Biology UPDATED
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:28 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
Chemicals
help build cells- macromolecules are chemicals that are essential to life
2
New cards
Cells
The Basic Unit of Life
3
New cards
Tissues
Made up of cells that have a similar structure and function
4
New cards
Organs
Made up of tissues that work together to carry out a specific function
5
New cards
Organ Systems
Group of organs that work together to carry out a specific function
6
New cards
Organisms
Made up of one or more organs
7
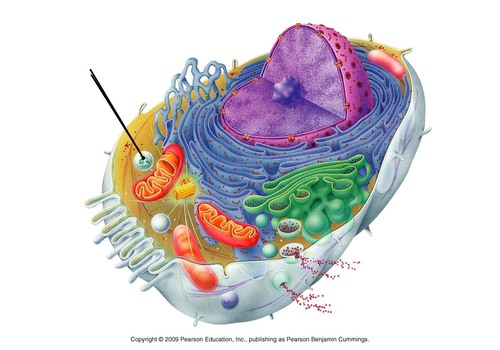
New cards
Cell Membrane
Identify the name that the arrow is pointing at
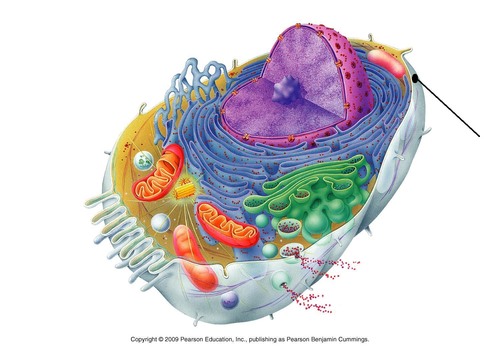
8
New cards
Defines the cell by acting as a barrier. It keeps cytoplasm in and substances located outside of the cell out.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
9
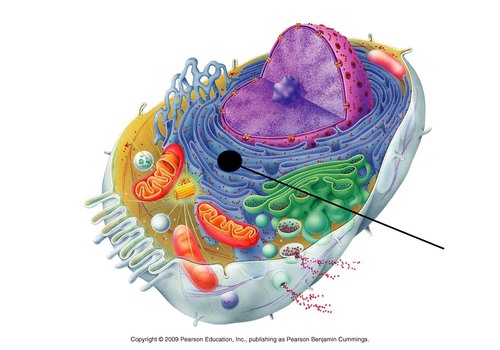
New cards
Cytoplasm
Identify the name that the arrow is pointing at
10
New cards
A general term that refers to cytosol and the substructures. Found within the plasma membrane, but not within the nucleus
What is the function of Cytoplasm?
11
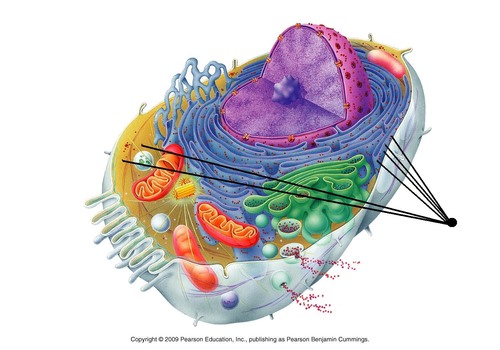
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Identify the name that the arrow is pointing at
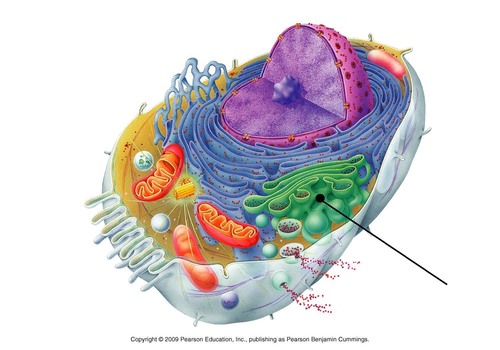
12
New cards
responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations
What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus?
13
New cards
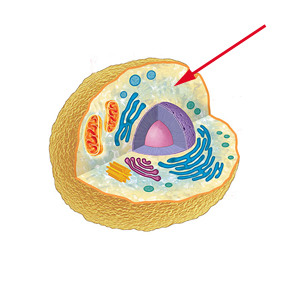
Nucleus
Identify the name that the arrow is pointing at
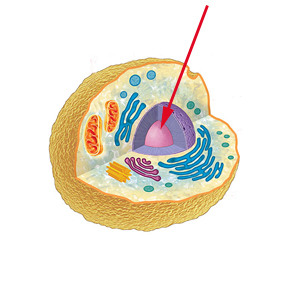
14
New cards
controls and regulates the activities of the cell
What is the function of Nucleus
15
New cards
Mitochondria
Identify the cell
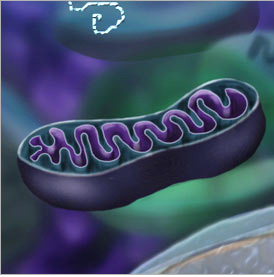
16
New cards
Described as the "powerhouses" of the cell because they produce most of a cell's ATP
What is the function of Mitochondria
17
New cards
Lysosomes
Identify the name that the arrow is pointing at
18
New cards
Organelles that function in the breakdown of various substances
What is the function of Lysosomes
19
New cards
Ribosomes
Identify the name that is the arrow is pointing at
20
New cards
involved in synthesizing proteins from amino acids. They read the RNA produced in nucleus and translate the genetic instructions to produce proteins. cells with high rate of protein synthesis have large number of ribosomes.
What is the function of Ribosomes
21
New cards
Rough ER
Identify the name that is the arrow is pointing at
22
New cards
involved with the production, folding, quality control and despatch of some proteins. And contains ribsomes on the surface
What is the function of Rough ER
23
New cards
Smooth ER
Identify the name the arrow is pointing at
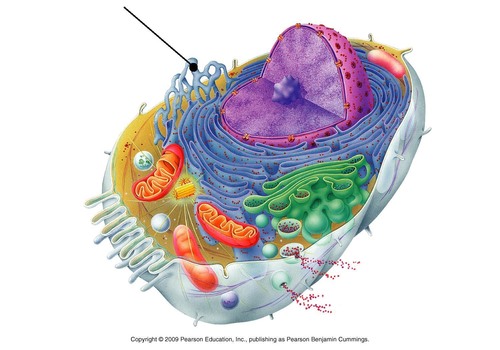
24
New cards
It synthesizes lipids, phospholipids as in plasma membranes, and steroids. Transports mostly lipids and doesn't contain ribsomes
What is the function of Smooth ER?
25
New cards
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
What are the five main stages of mitosis?
26
New cards
Interphase
The first stage of the cell cycle. It is when the cell grows and carries out its normal functions
27
New cards
Prophase
The second stage of the cell cycle. The chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear envelope also breaks down
28
New cards
Metaphase
The third stage of the cell cycle. The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
29
New cards
Anaphase
The fourth stage of the cell cycle. The chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell. Cell Division Begins
30
New cards
Telophase
The fifth and final stage of the cell cycle. A new nuclear envelope forms around chromosomes. The chromosomes uncoil and become less visible. The cell then divides into two daughter cells
31
New cards
Prophase II
The sixth stage of meiosis. In this stage, the daughter cells contain half of the chromosomes from the original cells
32
New cards
Metaphase II
The Seventh Stage of meiosis, in this stage, the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell again
33
New cards
Anaphase II
The eighth stage of meiosis. In this stage, the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell
34
New cards
Telophase II
The ninth and final stage of meiosis, in this stage, the cells divide into four genetically diverse daughter cells also known as haploids
35
New cards
Chromosomes
long, thread like structures that are round in the nucleus of the cell
36
New cards
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
How many chromosomes are in the human body?
37
New cards
Genes
The basic units of heredity and made up of DNA
- Responsible for Character
- Responsible for Character
38
New cards
structural genes
Responsible for the physical traits of an organism (ex color of your eyes)
39
New cards
Regulatory Genes
Controls the activity of other genes
40
New cards
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
What are the nitrogenous bases of DNA?
41
New cards
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
What are the nitrogeneous bases for RNA
42
New cards
two nucleotides that are bonded together with hydrogen bonds
A=T and C=G
A=T and C=G
What is a base pair
43
New cards
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid
44
New cards
64 (3 being stop codons)
How many possible Condons are there?
45
New cards
RNA Polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of RNA from nucleotides
46
New cards
Carries the genetric code from the DNA to the ribsomes in the cytoplasm
What is the function of mRNA
47
New cards
Helps assemble amino acids into proteins
What is the function of tRNA
48
New cards
Ribosomal RNA
The RNA that makes up ribosomes
49
New cards
Transcription
The process of making RNA to DNA
50
New cards
translation
The process of making proteins from RNA
51
New cards
What is an inheritance?
The process by which traits are passed from parents to their offspring
52
New cards
Mendel's law of inheritance states
There are two alleles for each trait. Alleles are alternative forms of a gene
53
New cards
genotype
The combination of two alles is called a
54
New cards
heterozygous
If the chomosomes contain two different alleles for a trait it is called
55
New cards
homogeneous
If the chomosomes contain two identical alleles for a trait it is called
56
New cards
The physical, visual manifestation of genes
What is a phenotype?
57
New cards
Dihybrid Cross
Refers to one involving more than one trait
58
New cards
Macromolecules
Large molecules that are essential for the structure and function of cells
59
New cards
Polymer
A macromolecule that is made up of smaller units called covalent bond-linked monomers
60
New cards
Dehydration
The formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants accompanied by the loss of a water molecule
61
New cards
Hydrolysis
The process of breaking down bonds to monomers
62
New cards
fatty acids and glycerol
What are lipids made out of?
63
New cards
Amino Acids
Proteins are made out of
64
New cards
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
What are monomers
65
New cards
Glucose and Fructose
What are common monosaccharides?
66
New cards
2 monosacharides bonded
What are disaccharides
67
New cards
many or multiple monosaccharides bonded together
What are polysaccharides
68
New cards
Animal fats and Oils
Triglycerides can be divided into
69
New cards
liquid
At room temperature oils are
70
New cards
saturated fats
Bonded by a single bond
71
New cards
unsaturated fats
Bonded by a double bond
72
New cards
Catalyst of chemical reactions
What is the function of Enzymes?
73
New cards
Steriods
cholesteral, aldosterone, and cortisol are known as
74
New cards
Long unbranched chains of monosaccharides
What are linear carbohydrates
75
New cards
Shorter chains of monosaccharides with branches
What are branched carbohydrates
76
New cards
Coiled chains of monosaccharides
What are Helix-Shaped Carbohydrates
77
New cards
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Lipids are composed of?
78
New cards
Store and transmit genetic information
What is the function of Nucleic Acids
79
New cards
Micro-organisms
tiny living organisms. They are to small to be seen with the naked eye and can only be seen with a microscope
80
New cards
Bacteria
Single-celled microorganisms that can live in many different environments and lacks a nucleus
81
New cards
Viruses
Even smaller than bacteria and can only be seen with an electron microscope
82
New cards
Protozoans
Single-celled microorganism that are found in water, soil, and air.
83
New cards
have no nucleus, and lack organelles.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell
84
New cards
any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus
What is a Eukaroytic Cell?
85
New cards
Fungi
Micro-organisms that are classifed as Eukaryotes causes dieases such as ring worm, and athlete's foot
86
New cards
Infectious Diseases
Can be spread from one person to another such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi
87
New cards
Noninfectious diseases
Are not caused by microorganisms and can not be spread from person to person (ex: cancer, heart disease, and diabetes)
88
New cards
Direct Contact
When the infectious agent comes into contact with the mucous membrane or broken skin of another person (can happen through shaking hands, kissing, or sexual contact
89
New cards
Indirect Contact
When an infectious agent comes into contact with an object or surface that another person will touch (ex: touching a doorknob that someone with the flu touched
90
New cards
Vectors
Living organisms that can carry and transmit infectious agent to humans and other animals most common being ticks, mosquitos and fleas
91
New cards
Microscope
An instrument used to enlarge objects so they can be seen more clearly
92
New cards
Light Microscopes
Microscopes that are dependent on a light source
93
New cards
Electron Microscope
Dependent on an electron beam. Used for seeing objects at a much higher magnification put to 150,000 size of specimen
94
New cards
transmission (TEM) and Scanning (SEM)
What are the two types of electron microscopes
95
New cards
Collagtive Properties
properties of solutions that depend on the ratio of the number of solute particles to the number of solvent particles in a solution, and not on the nature of the particles present
96
New cards
Boiling Point Elevation, Freezing Point, Depression, Osmatic Pressure, and Rovali's Law
What are some properties Colligative Properties
97
New cards
Gametogenesis
The process by which diploid germ cells give rise to haploid gametes
98
New cards
Squamous
Flattened- scale like cells are called
99
New cards
Cuboidal
Cube-shaped cells are called
100
New cards
Columnar
Long, thin cells are called