Ecology and the Environment Exam Style Qs
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
An increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can lead to an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Describe the possible consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect. (4)
m1: global warming m2: ice caps melt m3: rises sea levels m4: climate change m5: habitat destruction m6: extinction due to disruption of food chains m7: migration → distributes organisms → distributes disease → affects plant growth
Explain the consequences of fertiliser containing nitrates polluting a river (6)
m1: nitrates soluble/dissolve m2: rain/water m3: leaching plant growth m4: block sunlight → plants die → less photosynthesis → less oxygen m5: fish/animals die m6: eutrophication
(Oryx and) humans can control water loss by making their urine very concentrated. Describe how this is done. (6)
m1: receptors present in the nephron m2: hypothalamus controls water reabsorption m3: pituitary gland releases m4: ADH m5: increases ADH m6: kidney/nephron m7: collecting duct m8: more permeable m9: reabsorption of water
Suggest why desert animals are less active in summer than in winter. (3)
m1: warmer m2: avoid sweating and water loss m3: avoid overheating as respiration produces heat m4: because there’s less water in plants
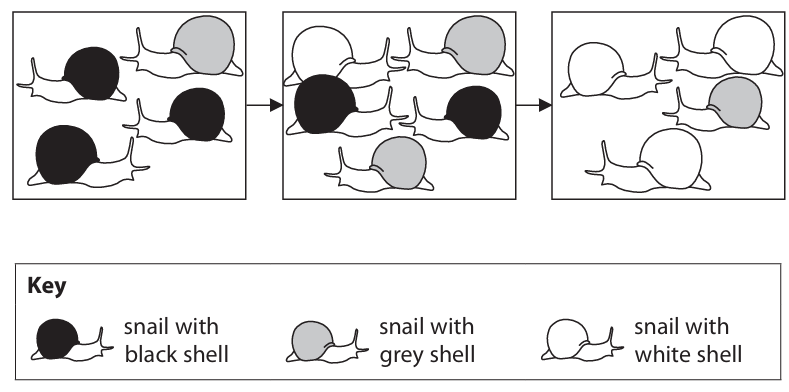
Use the information in the drawings to explain the process of natural selection (5)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: white snails survive → survival of the fittest m4: camouflaged → not eaten/killed m5: reproduce m6: pass on allele to offspring
Gazelles cannot maintain their top speed for a long time because a change in the type of respiration takes place in their muscle cells.
Explain how this change in respiration stops gazelles from running at a top speed for a long time. (3)
m1: anaerobic respiration m2: less oxygen m3: lactic acid → lower pH m4: denatures enzymes m5: less energy in the form of ATP
Zebras also try to avoid being caught by lions. It was thought that the striped coat of zebras helps to camouflage them.
A new theory suggests the striped coat evolved because it reduces the number of biting flies that feed on zebra blood.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain how a striped coat that reduces the number of flies feeding on zebra blood may have evolved. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: survival of the fittest m4: reproduction m5: pass on allele
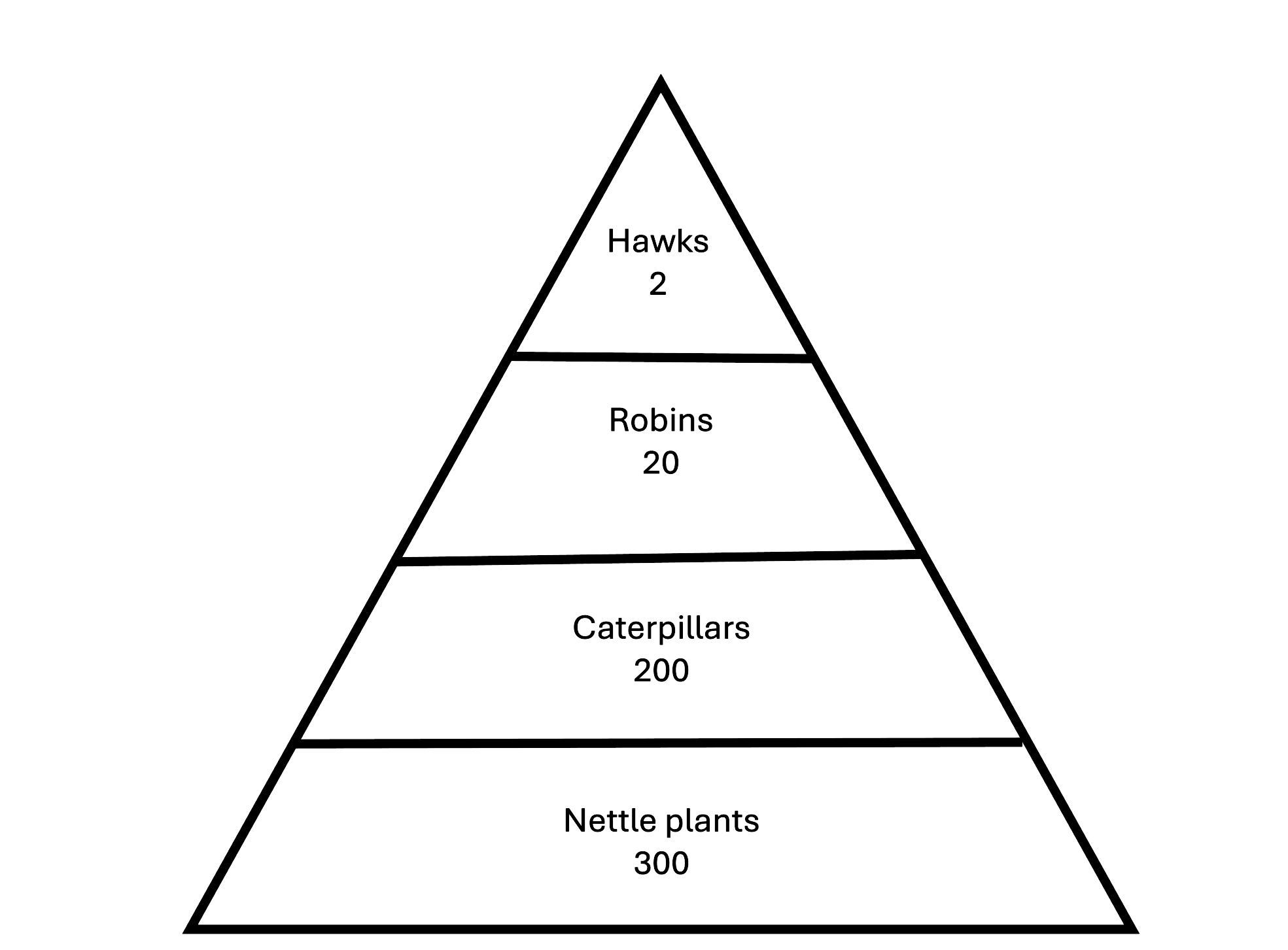
The total mass of the organisms at each level in the pyramid decreases as you move up the pyramid. Explain why. (4)
m1: energy loss m2: respiration m3: egestion → not digestion m4: not all of each organism eaten m5: some organisms decompose m6: movement m7: thermoregulation → heat loss
Describe how increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the air may cause global warming and explain the possible consequences of global warming (5)
m1: greenhouse gas m2: traps heat m3: ice caps melt → flooding m4: habitats destroyed, soil erosion, desertification m5: food chain disruption → extinction m6: migration → spread of disease → affects plant growth m6: climate change
Explain how feeding on mesophyll tissue will affect tomato production (3)
m1: lower production → fewer fruit → less growth
m2: fewer chloroplasts → less chlorophyll
m3: less photosynthesis
m4: less carbohydrate
Pesticide are no longer successful in controlling the pest because the population of resistant forms of the leaf miner has increased.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain why the population of resistant forms of the leaf miner has increased. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: random m4: survive → not killed m5: reproduce m6: pass on allele
Pheromone traps could also be used to control the leaf miner. Pheromones are smells that attract leaf miner males.
Design an investigation to find out if a pheromone trap would help to control the leaf miner.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences (6)
m1: increase pheromone and then remove the pheromone
m2: control species of insect, size of crops
m5: same temperature, time of year, location, size of field, etc
m3: several traps → repeat in many fields
m4: count number trapped in m6: given time period
Explain the advantages of reducing the mass of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. (5)
m1: reduces greenhouse effect m2: less global warming m3: less ice caps → melt → rise in sea level → flooding m4: less habitat destruction m5: less death/extinction m6: less migration m7: less climate change
The number of fish in the lake decreases over the 25-year period.
Explain how the changes in phosphate levels might cause the decrease in the number of fish (5)
m1: algae growth m2: block light m3: plant death → no photosynthesis m4: microbes m5: less oxygen m6: respiration
Commercial flower growers keep their plants in greenhouses under artificial light.
Describe an investigation to find out if the length of time that plants are exposed to light affects how long it takes for flowers to appear. (6)
m1: different light periods m2: same species m3: repeat m4: time to produce flowers m5: days m6: same temperature/light intensity/CO2
If waste from fish farms is released into rivers it will cause pollution.
Design an investigation to compare the pollution caused by waste released from the new type of fish farm with waste released from a traditional fish farm.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences. (6)
m1: use a traditional and a new type of farm
m2: control same species, same fish
m3: same mass of food
m4: same distance of farms/same depth in water
m5: same time of day
m6: repeat experiment
m7: measure mass of algae, mass of pondweed, O2 level, etc
An increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can lead to an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Describe the possible consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect. (4)
m1: global warming m2: ice caps melt m3: flooding m4: climate change m5: habitat destruction m6: extinction → disruption of food chains m7: migration → distribution of organisms
Fish are a good source of protein in the human diet.
Describe what happens to fish protein in the gut of a human. (5)
m1: digested m2: amino acids m3: stomach m4: protease m5: releases hydrochloric acid → low pH m6: small intestine m7: neutralises acid m8: optimum pH
Explain the consequences of fertiliser containing nitrates polluting a river (6)
m1: (nitrates) soluble m2: rain m3: leaching algal growth m4: block light m5: plants die m6: less oxygen m7: decomposers decay m8: fish/animals die m9: eutrophication
The peacock is a bird found in the jungle in India. The male has a large, colourful tail that he displays during courtship to attract a female to mate with.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to suggest how the peacock’s tail has evolved. (6)
m1: mutation m2: competition m3: selected by female m4: reproduce m5: offspring have more colourful tails m6: allele passed on m7: process continues m8: survival of the fittest → extinction of those with non colourful tails
Describe the events that take place from when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower to when seeds are formed (5)
m1: pollen tube m2: style m3: ovary m4: ovule → male gamete m4: fuses m5: female gamete m6: ovary becomes fruit
Suggest a method that could be used to estimate the population of fire ants in an area (4)
m1: using a quadrat, m2: count how many m3: multiply to get total for area m4: random m5: repeat
Describe how the tea grower could use a quadrat to estimate the total mass of tea plants growing in a large area of land. (3)
m1: use a balance m2: random m3: scale by multiplying m4: repeat
What is meant by the term selective breeding (4)
m1: human with the m2: desired characteristics m3: breed m4: repeat for many generations
Describe how you could use a quadrat to estimate the plant biomass in one of the regions. (4)
m1: use more than one m2: randomly m3: use scale m4: remove animals m5: multiply to total area
Describe an investigation to find out if keeping chickens indoors increases their growth (6)
m1: vary from indoors and outdoors m2: same species/size/age m3: control mass of food m4: control area of water m5: measure mass/length m6: of a time period m7: repeats
Describe an experiment you could do to find out the effect of pH on the growth of yeast. (6)
m1: vary pH → acid/alkali m2: same species/mass/number m3: same temp/volume of water m4: same nutrients m5: measure mass/bubbles in a given time period m6: repeat each pH
Nitrogenous waste released into the environment can cause eutrophication.
Describe the process of eutrophication and the effects that it can have on the environment. (5)
m1: plant m2: algae block light m3: less photosynthesis m4: decomposers m5: aerobic respiration m6: oxygen depletion m7: death of plants
Fish farms remove nitrogenous waste to improve the growth of fish.
Another method to improve the growth of fish is vaccination.
Explain how the process of vaccination improves the growth of fish. (4)
m1: dead m2: antigens m3: memory cells m4: secondary immune response
Fish farms remove nitrogenous waste to improve the growth of fish.
Another method to improve the growth of fish is vaccination.
Explain how the process of vaccination improves the growth of fish (4)
m1: dead m2: antigens m3: memory cells m4: immunity
Explain how a mutation in a gene can affect the phenotype of an organism. (3)
m1: mutation is random change to DNA
m2: change in nucleotides
m3: change in amino acid sequence
m4: changing enzyme
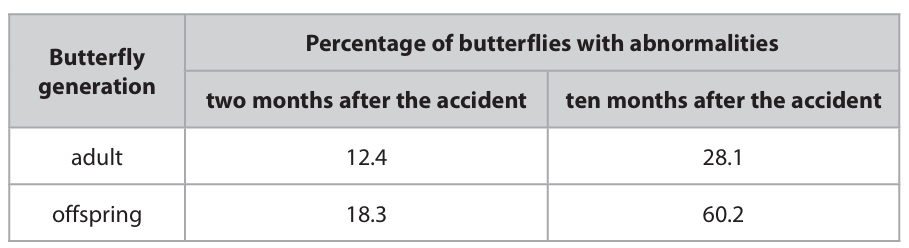
The scientists concluded that the increased level of radioactivity has led to an increased rate of mutation of DNA.
Discuss the scientists’ conclusion referring to data from the table to support your answer.
m1: increase in abnormal butterflies m2: due to longer exposure to radioactivity m3: recessive mutations may be carried by adults m4: if heterozygotes mate they produce abnormal offspring m5: there is no data before the accident m6: radioactivity is not measured
State three ways in which the structure of a DNA molecule differs from the structure of an RNA molecule (3)
m1: the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose while the sugar in RNA is ribose
m2: the base thymine is DNA is replaced by Uracil in RNA
m3: DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded
Describe the differences between the processes of transcription and translation (5)
m1: transcription occurs in the nucleus m2: transcription uses DNA to make RNA m3: transcription produces messenger RNA m4: translation takes place in the ribosome/cytoplasm m5: translation produces amino acid
The DNA molecule codes for the amino acids used to make proteins.
There are four different bases in DNA and 20 amino acids used to make proteins.
Use this information to show that a minimum of three bases on the DNA molecule is needed to code for each amino acid. (3)
m1: 43 = m2: 64 m3: 64>20 combinations required
Discuss why some farmers limit the amount of chemical fertilisers they add to their crops (5)
m1: increased soil concentration reduces water potential of soil m2: prevent water uptake m3: so plant wilts m4: damaging effect of leaching m5: causes eutrophication
Explain two reasons why a pyramid of biomass is better than a pyramid of numbers (2)
m1: biomass is quantitative
m2: biomass is usually upright
m3: numbers doesn’t take the size of the organism into account
Give three reasons why only ~10% of the energy & biomass is passed on at each stage in a food chain (3)
m1: some parts of the food are not digested by the organism
m2: some of the materials absorbed form excretory products
m3: some of the products are respired to release energy with loss of carbon dioxide and water
State 3 advantages of pesticides (3)
m1: Easily accessible and relatively cheap
m2: have an immediate effect
m3: kills the entire population of pests
State 3 disadvantages of pesticides (3)
m1: organisms they are meant to kill can develop a resistance to them
m2: non-specific chemicals and can kill other beneficial organisms
m3: they can be persistent chemicals