AP Microeconomics Unit 4: Imperfect Competition
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
perfect competition
a market structure in which a large number of firms all produce the same product
monopolistic competition
a market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but not identical
Oligopoly
A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market
Monopoly
A market in which there are many buyers but only one seller.
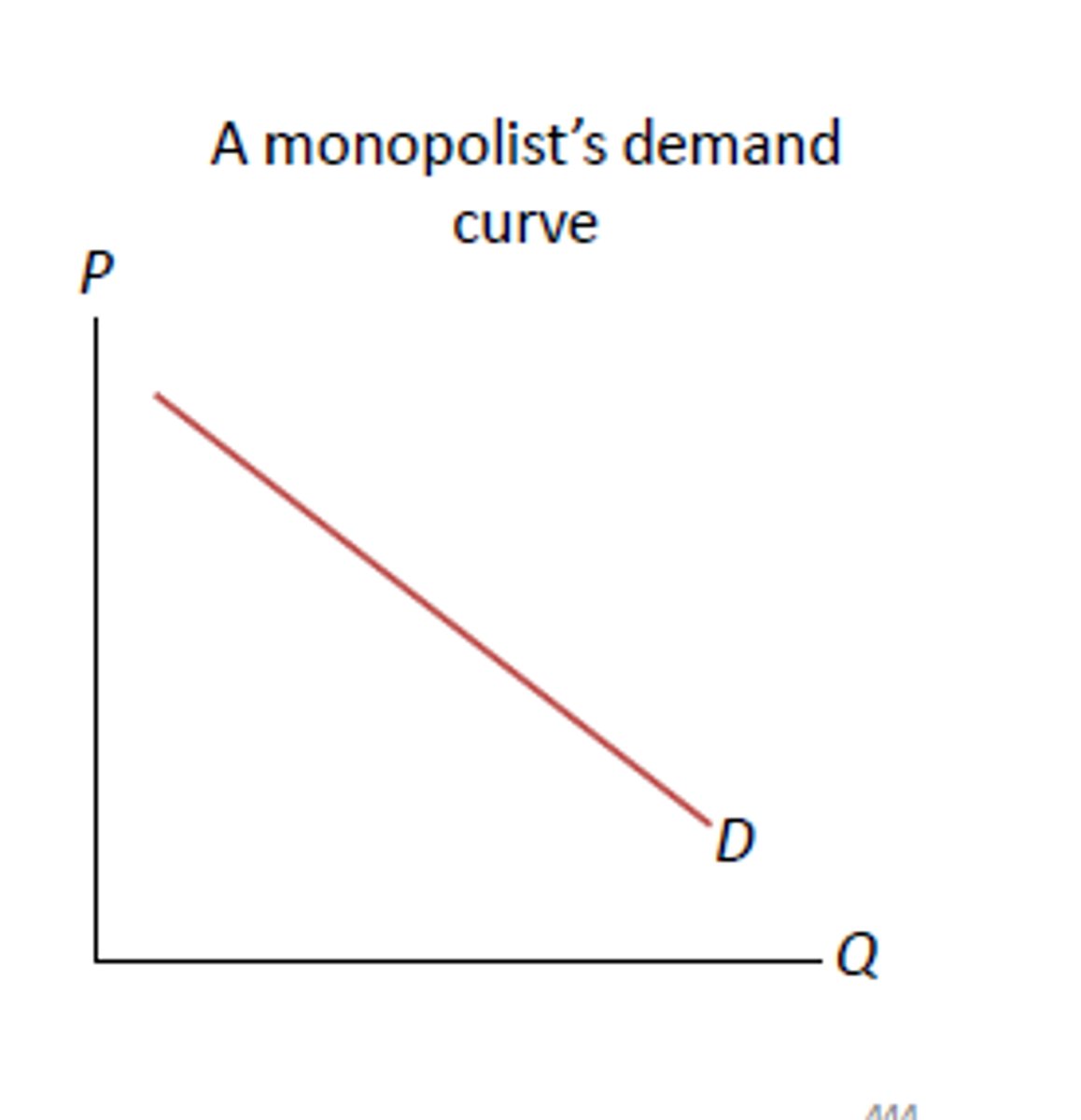
Why is demand greater than marginal revenue for all imperfectly competitive firms?
A firm must lower its price to sell more.
What are common barriers that prevent other firms from entering an imperfectly competitive market?
-Capital Costs: New investments are sometimes required to enter a market.
-Economies of Scale: Competitors can't compete with other firms who have much lower production costs. ...
-Legal Barriers To Entry.
-Marketing Barriers.
-Limited Market.
-Vertical Integration.
-Predatory Pricing.
demand for imperfectly competitive firm
three conditions necessary for a firm to price discriminate
-Firms must be able to control supply.
-Firms must prevent resale of products from one buyer to another.
-There must be a difference in price elasticities in the different markets for the product.
If a regular unregulated monopoly started perfectly price discriminating, what would happen to consumer surplus and deadweight loss?
The gap between the minimum ATC output and the profit maximizing output. Given current resources, the firm can produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to.
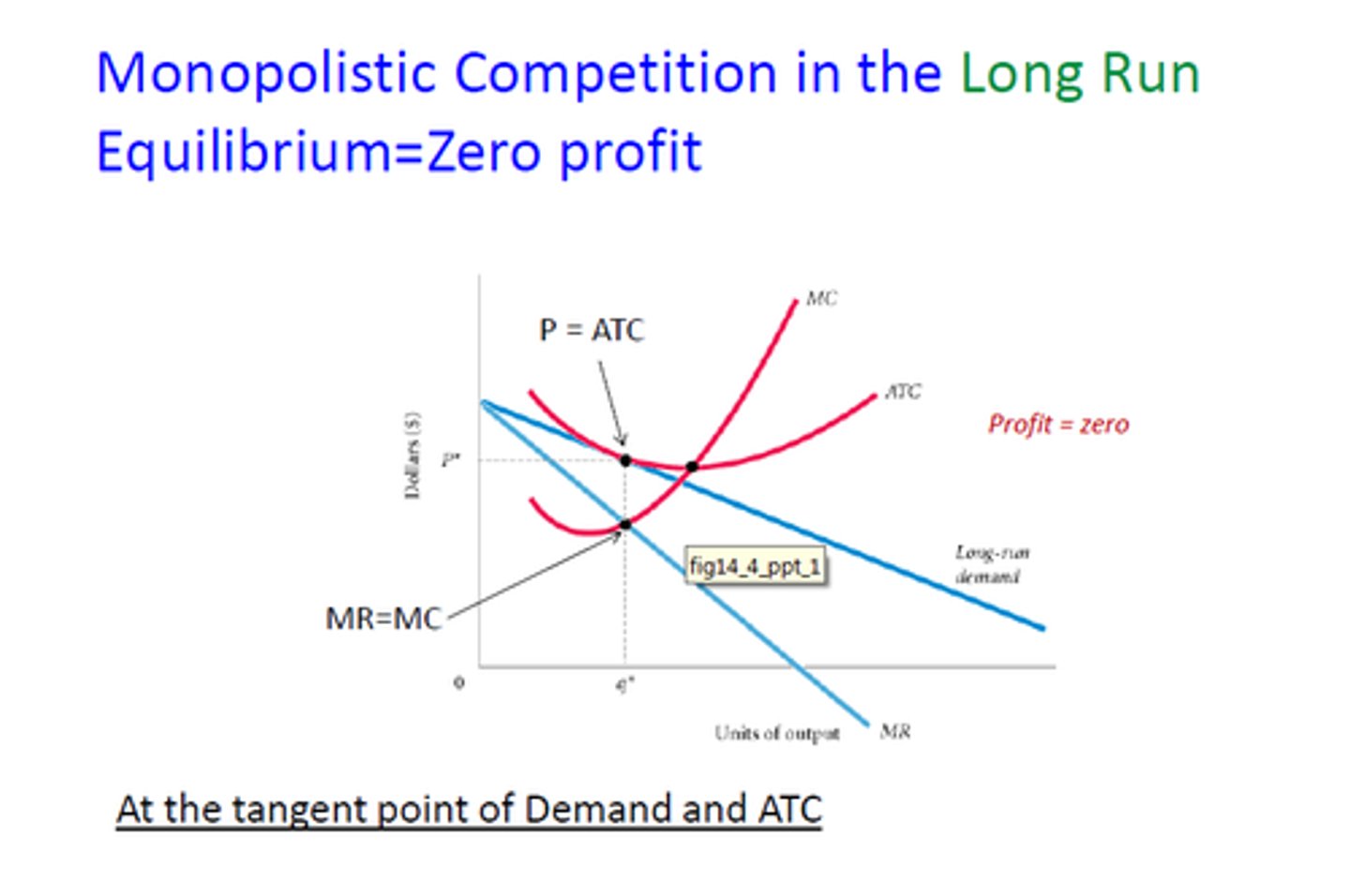
Monopolistic competition in the long run
How is monopolistic competition different from perfect competition?
Monopolistic = price makers
Perfect = price takers
If a monopolistically competitive firm is making a profit in the short-run, what will happen to the demand number of firms in the long run?
ATC increases
There is an increase in demand in the long run
Nash Equilibrium
a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the other actors have chosen