Ecosystems and global change
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Primary productivity
The rate that solar energy is captured and converted into chemical bonds by photosynthesis
Only 1% of solar energy is converted into chemical energy
Photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O + E(sunlight) → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Organisms use this energy for
Cellular respiration
growth
reproduction
Energy Path story
GPP (Energy created through photosynthesis)
Respiration (Tree uses some energy)
NPP (Energy left in oranges (GPP-Respiration)
GSP (Energy turtle gets from fruit)
Egested energy (Turtle poops peals)
Assimilated energy (Turtle uses it to live)
NSP (Energy left for reproduction)
Ecology Efficiency
The percentage of chemical energy transferred from on trophic level to the next
NSP/NPP
5-20% average at around 10%
Terrestrial energy pyramid
Energy becomes increasingly scares as it moves up trophic levels
The number of top carnivores provides an estimate of the health of an ecosystem
No more than 4 or 5 trophic levels
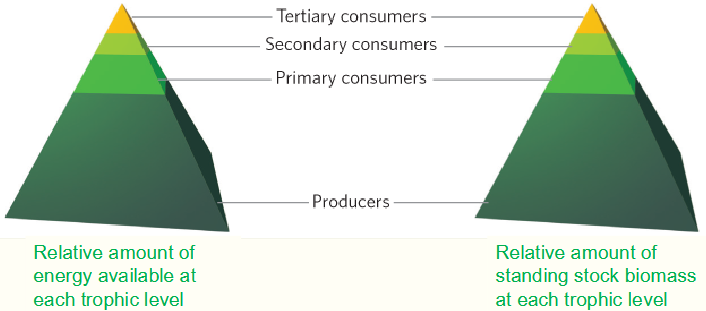
Standing stock biomass
The total weight of living organism within a defined area
Aquatic energy pyramids
The relative amount of energy at each trophic level is inversely related to the amount of standing stock biomass.
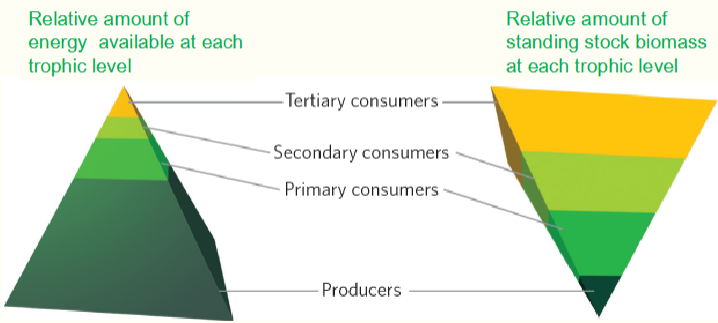
Phystoplankton as primary producers
They have an extremely high reproductive rate
so small population is ok
Bottom-Up control
When the abundance of producers determines the abundance of organisms
Top-down control
When the abundance of high level consumers determines the abundance of organism
DDT
1950s
A synthetic insecticide that kills insect borne human diseases
Damages liver, reproductive system, and causes cancer
Biological Amplification
Fat soluble poisons accumulate in zooplankton
When fish consume they get even more in their tissue and so on since higher trophic levels eat more!
Rachel Carson
Silent Spring (1962)
She exposes the dangers of biological amplification of industrial chemicals like DDT
Global nutrient cycles
Atmospheric nitrogen is converted into fixed nitrates by lightening and nitrogen fixing bacteria.
N2 into NO3-
Fixed nitrogen is used by plants and its also converted back into N2 and into N2O (a greenhouse gas)
Human impact on global nutrient cycle
modern industry and agriculture increased the rate of nitrogen fixation.
This has led to eutrophication and oxygen depletion
Increased N2O
Eutrophication
Too much nitrogen that leads to oxygen depletion through algal blooms
Algal blooms grow and then die
Decomposers use up a lot of oxygen to break down the algal and depeleat O2 levels in the water
Carbon cycle
Atmospheric CO2 is captures by photosynthesis and tuned into glucose and bioavailable forms of carbon
Plant biomass decompose or become fossil fuels
Respiration increases released CO2
Humans have altered this cycle by burning fossil fuels and releasing too much CO2
Climate change
Okjokull glacier (first to fully melt)
Increase in temperature cause by too much CO2 methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere (N2O)
Greenhouse Gas effect
Solar radiation warms earths surface and greenhouse gasses
The surface emits infra-red radiation (heat)
Water vapor increases (is a greenhouse gas)
Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide act as glass and hold in that heat
Triple threat for the ocean
The ocean absorbs 90% of the heat
It absorbs 25% of the CO2
So the ocean is warmer, has less oxygen, and is more acidic