NSG 316 EXAM 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:49 AM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
1
New cards
Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory Test
test sense of smell with familiar odor
2
New cards
Cranial Nerve II: Optic Test
test visual acuity and visual field with confrontation
3
New cards
Confrontation Test
gross measure of peripheral vision
-stand 2 fett from person
-have patient cover one eye, then cover your own eye opposite to the persons covered one
-hold finger as target midline between you and patient, slowly advance to periphery
-as person to say "now" as target is first seen
-stand 2 fett from person
-have patient cover one eye, then cover your own eye opposite to the persons covered one
-hold finger as target midline between you and patient, slowly advance to periphery
-as person to say "now" as target is first seen
4
New cards
Confrontation Test: normal
50 degrees upward
90 degrees temporal
70 degrees down
60 degrees nasal
90 degrees temporal
70 degrees down
60 degrees nasal
5
New cards
Cranial Nerve III, IV, VI: Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens Test
PERRLA
6 cardinal positions of gaze
6 cardinal positions of gaze
6
New cards
PERRLA
pupils equal, round, reactive to light (direct and consensual) and accommodation
7
New cards
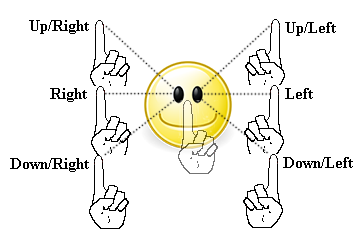
6 cardinal positions of gaze
right & up
right
right & down
left & up
left
left & down
right
right & down
left & up
left
left & down
8
New cards
nystagmus
back-and-forth oscillation of the eyes
9
New cards
nystagmus: amplitude
fine, medium or coarse movement
10
New cards
nystagmus: frequency
constant or fades after few beats
11
New cards
nystagmus: plane of movement
horizontal, vertical, rotary or combo
12
New cards
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal Test
Motor: asking the client to clench her teeth while you palpate the masseter (muscle of mastication)
Sensory- test light touch by having a client closer their eyes while you toucher her face gently with a wisp of cotton, patient identifies location
Sensory- test light touch by having a client closer their eyes while you toucher her face gently with a wisp of cotton, patient identifies location
13
New cards
What does the corneal reflex test?
CN V sensory, CN VII motor
14
New cards
Corneal reflex test
-remove contacts, bring cotton wisp from side, lightly touch cornea
NORMALLY: patient blinks bilaterally
NORMALLY: patient blinks bilaterally
15
New cards
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial Test
Motor: have client smile, frown, puff out her cheeks, raise her eyebrows, close her eyes tightly
Sensory: anterior 2/3 taste (sugar, salt, lemon juice)
Sensory: anterior 2/3 taste (sugar, salt, lemon juice)
16
New cards
Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Test
Whispered voice test
17
New cards
Cranial Nerve IX & X: Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Test
Motor: open mouth say "ahh" & gag reflex
NORMALLY: uvula and soft palate rise in midline
Sensory: CN IX does posterior 1/3 taste
NORMALLY: uvula and soft palate rise in midline
Sensory: CN IX does posterior 1/3 taste
18
New cards
Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Test
shrug shoulders
19
New cards
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal Test
say "light, tight, dynamite"
20
New cards
screening neuro exam
perform on well persons who have no significant subjective findings
21
New cards
complete neuro exam
perform on person with neuro concerns
22
New cards
neuro recheck exam
perform on person with demonstrated neuro defect, who requires period ic assessment
23
New cards
ansomia
Decrease or loss of smell occurs bilaterally
24
New cards
hemianopsia; hemianopia
Defective vision or blindness in one half of the visual field
25
New cards
ptosis
drooping eyelid
26
New cards
paresthesias
tingling, prickling, "pins & needles" (sensory loss)
27
New cards
diplopia
double vision
28
New cards
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
29
New cards
What are the test to evaluate cerebellar function?
Balance Test (Gait)
Romberg Test
Rapid Alternating Movements (RAM)
Romberg Test
Rapid Alternating Movements (RAM)
30
New cards
Balance Test (Gait)
-observe as the person walks 10 to 20 feet, turns and returns to the starting point
NORMALLY: gait is smooth, rhythmic and effortless opposing arm swing is coordinating
NORMALLY: gait is smooth, rhythmic and effortless opposing arm swing is coordinating
31
New cards
Romberg test
-ask client to stand with feet at comfortable distance apart, arms at sides, and eyes closed for ~20 seconds
NORMALLY: patient can maintain posture and balance
NORMALLY: patient can maintain posture and balance
32
New cards
Rapid Alternating Movements (RAM)
pat the knees with both hands, turn hands over, then faster
NORMALLY: done with equal turning and quick rhythmic pace
NORMALLY: done with equal turning and quick rhythmic pace
33
New cards
flaccidity
decreased muscle tone (hypotonia), muscle feels limp, soft, flabby
34
New cards
spasticity
increased muscle tone (hypertonia)
35
New cards
rigidity
constant state of resistance; resists passive movement in any direction (dystonia)
36
New cards
cogwheel rigidity
Increased tone is released by degrees during passive range of motion so it feels like small, regular jerks.
37
New cards
paralysis
decreased or loss of motor power
38
New cards
hemiplegia
Spastic or flaccid paralysis of one side of the body
39
New cards
paraplegia
symmetric paralysis of both lower extremities
40
New cards
quadriplegia
paralysis of all four extremities
41
New cards
paresis
weakness of muscles rather than paralysis
42
New cards
tic
involuntary, compulsive, repetitive twitching of a muscle group
43
New cards
myoclonus
Rapid, sudden jerk or a short series of jerks at fairly regular intervals. (ex: hiccup)
44
New cards
fasciculation
rapid continuous twitching of resting muscle without movement of limb
45
New cards
chorea
sudden, rapid, jerky, purposeless movement involving limbs, trunk, or face
irregular intervals, not rhythmic or repetitive
irregular intervals, not rhythmic or repetitive
46
New cards
athetosis
slow, writhing involuntary movements
47
New cards
tremor
involuntary contraction of opposing muscle groups resulting in rhythmic movement of one or more joints
48
New cards
rest tremor
occurs when muscles are quiet and supported against gravity (hand in lap), coarse and slow, partly or completely disappears with voluntary movement
49
New cards
intention tremor
worse with voluntary movement (like reaching to a target)
50
New cards
spastic hemiparesis
Arm is immobile against the body, with flexion of the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and fingers and adduction of shoulder; does not swing freely. Leg is stiff and extended and circumducts with each step (drags toe in a semicircle).
51
New cards
cerebellar ataxia
staggering, wide-based gait; difficulty with turns; uncoordinated movement with positive Romberg sign
52
New cards
parkinsonian (festinating)
Posture is stooped; trunk is pitched forward; elbows, hips, and knees are flexed. Shuffling gait. Difficulty with any change in direction.
53
New cards
scissors
knees cross or are in contact, like holding an orange between the thighs.
54
New cards
steppage or foot drop
slapping quality, looks like walking up stairs with no stairs there
55
New cards
waddling
weak hip muscles- when the person takes a step, the opposite hip drops, which allows compensatory lateral movement of pelvis
56
New cards
short leg
Leg length discrepancy >2.5 cm (1 inch).
57
New cards
cerebral palsy
damage to cerebral cortex from a developmental defect (infancy and childhood), intrauterine meningitis or encephalitis, birth trauma, anoxia
58
New cards
muscular dystrophy
a chronic, progressive wasting of skeletal musculature producing weakness contracture and respiratory dysfunction or death
59
New cards
Parkinsonism
loss of dopamine-producing neurons causing motor tract disorder
symptoms: resting tremor, bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity
symptoms: resting tremor, bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity
60
New cards
cerebellar
A lesion in one hemisphere produces motor abnormalities on the ipsilateral side.
61
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
chronic, progressive, immune mediated disease which axons experience inflammation, demyelination, degeneration and finally sclerosis
62
New cards
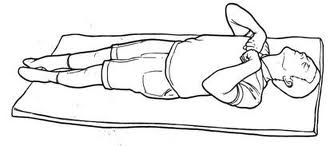
decorticate rigidity
upper: flexion of arm, wrist fingers, adduction of arms
lower: extension, internal rotation, plantar flexion
lower: extension, internal rotation, plantar flexion
63
New cards
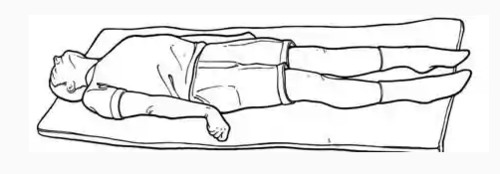
decerebrate rigidity
Upper: stiffly extended, adducted, internal rotation, palms pronated.
Lower extremities: stiffly extended, plantar flexion; teeth clenched; hyperextended back
Lower extremities: stiffly extended, plantar flexion; teeth clenched; hyperextended back
64
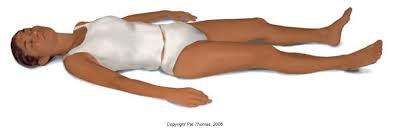
New cards
flaccid quadriplegia
complete loss of muscle tone and paralysis of all four extremities (completely nonfunctional brainstem)
65
New cards
Opisthotonos
prolonged arching of back, with head and heels bent backward (meningeal irritation)

66
New cards
stereognosis
Test the persons ability to recognize objects by feeling their forms, sizes and weights
67
New cards
position (kinesthesia)
test person's ability to perceive passive movements of extremities
68
New cards
Tactile discrimination (fine touch)
measure the discrimination ability of the sensory cortex
69
New cards
Graphesthesia
ability to "read" a number by having it traced on the skin
70
New cards
two point discrimination
test ability to distinguish separation of two simultaneous pin points on skin
71
New cards
extinction
simultaneously touch both sides of body at the same time, both sensations should be felt
72
New cards
point location
touch skin and withdraw stimulus promptly; ask person to put finger where you touched
73
New cards
peripheral neuropathy
Loss of sensation involves all modalities; loss most severe distally at feet and hands
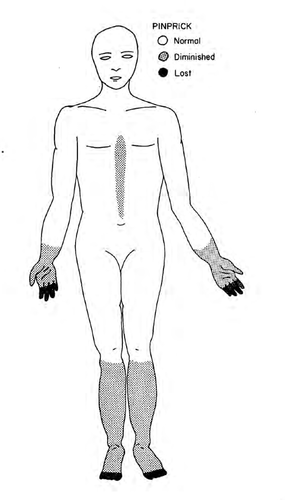
74
New cards
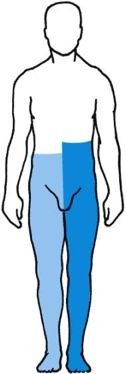
individual nerves or roots
Decrease or loss of all sensory modalities; corresponds to distribution of involved nerve
75
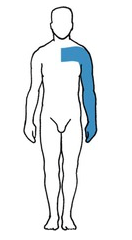
New cards
Spinal Cord Hemisection (Brown-Sequard Syndrome)
injury to one-half of the cord, causing contralateral loss of pain and temp
the ipsilateral side side of the lesion has paralysis and loss of vibration and touch sensation
the ipsilateral side side of the lesion has paralysis and loss of vibration and touch sensation
76
New cards
Complete transection of spinal cord
Complete loss of all sensory modalities below level of lesion; associated with motor paralysis and loss of sphincter control
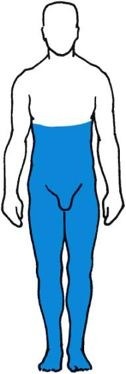
77
New cards
thalamus
loss of all sensory modality son the face, arm and leg on the side contrateral to lesion
78
New cards
cortex lesion
loss of discrimination on contralateral side; loss of graphesthesia, stereognosis, recognition of shapes and weights, finger findings
79
New cards
deep tendon reflexes (DTR)
measurement of stretch reflex reveals intactness of reflex arc at specific spinal levels and normal override on reflex of higher cortical levels
80
New cards
DTR scale
0 - no response
1+ - diminished low normal or occurs w reinforcement
2+ - normal
3+ - brisker than average may indicate disease
4+ - hyperactive w/ clonus, very brisk, indicative of disease
1+ - diminished low normal or occurs w reinforcement
2+ - normal
3+ - brisker than average may indicate disease
4+ - hyperactive w/ clonus, very brisk, indicative of disease
81
New cards
Clonus
test when reflex are hyperactive
82
New cards
how do you test clonus?
support lower leg in one hand and with other hand move foot up and down to relax muscle; then stretch muscle by briskly dorsiflexing fort, hold stretch
83
New cards
what do you normally and abnormally see in a clonus test?
NORMALLY: you feel no further movement
ABNORMALLY: note rapid rhythmic contractions of calf and foot
ABNORMALLY: note rapid rhythmic contractions of calf and foot
84
New cards
Tempomandibular Joint (TMJ) assessment
note smooth movement without limitations or tenderness, clicking or popping when jaw opens and closes
85
New cards
how do you assess the thyroid gland?
ask client to take a sip of water, hold in mouth, the swallow while palpating thyroid gland
-one hand palpates and the other displaces
-one hand palpates and the other displaces
86
New cards
what is abnormal in palpating the thyroid gland?
an enlarged thyroid
87
New cards
What does the nurse do next if the thyroid gland is enlarged?
LISTEN FOR BRUIT (turbulent blood flow)
check the area they drain from for source of the problem
check the area they drain from for source of the problem
88
New cards
how do you examine lymph nodes?
gentle circular motion of finger, palpate lymph nodes
89
New cards
visual acuity test: snellen chart
person 20 feet from chart, ask to read smallest line possible
90
New cards
what does 10/20 vision mean
patient reads 10 feet way what a normal person reads 20 feet away
91
New cards
visual acuity: jaeger card
normal: 14/14 without hesitancy or moving card
92
New cards
Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg Test)
Assess the parallel alignment of the eye axes by shining a light toward the person's eyes.
93
New cards
what is normal for the corneal light reflex test?
light reflection on cornea should be in same spot on each eye
94
New cards
pupillary light reflex
normal constriction of pupils when bright light shines on retina
95
New cards
direct light reflex
constriction of the same-sided pupil
96
New cards
consensual light reflex
simultaneous constriction of the other pupil
97
New cards
red reflex
red glow that appears to fill the person's pupil caused by reflection of light of inner retina
98
New cards
what is a normal finding for the whispered voice test
person can repeat back a the combo of letters and numbers
99
New cards
tuning fork test
Measure bone and air conduction of sound
100
New cards
what is vestibular apparatus and what test is used?
a sensory organ for detecting sensations of equilibrium.
-romberg test
-romberg test