Epistemology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is Epistemology? What does it study?
epistemology is study of theory and knowledge
Episteme ‘knowledge’
Logos ‘rational study’ or ‘theoretical inquiry’
A Posteriori knowledge
Knowledge is based on experience
sense perception is the only valid source of knowledge
the human mind has nothing except what experiences are put there
A Priori knowledge
you are born with some knowledge
we get info from senses but doesnt give deep knowledge or distinct ideas
you dont have to observe the world to gain knowledge
Empericism
all knowledge is from experience- content or derived
All true knowledge is:
A POSTERIORI— it depends on experience
Who were empiricists?
Aristotle
Thomas Aquinas
Francis Bacon
Thomas Hobbes
John: Locke, Stuart Mill
Karl Popper
George Berkeley
David Hume
Charvaka (“Sweet Speaking" ) Indian Philosophers
Rationalism
theory that reason rather than experience is the foundation of certainty in knowledge (w/o help from senses)
thinking/ration is the source of knowledge
we can reason stuff abt the world
Who were rationalists?
Plato
St. Augustine
B. Spinoza
Anne Conway
Gottfried Leibniz
Georg Hegel
Rene Descartes
Shankara- Indian philosopher
Most were mathematicians first
What are Innate ideas?
ideas present from birth, we are born w them
descartes use this to answer "how do clear and distinct ideas come to the mind if not senses?"
we are born w these ideas fully formed but are hidden in mind
as you grow the ideas emerge into a persons awareness
ie. logic and math
Kuhn - Opposition to Popper**
thought we should “think of scientific knowledge as the product of communities of scientists who accept and work with that knowledge”.
Popper: scientists are always trying to disprove theories but it doesn’t happen often (they cling to smt for decades without results that match)
Kuhn says: he ignores that scientists work in communities + in uni are trained to accept certain theories & research method
Kuhn - Indoctrination**
Scientists get “long indoctrination” into accepted theories / research methods.
form a “paradigm” of what science is for that community.
You are taught the paradigm of the community you want to join.
Scientists working in the field accepted the theory and use it to guide their research.
so science doesn’t grow gradually as per inductionsit / falsificationists.
Science leaps forward through major revolutions.
Scientists tend to hold on to some theories even if some observations show up that do not fit into the theory - called anomalies.
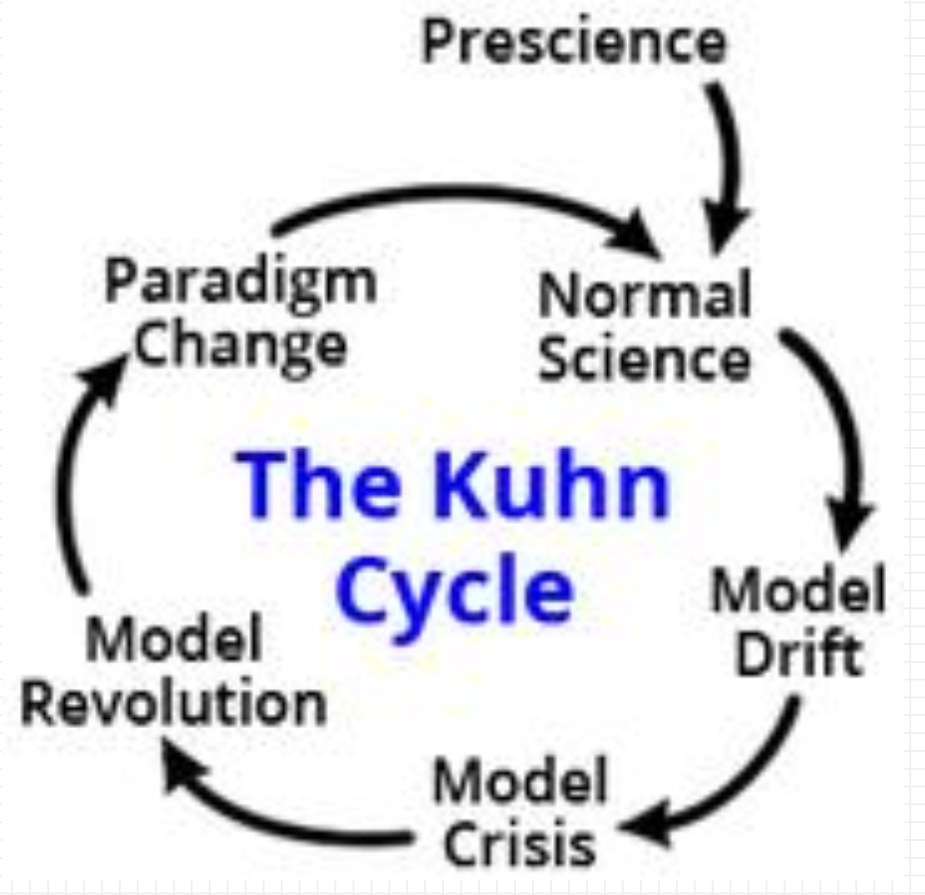
Kuhn Cycle
happens when there are too many anomalies, crisis happens
new theory developed bc scientists rethink what they know
revolution occurs
newer scientists believe it firmly, becomes paradigm
Descartes
Stated we could not use our senses—they could be deceiving.
indubitability- wanted to prove philosophical truths in the same way of proving a math theory
Genuine knowledge comes from clear and distinct ideas in our minds.
Cogito Ergo Sum
I think therefore I am
descartes goofy ahh said this
John Locke
Primary Qualities – exist even if no one was observing
size, position, shape – can be measured.
Secondary– wont exist if no perceiver present
colour, sound, texture, movement.
Every entity has primary and secondary qualities
George Berkeley
All qualities are mind dependent, rejected Locke
Primary qualities could be subjective, physical things are just collections of ideas, not solid matter
e.g. A coin looks round from one angle, flat from other.
Reality is made of minds (like yours, mine, and God’s) and the ideas they perceive.
If nobody (not even God) perceived something, it wouldn’t exist.
subjectivist
Esse est percipi
To be is to be perceived
Berkeley
Humes skepticism
Hume pushed Locke and Berkeley's empiricism → skepticism
skepticism is denial of the possibility that we know for certain abt anything
Hume is credited w/skepticism
Kant Transcendental Idealism*
our knowledge of reality is from reason, but content is from senses
Think of knowledge as a rope, you need strands woven together to create a strong rope.
believed reason can also contribute to our knowledge.
accepted that experience is the only basis of knowledge of reality
Kant- Phenomenal world
agrees with hume, knowledge comes from senses but the mind arranges it to make sense
mind organizes into phenomenal and noumenal world
Phenomenal: the world made by our mind is the only world we will know
sensations are organized by mind
objects are in causal relationship
Kant- Noumenal World
might be the acc world that our mind doesnt know
we will never know what this world is acc like
it might not have objects since we dk how its like
we may never know if things happen by change (no cause and effect)
Inductionism- Bacon
relationship between scientific theories and our observations of the world
primary tool of scientific method: Using many individual experiences or observations to come up with broad, likely patterns or laws
go from specific examples → general assumptions
“by far the best proof is experience”
Bacon-Empericism
Father of empiricism
Don’t just accept views of others (e.g. Greek philosophers)
Investigate nature by:
Careful sense observation & experimentation, collect as many facts as possible, analyze, derive laws.
John Stuart Mill- 3 features of scientific method
1. Collect as many facts as possible abt topic
2. Make general rules from specific facts.
3. Continue to accumulate more particular facts to see if generalizations hold true. More instances = more confirmation.
Karl Popper - falsification
true science can survive being claimed false
if it survives being called false=true science
the more attempts to disprove=the more reliable theory is
pseudoscience: when scientists make theories and always try to prove it right bc it gives credibility to all kinds of “science”
all scientific theories are probable, open to revision
Descartes wax meditation **
put a cold plate of wax near fire (it is cold, hard, see-thru, etc) and come back in 10 mins now it is (yellow, liquid, sticky, etc)
Sensory perception cannot be the source of true knowledge about the wax
argues we understand the wax’s essence through reasoning
senses deceive us
Leibniz’s theory of innate ideas
agreed we dont acquire our knowledge of the most basic truths by observing the world
those truths have to be somewhat innate (born with)
claimed innate ideas are "tendencies" or "dispositions"
experiences shape T&D -> fully formed idea
Locke’s blank slate
“Tabula Rasa” → “Blank Slate”
experience affects our mind
the fact that kids dont have certain ideas is proof innate ideas dont exist
physical objects exist outside of us, they are independent of our perception
our knowledge of stuff is acc our knowledge of our ideas of things
Kant - Categories
mind organizes according to 12 relationships
causality (1), Plurality, Space, Time, Unity,etc…
we cant see causality bc its between objects
causality exists in the mind, connects earlier sensations to later ones
the world we see : mind constructed
mind organizes the senses and objects we see