Light
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
def of light
electromagnetic radiation that is a form of energy & travels
what is the relationship of the electric & magnetic fields in electromagnetic radiation?
perpendicular to each other & to the direction of propagation
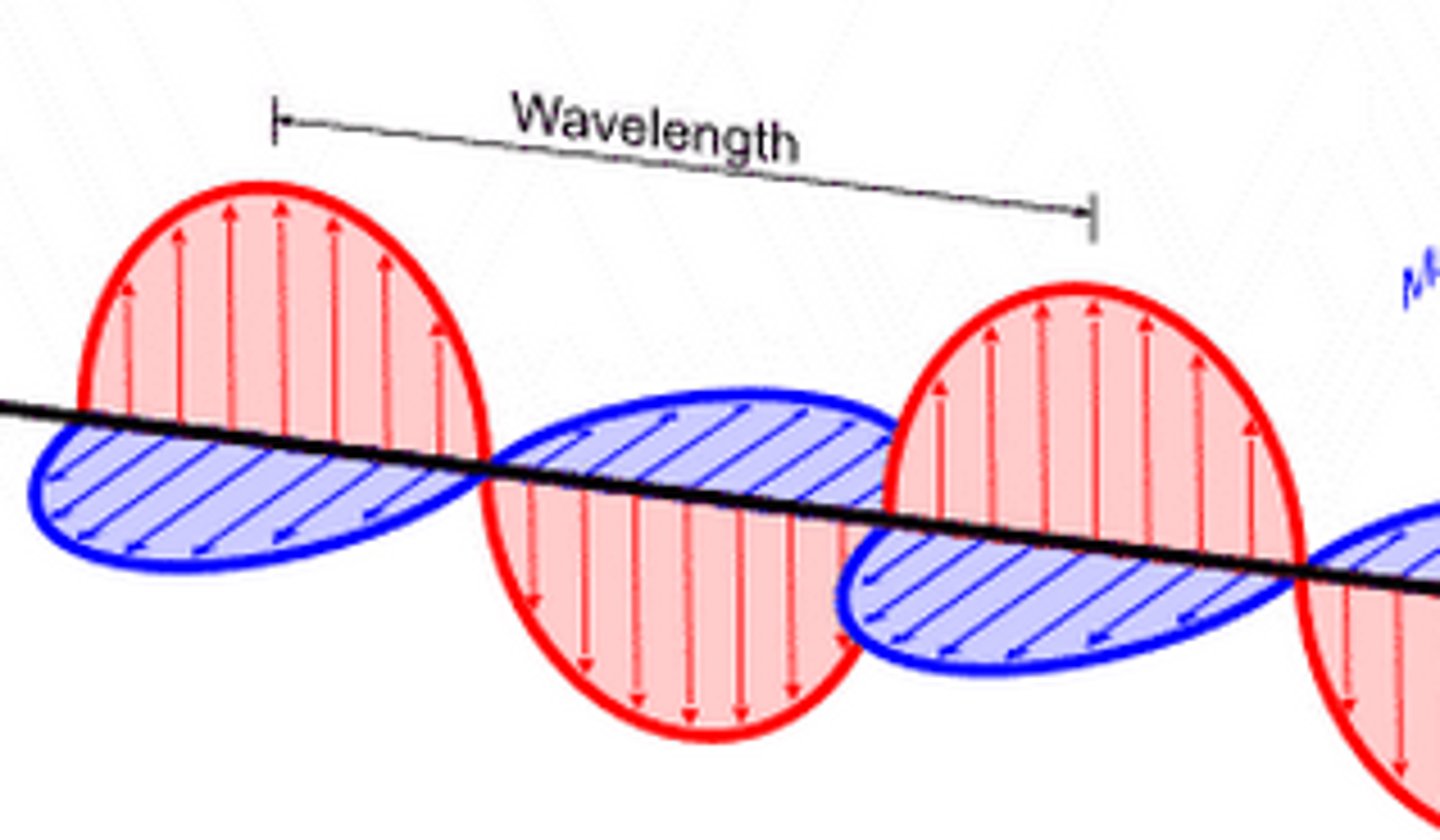
def of wavelength
distance between the adjacent peaks of the wave
def of frequency
number of waves passing a given point each second
equation for wavelength & frequency
c = λf
speed of light in a vacuum
3.00 x 10^8 m/s
equation for speed of light NOT in a vacuum
vm = c/n
(n = index of refraction)
visible light is between ____ nm
380-760 nm
def of monochromic light
single wavelength
def of achromatic light
equal mixture of all visible wavelengths ("white light")
what is the photoelectric effect?
the emission of electrons from a metal when light is shined on it
decrease wavelength = increase speed of e-
increase intensity = increase # of e-
Planck's constant
6.626 x 10^-34 J*s
equation for energy of a photon
E = h*f
the cornea absorbs UV___ light, which can lead to ____
C
solar keratitis
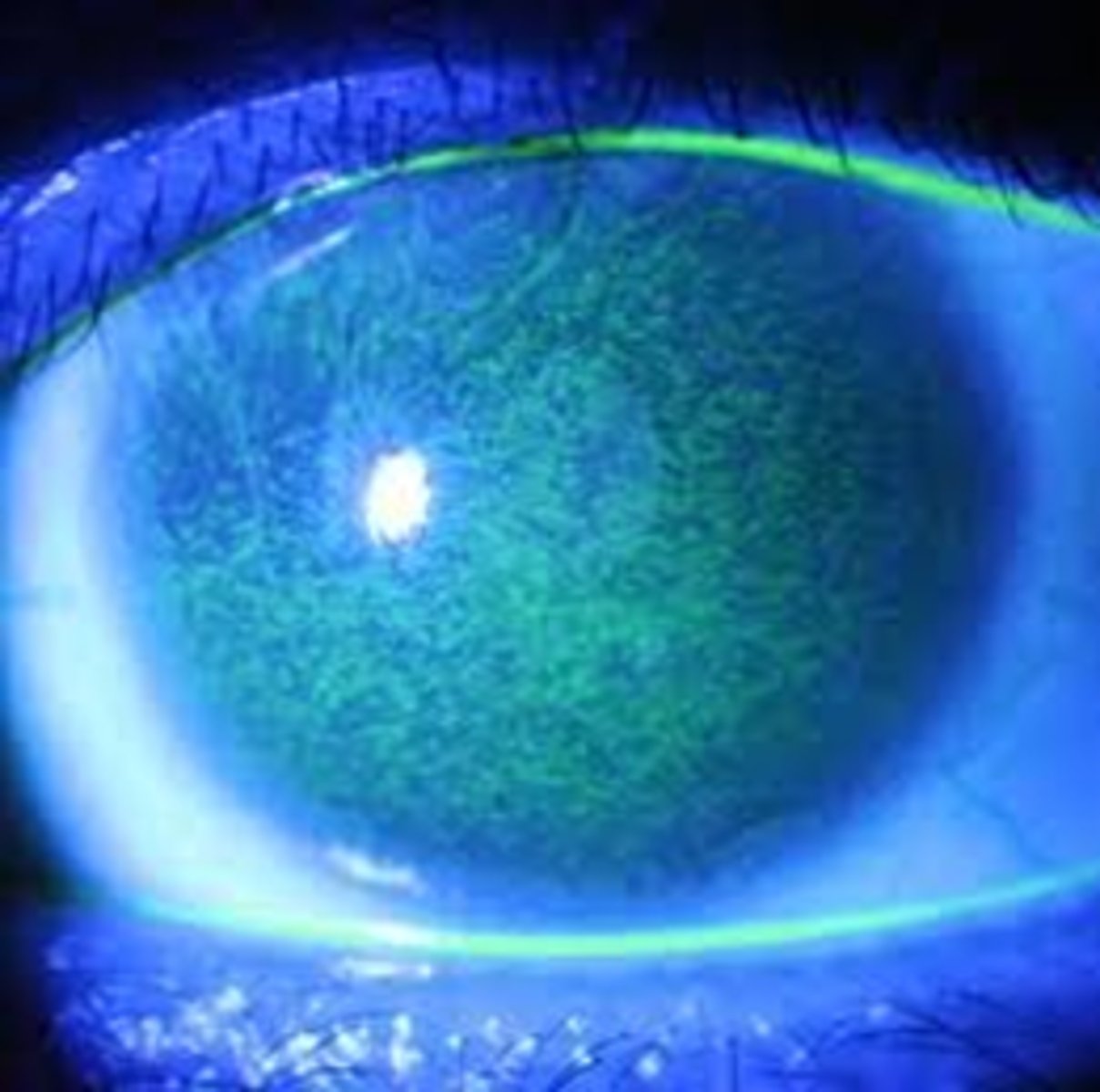
the lens absorbs UV___ light, which can lead to ____
A & B
cataracts
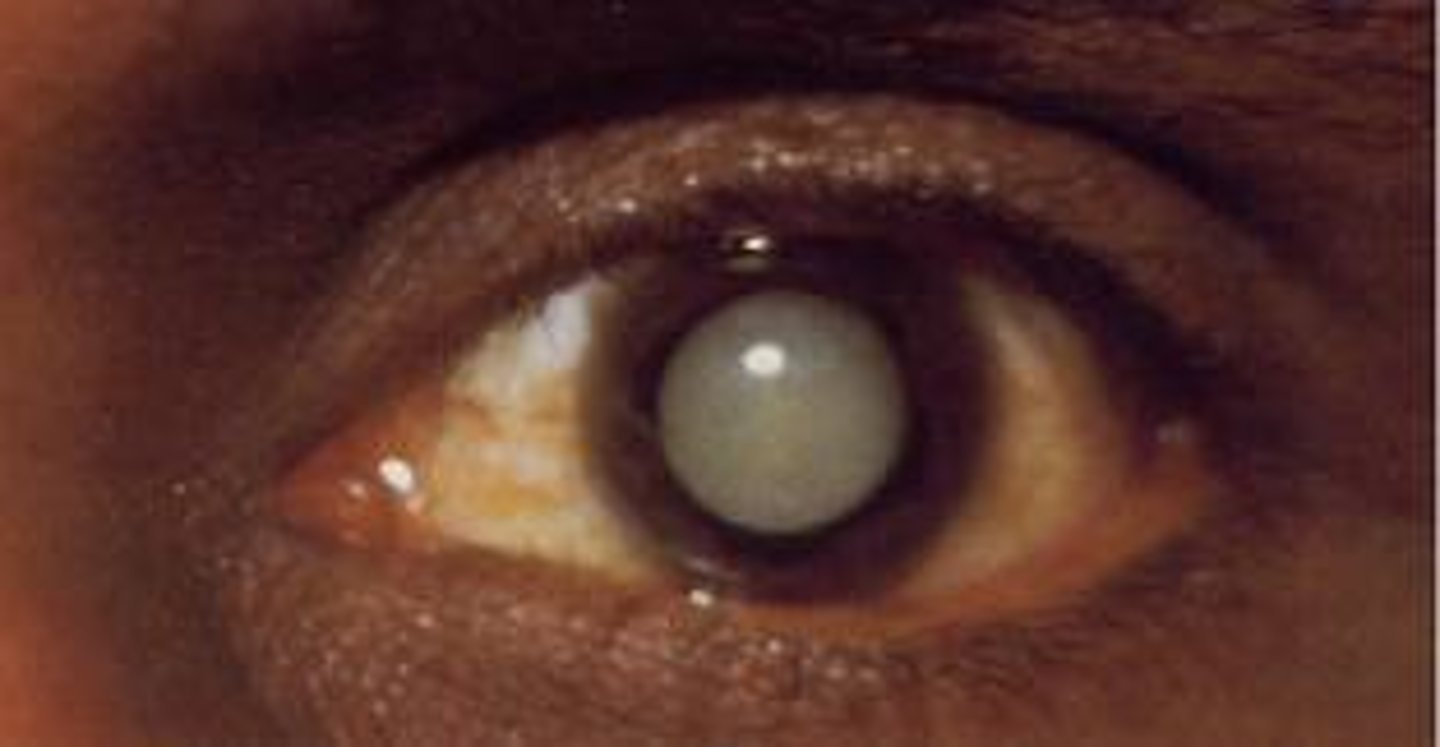
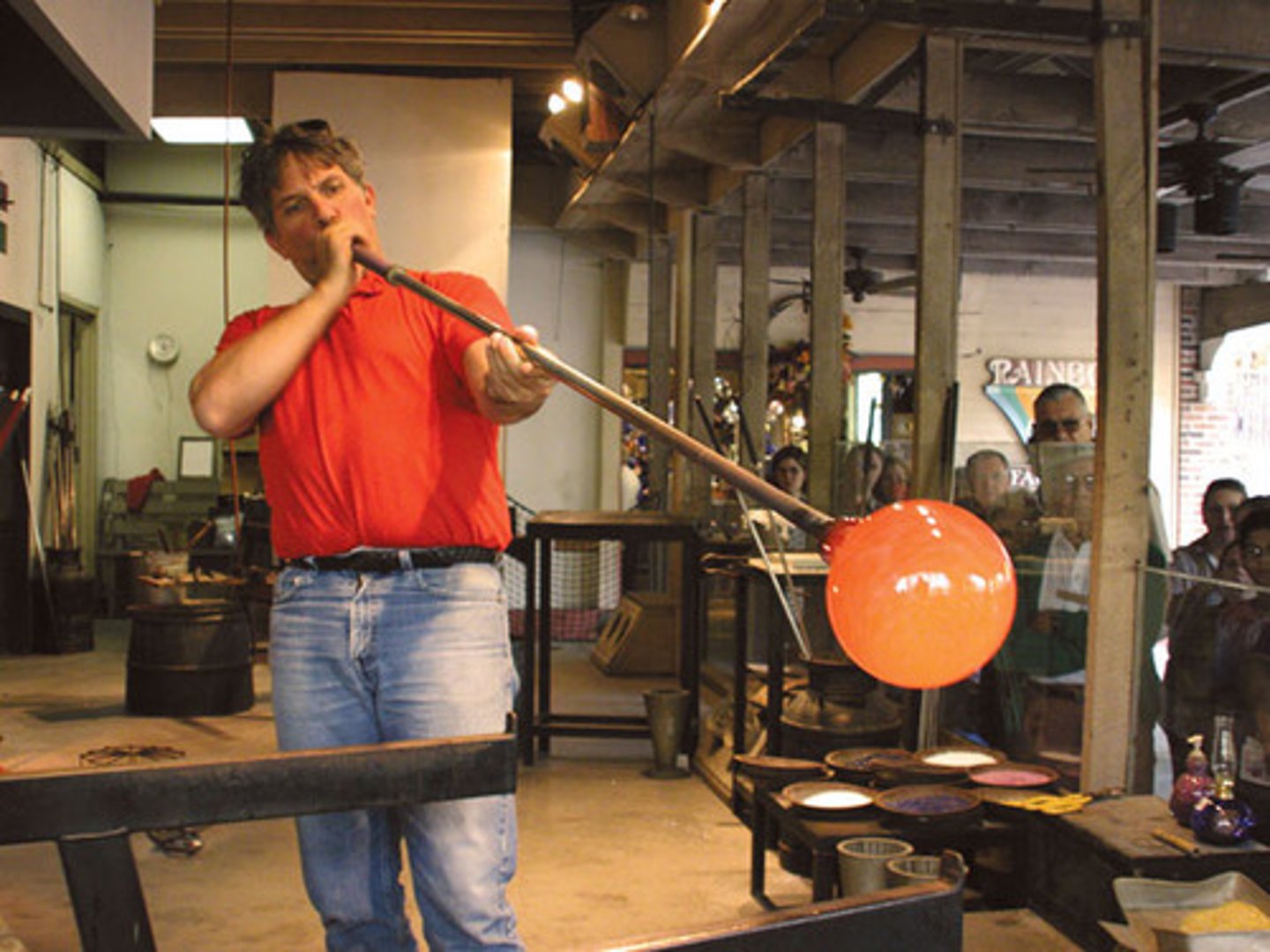
the ____ absorbs infared light, which can lead to ____
lens
glass blower's cataract

at short wavelengths, the ____ nature of light is accentuated
quantum
interference, diffraction, and polarization are examples of _____ optics
wave
absorption, fluorescence, and lasers are examples of _____ optics
quantum
the energy of a light wave is determined by its...
amplitude
def of wave
disturbance that propagates through the available space or medium
def of transverse wave
oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of propagation
def of longitudinal wave
oscillation is parallel to the direction of propagation
def of periodic wave
waves that repeat at regular intervals
def of period
length of each repeating cycle of a periodic wave
def of harmonic/sinusoidal wave
a type of periodic wave that can be described by a single sine function (y = A sin p)
what function is used to define harmonic/sinusoidal waves?
y = A sin p
(p = phase)
t or f: the sum/difference of harmonic waves is always a harmonic wave
false
if 2 or more harmonic waves have the same frequency, then their sum will also be a harmonic wave
if 2 or more harmonic waves have different frequencies, then their sum will NOT be a harmonic wave
when a phase represents space, what is the period?
wavelength
when a phase represents time, what is the period?
temporal period (T)
what is the relationship between temporal period & frequency?
f = 1/T
equation for phase difference (hint: there are 2)
phase represents space: (distance/lamda)*2π
phase represents time: (interval/T)*2π
what is the phase difference between a crest of a wave & the neighboring trough? (assume harmonic wave)
π
what is the wavelength of a harmonic wave? (in radians)
2π
what is the distance between a crest of a wave & the neighboring trough? (assume harmonic wave)
lambda/2
what is the time difference between a crest of a wave & the neighboring trough? (assume harmonic wave)
T/2
equation for velocity of a wave
v = wavelength * frequency
v = wavelength / temporal period
t or f: wavelength AND frequency change when light enters a new medium (with a different index of refraction)
false, wavelength changes but frequency does not
t or f: when light enters a new medium, its color changes due to its change in wavelength
false, color is based on what the wavelength is in a vacuum
t or f: all harmonic waves are sinusoidal waves, but not all sinusoidal waves are harmonic waves
false, it is the other way around
all sinusoidal waves are harmonic
however, not all harmonic waves can be described using a sine function
def of intensity
energy of a wave, per unit area, per unit time
equations for intensity & amplitude
I = A^2
what is the equation for relative intensity?
Irel = I2 / I1 = (A2 / A1)^2
what is another term for intestity?
irradiance
equations for superposition (2)
yr = y1 + y2
Ar sin pr = A1 sin p1 + A2 sin p2
equation for constructive interference
p1 = p2
constructive interference is _____ phase
destructive interference is ______ phase
constructive: in phase
destructive: out of phase (by 180 degrees)
in order to have constructive interference, you need... (2)
same frequency & in phase
in order to have destructive interference, you need... (2)
same frequency & out of phase (by 180*)
what is the relationship between p1 & p2 in constructive interference?
p1 = p2
what is the relationship between p1 & p2 in destructive interference?
p2 = p1 + 180*
def of interference
the combination of 2 or more waves with the same frequency to form a resultant wave in which the displacement is either reinforced or canceled
in a ripple tank, the locations with destructive interference are called _____
locations with constructive interference are called ______
destructive: minima
constructive: maxima
incoherent vs. coherent light sources
coherent = the difference between the phase is constant
incoherent = the difference between phases is constantly changing
for light to have interference, the two sources have to be...
coherent
equation for resultant intensity of coherent waves
Ir = Ar^2
Ir = A1^2 + A2^2 + 2A1A2cos(p1-p2)
equation for average resultant intensity of incoherent waves
Ir (avg) = I1 + I2
when 2 harmonic waves of DIFFERENT frequencies are superposed, what is the resultant waveform?
periodic, but not harmonic
in Young's double-slit experiment, constructive interference corresponds with...
illuminated bands (maxima)
in Young's double-slit experiment, destructive interference corresponds with...
unilluminated bands (minima)
Young's slit experiment revealed what property of light?
wave
if light only had particle property, what would Young's experiment had looked like?
only 2 lines of light would appear
why does Young's experiment support the wave model of light?
multiple lines of light appear on screen, which is an interference pattern formed by a wave
the distance between the 2 slits in a double-slit experiement is designated by the letter...
h
the distance between the screen and the slits in a double-slit experiment is designated by the letter...
t
the distance between the center of the screen to a point of interest on the screen in a double-slit experiment is designated by the letter...
x
the path difference between the 2 sources in a double slit experiment is designated by the letter...
w
what are the equations for w in a double-slit experiment?
w = mλ
(m = order of the fringe)
w = xh/t
what is the equation for x (linear location of a fringe) in a double-slit experiment?
x = mλt / h
what is the equation for θ (angular location of a fringe) in a double-slit experiment?
θ = mλ / h
maxima appear at m = ...
0, 1, 2, etc
minima appear at m = ...
0.5, 1.5, 2.5, etc
linear separating of fringes equation
s = λt / h
angular separation of fringes equation
δθ = (lamba) / h
if wavelength is increased, fringe separation _____
increases
if wavelength is decreases, fringe separation _____
decreases
if distance to the screen (t) is increased, then fringe separation ____
increases
if slit separation (h) is decreased, then fringe separation ____
increases
θ λ δ
when is acuity testing by interference fringes used?
to determine whether someone is a good candidate for cataract surgery or not
what is the minimum intensity (Imin) for a partially coherent wave?
Imin = x% 0 + (1-x%) (2I1)
what is the maximum intensity (Imax) for a partially coherent wave?
Imax = x% (4I1) + (1-x%) (2I1)
what happens to the visibility/contrast of the interference fringes if the light is partially coherent?
reduced
equation for the contrast of partially coherent light
contrast = (Imax - Imin) / (Imax + Imin)
the degree of coherence is the same value as...
fringe visibility
degree of coherence is reported using _____, while fringe visibility is reported using ____
degree of coherence = percent
fringe visibility = decimal
when the maximum from one interference pattern lines up with the minimum from the other, what happens to the fringe visibility?
drops to 0
what is the relative intensity of 2 interference patterns? (lateral coherence effect)
Ir = Ip1 + Ip2
(if there are more than 2, continue to add them together)
to observe interference with better visibility, the angular size needs to be ___(larger/smaller)___
smaller
θs << λ/h
to observe interference with better visibility, the slit separation needs to be __(larger/smaller)___
smaller
h << θs/λ
when θs gets larger, what happens to the interference pattern?
more misaligned. (decreased visibility)
θs represents...
angular size of light source
equation for lateral coherence length
Lw = λ/θs
what does Lw (lateral coherence length) represent?
maximum slit separation (h) for visible fringes
def of light diffraction
light bending around an object
in order to observe diffraction, what conditions need to be met by the opening & the wavelength?
opening needs to be smaller than the wavelength
(smaller openings & longer wavelengths work best)
def of diffraction grating
an array of identical, equally-spaced slits
equation for path difference between neighboring slits
w = h sin θ
when adding a third slit, how does this change the number of maxima?
does not change
when added a third slit, how does this change the number of minima?
doubles