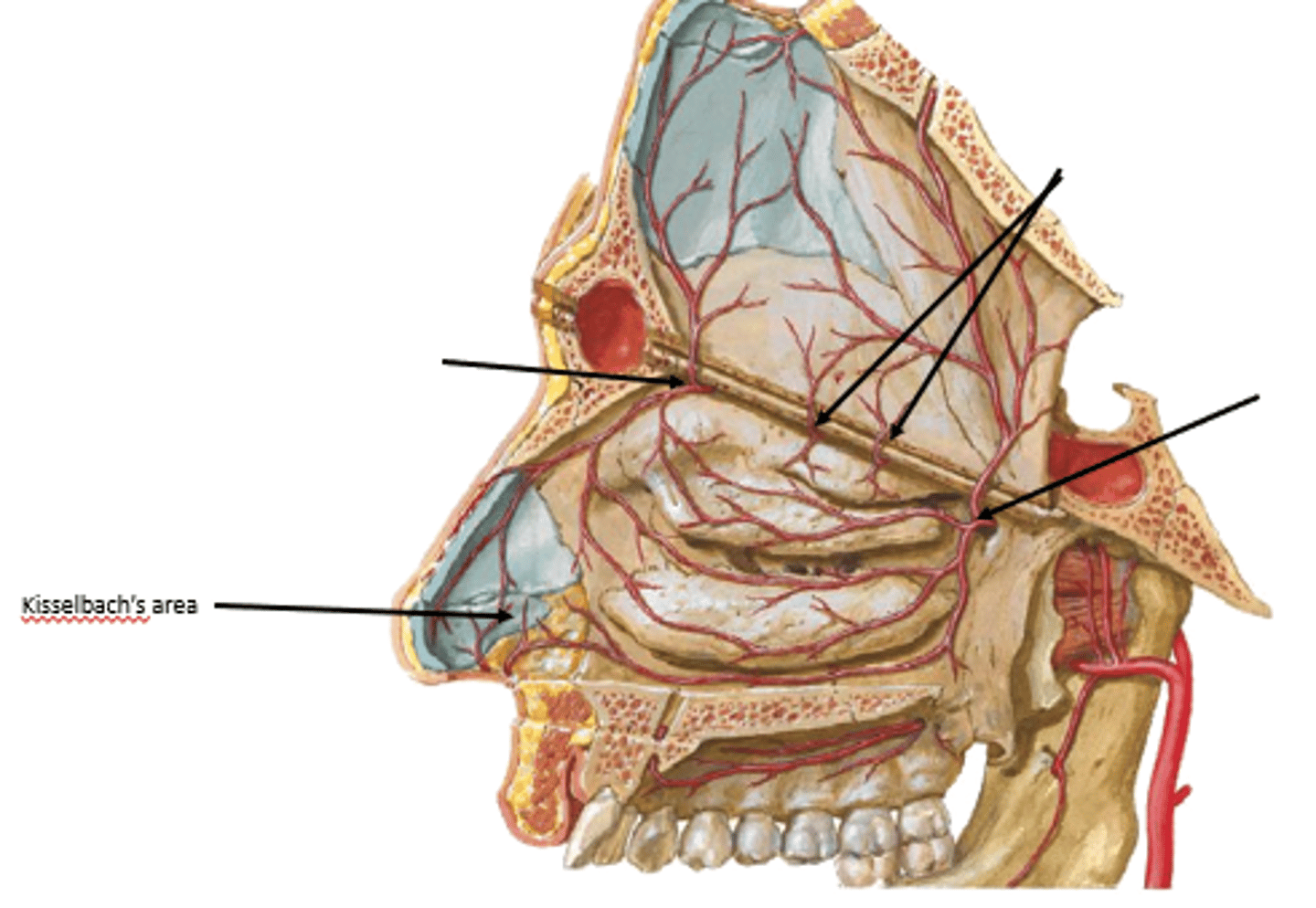
What is Kisselbach's area?
Site of arterial anastomosis of all nasal branches
Site for nose bleeds
Branches of maxillary nerve (V2)
nasopalatine nerve and posterior superior/inferior lateral nasal nerves
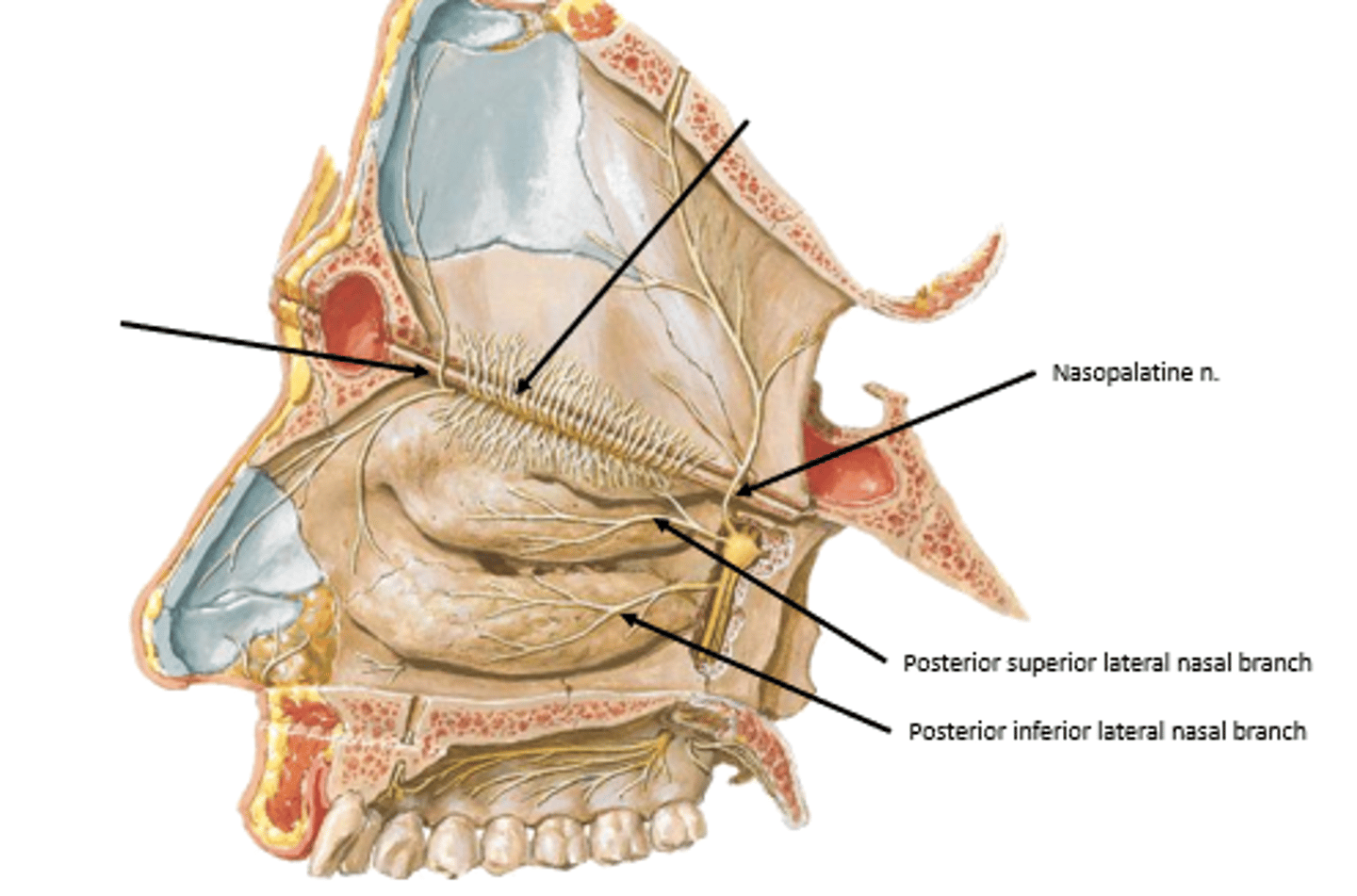
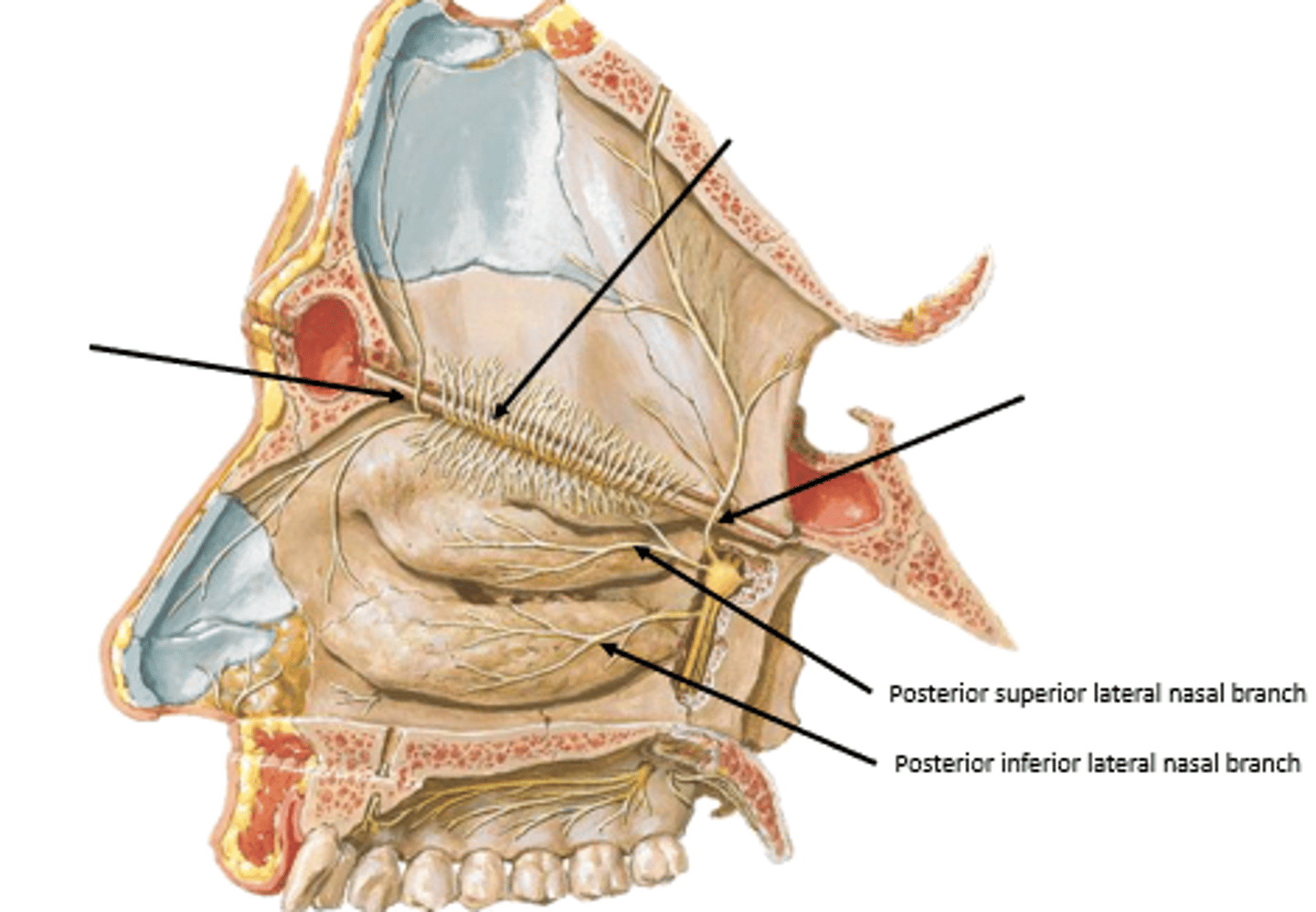
posteroinferior mucosa:
what nerve supplies the septum of the nasal cavity?
nasopalatine nerve
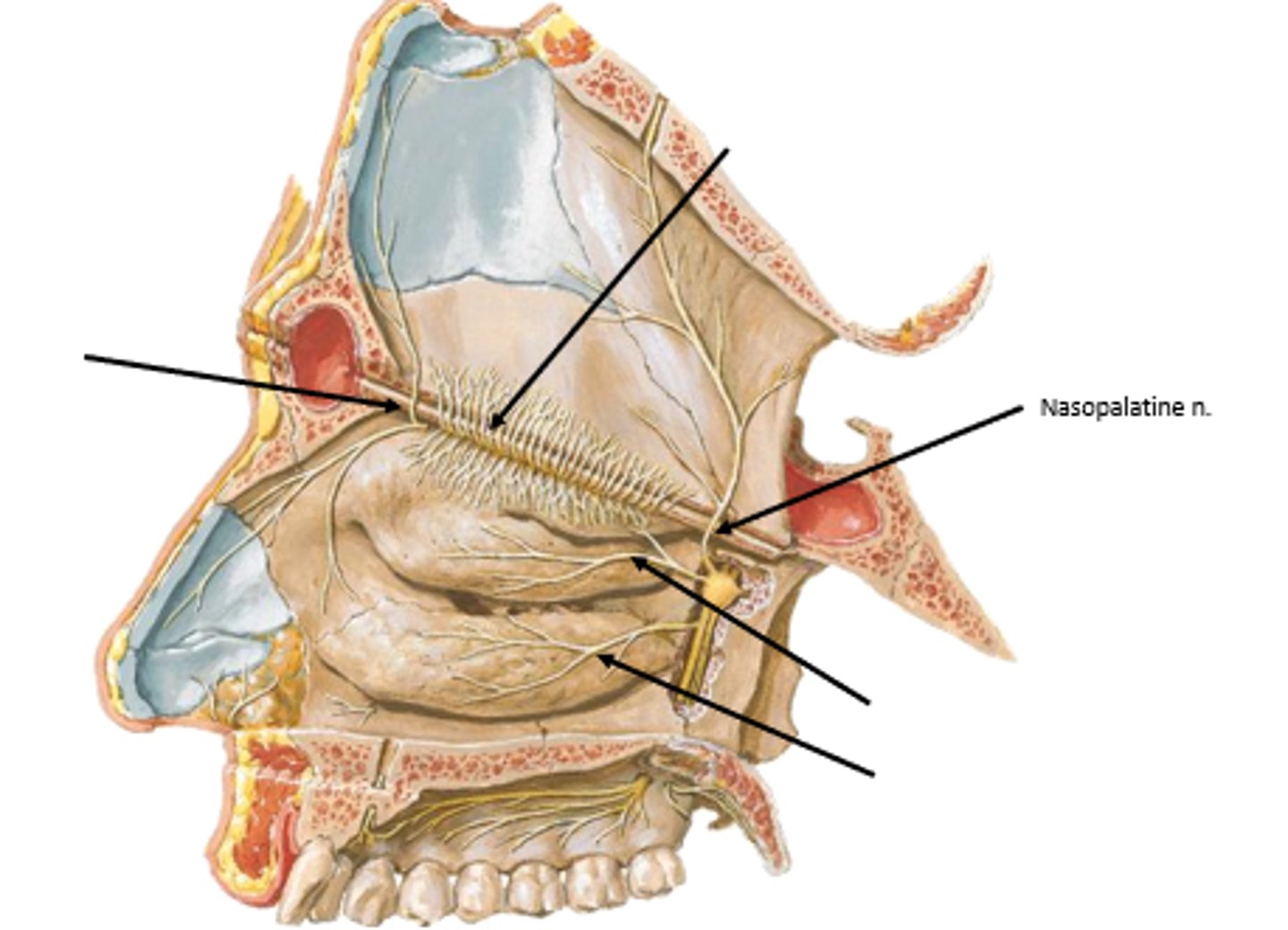
posteroinferior mucosa:
what nerve supplies the lateral walls of the nasal cavity?
posterior superior/inferior lateral nasal branches
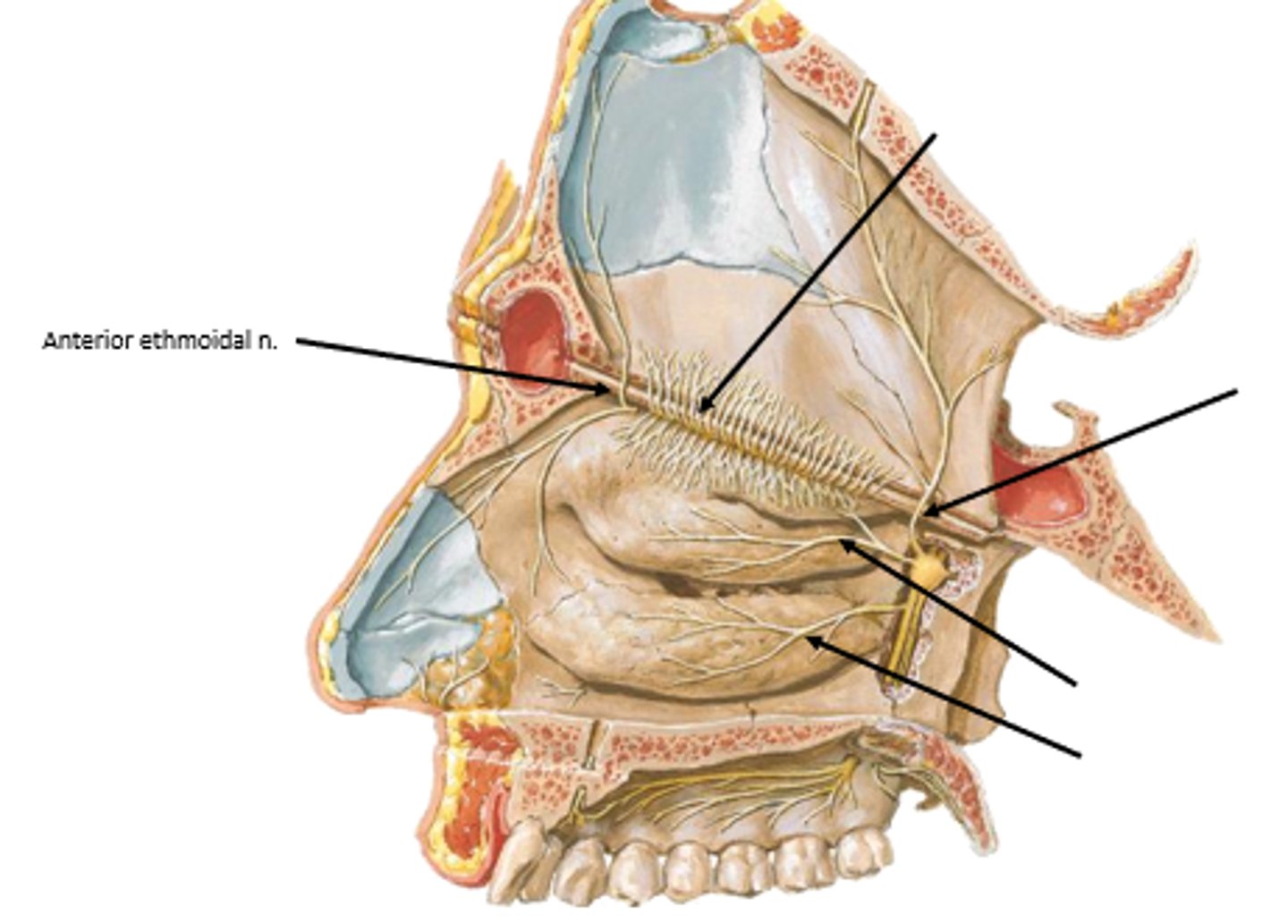
anterosuperior mucosa:
what nerve supplies this area? what branch is it from
anterior/posterior ethmoidal nerves
Branched from ophthalmic nerve (V1)
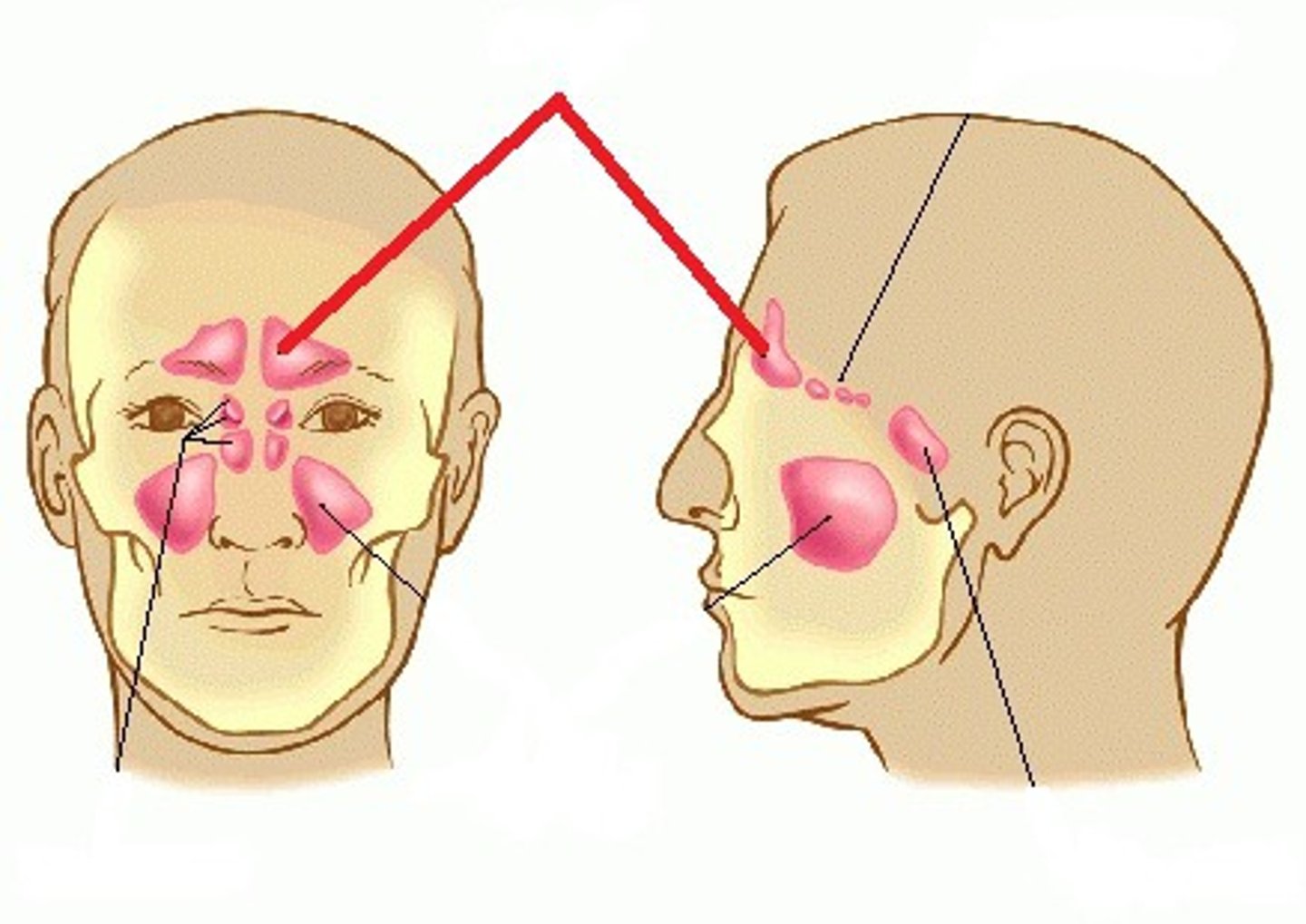
What are the paranasal sinuses?
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillary
They are air filled extensions of the nasal cavity
frontal sinus
1. is what
2. drains through what
o between outer, inner tables of frontal bone
o drains through frontonasal duct into middle nasal meatus
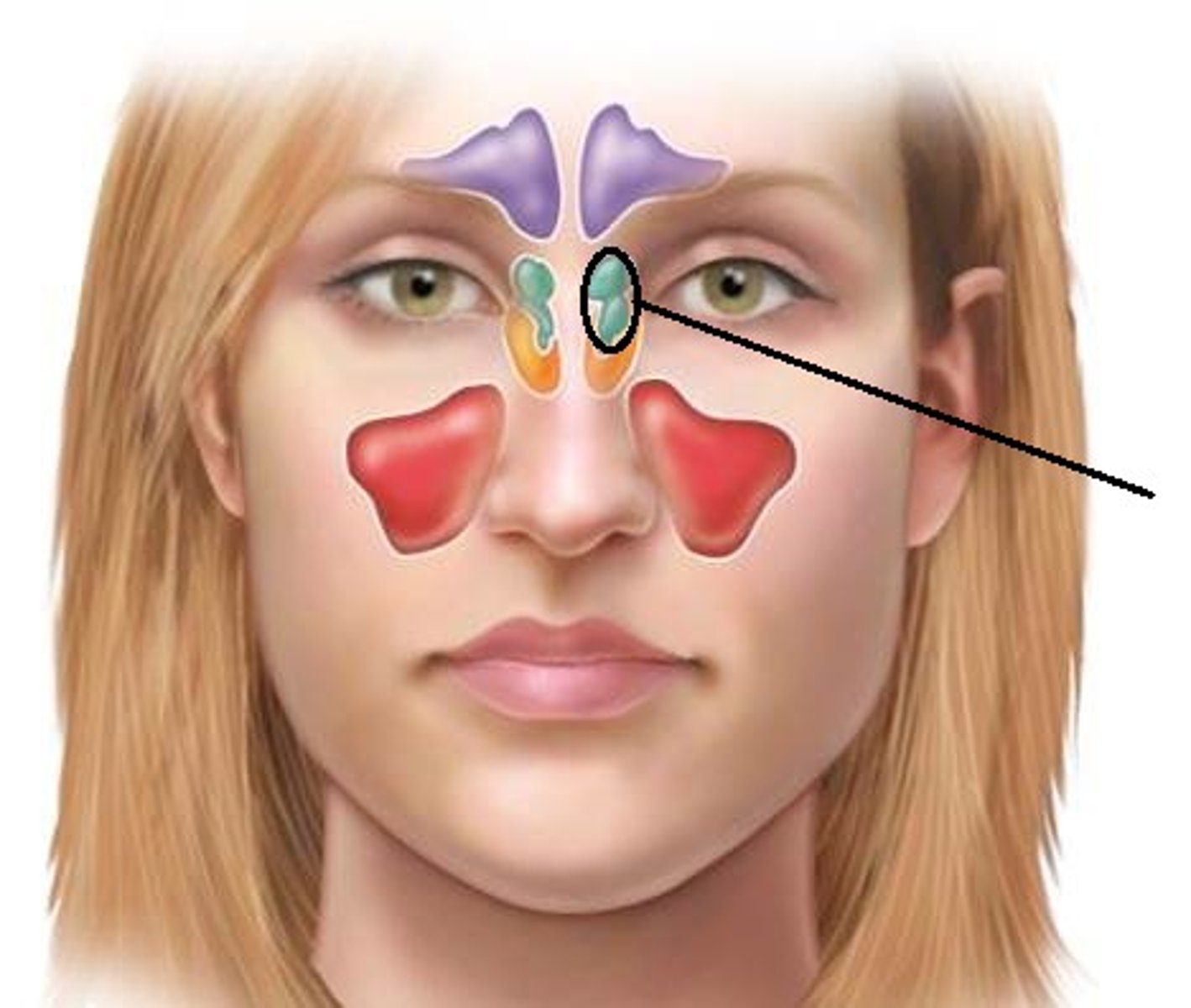
ethmoidal cells (sinus)
1. is what
2. drains through what
anterior ethmoidal cells drain into middle nasal meatus through ethmoidal infundibulum.
sphenoidal sinus
o located in body of sphenoid
o separated by a bony septum
o drains through posterior roof
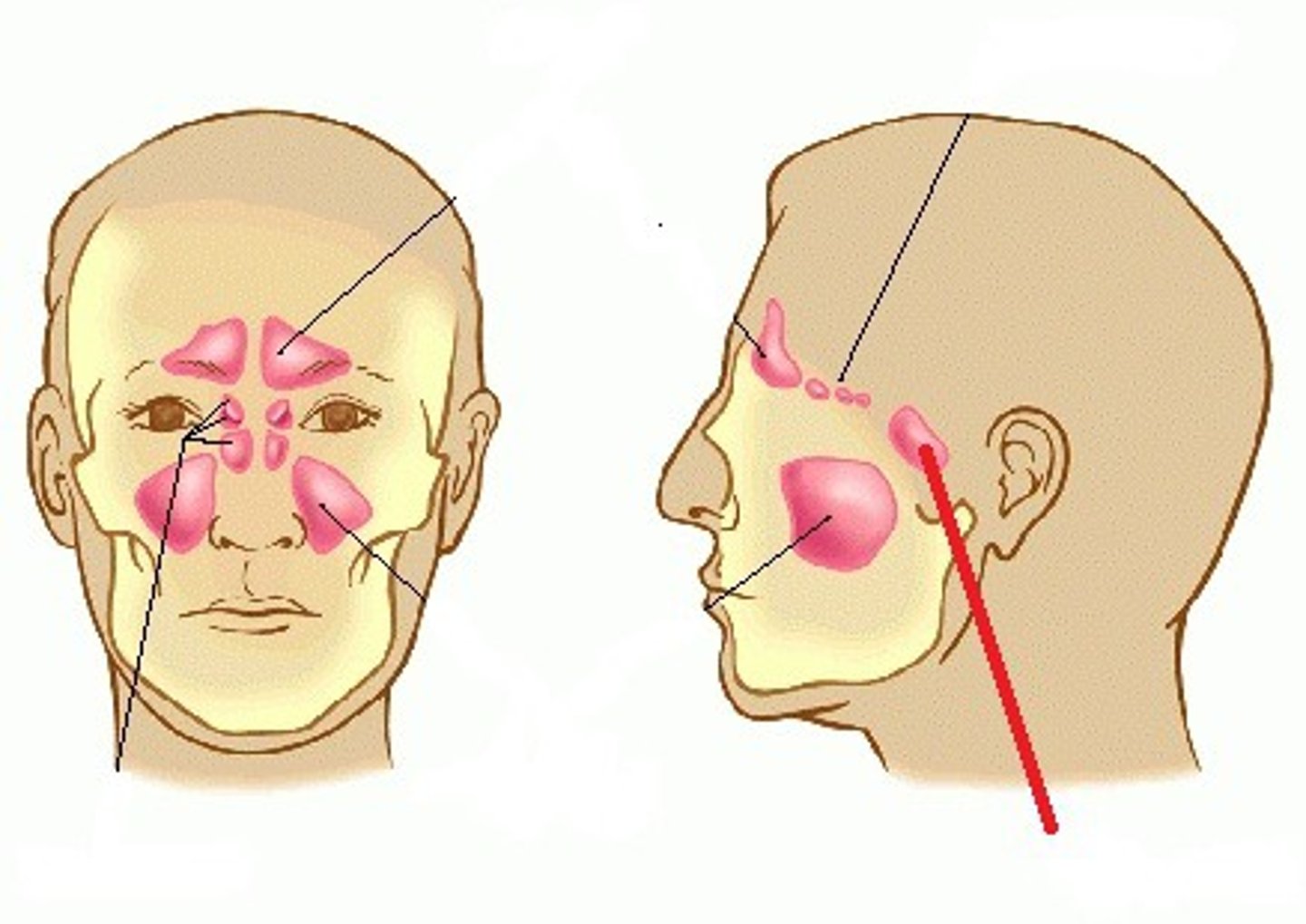
maxillary sinus is the largest or smallest of the sinuses?
largest
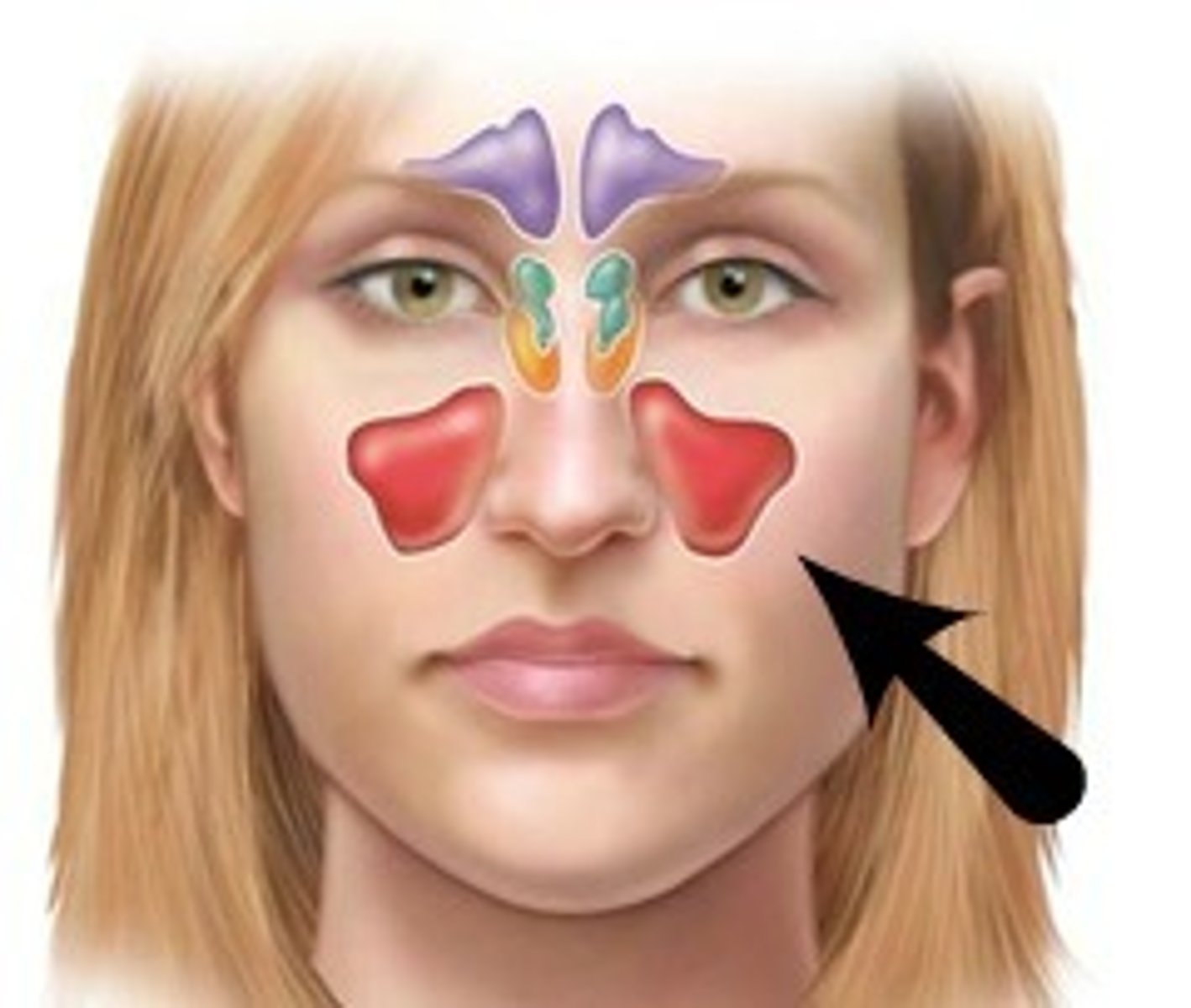
semilunar hiatus: what is it's significance
The maxillary sinus opens into this sickle shaped mucosal feature of the middle nasal meatus
what are the two parts of the oral cavity?
vestibule and oral cavity proper
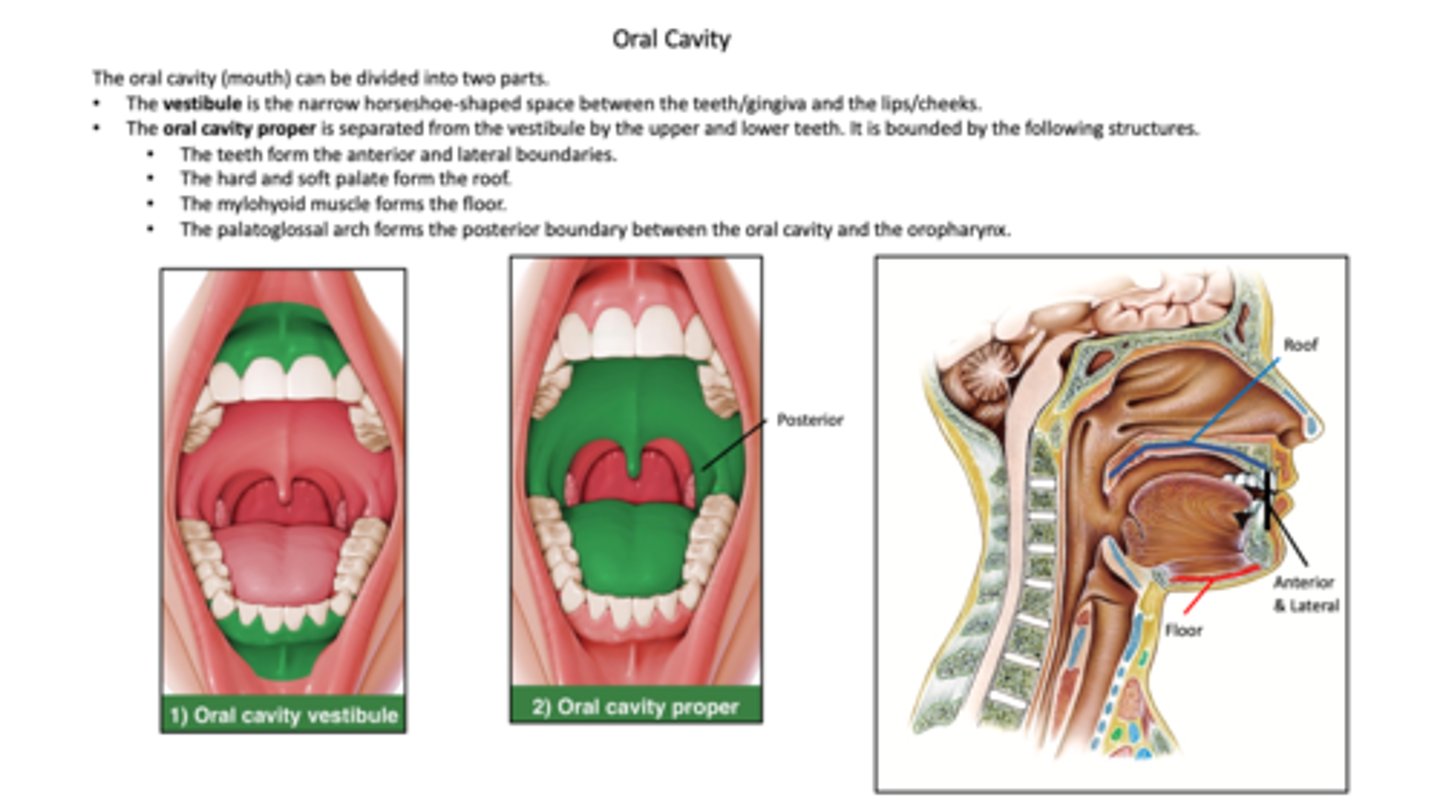
What is the oral vestibule?
space between teeth and lips
what is the oral cavity proper?
site of mastication, lingual manipulation, tasting
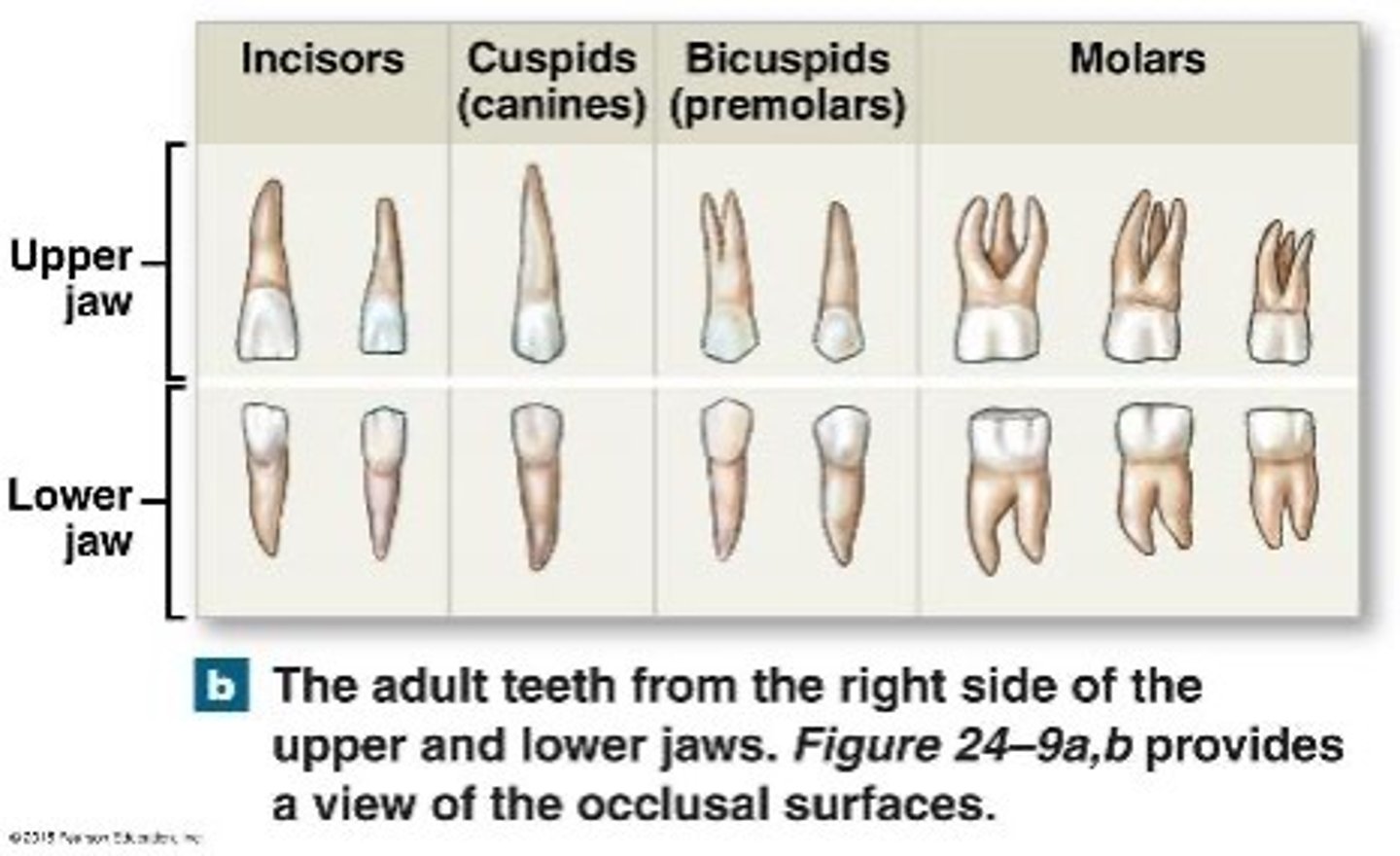
what are the 4 types of teeth and their jobs?
1. incisors - thin cutting edges
2. canines - single prominent cones for tearing
3. premolars (bicuspids) - two cusps for crunching/grinding
4. molars - three or more cusps for crunching/grinding
what are the 2 portions of the palate?
hard palate and soft palate
what is the hard palate?
o concave
o formed by palatine processes of maxillae, horizontal plates of palatine bones
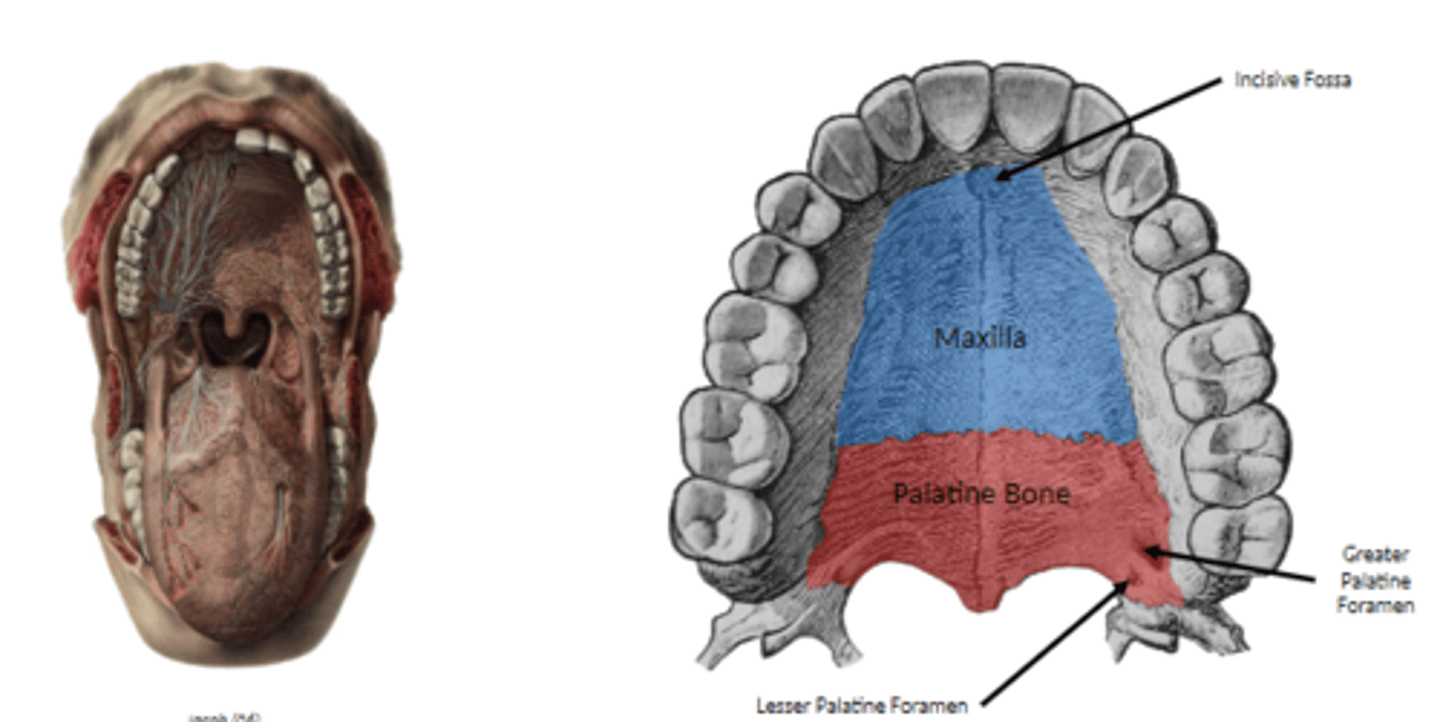
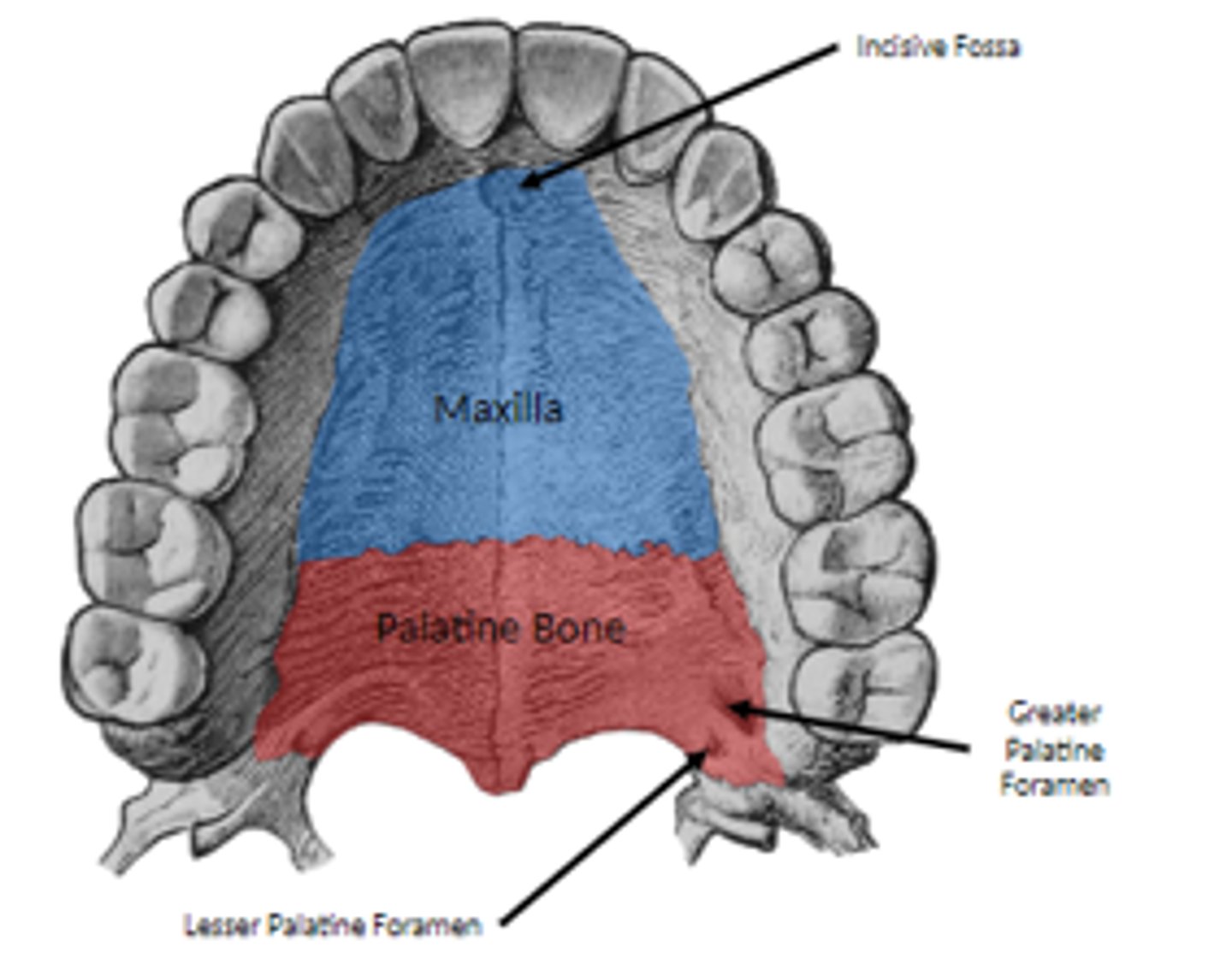
what foramen does the hard palate have? (3)
what structures pass through them?
o incisive fossa
§ passage of nasopalatine nerves
o greater palatine foramen
§ greater palatine vessels, nerve emerge from this foramen, run anteriorly
o lesser palatine foramina
§ found posterior to greater palatine foramen
§ transmit lesser palatine nerves, vessels to soft palate
what is the soft palate?
o movable posterior third of palate
o curved free margin posteroinferiorly, from which uvula
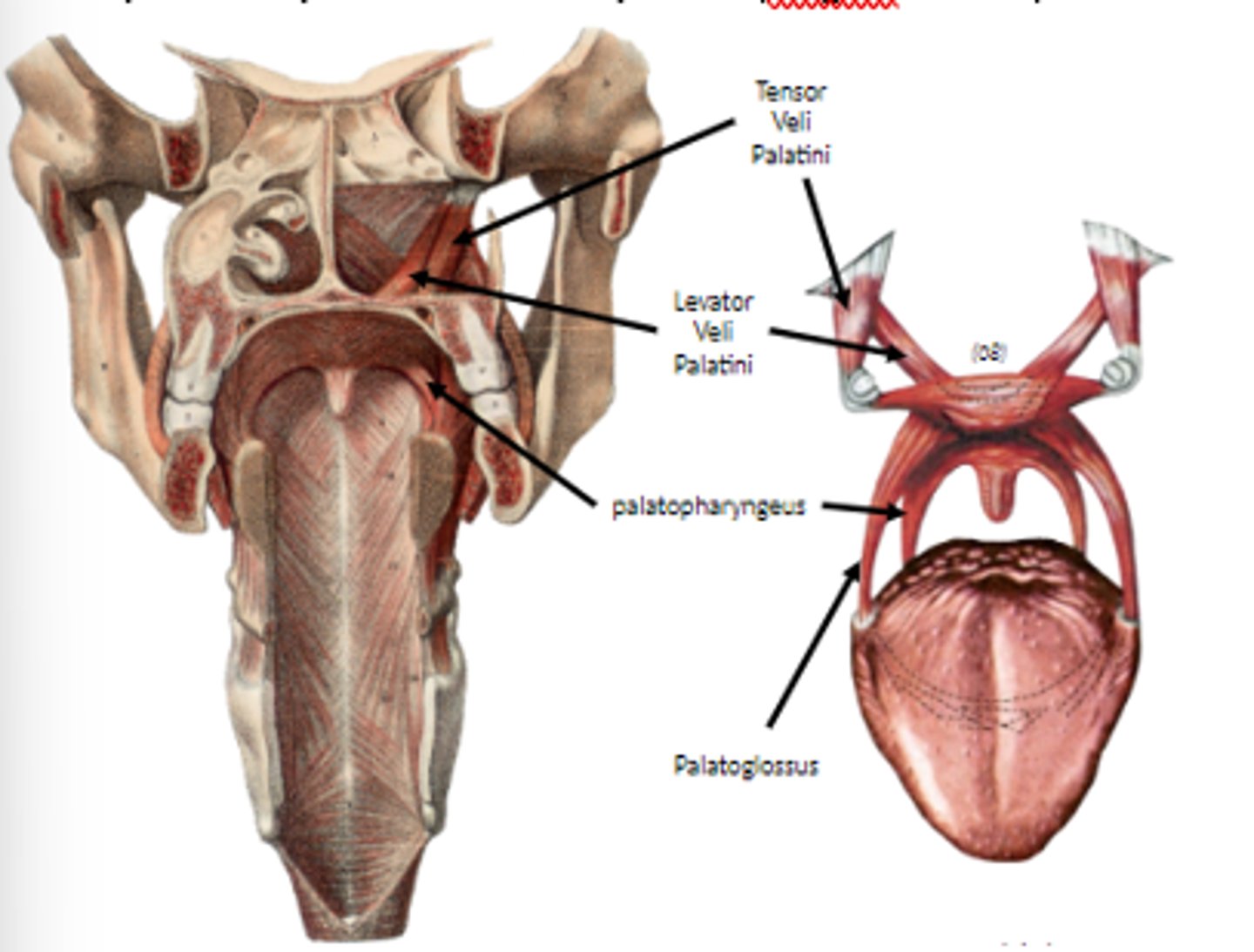
what are the muscles of the soft palate?
Tensor veli palatini
levator veli palatini
palatoglossus
palatopharyngeus
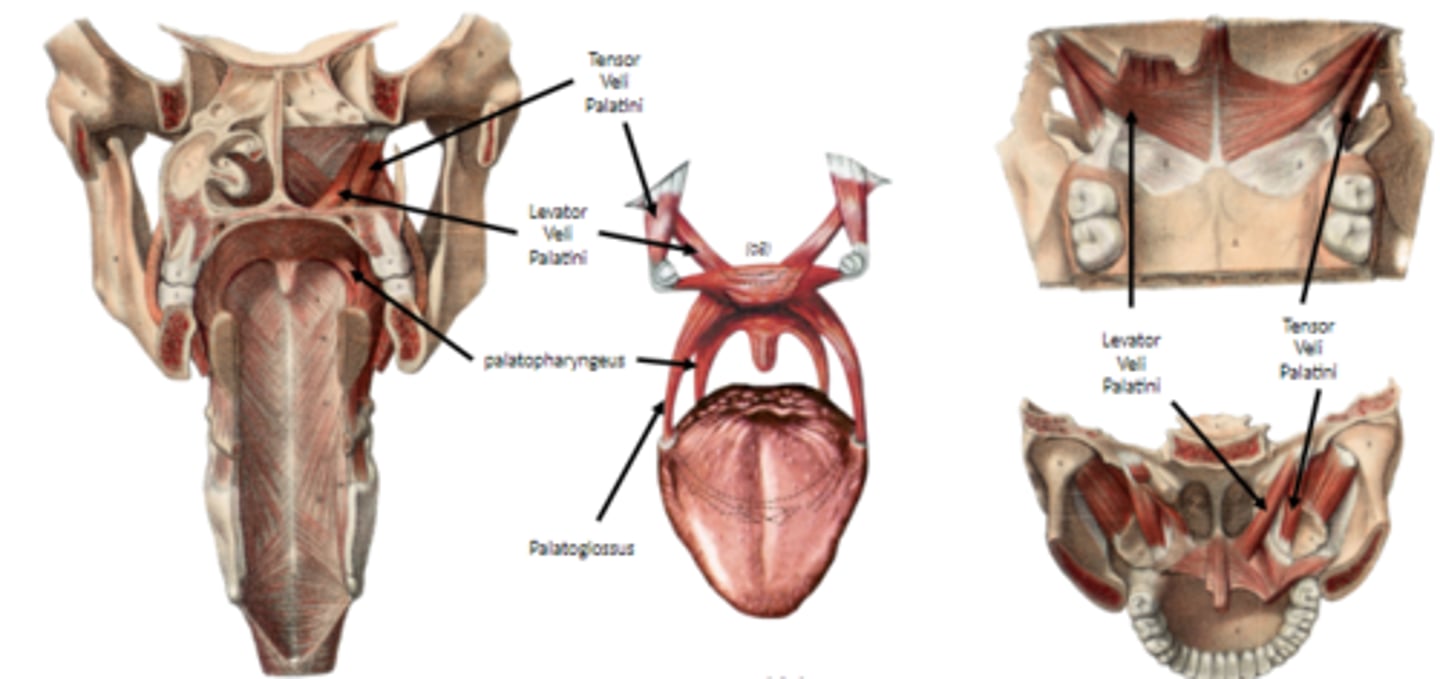
what are the muscles of the soft palate primarily innervated by?
CNX, VAGUS
what muscle is the exception in the muscles of the soft palate, and is not innervated by Vagus nerve?
tensor veli palatini - innervated by mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve,
tensor veli palatini m.
line of pull generates tension in soft palate
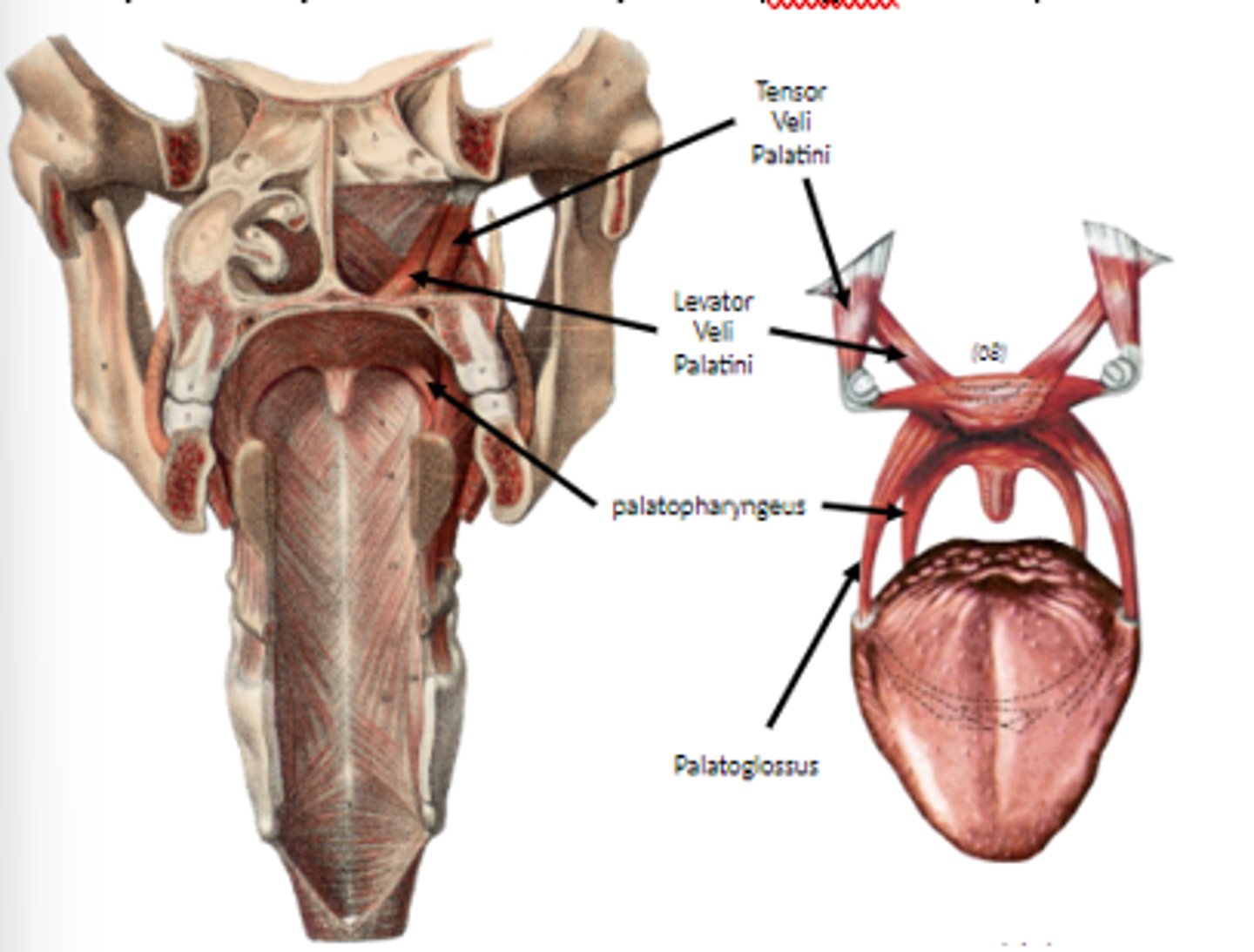
levator veli palatini
o Contracts to elevate soft palate in latter stages of swallowing
o Pulls the soft palate superiorly
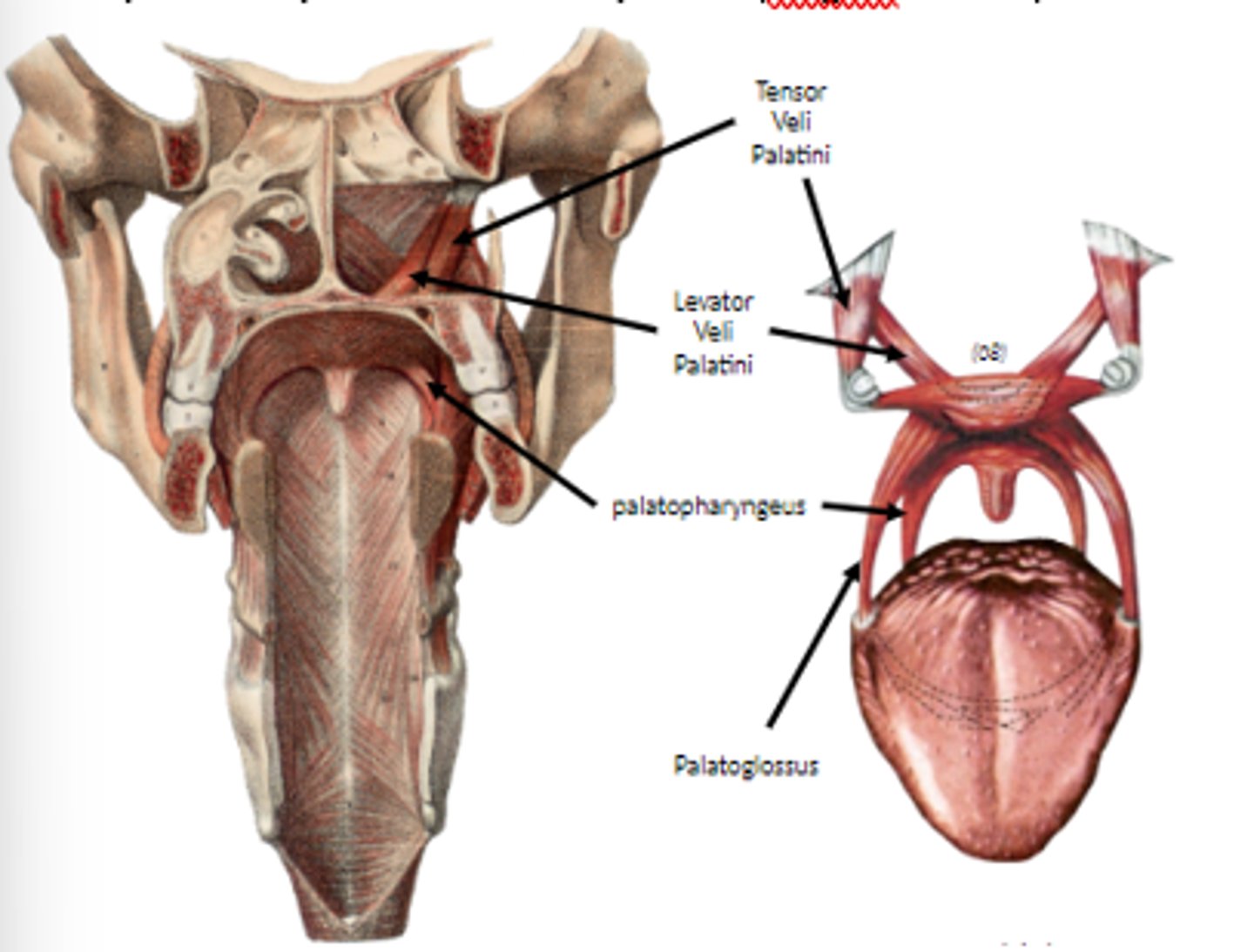
palatoglossus m.
Depresses soft palate against tongue
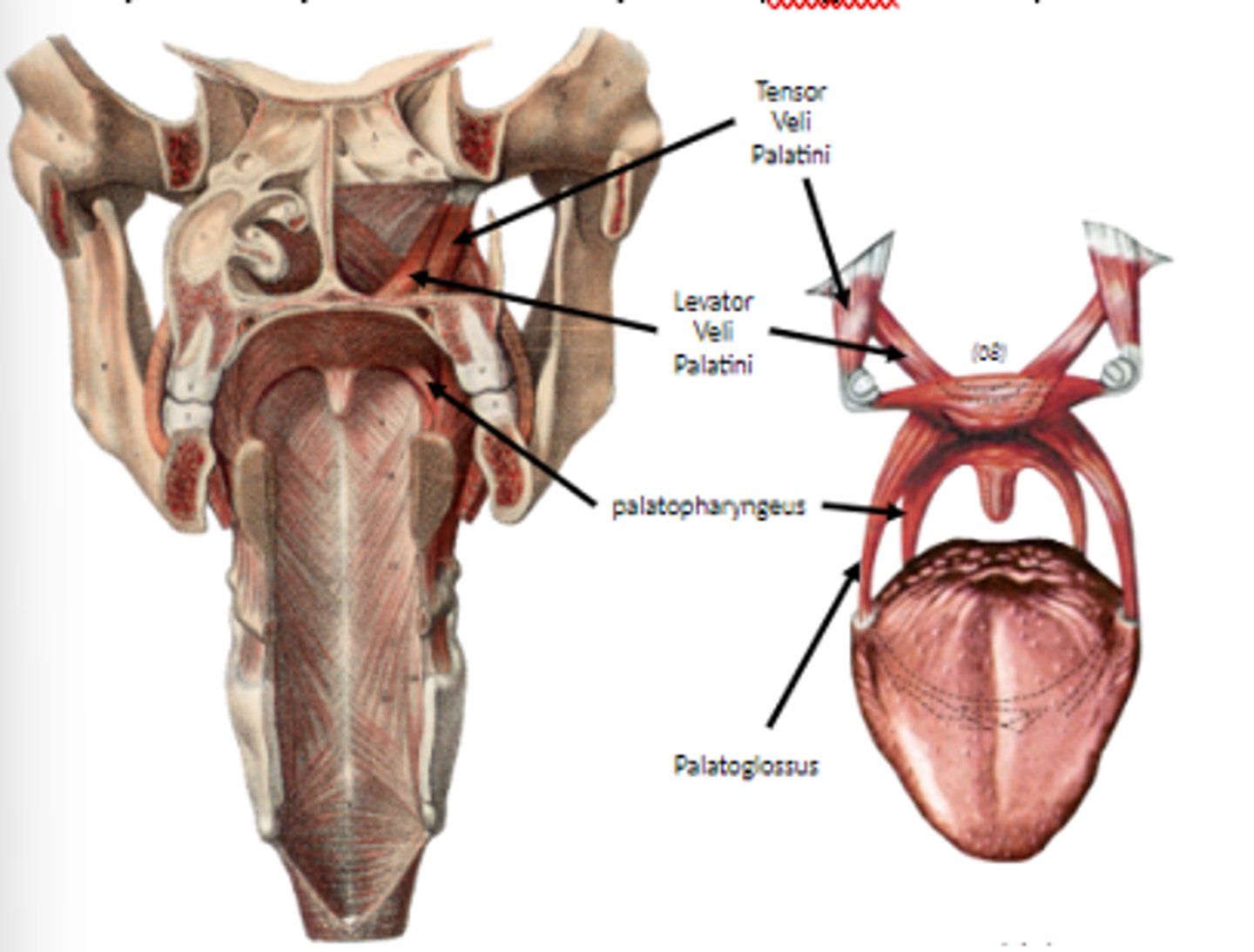
palatopharyngeus m.
Depresses soft palate, elevates phanyngeus
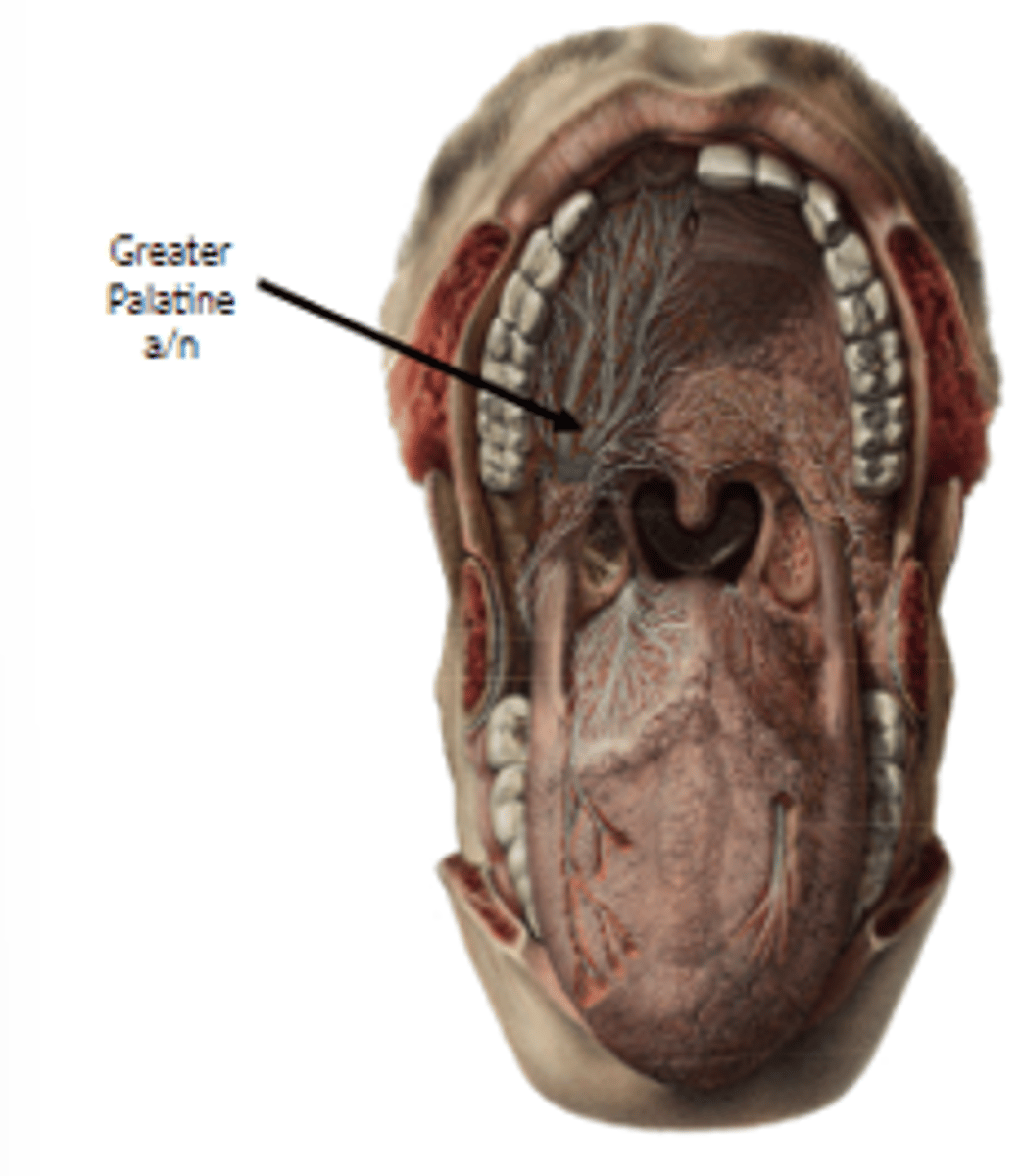
what is the hard palate supplied by (artery & nerve)?
greater palatine artery/nerve
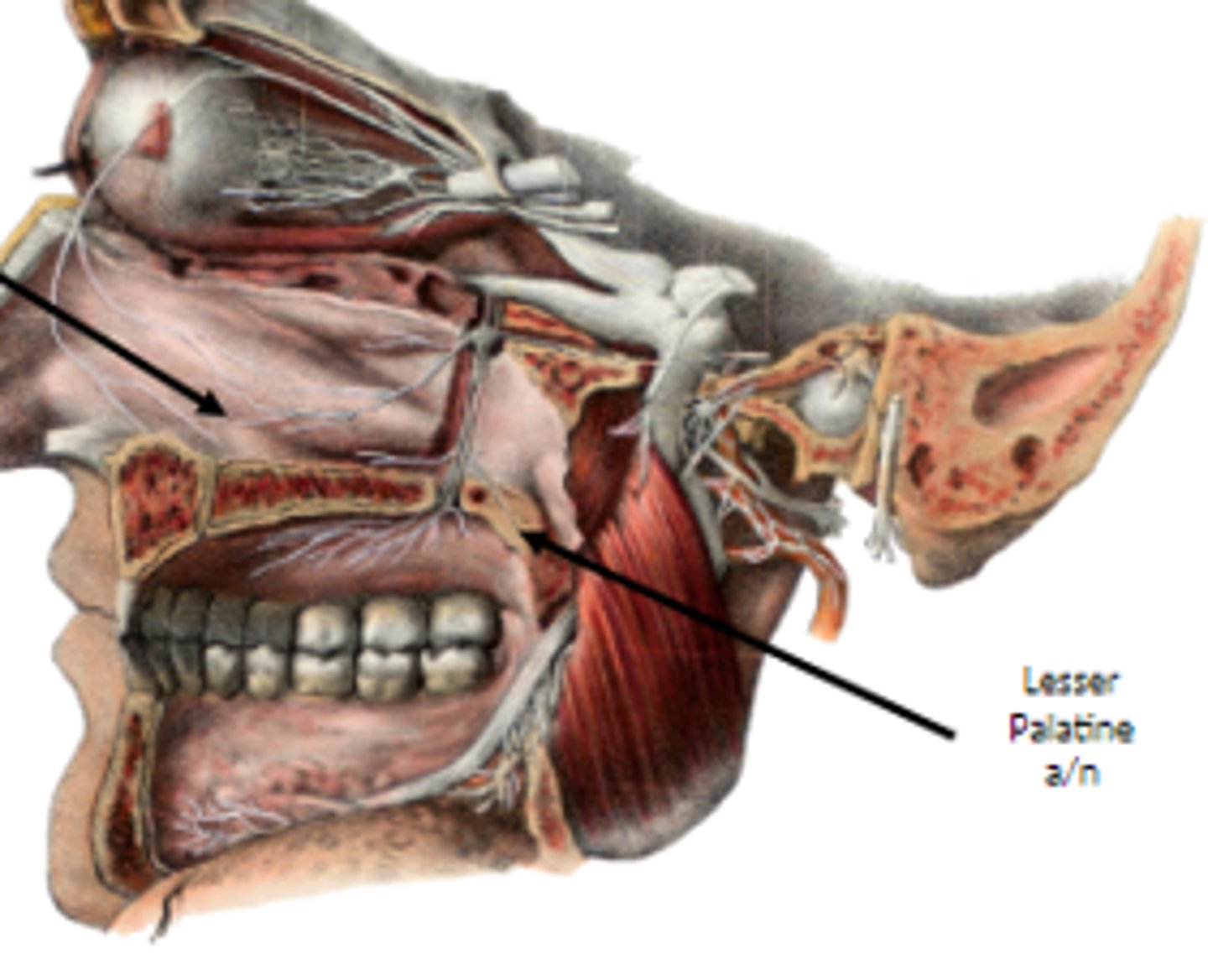
what is the soft palate supplied by (artery & nerve)?
lesser palatine artery/nerve
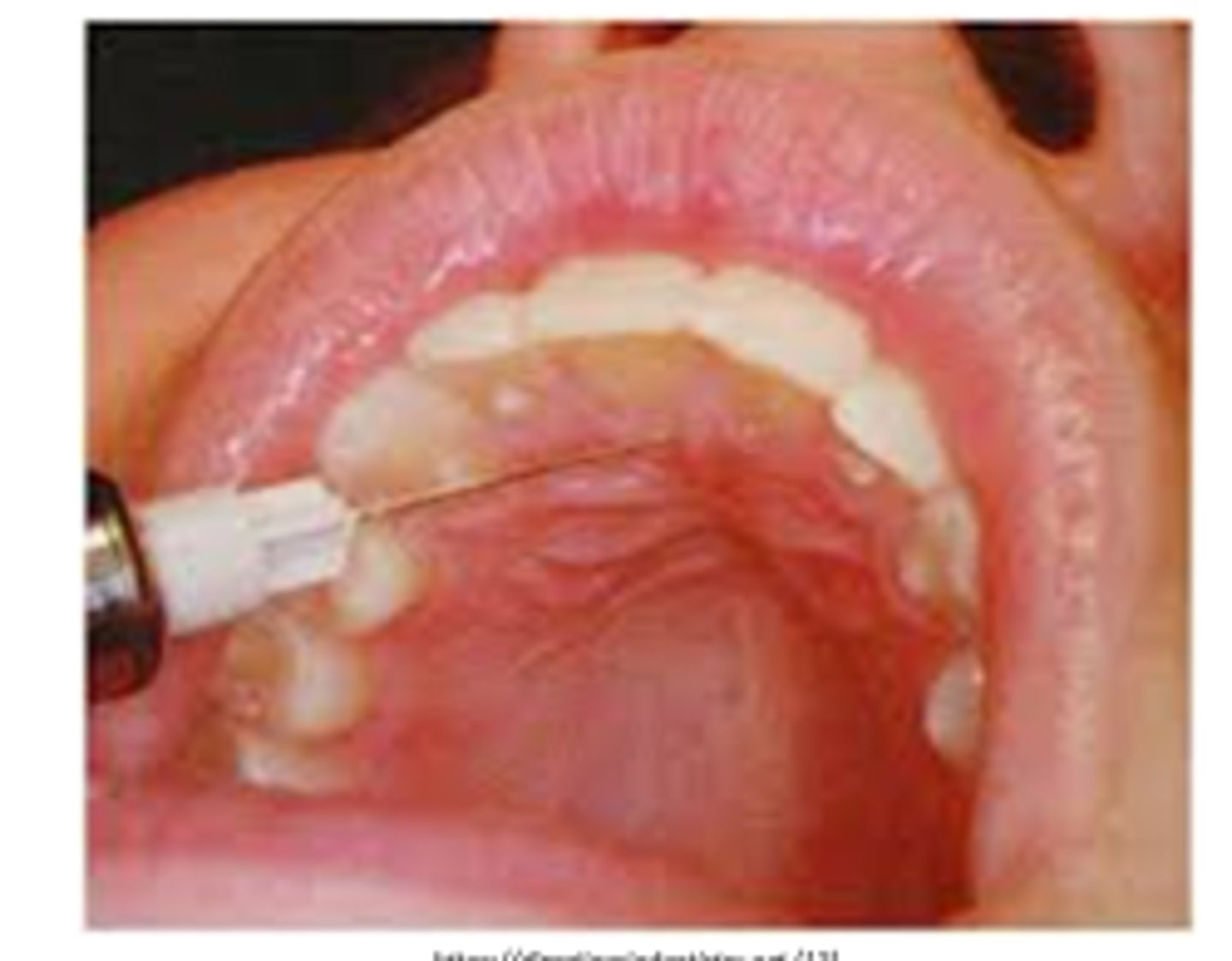
Nasopalatine nerve block is indicted when
• when treatment requires anesthesia of the lingual aspect of multiple anterior teeth
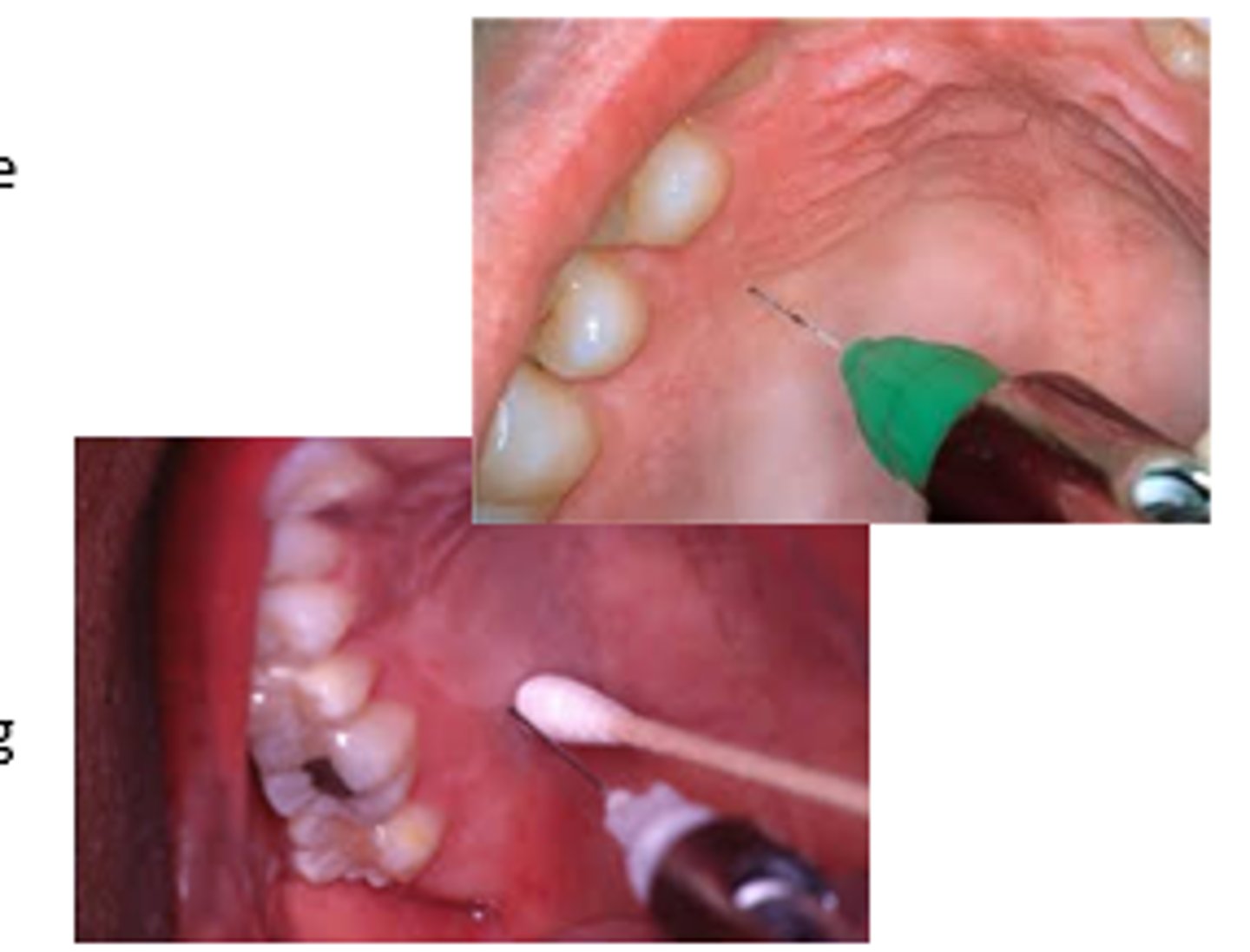
Greater palatine nerve block is indicted when
when treatment requires anesthesia of the palate
what's the purpose of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
change shape of tongue
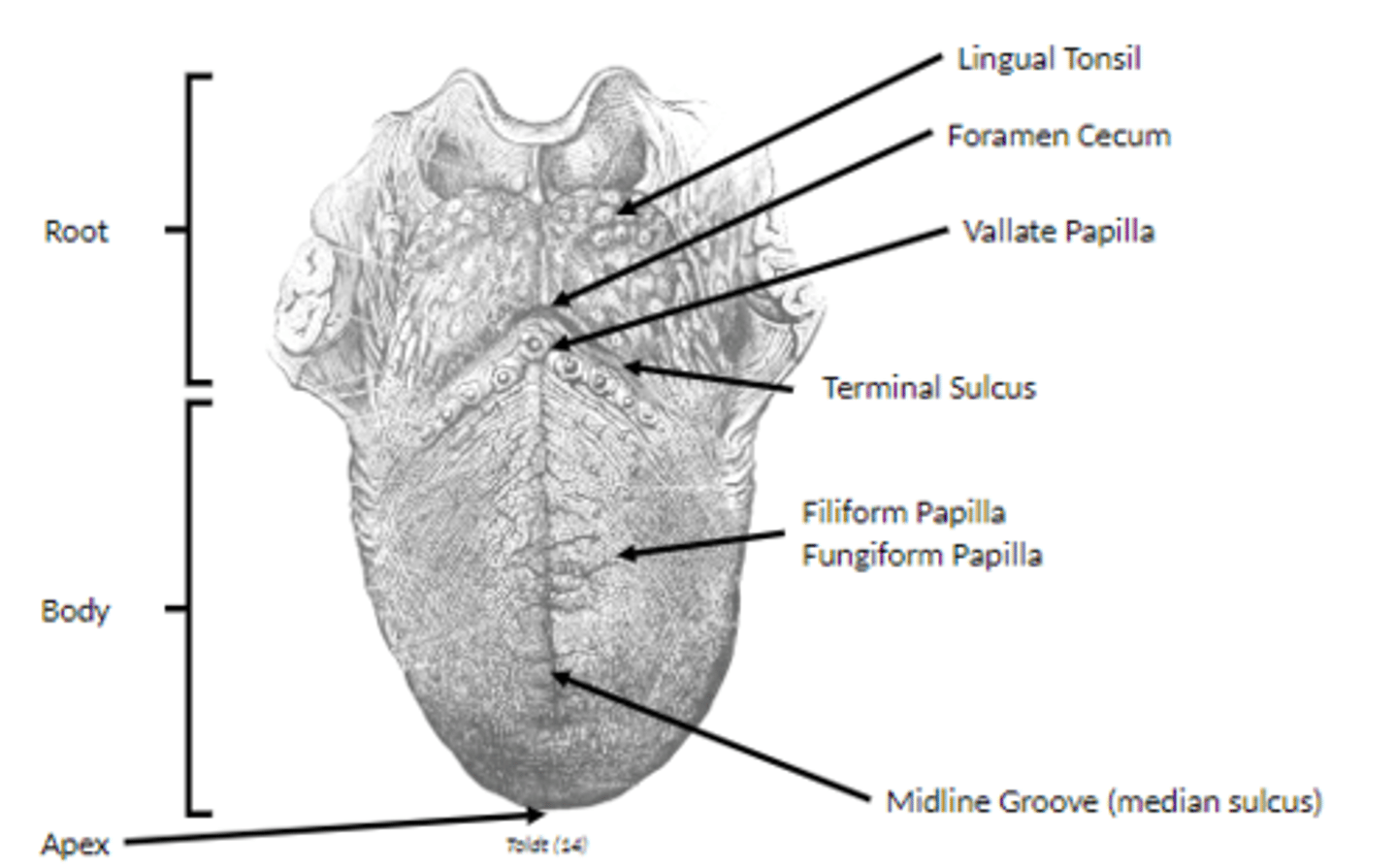
what's the purpose of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
change position of tongue
what are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Palatoglossus
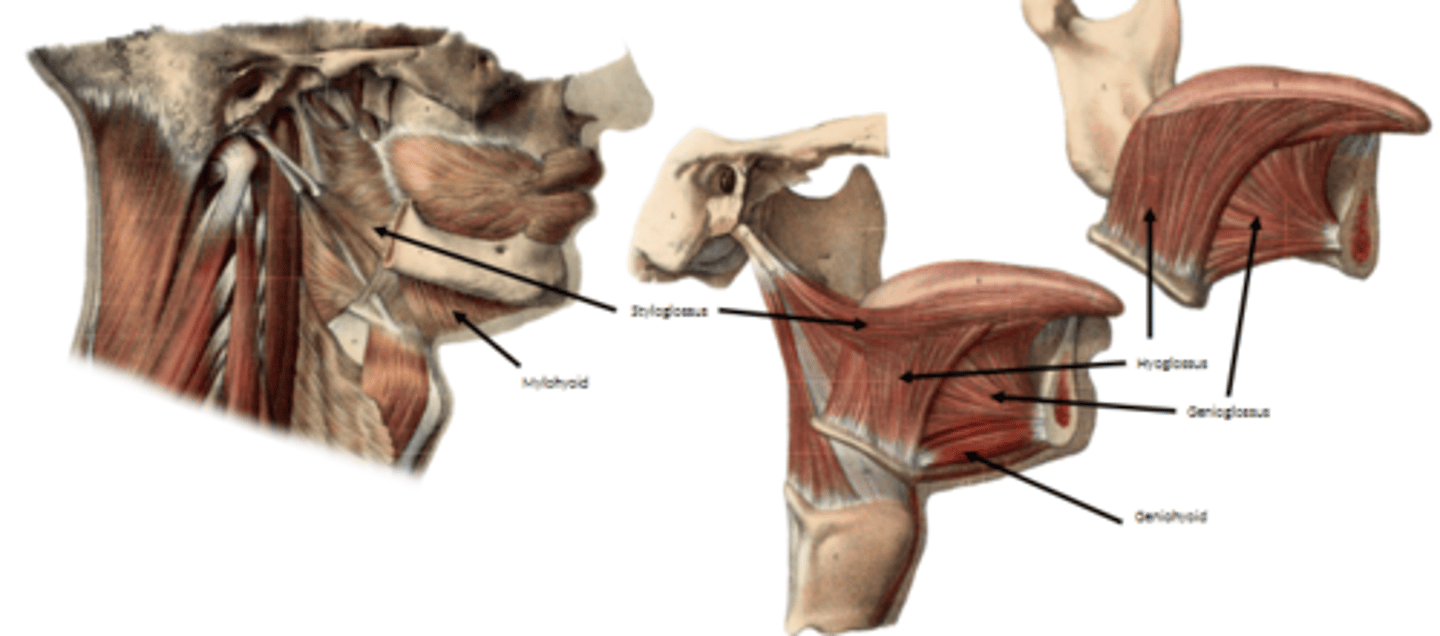
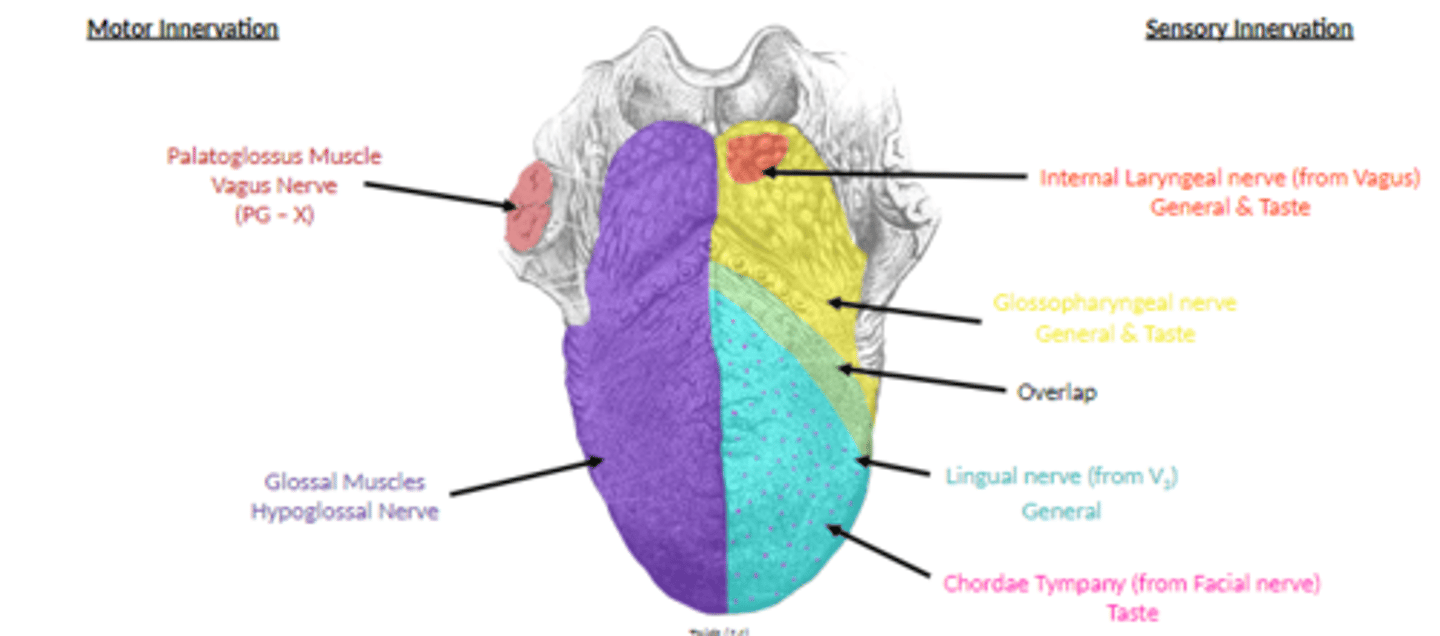
extrinsic muscles of tongue is innervated by what nerve
hypoglossal nerve
what muscle is NOT innervated by the hypoglossal nerve?
palatoglossus m.
state the innervation of palatoglossus m.
vagus
genioglossus
action
tongue protrusion (STICKING TONGUE OUT)
hypoglossus
action
depresses tongue
styloglossus
action
retracts tongue
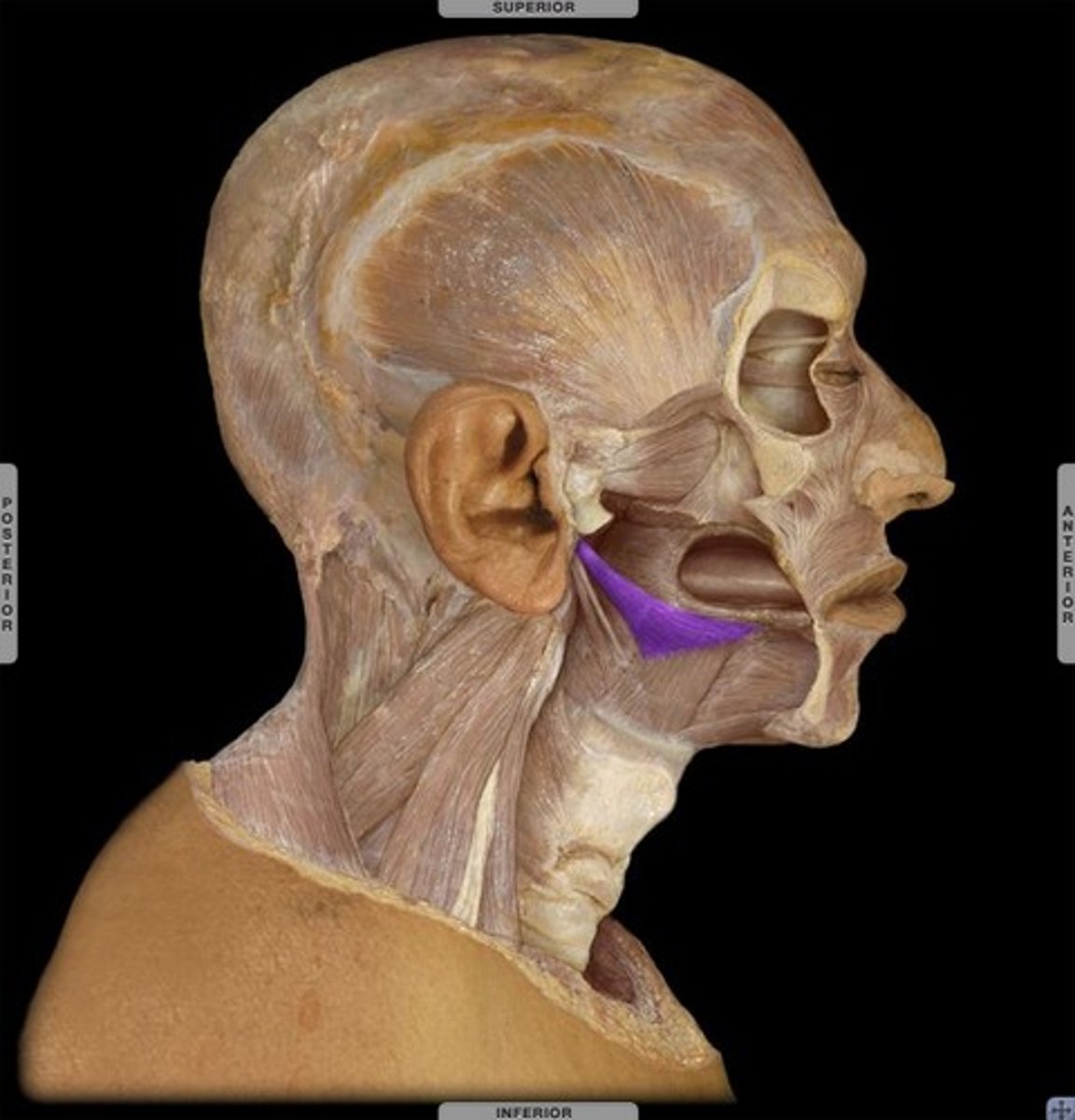
palatoglossus
action
elevates tongue
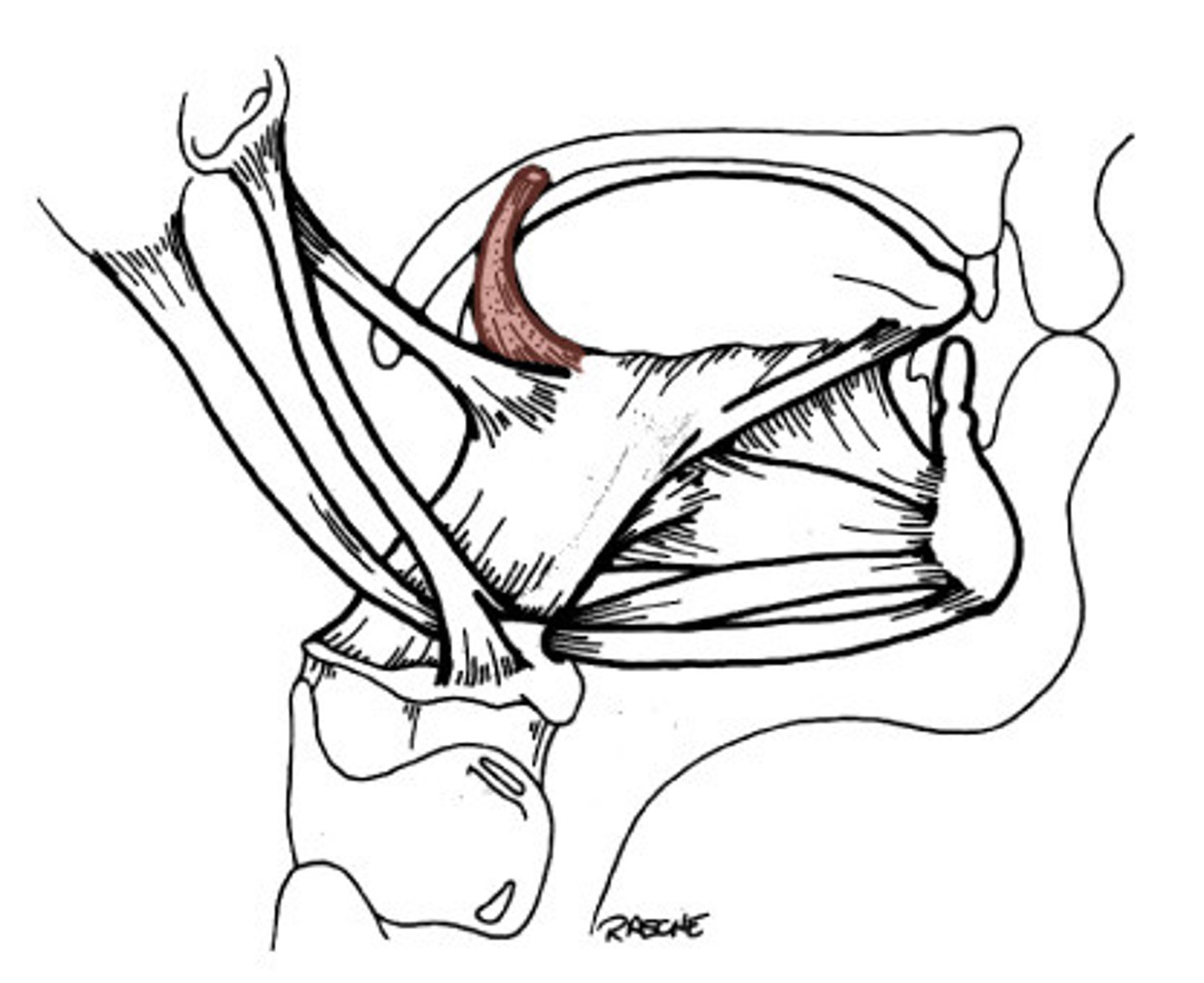
whats the main 3 innervations of the tongue?
lingual n. (from trigeminal) - gen sen anterior 2/3
chorda tympani (from facial) - taste anterior 2/3
lingual branch of glossopharyngeal - general/special sensation (touch, temperature, taste) to posterior 1/3rd of tongue
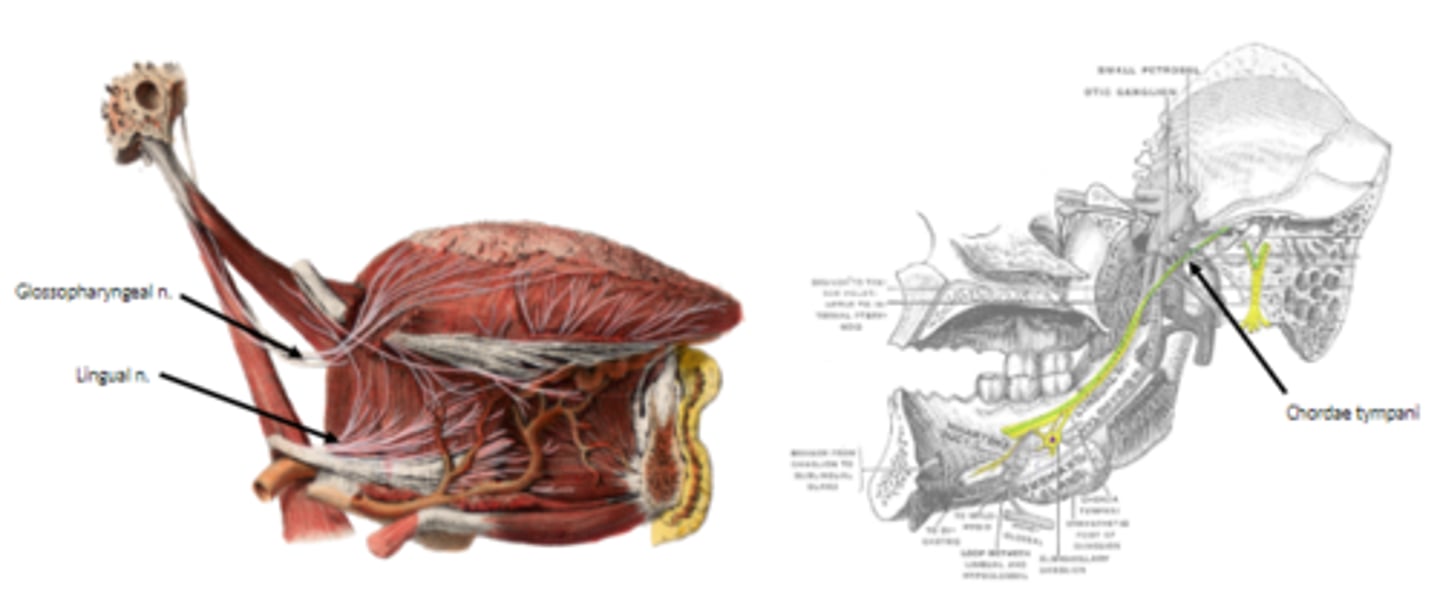
internal laryngeal nerve (CN X)
supplies mostly general (some taste) sensation to a small region of tongue anterior to epiglottis.
motor innervation and sensory innervation of tongue
...
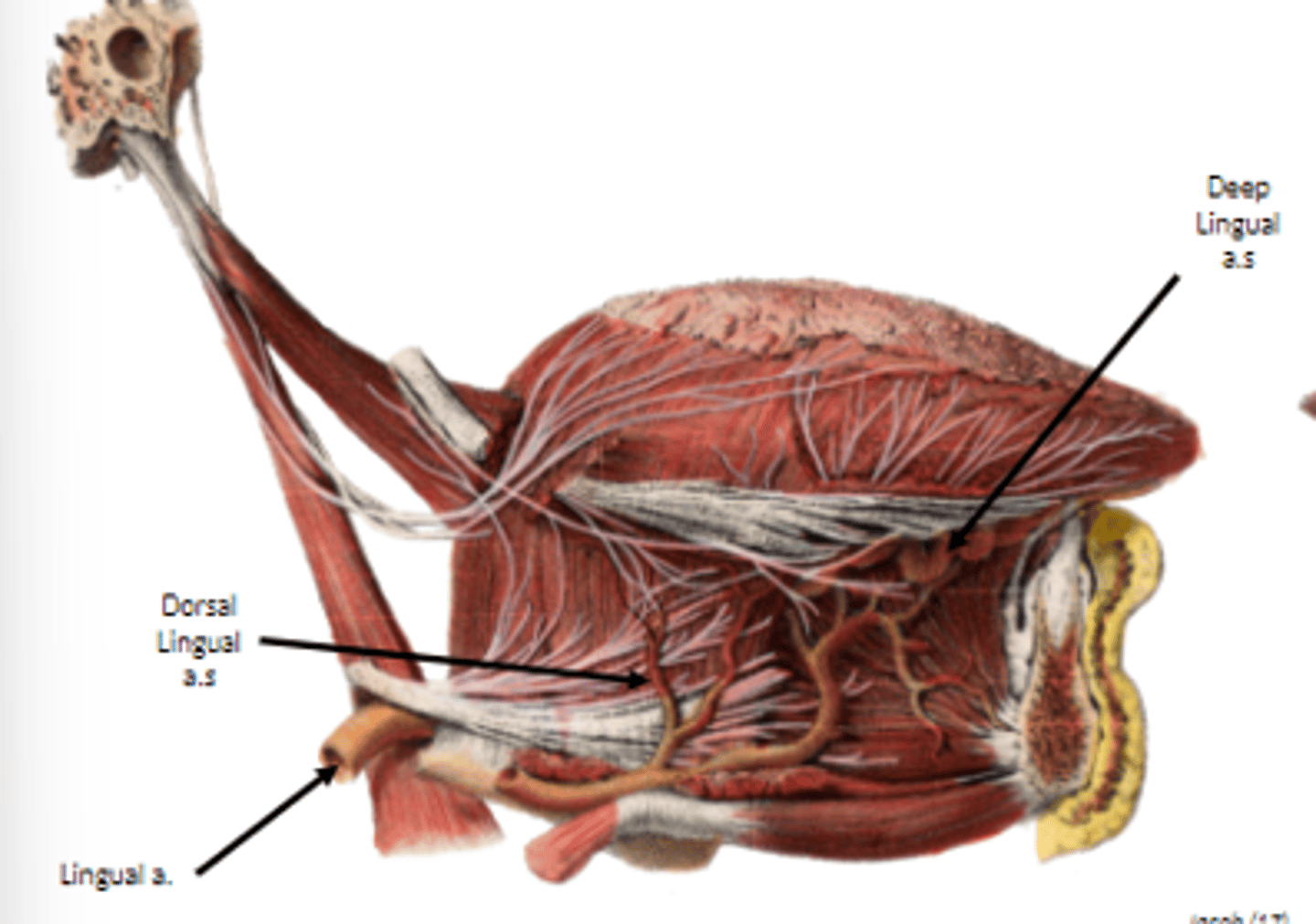
what is the main vascular supply to the tongue?
lingual artery off the external carotid artery
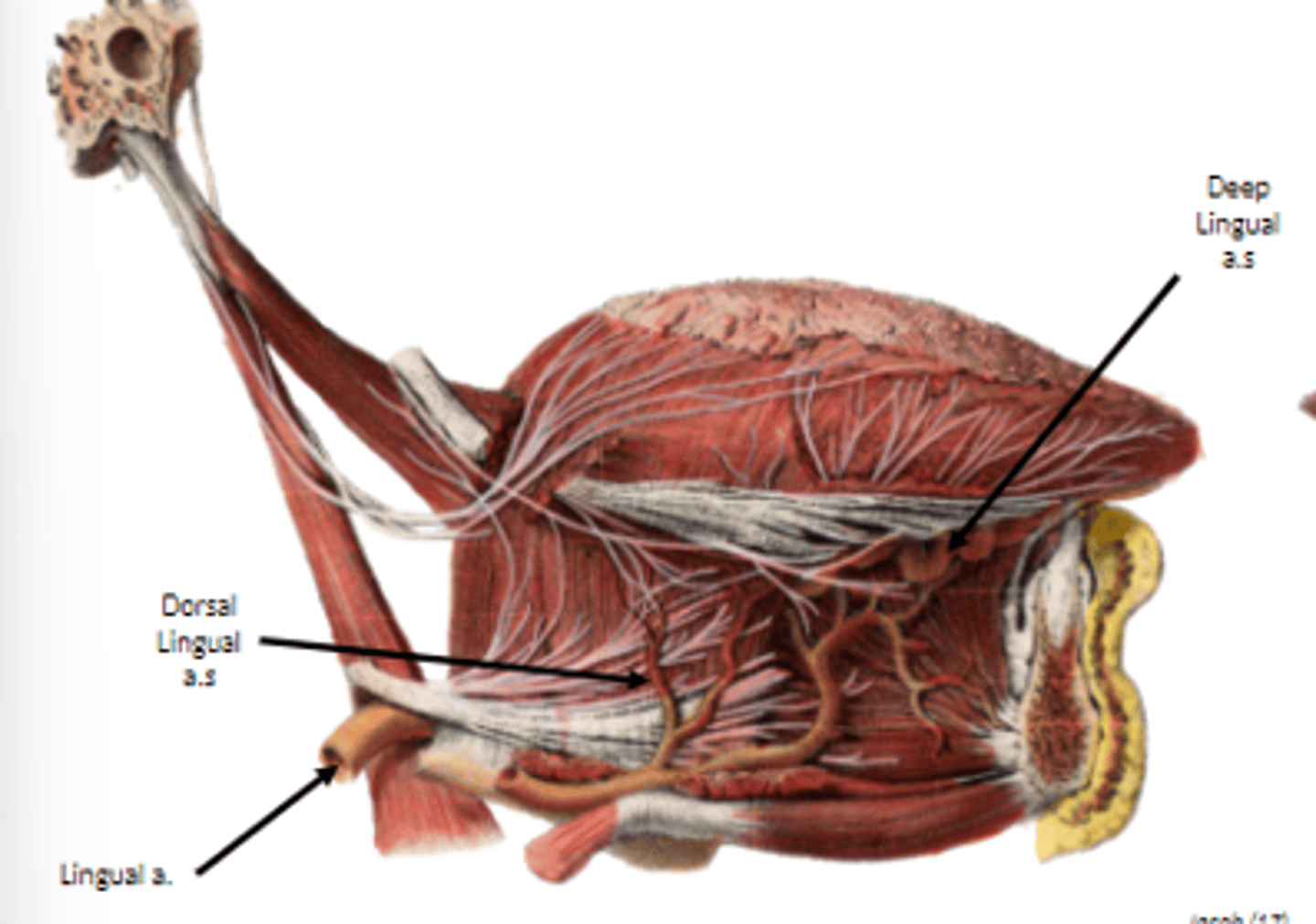
dorsal lingual arteries supply
root of tongue
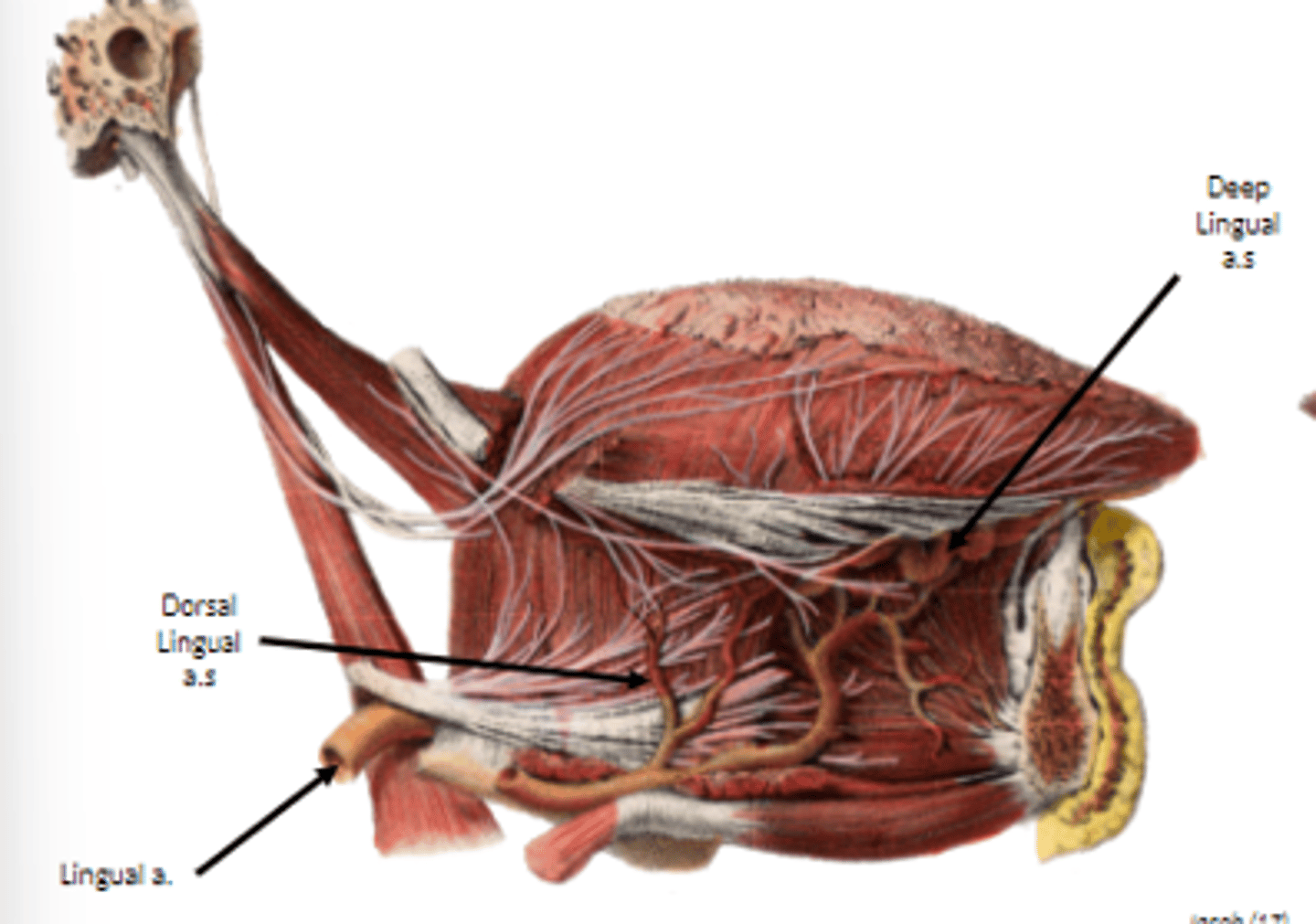
deep lingual arteries supply
body of tongue
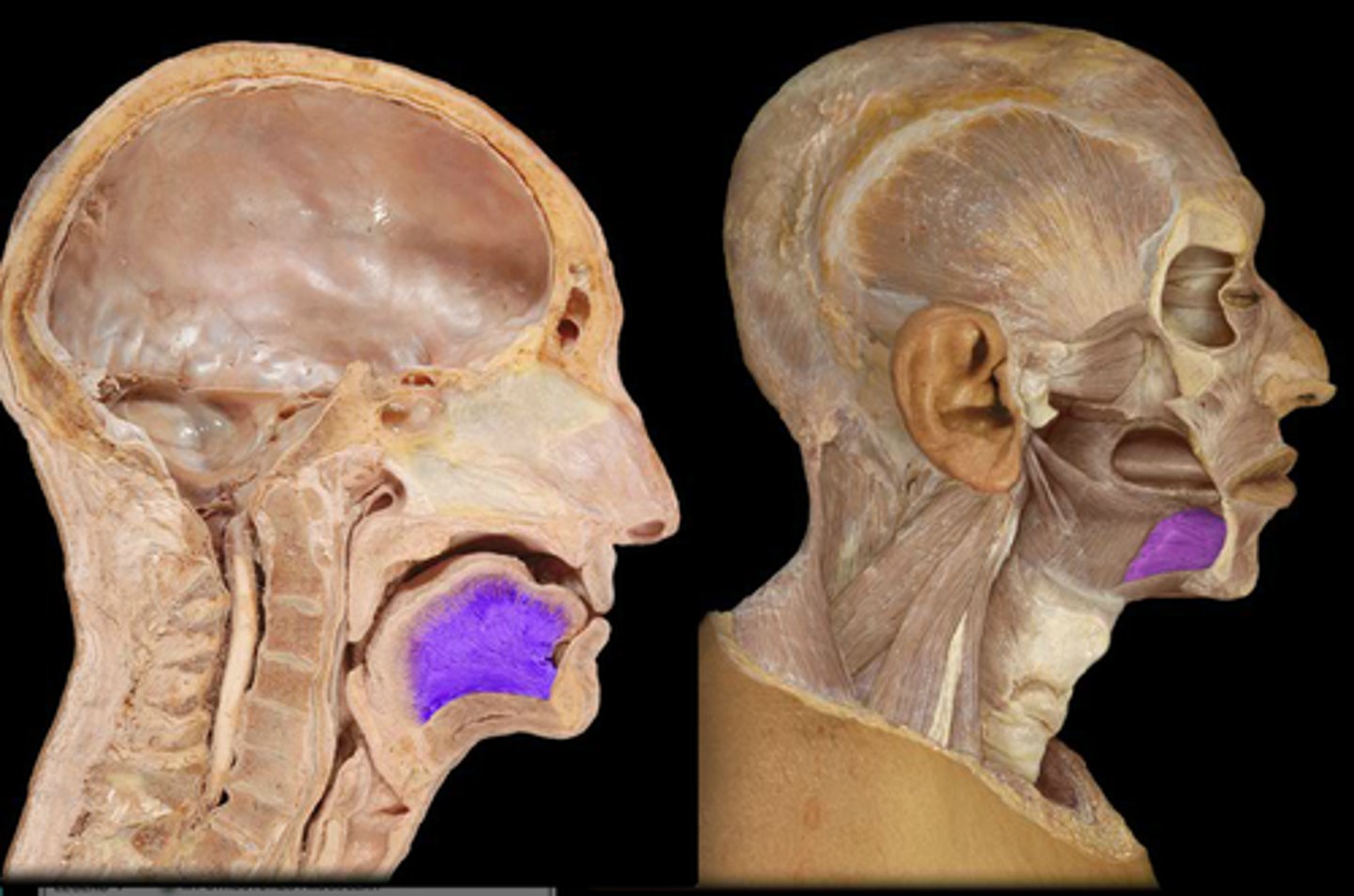
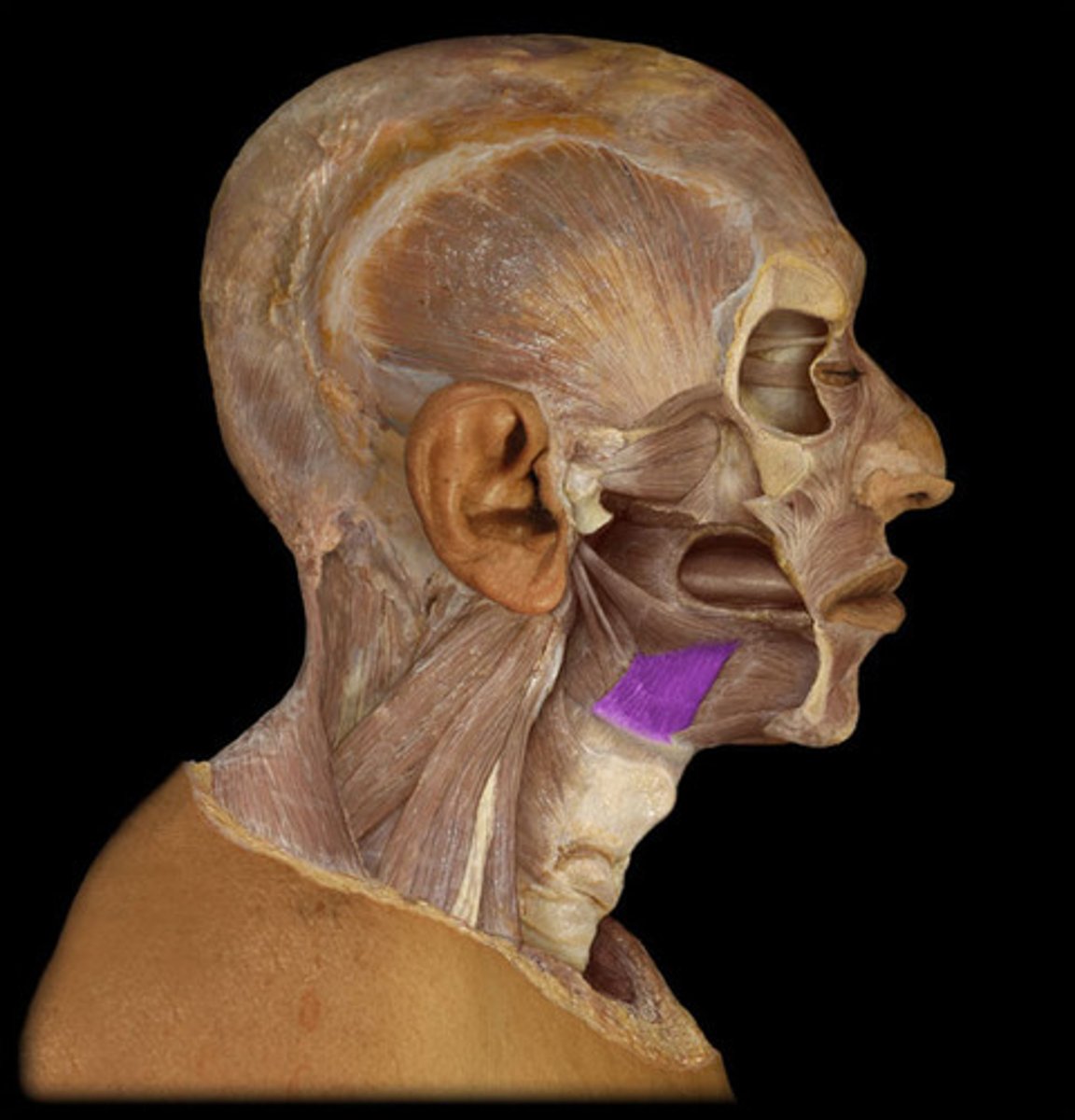
what are the 4 glands?
Parotid Glands
· largest salivary glands
Submandibular Glands
Sublingual Glands
· smallest almond-shaped glands
Mucous Glands
· distributed throughout oral cavity:
· moisten mucous membrane
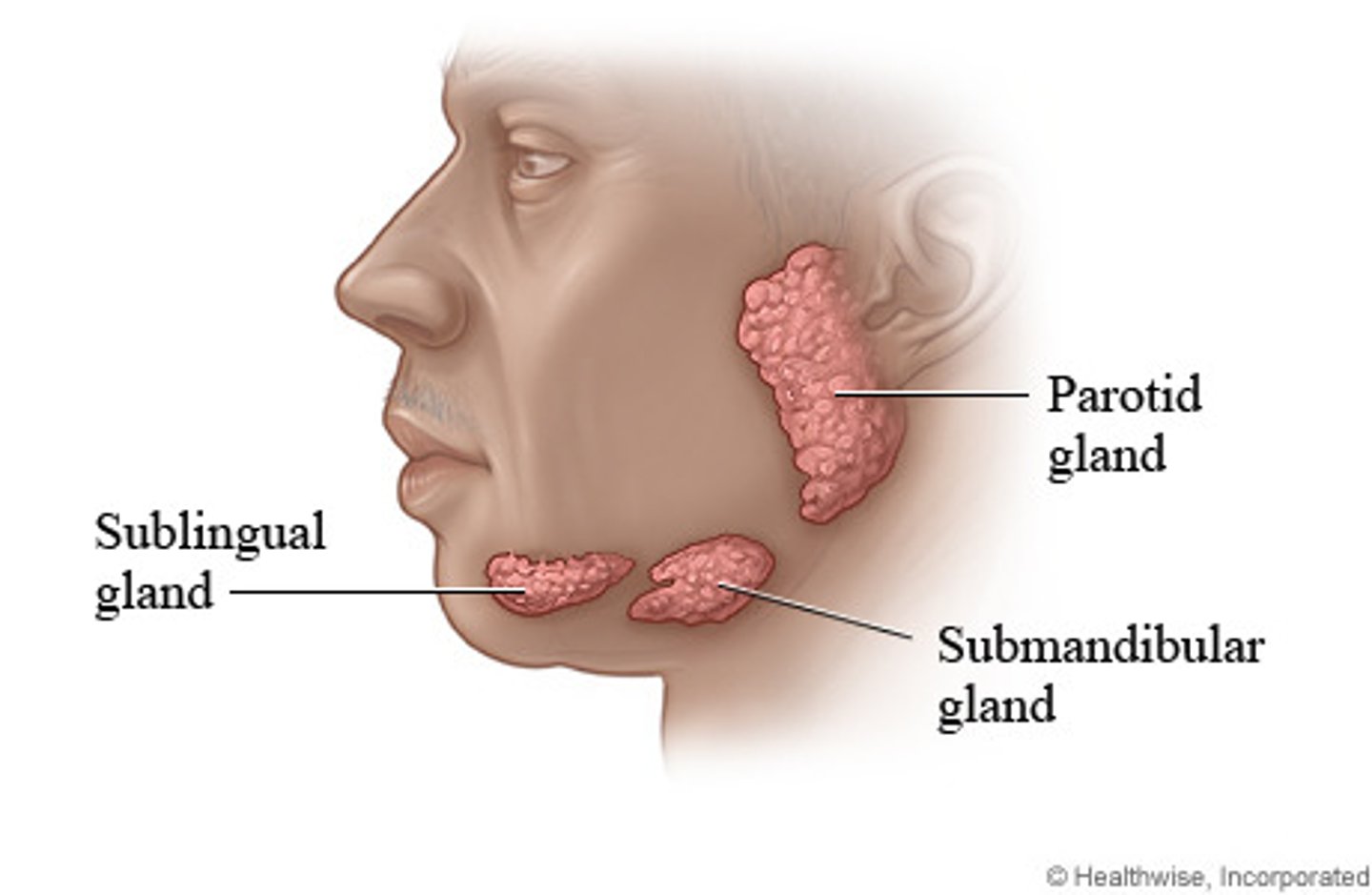
Parotid gland innervated by
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
submandibular and sublingual glands innervated by
· innervated by the chorda tympani nerve (CN VII)