Angle Anatomy & Aqueous Humor Outflow
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
ciliary body band
appearance:
light gray to dark brown
extends from ora serrata to SS
width varies depending on iris contour
function:
aqueous humor production
most posterior structure of angle
scleral spur
appearance:
white or gray band
prominent b/t the darker CB & TM
function:
point of attachment b/t sclera & ciliary muscles
trabecular meshwork
appearance:
gray to brown band
anterior is more pigmented than the posterior
function:
drainage of aqueous humor
Schlemm’s canal lies behind posterior 2/3 of TM
Schwalbe’s line
appearance:
thin, glistening white line
function:
marks the end of Descemet’s membrane
transition from cornea to sclera
iris, ciliary body band, scleral spur, trabecular meshwork, Schwalbe’s line
list the structures of the angle from most posterior to anterior
4
angle width: 35-40deg
most posterior structure: CB band
description: wide open
probability of closure: impossible
3
angle width: 20-35deg
most posterior structure: CB band or scleral spur
description: open
probability of closure: improbable
2
angle width: 10-20deg
most posterior structure: scleral spur/TIM
description: narrow
probability of closure: possible
1
angle width: 10deg
most posterior structure: anterior TM
description: extremely narrow
probability of closure: probable
0
angle width: 0deg
most posterior structure: none
description: closed
probability of closure: closed
inferior
which angle is the widest?
superior
which angle is the narrowest?
temporal
which mirror is usually more narrow than the others
direct gonioscopy
uses Koeppe lens
high plus CL
allows for 360 visualization of the angle
not commonly performed b/c pt must be supine & circle the supine pt while observing with a handheld slit & separate light source
3 mirror indirect gonioscopy
contains 2 mirrors to view retina & 1 to view AC angle
central Hruby lens that shows the posterior pole
advantages:
good stability
excellent optics
used for AC angle evaluations & posterior & peripheral fundus eval
disadvantages:
must rotate to see all the angles
increased exam time
may increase pt discomfort
insertion & removal are more involved
4 mirror indirect gonioscopy
all 4 mirrors have the same angle & used to view AC angle only
central Hruby lens that shows posterior pole
can have a handle or not
can have a flange or not
advantages:
can view all quadrants of the same angle w/o needing to rotate
more user & pt friendly
may be used for indentation gonio
disadvantages:
no mirrors for peripheral fundus view
requires greater operator skill
d shaped mirror
60deg angle
offers view of AC angle
rectangular mirror
66deg angle
offers views of the retina b/t the equator & beginning of ora serrata
trapezoidal mirror
76 deg angle
offers view of the retina b/t the posterior pole & equator
Scwalbe’s line
when doing the corneal wedge technique, what structure is highlighted?
posterior embryotoxon
normal finding
thickened Schwalbe’s line
benign finding in ~20% of population
most often associated with pathological findings of the iris & cornea
iris processes
normal finding
fine, lacy projections of peripheral iris tissue extending to the sleral spur or TM
easily seen in brown eyes
does not impede TM outflow
peripheral anterior synechiae
abnormal finding
adhesions of the peripheral iris to the angle wall
very thick fibers that extend from iris root to SS/TM/Sl
not always present 360deg
associated w/ closed angles & past or present inflammation
large areas can be problematic
indentation gonioscopy
used to distinguish b/t an angle closed by pupillary block & peripheral iridotomy; typically done with a 4 mirror
pigmentary dispersion syndrome
findings:
Kruckenberg spindle
transillumination defects
sampolesi’s line
demographics:
more common in males
males present in 30s
females present in 40s
more common in myopes
associated w/ concave iris & posterior iris insertions
pt have significantly flatter corneas
pathology:
iris touches lens zonules, resulting in iris pigment being rubbed off & entering the AC, clogging the TM
pseudoexfoliation syndrome
flaky material on anterior lens capsule at pupillary margin
material builds up in angle
frosting of lens zonules
hyphema
collection of blood in the AC due to trauma; risk of increased IOP
angle recession
due to trauma, further back AC angle; small percentage develop glaucoma
PDS
trans-illumination defects of the mid-peripheral iris are most commonly associated with what condition?
CB to left of iris, then SS, TM, SL
when viewing the temporal angle of the pt’s left eye with the 4 mirror gonio lens, how are the structures seen in the mirror?
schwalbe’s line
in the event of an anterior chamber angle closure, which structure would you most likely see with the 3 or 4 mirror gonio lens?
indentation gonioscopy with an un-flanged 4 mirror goniolens
on a 3 mirror gonio, you determine that the anterior chamber is completely closed 360deg, how would you distinguish if the angle was held closed by PAS or if it could potentially be opened by laser surgery?
trapezoidal mirror
if you want to view the mid-peripheral retina, which element of the 3 mirror goniolens would you use?
the limbus prevents a direct view of the AC angle, as do internal reflections
why was gonio developed?
ciliary body
in the event of an anterior chamber angle closure, which structure would you least likely see with 3 or 4 mirror goniolens?
rectangular mirror
if you want to view the peripheral retina, which element of the 3 mirror goniolens would you use?
performs a 4 mirror gonio & finds ½ the TM in at least 2 quadrants
with angles that appear narrow using Van Herick angle estimation, it is safest to proceed with dilation when the clinician does what?
d shaped mirror
if you want to evaluate the pt’s AC angle for damage following trauma, which mirror on the 3 mirror goniolens should be used?
ciliary body
angle structure best described as a brown band when viewed during gonio & is responsible for producing the aqueous humor
trabecular meshwork
angle structure that is best described as a gray to brown band when viewed during gonio & is responsible for the filtering portion of the angle
pseudo-exfoliation syndrome
TID of the pupillary margin are most commonly associated with what condition?
scleral spur, grade 2
what is the most posterior structure in this image & what would you grade it?

ciliary body band
what is the most posterior structure in this image
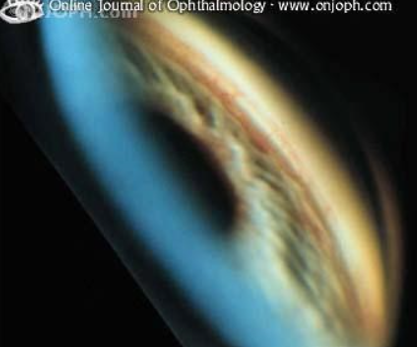
ciliary body band
what is the most posterior structure in this image
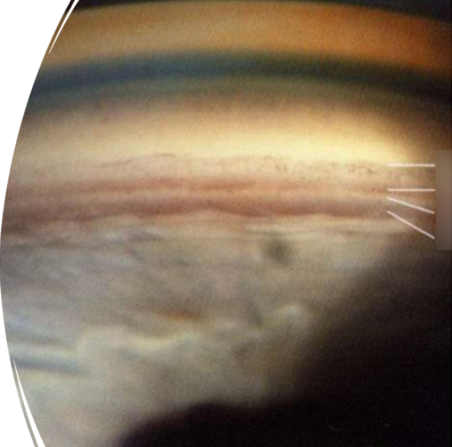
schwalbe’s line, grade 0
what is the most posterior structure in this image & what is the grade
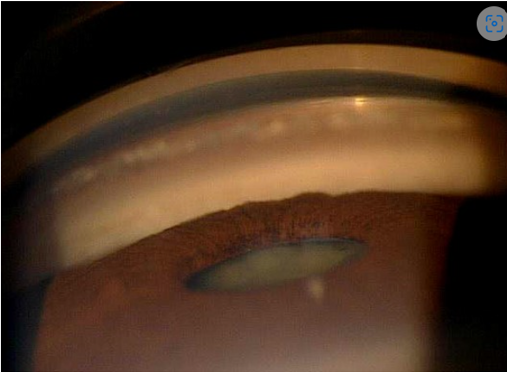
ciliary body band
what is the most posterior structure in this image

iris processes
what is the finding shown in this image?
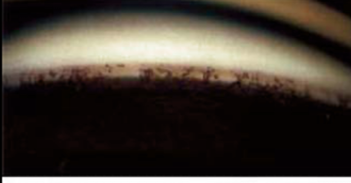
iris processes
what is the finding shown in this image?

neovascularization of the angle
what is the finding shown in this image?

blood in schlemm’s canal
what is the finding shown in this image?
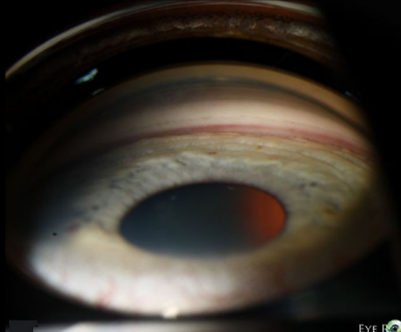
pigment deposition from PDS or PXS
what is the finding shown in this image?
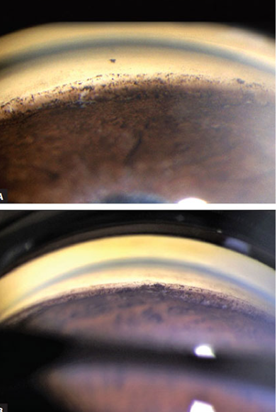
ciliary body band, grade 4
what is the most posterior structure shown & what is the grade?

Schwalbe’s line, end of descemet’s membrane & transition from cornea to sclera
what is the most posterior structure shown here & what is the function?
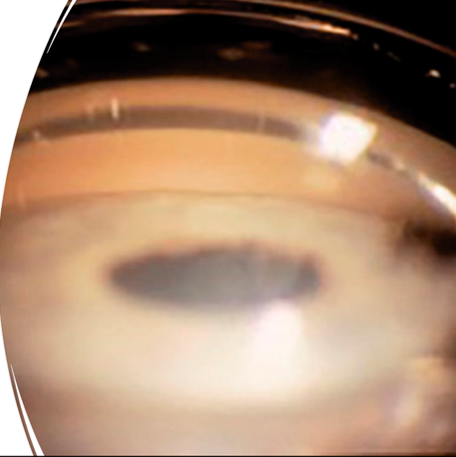
posterior pole of the retina
the central Hruby lens of the 3 & 4 mirror goniolenses is used to view what?
ciliary body band
identify the red arrow structure
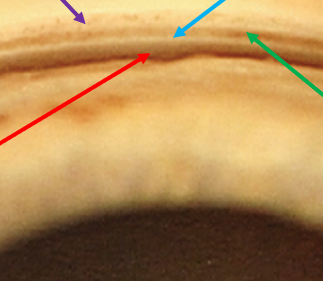
schwalbe’s line
identify the purple arrow structure
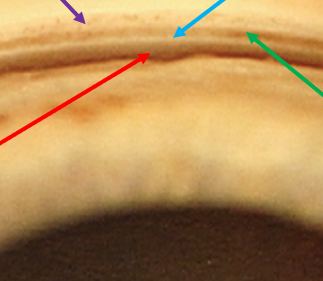
scleral spur
identify the blue arrow structure
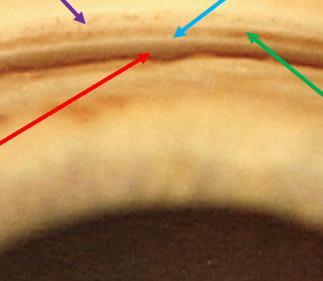
trabecular meshwork
identify the green arrow
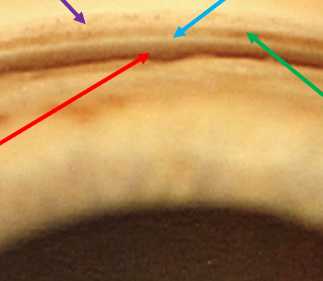
posterior embryotoxin
identify
iris processes
identify
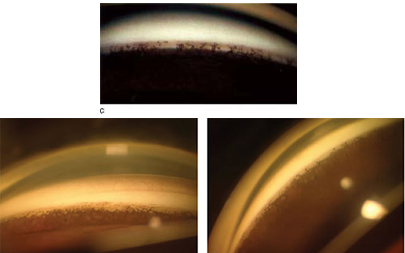
peripheral anterior synechiae
identify

PDS Kruckenberg spindle
identify
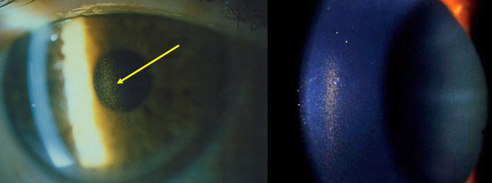
TID
identify
TID from PDS
identify
pigment deposits in angle from PDS
identify
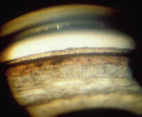
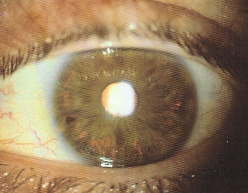
pseudo exfoliation syndrome
identify
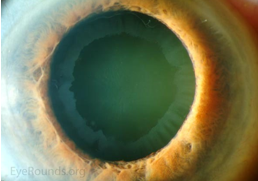
blood in Schlemm’s canal
identify
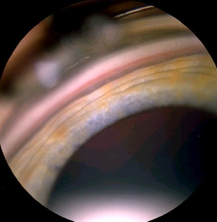
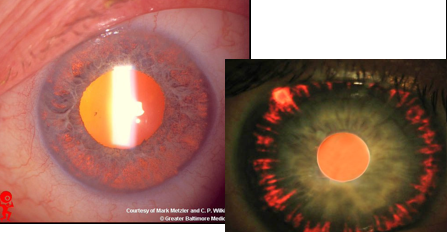
neovascularization
identify
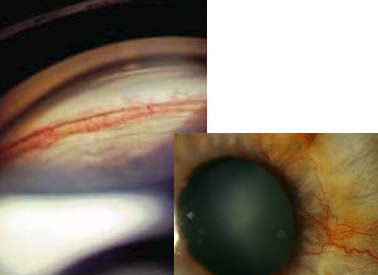
neovascularization
identify
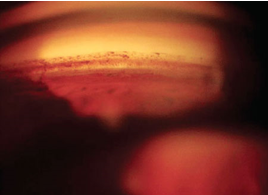
MIGS
identify
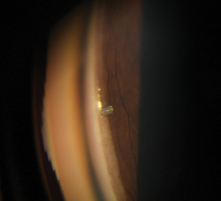
ALT
identify

8 ball hyphema
identify
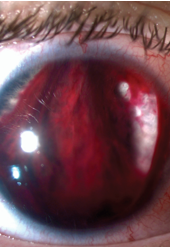
general hyphema
identify
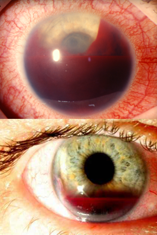
angle recession
identify

angle recession
identify
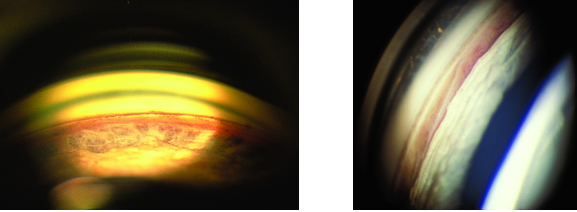
anterior synechiae
identify
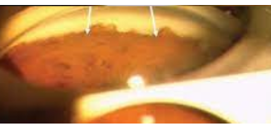
anterior synechiae
identify
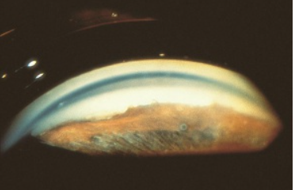
anterior synechiae
identify
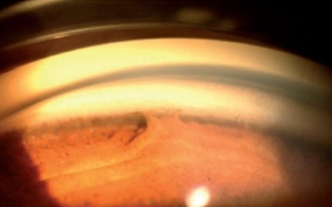
neovascularization of the angle
identify
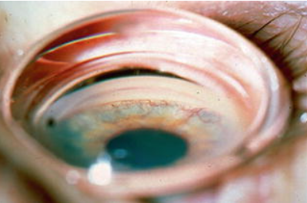
ciliary body band, aqueous humor production
identify the most posterior structure shown in this image & what is its function?
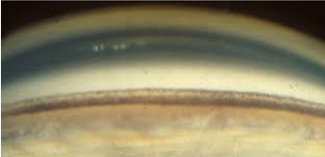
Schwalbe’s line, trabecular meshwork, scleral spur, ciliary body
list the angle structures from most anterior to most posterior