Chapter 8: Valuation Using the Income Approach / Income Capitalization
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the rationale behind this approach?
The valuing basis is an investment —> Used for determining the value of a property based (i) on the income it is expected to produce / cash flows
What is it oftenly called?
Income capitalization, in which “capitalization” means to convert future income into a present value
What are the two ways to Income Valuation?
(i) Direct capitalization and (ii) Discounted All Expected Future Cash Flows at Discounted Rates (DCF)
What is the Direct Capitalization?
The value estimates are based on a ratio or multiple of expected NOI over the next 12 months
“Multiple” is obtained from sales of comparable properties
Similar in spirit to valuing a stock using a price/earnings multiple
What are the two types of leases?
level lease payments and the other one where rent goes up
What are the general types of commercial RE leases? Explain all types
(i) Straight leases: tenant pays a fixed rent amount for the entire duration of the lease term, with no scheduled increases or adjustments.
(ii) Step-up graduated lease: rent increases at specified intervals during the lease term. These increases are pre-determined and built into the lease agreement, making rent escalation predictable for both the tenant and the landlord.
(iii) Indexed lease: rental payments are tied to a specific economic index, typically to account for inflation or changes in the cost of living.
(iv) Percentage lease: base rent plus percentage of tenant’s sales; allows landlord to share success of business
(v) Apartment leases: legal agreement between a landlord and a tenant that outlines the terms and conditions under which the tenant rents an apartment unit
What is a Potential Gross Income (PGI)? and its other name
Also called Potential Gross Revenue (PGR), rental income assuming 100% occupancy and no collection losses; estimated property cash flows on an annual basis.
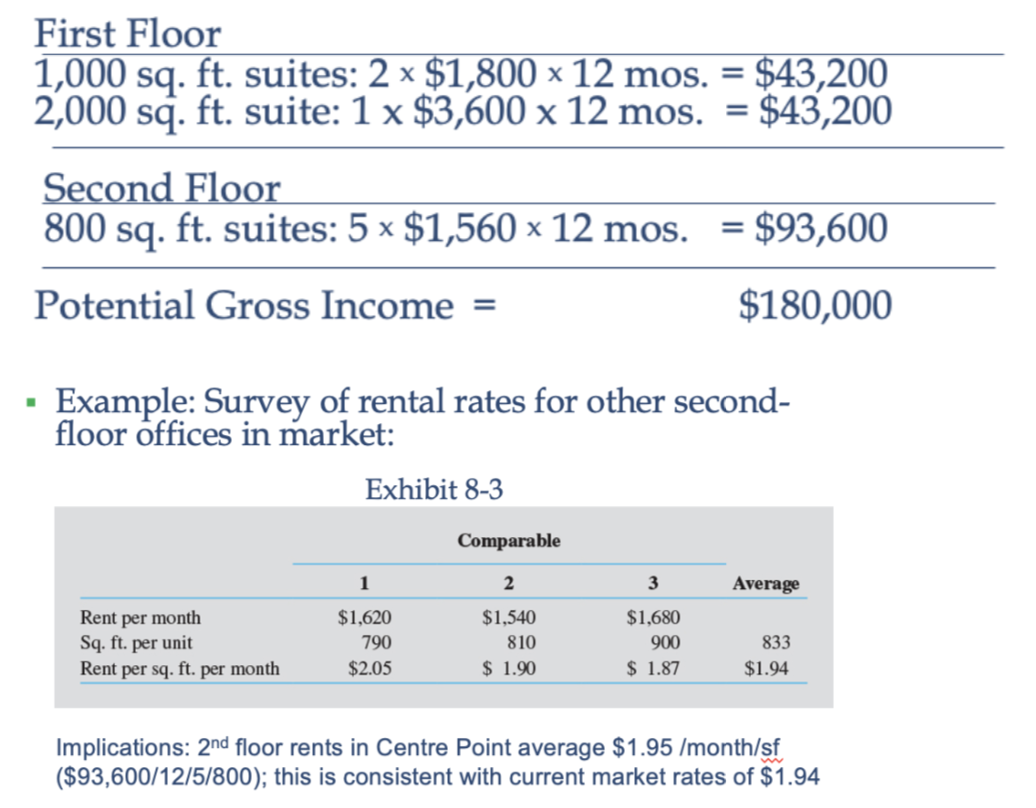
What is Effective Gross Income (EGI)?
Is calculated by subtracting [-(Vacancy & Collection Loss) + Miscellaneous income]
VC-vacancy & collection loss is based on:
Historical experience of subject property
Competing properties in the market
Natural vacancy rate
Miscellaneous income
Garage rentals & parking fees (office)
Laundry & vending machines (apts., office)
Clubhouse rentals (apts.)
![<p>Is calculated by subtracting [-(Vacancy & Collection Loss) + Miscellaneous income]</p><ol><li><p><strong>VC-vacancy & collection loss is based on:</strong></p><ul><li><p>Historical experience of subject property</p></li><li><p>Competing properties in the market</p></li><li><p>Natural vacancy rate</p></li></ul></li><li><p><strong>Miscellaneous income</strong></p><ul><li><p><span>Garage rentals & parking fees (office)</span></p></li><li><p><span>Laundry & vending machines (apts., office)</span></p></li><li><p><span>Clubhouse rentals (apts.)</span></p></li></ul></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ff4d583-d939-4f6d-843f-fa76c7ae510f.png)
What is Operating Expenses? and explain the two types of such expenses
Ordinary & regular expenditures necessary to keep a property functioning competitively; two types:
(i) Fixed - Expenses that do not vary with occupancy (in short-run); hazard insurance and local property taxes
(ii) Variable - Expenses that tend to vary with occupancy; utilities, maintenance, & supplies
What is not included in the OE?
Not included:
Mortgage payments
Tax depreciation
Capital expenditures
Leasing commissions
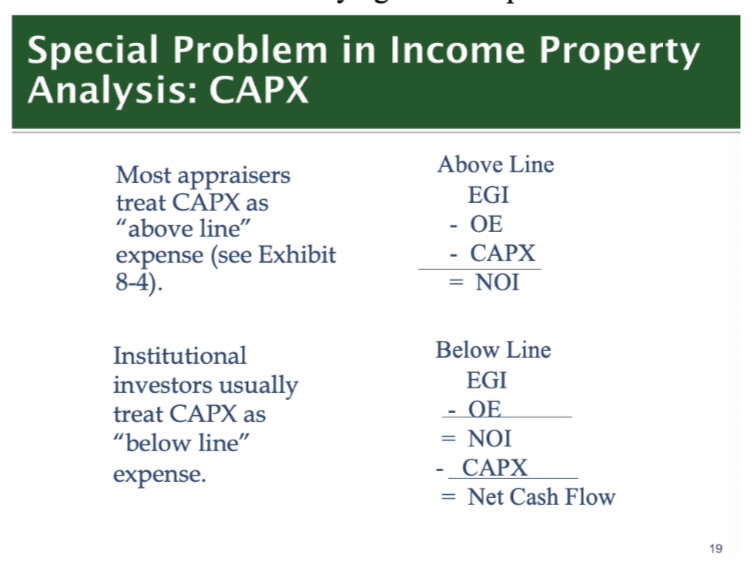
What is Capital Expenditures (CAPX)? differentiate above and below line
Non-recurring expenditures that increase value of structure / prolong its useful life (e.g., roof replacement, HVAC replacement)
What is the first-year pro forma (next 12 months)?
What is NOI?
The Net Operating Income is income less expenses with a multiple you use from sale
Focuses on the income produced by the property after operating expenses, but before mortgage payments and the payment of income taxes
Is a property’s dividend
Must be sufficient to:
(i) Service the mtg debt and
(ii) Provide equity investor with an acceptable return on equity
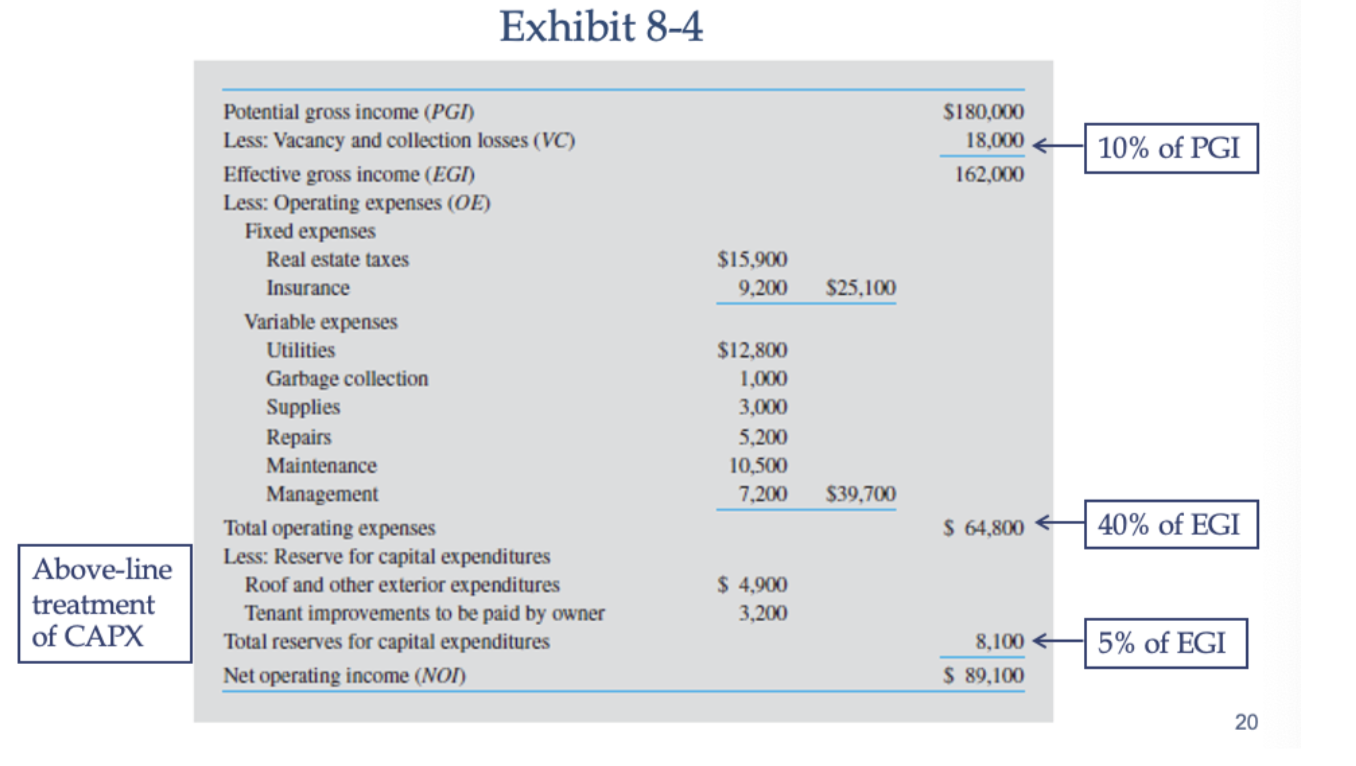
How to calculate NOI?
(i) Begin with PGI (potential gross income) which is the idealized income assuming 100% occupancy and timely recent collection
(ii) Then, you have to add misc. expense which is like parking revenue, laundry machine rentals
(iii) Then we have to subtract vacancy (when its empty;fixable because in the case that its empty just find someone to fill it in) and collection loss (when tenant is there but they're not paying rent; not fixable bc in the case that they are filing for bankruptcy and they're still there like it's a hard fix )
(iv) Then we get the EGI after (PGI+MI) - VC
(v) Then subtract the (operating expenses which is like utilities, property taxes, and maintenance + capital expenditures → is the account for major, infrequent expenses like roof replacement or HVAC upgrades; this can either be done “above-line” (deducted before arriving at NOI) or “below-line” (subtracted from NOI).)
(vi) Then we arrive at net operating income
(vii) Finally, NOI = EGI - OE - CAPX.
What is the first step in direct capitalization?
Obtain estimates of car rates Ro (cap rate) from market using “direct market extraction”
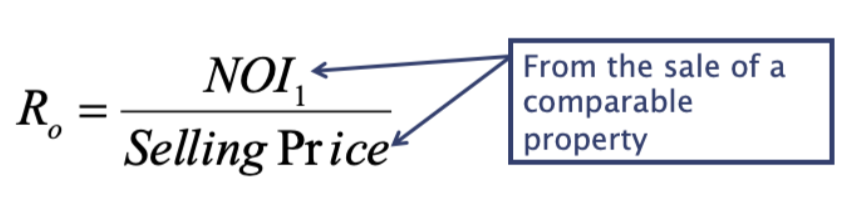
What is the second step in direct capitalization?
Divide subject’s NOI by weighted average of RoS abstracted from the market to obtain an estimate of value for the subject property
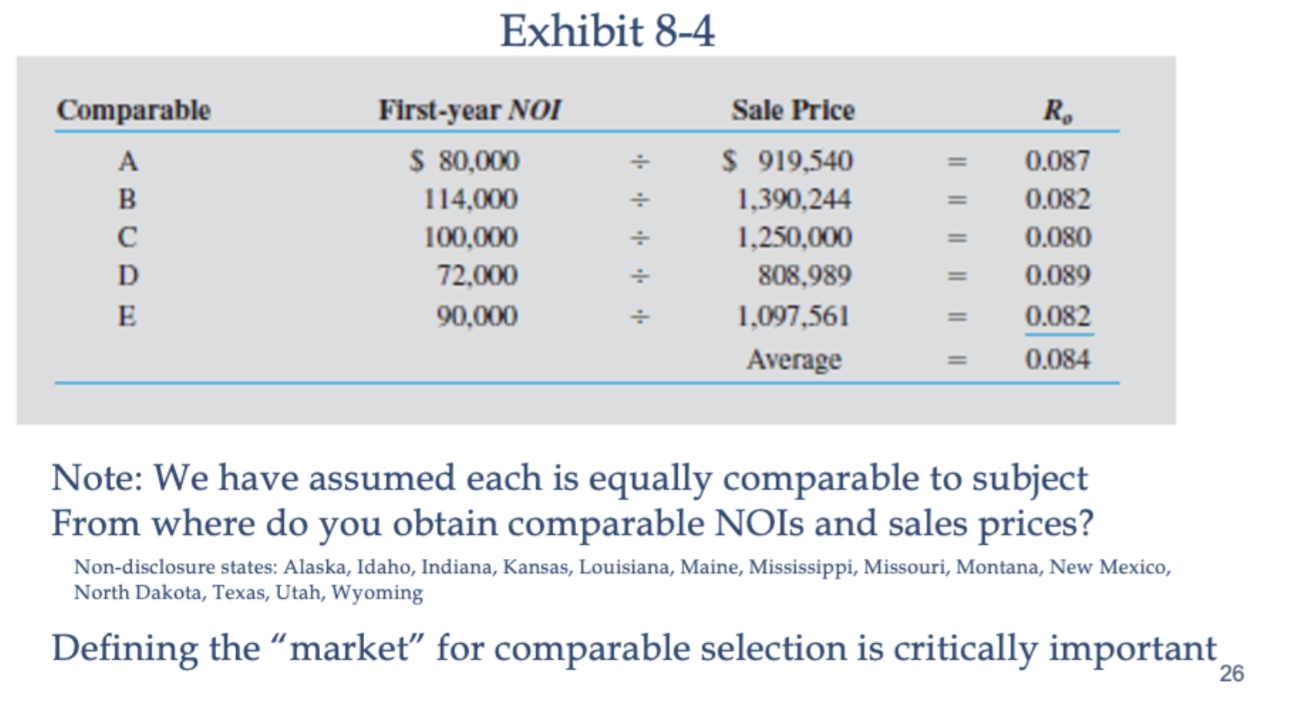
What is the third step in direct capitalization?
Compute estimated market value using expected first year NOI (i.e., next 12 months)
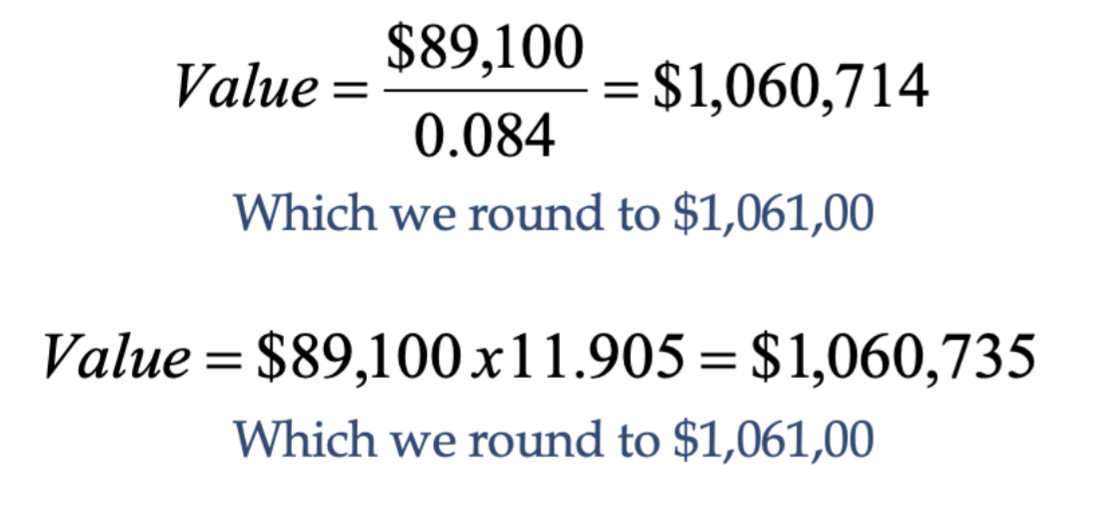

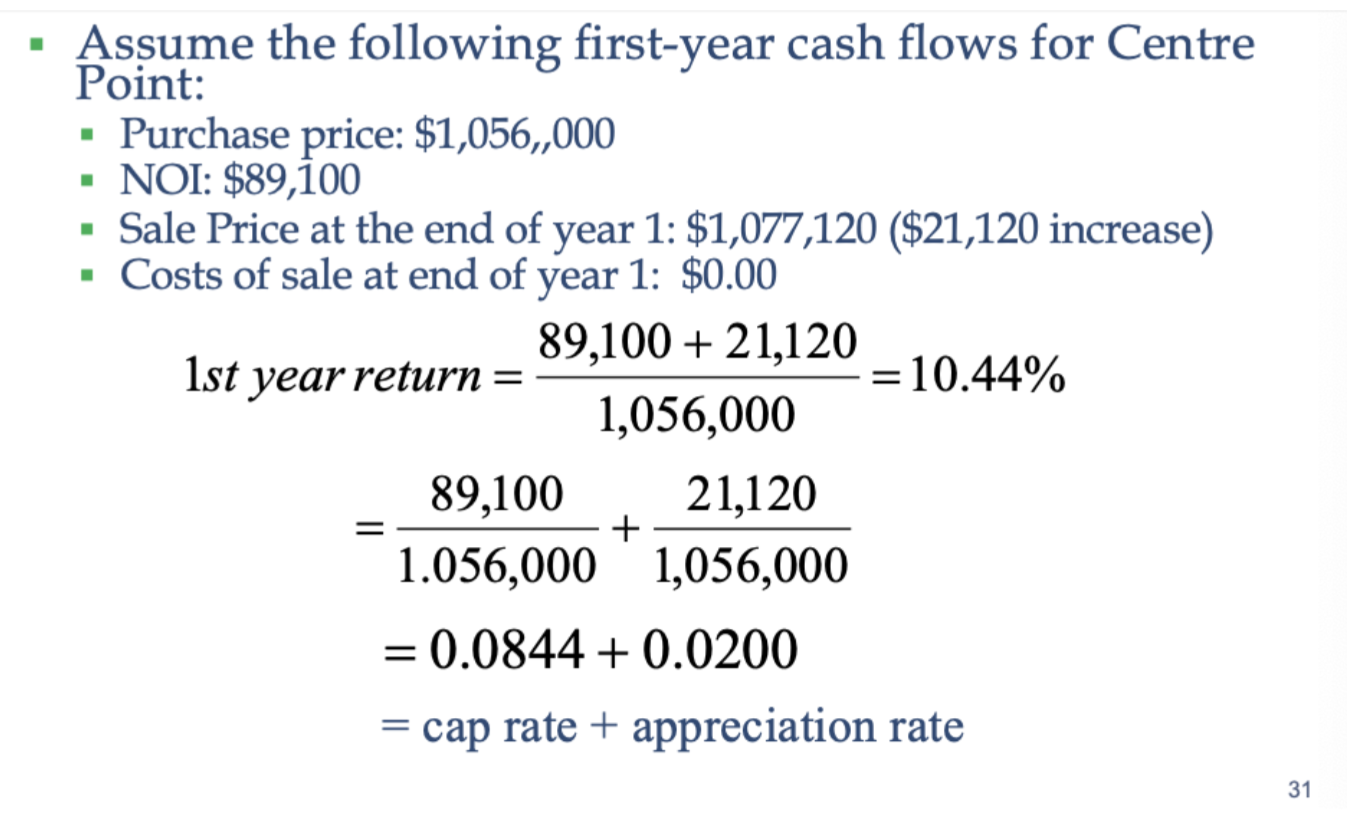
What is a cap rate?
Estimate the rate of return on an income-producing property.
It represents the relationship between a property’s Net Operating Income (NOI) and its current market value or purchase price.
The cap rate is typically expressed as a percentage and is used by investors to assess the potential profitability of a real estate investment.
Direct capitalization only uses first year NOI, but Ro reflects all future cash flows
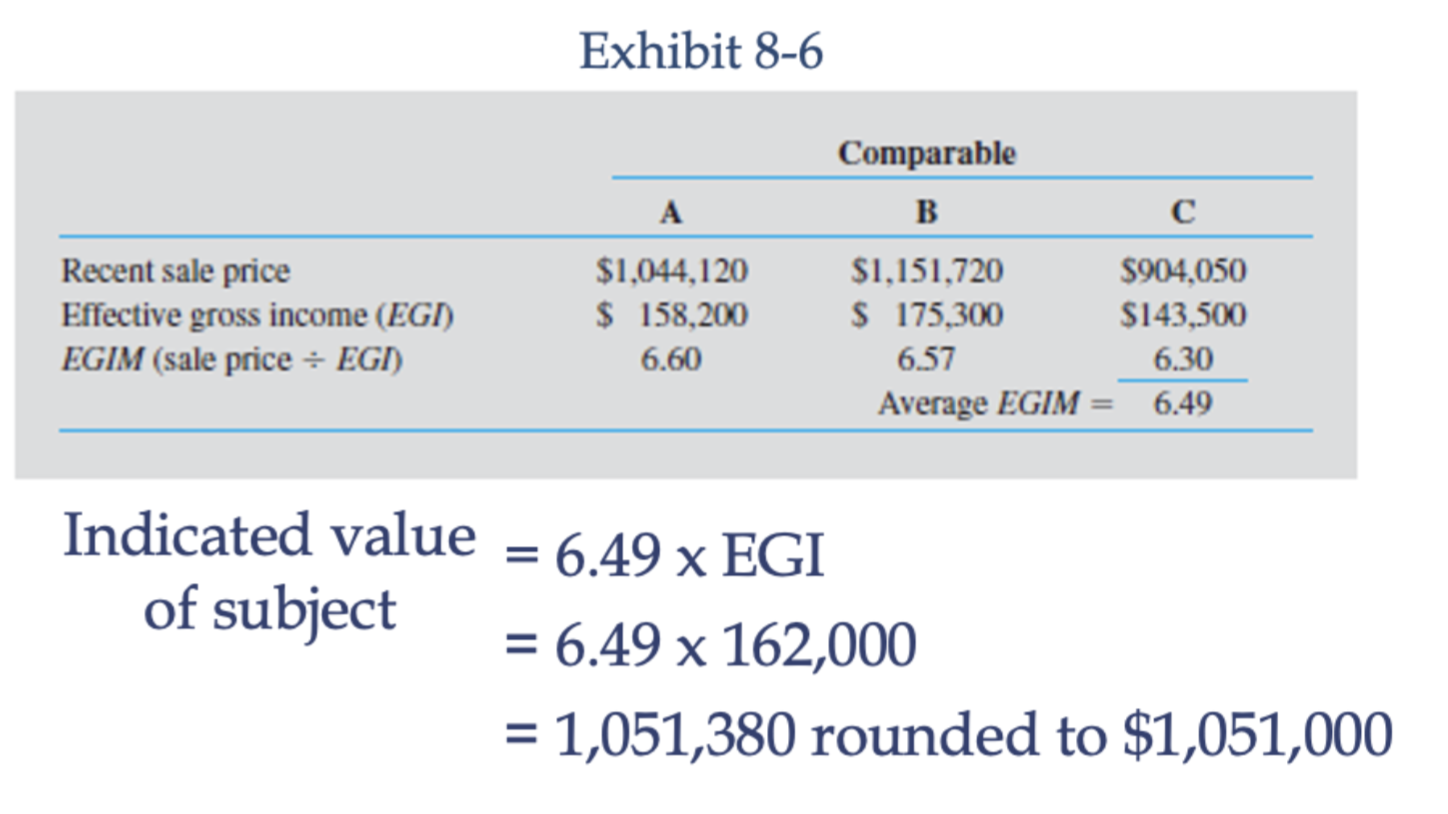
What is the Effective Gross Income Multiplier?
formula: EGIM = Sale Price / Effective Gross Income
Quick indicator of value for smaller rental
Roughly equal operating expense percentages across subject & comparable properties
Assumes market rents are paid
Best used for properties with short-term leases (apartments & rental houses)
What are the three approaches to estimating market value? and define each
Sales Comparison Approach: estimates a property’s value by comparing it to similar properties that have recently been sold in the same area; for residential properties and vacant land
Cost Approach: the property’s value on the cost to replace or reproduce the existing structure with a new one, minus depreciation, plus the land value; useful for new buildings, unique or specialized properties, and properties not frequently sold, like schools, churches, or government buildings: new buildings, unique or specialized properties, and properties not frequently sold, like schools, churches, or government buildings.
Income Approach: values a property based on the income it generates, converting this income into an estimate of value. This approach uses capitalization rates (cap rates) applied to the net operating income (NOI) of the property.