Homeostasis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is homeostasis?
Our body’s tendency to maintain internal conditions despite external conditions
What is negative feedback?
process which stabilizes itself by reducing its output when the output’s effects are too great
Examples :
Body temperature
Breathing
Water balance
Blood sugar
Thermoregulation
What are the 2 hormones that assist in regulating blood sugar + info on them, how they do it?
Insulin
Made by beta cells
Lowers blood glucose levels
Helps cells take in glucose
Glucagon
Made by alpha cells
Raises blood glucose levels
Stimulates liver to release stored glucose
Body’s response to heat and cold
Heat:
Physiological : -sweating, dilation of blood vessels, thirsty
Behavioural: -drink water, find shade
Cold:
Physiological: -shivering, constriction of blood vessels
Behavioural: -putting on gloves, seeking places with warmth, moving around to create heat
What is the purpose of the nervous system?
Detects stimuli (changes inside and outside the body)
Processes and interprets information
Sends rapid signals to muscles and glands
Coordinates responses to maintain homeostasis
Structure of Neuron
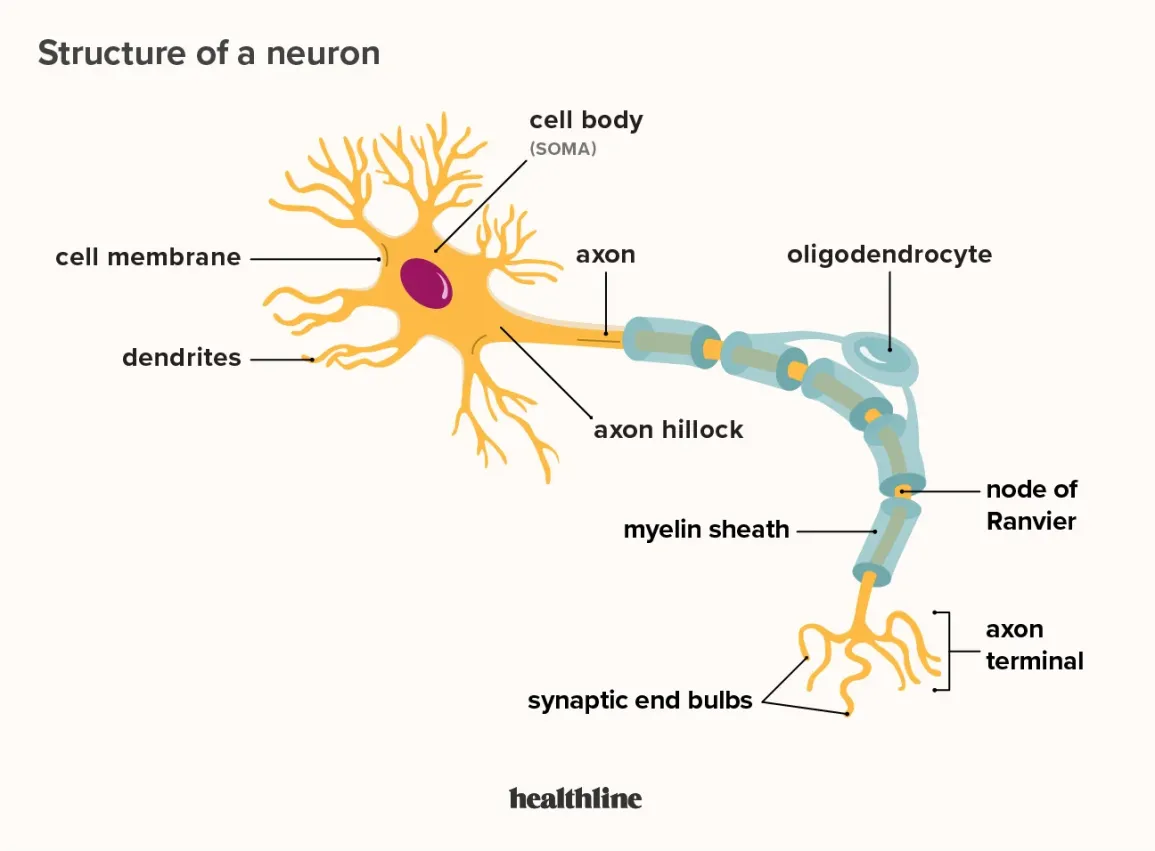
Compare electrically controlled and chemically controlled ion channels/gates in neurons
Electrically controlled channels/gates:
Neurons have a resting membrane potential (~–70 mV) caused by unequal ion distribution (more K⁺ inside, more Na⁺ outside)
Action potential starts when a stimulus makes the membrane voltage more positive (depolarization)
If the voltage reaches the threshold (~–55 mV), voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open → Na⁺ rushes in → rapid depolarization
Voltage-gated K⁺ channels open afterward → K⁺ flows out → repolarization (restoring negative inside)
Chemically controlled channels/gates:
Found mainly on dendrites and cell body at synapses
Open when a neurotransmitter binds to it
ions (like Na⁺) flow in
If enough ligand-gated channels open and the voltage reaches the threshold (~–55 mV) → triggers an action potential
After the action potential starts, voltage-gated channels take over to accelerate it down the axon
Compare sensory, inter, and motor neurons
Sensory neuron: brings info from body → brain/spinal cord
Interneuron: processes info inside the CNS
Motor neuron: sends info from brain/spinal cord → muscles/glands
How is action potential formed?
Neuron at rest has a resting membrane potential (~–70 mV)
Stimulus causes graded potential → small local change in voltage
If voltage reaches threshold (~–55 mV) → voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open
Na⁺ rushes in → depolarization (inside becomes more positive)
Voltage-gated K⁺ channels open once hits +30mV → K⁺ flows out → repolarization
How does action potential move along the axon?
Depolarization at one part of the axon triggers voltage-gated channels in the next section
Action potential travels down the axon in a wave
Myelin sheath speeds this up via saltatory conduction (jumps between Nodes of Ranvier)
How does action potential cross a chemical synapse?
Action potential reaches axon terminal → voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels open
Ca²⁺ enters → triggers vesicles to release neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters bind to ligand-gated channels on postsynaptic neuron
Postsynaptic membrane depolarizes → may trigger new action potential across next neuron
Autonomic Nervous System + Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
Sympathetic:
Prepares the body for “fight or flight” situations
Increases heart rate, breathing, and blood flow to muscles
Dilates pupils and airways
Purpose: Get the body ready for stress, danger, or activity
Parasympathetic:
Promotes “rest and digest” activities
Slows heart rate and breathing
Stimulates digestion and energy storage
Purpose: Conserve energy and maintain normal body functions
Head lobes + Describe
Frontal: voluntary movement, decision-making, personality
Parietal: processes touch and spatial awareness
Occipital: vision
Temporal: hearing, memory, language comprehension
Brain Structure Functions
Medulla oblongata: controls involuntary functions like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion
Thalamus: relays sensory information to the appropriate part of the brain
Cerebellum: coordinates balance, posture, and voluntary movement
Corpus callosum: connects the two hemispheres of the brain and allows them to communicate
What is the purpose of the excretory system?
removing metabolic waste products and other toxic substances from the body
To maintain homeostasis, we must excrete to regulate our ionic balance and pH balance
Regulates fluids and waste
Structures of the kidney
Renal cortex: outer layer of the kidney; contains nephrons and filters blood
Nephron: functional unit of the kidney; filters blood and forms urine
Glomerulus: network of capillaries in the nephron; filters water, ions, and small molecules from blood
Bowman’s capsule: cup-shaped structure surrounding glomerulus; collects the filtrate from blood
Loop of Henle: part of nephron tubule; concentrates urine by reabsorbing water and salts
Three stages of urine formation
Filtration
Occurs in the glomerulus
Blood pressure forces water, ions, and small molecules out of blood into Bowman’s capsule
Cells and large proteins stay in the blood
Forms filtrate (pre-urine)
Reabsorption
Occurs in the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule
Useful substances (glucose, amino acids, water, ions) are reabsorbed back into the blood
Ensures the body keeps what it needs
Secretion
Occurs in the distal tubule and collecting duct
Additional wastes, H⁺, and drugs are secreted from blood into tubule
Helps maintain pH and remove extra waste
Pituitary Gland
Considered ‘master gland’
Located within the cranium
Two lobed gland within cranial cravity
Produces hormones that control other endocrine gland
Split into Anterior and Posterior lobe
Portal vein connects pituitary gland to capillaries within hypothalamus
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Makes up approx. 80% of pituitary gland
Responsible for secreting several major hormones into the bloodstream (including those that then drive hormone secretion in other glands)
For the 6 major hormones secreted by this gland, the hypothalamus signal the gland to secrete them
Posterior Pituitary Gland
Responsible for storing and releasing two important hormones
Located on the back of the Pituitary gland
Contains ADH and Oxytocin, told by Hypothalamus when to store and release them through nerve signals
Pancreas Location and Function + Component
Location: Located between small intestine and the spleen
Function: Regulating blood sugar through production of hormones such as insulin and glucagon
Islets of Langerhans
Clusters of cells in the Pancreas which contain
Alpha cells
Produce glucagon
Beta cells
Produce insulin
How do Adrenal Glands help raise blood sugar levels?
Adrenal cortex (outer part of adrenal glands) secrete hormone called glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids help raise blood sugar by:
Stimulating the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Reducing how much glucose body cells take in, so more stays in the blood.
Promoting the breakdown of fats and proteins, releasing fatty acids and amino acids into the blood to be used as fuel when glucose is low.
Thyroid Structure + Function
butterfly-shaped endocrine gland in the neck that regulates metabolism, growth, and development by producing and releasing thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin
Parathyroid Structure + Function
The parathyroid glands are four small, oval-shaped endocrine glands located on the back of the thyroid gland that regulate blood calcium levels by producing parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Adrenal Glands Structure + Function
two small, triangular glands located on top of the kidneys that are crucial endocrine glands for regulating metabolism, stress response, blood pressure, and more
Testes Structure + Function
The testes are the male gonads, oval-shaped organs in the scrotum that function as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. As an endocrine gland, they produce and secrete hormones like testosterone
Ovaries Structure + Function
The ovaries are female endocrine glands with a structure of outer and inner layers, including the cortex (housing eggs and follicles) and medulla (containing blood vessels). Their function as endocrine glands is to produce hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and fertility, as well as other hormones like inhibin and testosterone