sedative hypnotics - dr austin
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
idk if we need to know
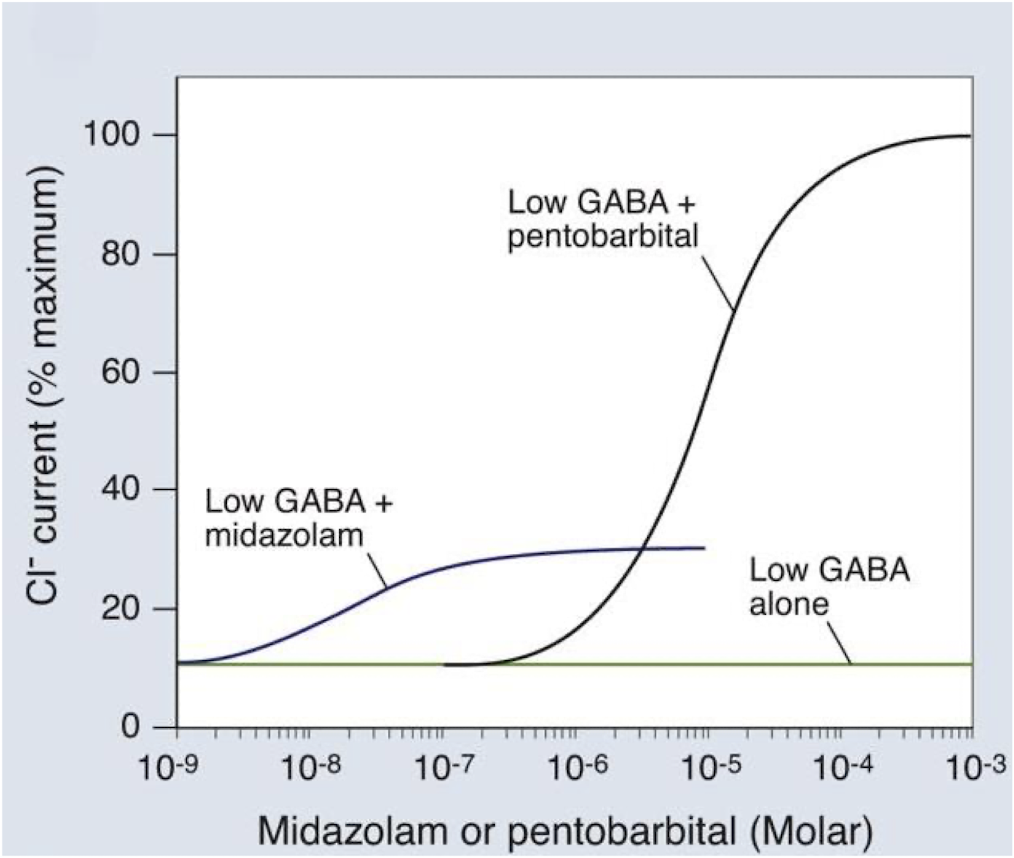
what is more efficacious?
a. midazolam (benzodiazepine)
b. pentobarbital (barbiturate)
b.
idk if we need to know
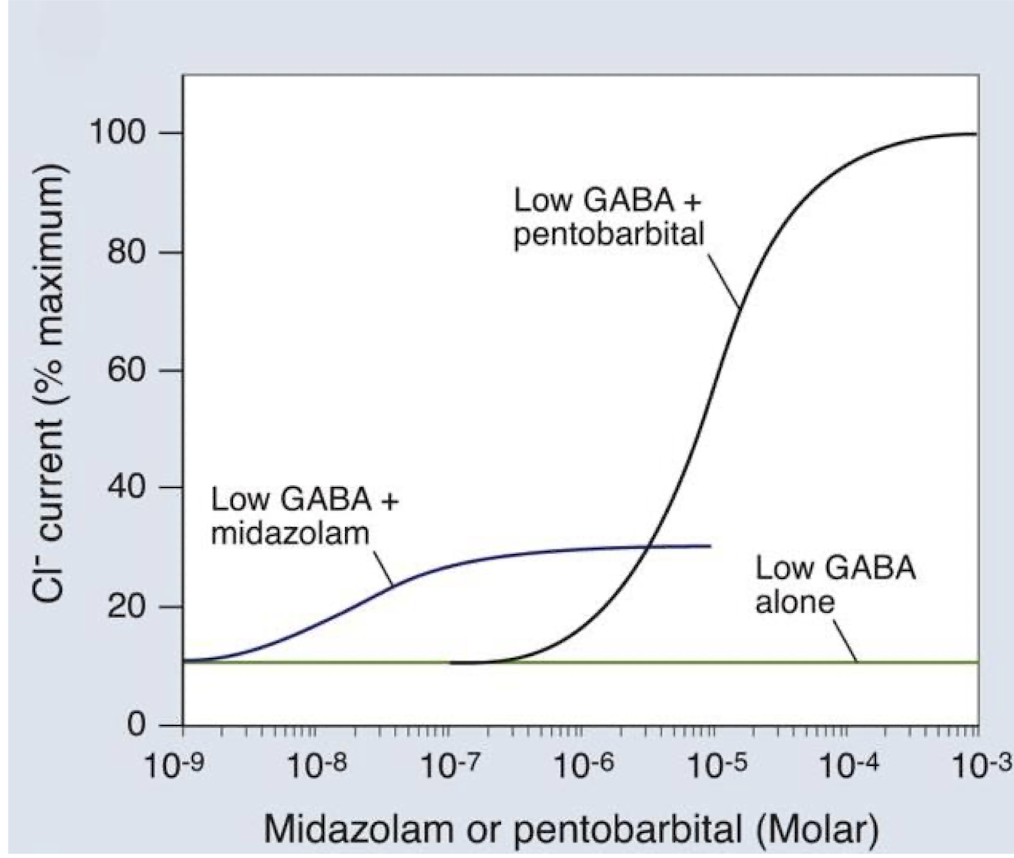
what is more potent?
a. midazolam (benzodiazepine)
b. pentobarbital (barbiturate)
a.
idk if we need to know
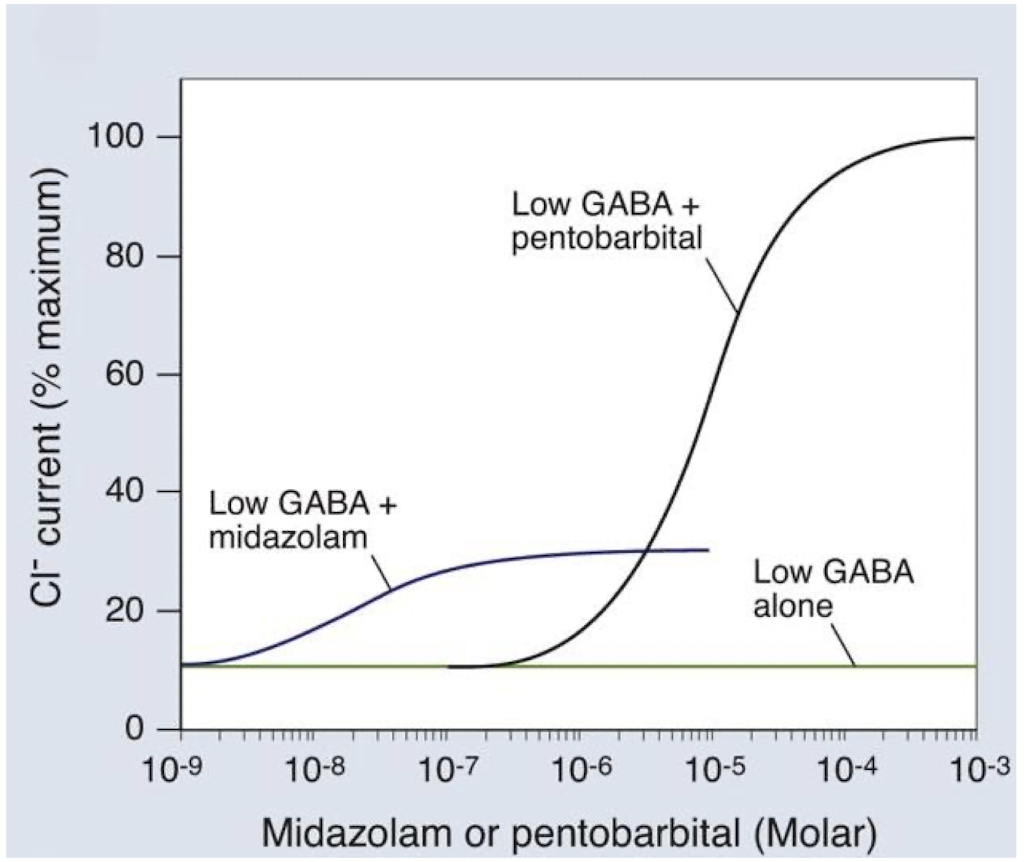
what is safer?
a. midazolam (benzodiazepine)
b. pentobarbital (barbiturate)
a.
what kind of insomnia lasts days to weeks?
a. transient
b. acute
c. chronic
a.
what kind of insomnia lasts weeks to months?
a. transient
b. acute
c. chronic
b.
what kind of insomnia lasts years?
a. transient
b. acute
c. chronic
c.
what kind of insomnia is difficulty falling asleep upon going to bed and is frequently associated with anxiety disorders?
a. onset insomnia
b. middle insomnia
c. late (terminal) insomnia
a.
what kind of insomnia is difficulty maintaining sleep; waking up during the night and is frequently associated with pain disorders?
a. onset insomnia
b. middle insomnia
c. late (terminal) insomnia
b.
what kind of insomnia is early morning waking and is frequently associated with depression disorders?
a. onset insomnia
b. middle insomnia
c. late (terminal) insomnia
c.
list psychological causes of insomnia
anxiety
depression
psychosis
behavioral patterns
substance use/abuse
stress
list physiological causes of insomnia
cardiovascular
endocrine
autonomic disorders
pain
fatigue
GERD
apnea
medications
what lifestyle change is recommended as nonpharm therapy?
reduce stress and anxiety
list ways to improve sleep hygiene
minimize daytime napping
eat meals on regular schedule
practice relaxing behaviors at bedtime and go to bed around the same time nightly
minimize use of electronic devices in bedroom
what substances should we avoid, especially near bedtime?
caffeine
alcohol
nicotine
list pharm therapies for insomnia
benzodiazepines
benzodiazepine receptor agonists
melatonin receptor agonist
orexin antagonist
barbiturates
only short term
OTC/herbal therapies
antihistamines
lavender
melatonin
chamomile
valerian root
passionflower
can we use benzos in pregnancy?
no
idk if we need to know
how do benzos modulate sleep stage distribution?
increase length of stage 2 sleep
decrease length of stage 3, 4, and REM sleep
T/F benzos are not recommended long term
TRUE
benzodiazepines bind to __________ receptor between alpha and gamma subunits
GABAA
what is the effect of benzodiazepines?
a. increase frequency of chloride channel opening
b. decrease frequency of chloride channel opening
c. increase frequency of sodium channel opening
d. decrease frequency of sodium channel opening
a.
benzodiazepines are weak positive ___________
a. allosteric agonists
b. allosteric antagonists
c. inverse agonists
a.
when does the chloride channel open more frequently?
when all 3 of the sites are bound (2 GABA, 1 BZD)
what are the contraindications of benzodiazepines?
risks from concomitant use with opioids
abuse, misuse, and addiction
dependence and withdrawal reactions
angle-closure/untreated glaucoma
pregnancy/lactation
benzodiazepines can be extremely dangerous and sometimes fatal when combined with _______
CNS depressants
(ex: opioids)
what is the antagonist of GABAA benzodiazepine site, given IV for overdose/anesthesia reversal?
flumazenil (romazicon)
what is the onset and half-life of flumazenil (romazicon)?
onset: 6-10 minutes
t1/2: 40-80 minutes —> much shorter than agonists because of the ethyl ester
flumazenil (romazicon) is a benzodiazepine antagonist/reversal agent and may cause ________ (SATA)
a. respiratory depression
b. seizures
c. withdrawal
d. flushing
b. c.
ethanol also acts on the GABAA receptor. should flumazenil be considered for a patient experiencing severe respiratory depression following excessive alcohol consumption?
NO — won’t block that site
which functional group of temazepam (restoril) allows it to undergo conjugation?
hydroxyl group
how is temazepam (restoril) metabolize? major vs minor
major: conjugation
minor: demethylation
which of the following is a benzodiazepine?
a. zolpidem (ambien)
b. zaleplon (sonata)
c. eszopiclone (lunesta)
d. temazepam (restoril)
d.
list the benzodiazepine receptor agonists
zolpidem (ambien)
zaleplon (sonata)
eszopiclone (lunesta)
where do benzodiazepine receptor agonists bind?
GABAA receptors — selectivity for alpha1 subunits
they require binding of GABA in order to exert effect
benzodiazepine receptor agonists are selective for alpha1 subunit containing GABAA receptors, which REDUCES _________ effects
anxiolytic
antiepileptic
muscle relaxant
benzodiazepine receptor agonists are selective for alpha1 subunit containing GABAA receptors, which CONSERVES _________ effects
sedative
amnesic
T/F benzodiazepine receptor agonists maintain a risk of tolerance/dependence and are schedule IV controlled substances
TRUE
list the available formulations of zolpidem (ambien)
lowkey he said just to know that there’s multiple formulations available
tablet
sublingual CR (approved for terminal insomnia)
oral spray
idk if we need to know
how is zolpidem (ambien) metabolized?
CYPs
3A4
2C9
1A2
what pregnancy category are the benzodiazepine receptor agonists?
a. Pregnancy A
b. Pregnancy B
c. Pregnancy C
d. Pregnancy D
c.
what benzodiazepine receptor agonist has the fastest onset and shortest half-life? hint: it’s the one that isn’t used for both falling asleep and staying asleep; ONLY for falling asleep
a. zolpidem (ambien)
b. zaleplon (sonata)
c. eszopiclone (lunesta)
b.
idk if we need to know
how is zaleplon (sonata) metabolized?
CYP 3A4
aldehyde oxidase
what benzodiazepine receptor agonist is an enantiomer of zopiclone (R or S)?
a. zolpidem (ambien)
b. zaleplon (sonata)
c. eszopiclone (lunesta)
c.
T/F the half life of eszopiclone (lunesta) is LONGER in elderly patients
TRUE - normal is 6 hours
idk if we need to know
how is eszopiclone (lunesta) metabolized?
CYPs
3A4
2E1
which benzodiazepine receptor agonists help you fall asleep and cause physical dependence? (SATA)
a. zolpidem
b. eszopiclone
c. zaleplon
a. b. c.
what benzodiazepine receptor agonists help you stay asleep and cause rebound insomnia (for sure)? (SATA)
a. zolpidem
b. zolpidem SL
c. zolpidem CR
d. zolpidem spray
e. eszopiclone
f. zaleplon
c. e.
what is melatonin’s role in the body?
utilizes light-dark information from retina
synchronizes sleep-wake cycle
influences circadian rhythm
what dose of melatonin may cause drowsiness in 30 minutes, persisting for about 1 hour?
a. 1-2 mg
b. 2-4 mg
c. 3-5 mg
d. 5-10 mg
c.
list ADRs of melatonin
next-day drowsiness
nausea
irritability
when may melatonin be useful?
jet lag
other meds failed/contraindicated
is melatonin an acid or base?
a. acid
b. base
apologies it’s a trick question
it’s neutral!!!! has an amide
what drug class is ramelteon (rozerem)?
a. benzodiazepine
b. benzodiazepine receptor agonist
c. melatonin receptor agonist
d. orexin receptor agonist
c.
rameleteon (rozerem) selectively binds ________ receptors is suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in hypothalamus
a. GABA
b. MT1 and MT2
c. OX1 and OX2 receptors
b.
since ramelteon (rozerem) has no effect on GABA, what effects are NOT seen compared to benzodiazepine receptor agonists?
no dependence/abuse potential
not a scheduled drug
no withdrawal or rebound insomnia
what drug is metabolized by CYP1A2, is not recommended in severe hepatic impairment, and is pregnancy category C?
ramelteon (rozerem)
list ADRs of ramelteon (rozerem)
dizziness
fatigue
depression
idk if we need to know
what is the half life of ramelteon (rozerem)? what is the half-life of the active metabolite?
t1/2: 1-3 hours
active metabolite: 2-5 hours
what drug blocks wake-promoting neuropeptides orexin A and orexin B by binding OX1 and OX2 receptors?
a. suvorexant (belsomra)
b. ramelteon (rozerem)
c. eszopiclone (lunesta)
d. temazepam (restoril)
a.
what drug is metabolized by CYP3A4, is not recommended in severe hepatic impairment, is pregnancy category C, and is schedule IV?
suvorexant (belsomra)
list ADRs of suvorexant (belsomra)
drowsiness
headache
dizziness
diarrhea
what is suvorexant (belsomra) contraindicated in?
a. narrow angle glaucoma
b. narcolepsy
c. seizures
d. depression
b.
what antihistamines are used for occasional sleeplessness/insomnia? (SATA)
a. doxylamine
b. diphenhydramine
c. promethazine
d. hydroxyzine
a. b.
what antihistamines are used for operative/situational sedation? (SATA)
a. doxylamine
b. diphenhydramine
c. promethazine
d. hydroxyzine
c. d.
T/F long-term medication-only therapy is recommended for treatment of insomnia
FALSE - long-term med-only is NOT recommended
practice
which statement correctly describes benzodiazepines?
a. structurally similar to GABA
b. structurally similar to glutamate
c. agonist at GABA binding site of GABAA receptors
d. agonist at allosteric site of GABAA receptors
d.