Microbiology Lab 1A
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What is microscopy?
The use of microscopes to view objects too small to be seen with the naked eye.
What type of microscope is used in this lab?
Compound bright-field (light) microscope
What does “bright-field” mean?
Specimen appears dark against a bright background
What is a compound microscope?
A microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify an image.
What is a simple microscope?
A microscope that uses a single lens.
What types of organisms are viewed at low magnification?
Large eukaryotic microorganisms
What type of organisms require the highest magnification?
Small prokaryotic microorganisms (bacteria)
What is electromagnetic radiation (EMR)?
Energy that travels in waves
What type of EMR does a light microscope use?
Visible white light
What is the wavelength range of visible light?
400 nm to 750 nm
What is wavelength (λ)?
The distance between wave crests or troughs.
As wavelength decreases, what happens to energy?
Energy increases
As wavelength increases, what happens to energy?
Energy decreases
What types of EMR are more energetic than visible light?
UV, X-rays, gamma rays
What types of EMR are less energetic than visible light?
Infrared, microwaves, radio waves
What colors make up the visible light spectrum?
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
What mnemonic helps remember the visible spectrum?
ROY G BIV
Which color has the longest wavelength?
Red
Which color has the shortest wavelength?
Violet
Which color is most energetic?
Violet
Which color is least energetic?
Red
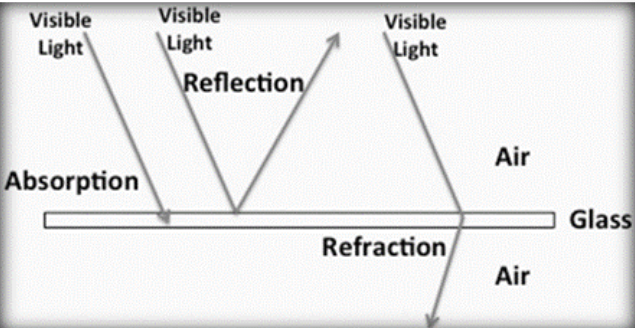
What is reflection?
Light bouncing off a surface
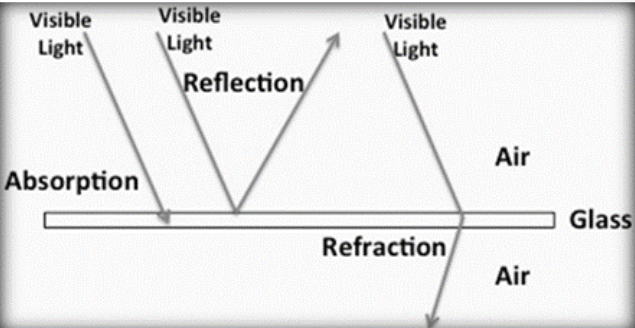
What is absorption?
Light being taken in by a material
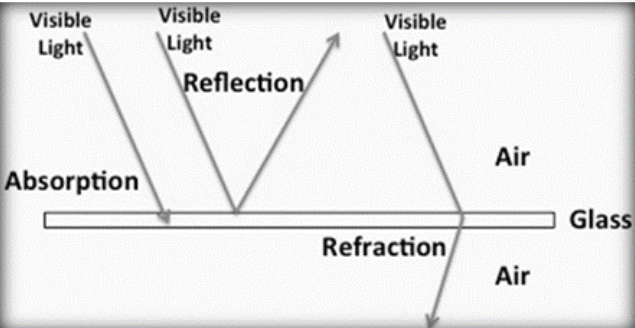
What is refraction?
Bending of light as it passes between different media
Which property of light is most important for microscopy?
Refraction
Why is refraction important in microscopy?
It affects image clarity and resolution
How many objective lenses does the microscope have?
Four
What type of lenses do objectives contain?
Bi-convex lenses
What does parfocal mean?
Image remains nearly in focus when changing objectives.
What does parcentric mean?
The object stays centered when changing objectives
Why are parfocal microscopes important?
They reduce refocusing time and prevent damage.
Which objective lens requires immersion oil?
100X oil objective
Why is immersion oil used?
To reduce refraction and increase resolution.
What is special about immersion oil?
It has the same refractive index as glass.
What happens if oil is not used with the 100X objective?
Image will be blurry and unclear
What should the 100X objective look like when properly focused?
It is directly in the oil
What is the magnification of the scanning lens?
4X
What is the purpose of the 4X objective?
Scanning large specimens and locating areas of interest
Why can’t bacteria be seen at 4X?
Magnification is too low
What type of light is used for 4X?
Used with lowest amount of light, controlled by condenser diaphragm
What is the magnification of the low-power lens?
10X
Why is 10X important for bacteria viewing?
It is used to focus before switching to 100X oil
What type of light is used for 10X?
Used with lowest amount of light
What is the magnification of the high dry lens?
40X
Why is it called “high dry”?
High magnification without oil
What type of light is used for 40X?
Used with moderate amount of light
What is the magnification of the oil immersion lens?
100X
What focus knob is used at 100X?
Fine focus only
What type of light is used for 100X?
Used with highest amount of light, controlled by condenser diaphragm
What is the magnification of the ocular lens?
10X
How do you calculate total magnification?
Objective magnification × ocular magnification
What is total magnification using a 40X objective?
400X
What is total magnification using a 100X objective?
1000X
What is resolution?
The ability to distinguish two close objects.
What happens to resolution as magnification increases?
Resolution increases
What is the field of view?
The circular area visible through the microscope
What happens to field of view as magnification increases?
It decreases
Why should multiple fields of view be observed?
To get a complete view of the specimen
What is working distance?
Distance between the objective lens and the slide
What happens to working distance as magnification increases?
It decreases
At which magnification is working distance smallest?
100X oil
What is depth of field?
Thickness of specimen that remains in focus
What happens to depth of field as magnification increases?
It decreases
Why can bacteria not be seen if the slide is upside down at 100X?
Depth of field is too shallow
How does light requirement change with magnification?
Higher magnification needs more light
What controls the amount of light passing through the specimen?
Condenser diaphragm
What is the ocular lens?
Lens you look through
Why must oculars be adjusted?
To match the distance between your eyes
What is the stage?
Platform that holds the slide
What moves the slide?
Slide control knobs
What are objective lenses mounted on?
Revolving nosepiece
What is the condenser lens?
Focuses light onto the specimen
What is the diaphragm?
Controls the amount of light
What does the coarse focus knob do?
Moves stage quickly
When is coarse focus used?
Only at low magnification (4X, 10X)
What does the fine focus knob do?
Makes small focus adjustments
When is fine focus used?
At higher magnifications
What paper is used to clean lenses?
Lens paper only
What paper is used to clean the stage/body?
Blotting / bibulous paper
What objective must be used before switching to 100X oil?
10X
Why should the stage not be moved during oil immersion?
To maintain focus
What objective should never be dragged through oil?
40X
What does “directly proportional” mean?
Both variables increase or decrease together
What does “inversely proportional” mean?
One variable increases while the other decreases
What does “X” mean in magnification?
Times magnified
Magnification vs resolution
Directly proportional
Magnification vs objective length
Directly proportional
Magnification vs light required
Directly proportional
Magnification vs field of view
Inversely proportional
Magnification vs working distance
Inversely proportional
Magnification vs depth of field
Inversely proportional