Cardiology - Exam 1: Don't Be Still, My Heart
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
251 Terms
Don't forget the take-home cases!
Also extra credit, the live animal exam, and stress points
T/F: Cats with heart failure cough
False
What are respiratory signs of acute, severe left heart failure in dogs?
Coughing and pulmonary edema
How does heart disease cause coughing with the absence of pulmonary edema?
An enlarged heart can press on the trachea
Dyspnea first manifests as increased _______, and can later worsen with pulmonary edema, leading to increased _______
Rate; Effort
Pleural effusion leads to an issue of the lungs expansion, leading to what signs?
Increased respiratory rate with short, shallow breaths
Inadequate oxygen to the brain leading to collapse is ______, which needs to be differentiated from a seizure
Syncope
Fluid accumulation in the abdomen is called ______
Ascites
Ascites is associated with ______ heart failure
Right (Heartworm disease)
Ascites can cause what lung sign?
Dyspnea
A clot at the trifurcation of the aorta in the sacral area is called _______, and causes paresis in cats
Saddle thrombus
Saddle thrombus is associated with heart disease in cats, and includes what signs of the distal limbs?
Cold and cyanotic feet
T/F: A dyspneic patient is concerning but considered stable
False, not stable
If the owner can feel that the heart rhythm is off, you should think ________
Atrial fibrillation
What must immediately be done with a dyspneic patient?
Oxygen supplementation, often with a truncated physical so that you can stabilize before you diagnose
A key sign in right heart disease is distended _______ veins
jugular
Increased inspiratory breaths tends to be a problem with the _______
Upper airway
T/F: peripheral edema (in the limbs) is associated with heart disease
False
What is an easy method to help distinguish whether the problem lies in the airway and not the heart?
Palpate the trachea, and a cough would indicate it is the airway, not the heart
Cats with asthma tend to have a strong ________ breathing
Expiratory
Cat murmurs are heard best on what area?
The sternum
The S1 sound is caused by ____ valve closure, while S2 is caused by _____valve closure
AV; aortic and pulmonary
T/F: You should always hear only two sounds when listening to the heart
True, three is abnormal in small animals
T/F: Loudness of a murmur correlates to severity
False, a super quiet murmur could mean valve has failed completely
What happens if a murmur goes from a grade 4 to a grade 1 instantly?
A chordae tendinae rupture
Loud crackles from the lungs indicates _____, while quiet ones indicate _____
Asthma in cats; Pleural effusion
T/F: The strength of pulses indicates blood flow
False, might just feel strong
Elbow abduction is a sign of severe ____
Dyspnea (need room to breath)
Recall, if the owner says the heart rhythm is off, think _______
Atrial fibrillation
Jugular distension and ascites is ______ sided heart failure, while pulmonary edema is ______ sided heart failure
Right; Left
Quiet heart sounds indicate that it is ______ and quiet lung sounds indicate that it is ____
Pericardial; Pleural
Coughing cat indicates ____ while coughing dogs indicate ____
Asthma/worms ; Respiratory
What is the most important contractile element for the heart?
What about relaxing?
Calcium contracts!
Magnesium relaxes
What is the surface recording of average electrical activity of the heart?
ECG
T/F: ECG measures contraction
False, just electrical activity
Each different angle of an ECG is called ______
a lead
What deflection shows when an electrical impulse travels toward a positive electrode?
Upward deflection
What two cases produce a flatline?
When electrical forces are equal, or
When there is no electrical activity
Atrial contraction follows the _____ wave
P wave (atrial depolarization)
Ventricular contraction follows the _______ wave
QRS (Ventricular depolarization)
Activation of the conduction system is called the _____ segment
P-R
________ events always precede mechanical events
electrical
The P wave is caused by depolarization of the _______, while the QRS wave is caused by the depolarization of the ______
Atria; Ventricles
The T wave represents __________
Ventricular polarization (end of contraction)
Heart muscle contractions are due to what type of polarization?
Depolarization
What pump causes depolarization?
Na/K pump
Recall that the inside of a myocardial cell is more ______ when referring to polarity
negative
What ion enters first and quickly, and which ion follows but slower?
Na+ enters quickly, Ca2+ channels open slower
Sarcoplasmic reticulum and T tubules release ______, causing contractions
Ca2+
When ______ leaves the cells, it signals the end of contraction, and the cell returns to a more ______ state
K+; negative
What polarization is when heart muscle relaxes and electrolytes move back across cell membrane?
Repolarization
______ wave is for ventricular repolarization
T wave
Every ________ wave must have a T wave
QRS (P wave is unnecessary)
The ability of the heart to beat without needing to be activated is _______
Automaticity
The _______ is the primary pacemaker and is the fastest
SA node
Recall the three pacemakers, in order of fastest to slowest
SA node, AV node, and purkinje fibers
If the fastest pacemaker fails, it reverts to the next fastest pacemaker. This process is known as ....
An escape
When there is an irritable focus, meaning a slow pacemaker takes over as the fast one, it is called ______
Aberrant rhythm
The electrical stimulus reducing the resting potential to cause a contraction is called _______
Excitability
The ____ period is when no stimulus will cause contraction, while the _____ period will cause a contraction if the stimulus is great enough
Refractory; Relative refractory
The _______ period is why the heart does not remain contracted during tetanus
Relative refractory, allows for relaxation
Activation of a muscle cell produces activity in the next cell, called _______
Conductivity
Conductivity velocity is the fastest in ________
Purkinje Fibers
T/F: ECG measures stimulus for contraction, not the contraction itself
True
_______ is how we can measure contractions
Echocardiogram
ECGs are typically done in what lateral recumbency?
Right
ECGs have a speed of _____ mm/sec
50
T/F: Complexes will be pushed together more the faster the paper speed
False, complexes will be more spread out, since the pen moves at the same speed, but over more paper
What is the advantage of a faster paper speed? What about a slower paper speed?
A faster paper speed (50) allows you to see individual complexes more clearly, while a slower paper speed (25) gives you more complexes to compare
The standard sensitivity of ECG is 1 cm = ____ mV
1
What are the bipolar leads?
What are the unipolar leads?
Bi: I, II, III
Uni: aVR, aVL, aVF
What does aVR, aVL, and aVF mean?
aVR means right arm,
aVL means left arm, and
aVF means left foot
If the impulse is away from the positive electrode, the deflection is ______
negative or downward
R wave should be positive in lead ____
one
In the QRS wave, which are positive?
R is positive,
Q and S are negative
Give the action of the following:
P.
QRS.
T.
P is atrial contraction,
QRS is ventricular contraction, and
T is ventricular relaxation
Normal mean electrical axis (MEA) points to the ______
Left ventricle
Normal MEA in dogs is ____ to _____.
What about cats?
Dogs: +40 to +100
Cats: 0 to +160
What lead should you select to calculate MEA?
The isoelectric lead (positive and negative deflections are equal)
Once you have the isoelectric lead, what lead should you locate on the diagram?
The lead 90 degrees to the isoelectric
Once you have the perpendicular lead to the isoelectric, what side of that lead should you pick?
If complexes are upright, pick the positive side.
Else, pick negative
Example: The isoelectric lead is aVL, and the perpendicular lead complexes are upright. What is the MEA? Is it normal?
MEA = +60
Cat normal = 0 - 160
Dog normal = 40 - 100
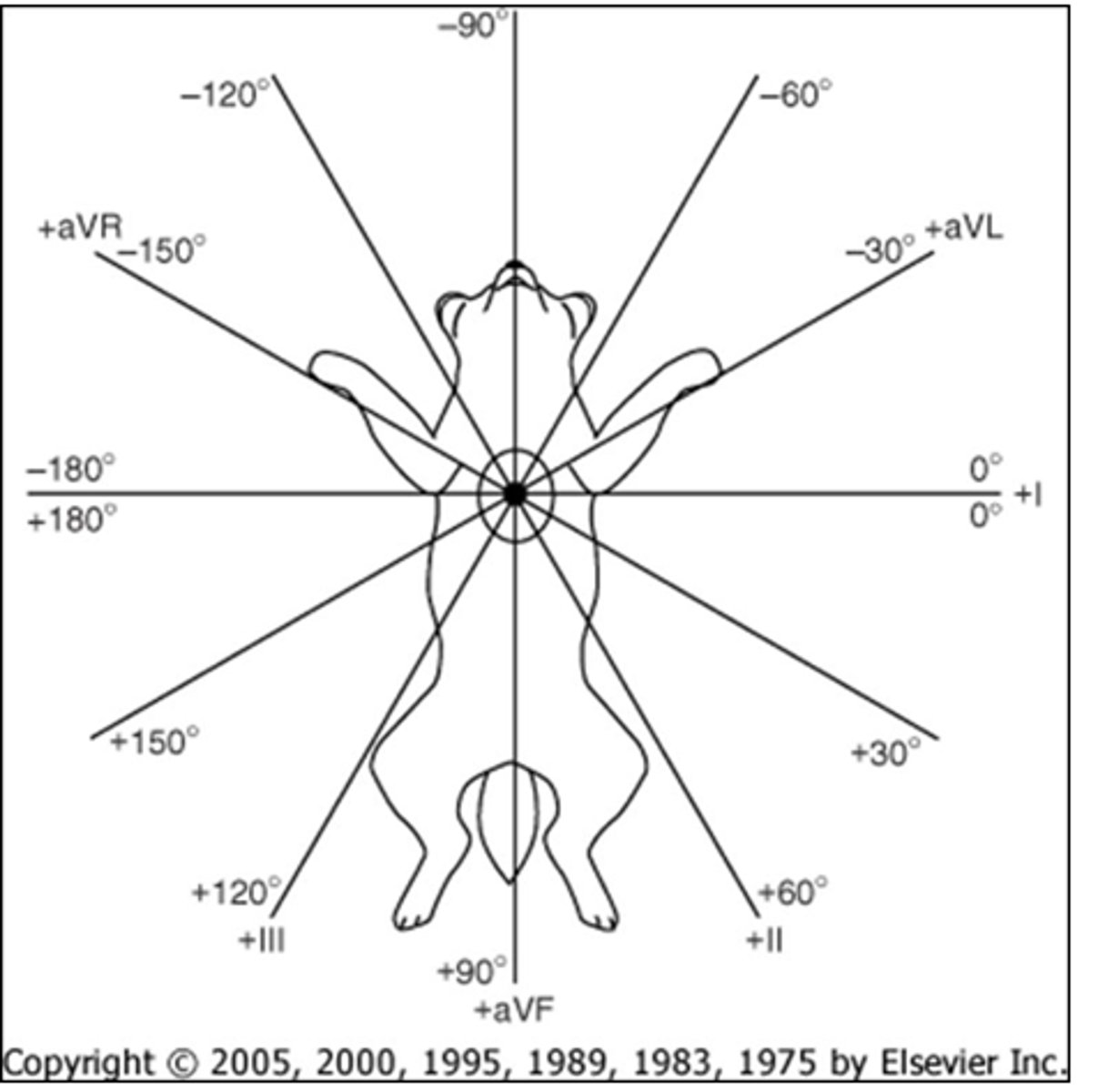
What degrees would indicate a right axis shift in dogs? How about cats?
Dogs range from +100 to -90, while
Cats range from +160 to -90
What are some common causes of right axis shift?
Something is wrong with the right side of the heart, like hypertrophy
What is the range of a left axis shift?
Dogs range from +40 to -90, while
Cats range from 0 to -90
T/F: A left axis shift is common
False, because the left side is normally large
If you see a cat with marked left axis deviation, or any ECG changes, you should say "Obviously that is ________" and sound really smart
Left anterior fascicular blocks
Increased size of P wave indicates _____
Atrial enlargment
Increased height of the R wave indicates ______
Left ventricle enlargement
A deep S wave indicates ______
Right ventricle enlargement
What rate would be associated with an escape rhythm?
Slow rate
What rate would be associated with an irritable focus?
Fast rate
If the ECG is irregularly irregular (all over), then it is _____
Atrial fibrillation
What are the three ways the heart can respond to increased demand?
Increases in heart rate,
Cardiac dilation (increase stroke volume), and
Hypertrophy (greater contractility)
T/F: Cardiac dilation always increases stroke volume
False, only to a point
What are the two types of hypertrophy?
Physiological, which is normal and good (exercise, good, only increases 10 - 20%), and
Pathological, which decreases function (4 fold increase in weight, congenital)
Primary cardiac hypertrophy is due to _______
Mutations in the cells
Secondary cardiac hypertrophy is due to _____
Sustained increase in cardiac workload
Secondary cardiac hypertrophy includes volume overload and pressure overload. What do these terms mean?
Volume overload is too much blood in the ventricle, leading to a more difficult contraction.
Pressure overload is often due to stenosis in vasculature, meaning that it is harder to pump blood through the thinner vessels
Pressure overlaod is associated with ______ hypertorphy
Volume overload is associated with _____ hypertorphy
Concentric (just hypertrophy), and
Eccentric (dilation + hypertrophy)