🧠 Nucleus
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Nucleus Functions
Genetic Material Management
Storage, replication, and repair of DNA
Gene Expression
Transcription: production of mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
RNA splicing: processing of RNA
Ribosome Production
Synthesis of ribosomal subunits
Storage, Replication, and Repair of Genetic Material
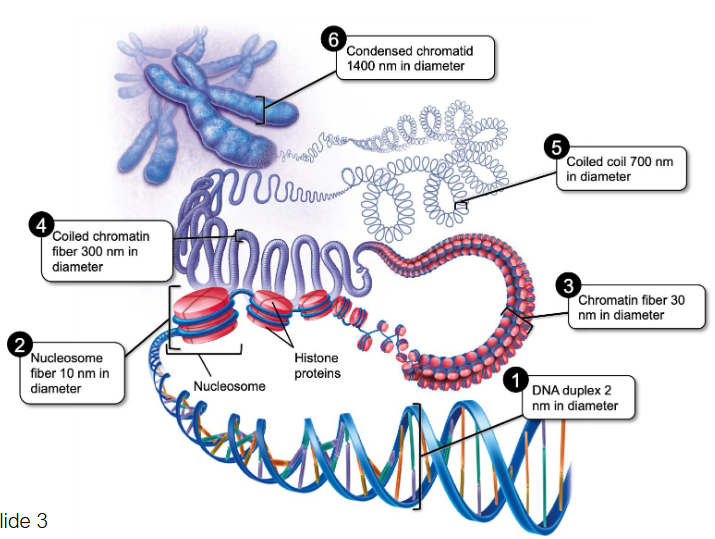
DNA Structure and Organization
DNA duplex
2 nm in diameter
DNA is complexed with histones to form nucleosomes
Nucleosome is 8 core histone proteins + DNA wrapped around 1.65 times = Euchromatin
Histone H1 is the 9th protein that stabilizes the wrap
Histone + DNA wrap height = 10 nm
Histones fold in on each other (like an elastic band) - Make chromatin fibers
30 nm diameter
Chromatin coils
300 nm in diameter
Coils coil
700 nm in diameter
Fibers are tightly coiled to produce condensed chromatids
Total width of 2 sister chromatids: 1400 nm
Stretched end-to-end, DNA molecules in a single human cell would measure about 2 meters (roughly 6 feet)
DNA Damage Sources
UV light exposure
Replication errors
Chemical exposure
Cellular metabolism
Ionizing radiation
DNA Repair Mechanisms
DNA repair machinery corrects damage
Expression of Genetic Material
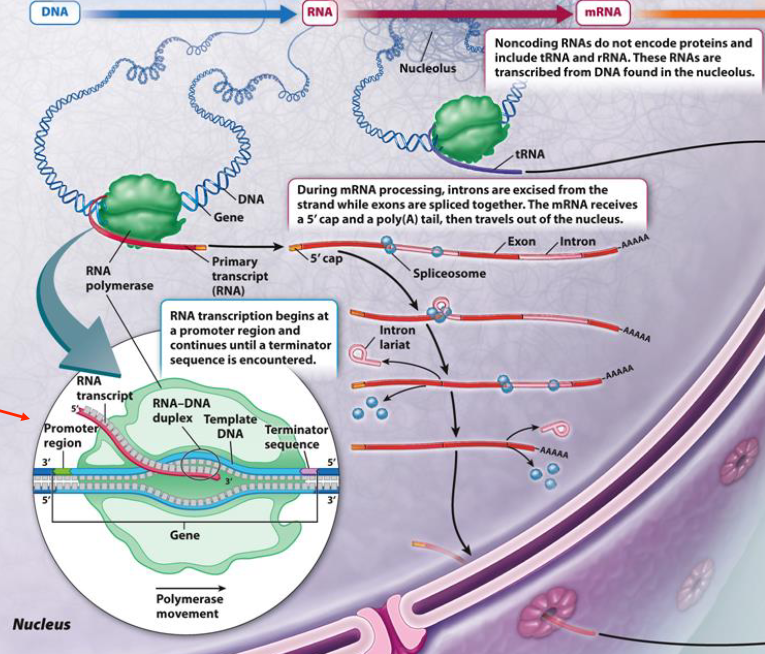
Transcription
Transcription produces mRNAs, tRNAs, rRNAs, and other types of RNA (e.g., miRNA, eRNAs, piRNAs)
Promoter region: Controls transcription initiation
RNA received 5’ cap and poly-A tail
RNA Splicing
RNA splicing occurs before nuclear export of mRNAs, removes introns and joins exons
Note
This is an oversimplification of the complex process of gene expression
Ribosome Biosynthesis
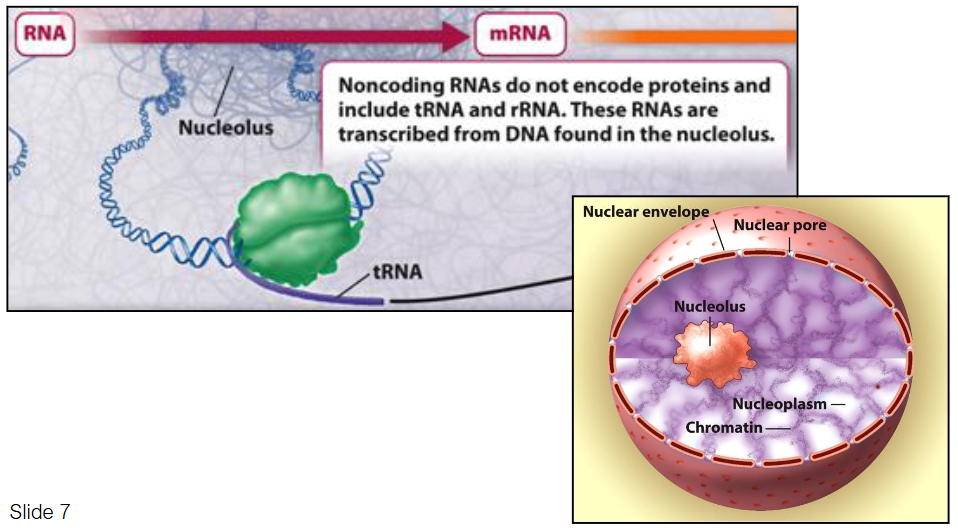
Noncoding RNAs (e.g., tRNA and rRNA) do not encode proteins
These RNAs are transcribed from DNA located in the nucleolus
Extra info:
rRNA is transcribed in the nucleolus from ribosomal DNA (rDNA)
rRNA combines with ribosomal proteins (imported from cytoplasm) to form ribosomal subunits
These subunits are then assembled into large and small ribosomal subunits in nucleolus
rRNA and ribosomal proteins form functional ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis
Ribosomal subunits are exported to cytoplasm
In cytoplasm, subunits assemble to form functional ribosomes, which begin process of translation (protein synthesis)
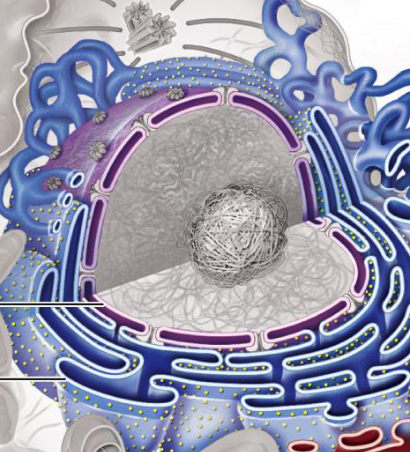
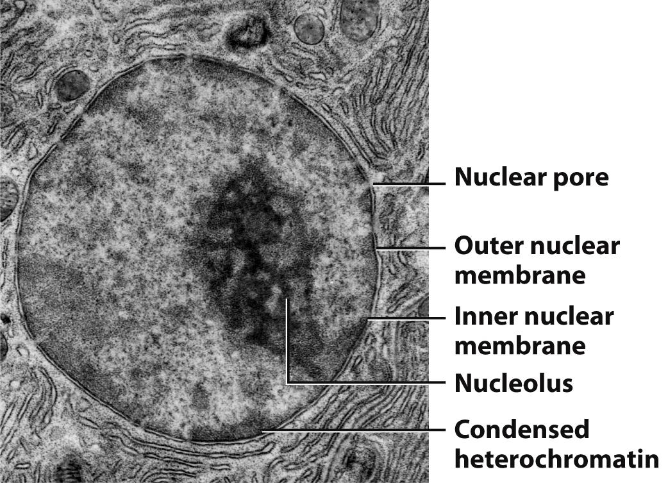
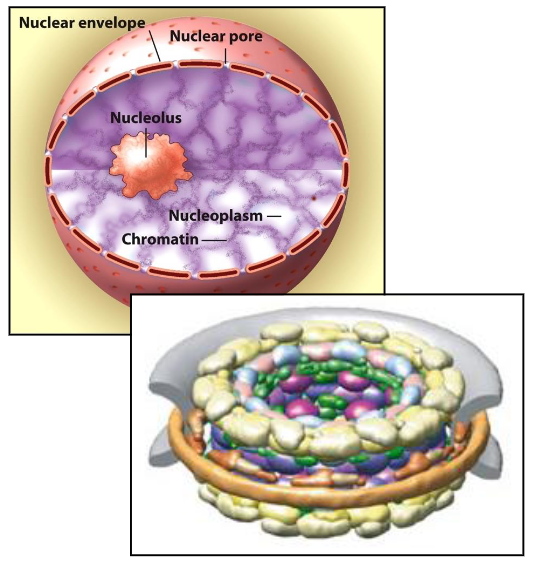
Nuclear Structure
Nuclear envelope: Double-layer membrane surrounding the nucleus
Nuclear membrane: Composed of an inner and outer lipid bilayer
Nuclear pores: Channels that allow material to pass between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Nuclear lamina: Meshwork of intermediate filaments providing structural support to the nucleus
Nuclear content:
Chromatin: DNA wrapped around histone proteins, organized into chromosomes
Nucleoplasm: Fluid inside the nucleus, containing enzymes, nucleotides, and other molecules
Nucleolus: Substructure in the nucleus responsible for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis and ribosome assembly
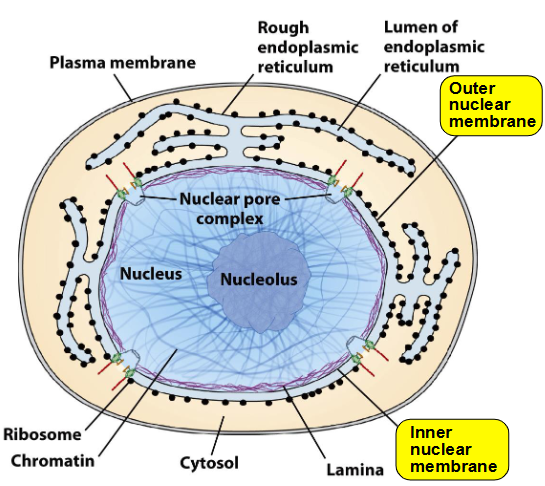
Nuclear Envelope Structure
2 parallel phospholipid bilayers separated by 10-50 nm space
Outer nuclear membrane (ONM):
Binds ribosomes
Continuous with rough ER
Inner nuclear membrane (INM):
Contains integral proteins
Connects to nuclear lamina
Importance of Nuclear Envelope
Separates nuclear content from cytoplasm
Separates transcription and translation processes
Selective barrier that allows limited movement of molecules between nucleus and cytoplasm
Nuclear Lamina
Supports nuclear envelope
Thin meshwork of filamentous proteins:
Lamins (intermediate filaments) found in animal cells only
Plants have nuclear lamina, but not made of lamin protein (equivalent proteins in plants is unknown)
Bound to inner membrane of nuclear envelope (NE) by integral membrane proteins
Provides structural support for nuclear envelope
Attachment sites for chromatin (e.g., heterochromatin)
Nuclear lamina forms meshwork next to nucleoplasmic leaflet of inner nuclear membrane
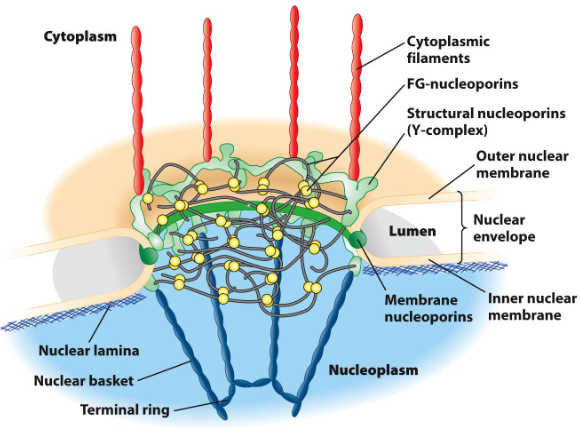
Nuclear Pores
1 μm in diameter
Perforate nuclear envelope
Small molecules and ions passively diffuse
Large proteins and RNA require active transport
Gateways between cytoplasm and nucleus
3000-4000 pores/nucleus
Pores are located where inner and outer membranes fuse
Complex structure involving arrangement of different types of proteins
Nuclear Pore Complex
Composed of nucleoporins (NUPs) – a large family of proteins
Octagonal symmetry / basket-like structure
Projects into cytoplasm and nucleoplasm
The nuclear pore complex is a supramolecular complex
Supramolecular = Very large and complex molecule
15-30 times the size of a ribosome
Passive diffusion of molecules that are 40 kDA or less
Fast
100 molecules/minute/pore
Regulated movement of larger molecules
Slow
6 molecules/minute/pore
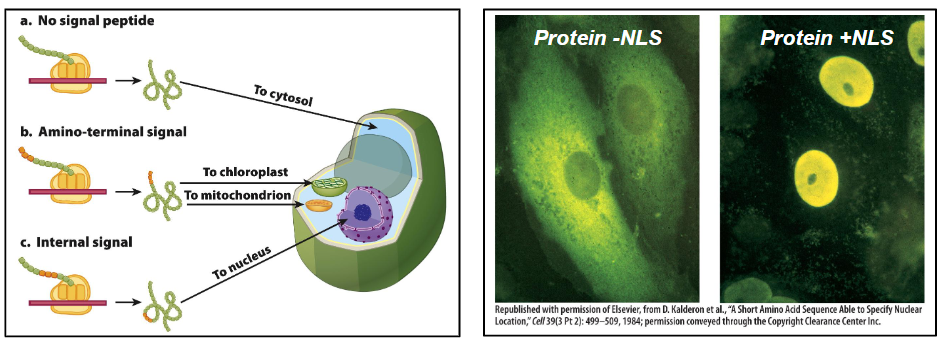
Nuclear Import
Requires a Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS)
NLS consists of several positively charged amino acids within the protein sequence
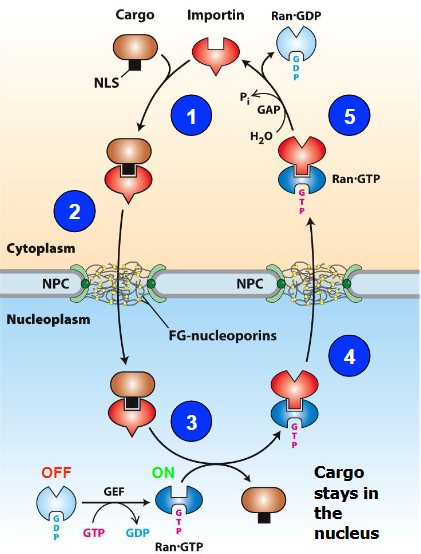
Nuclear Import Mechanism
Protein with NLS (cargo) interacts with Importin protein in cytoplasm
Cargo/Importin complex interacts with FG-NUPs at the NPC and enters the nucleoplasm
Ran-GTP interacts with Importin; cargo dissociates and stays in nucleoplasm
Ran-GTP/Importin complex exits nucleus through NPC
GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP
Importin released into cytoplasm finds new cargo
Ran-GTP
OFF with GDP
ON with GTP
Step 3 - Conformational change after being turned on allows for Ran-GTP to let go of cargo
Cargo stays in nucleus
Nucleocytoplasmic Trafficking
Nuclear import/export are critical for cellular function
Nucleotides for transcription
Structural proteins (e.g. lamins)
DNA packaging proteins (e.g. histones)
Proteins for DNA replication, repair, and transcription
Proteins for RNA processing (splicing) and export
Proteins for ribosome synthesis and export
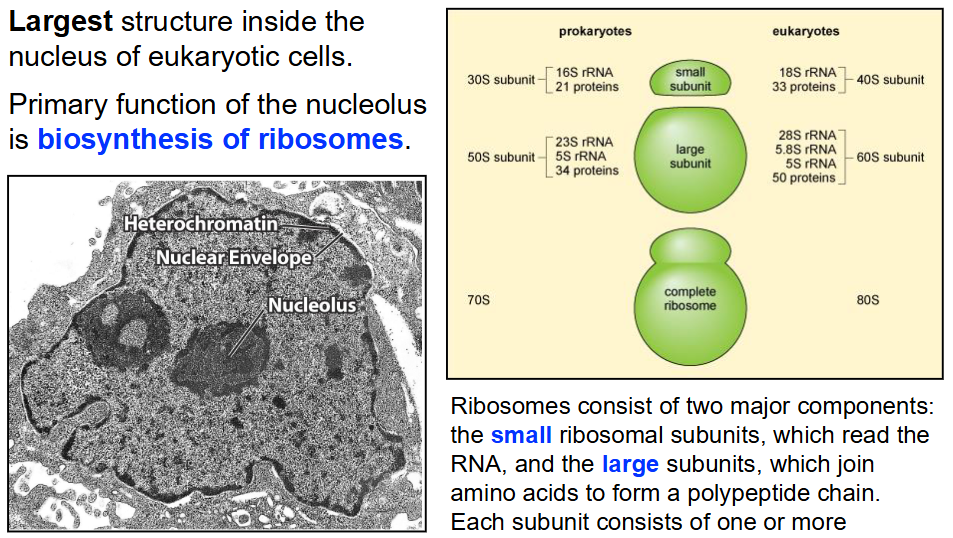
Nucleolus
Largest structure inside nucleus of eukaryotic cells
Primary function: Biosynthesis of ribosomes
Ribosomes consist of:
Small ribosomal subunits (reads RNA)
Large subunits (joins amino acids to form polypeptides)
Each subunit consists of:
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules
Ribosomal proteins
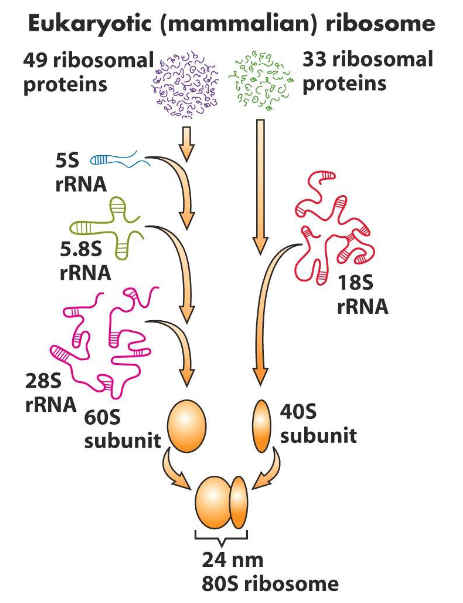
Prokaryotes have 70S ribosome (30S in small, 50S in large)
Eukaryotes have 80S ribosome (40S in small, 60S in large)
Ribosome Biosynthesis
Synthesis of ribosomal rRNAs:
5.85 rRNA
18S rRNA
28S rRNA
5S rRNA
rRNA processing
Assembly of subunits:
rRNA + ribosomal proteins
40S and 60S subunits exported to cytoplasm
Assemble into 80S ribosomes