Anatomy of the brain
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms

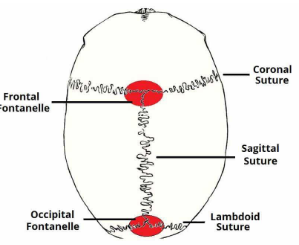
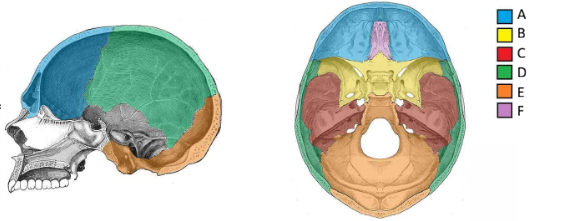
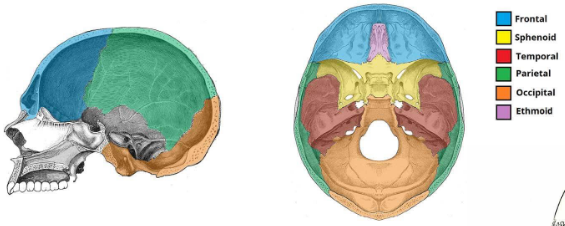
Where does the spinal cord start and end?
medulla oblongata to conus medullaris (L1/2)
What does the cerebrum contain?
Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
Limbic system
What divides the 2 cerebral hemipsheres?
falx cerebri
What does the left side of the brain control?
Right sided motor function
Right sided sensory function
Right sided body image
Right side of visual field
Bilateral audio
Speech
Writing
Language
What does the right side of the brain control?
Left sided motor function
Left sided sensory function
Left sided body image
Left side of visual field
Bilateral audio
Spatial perception
Facial recognition
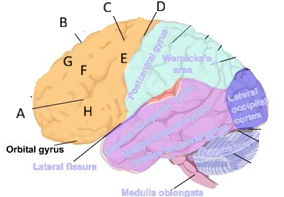
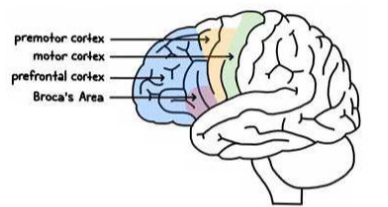
Premotor cortex function
Planning and co-ordination
Sequential movements
Supplementary motor cortex
Postural movements
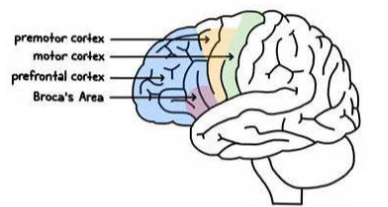
Primary motor cortex function
• Voluntary, skilled movements of skeletal muscle
• Somatotropic organisation
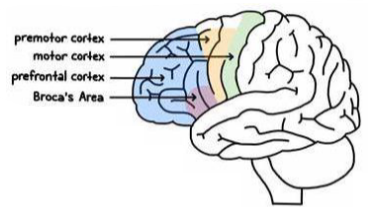
Prefrontal cortex function
• Higher cortical functions
• Decision-making, problem-solving, planning, organisation, motivation, emotional regulation
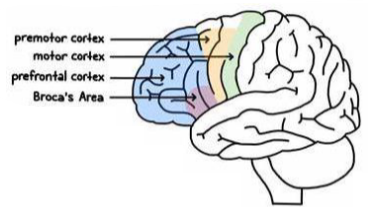
Broca’s area function
• Dominant hemisphere
• Production of language
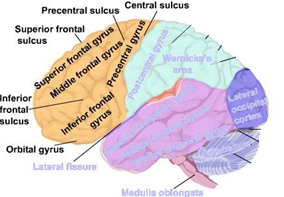
Where is the primary motor cortex located?
within the precentral gyrus
& It gives rise to 60% to 80% of the corticospinal tract (CST)
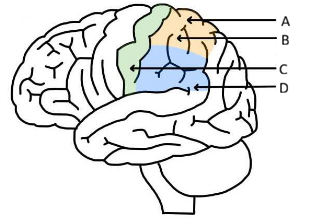
Function of the Primary somatosensory cortex (post central gyrus)
Receives and processes sensory information from the contralateral side of the body
Localisation of sensation
Pain, temperature, crude touch
Fine touch, proprioception
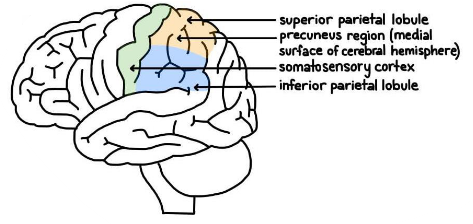
Parietal association cortex function
Superior parietal lobule: Interpretation and integration of sensory input
Inferior parietal lobule: Integration of visual and auditory information from the occipital and temporal lobes (includes angular and supramarginal gyrus)
Spatial orientation
Calculation and language
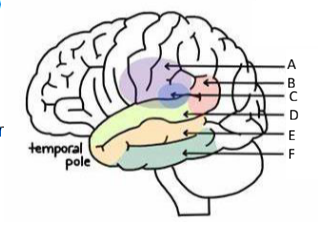
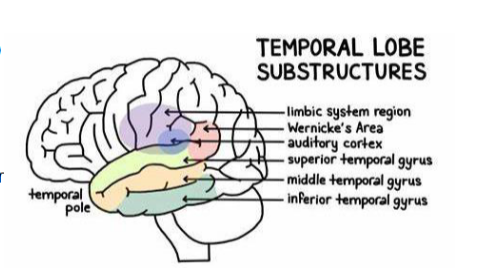
Location and function of the primary auditory cortex
superior temporal gyrus
Perception of sound
Location and function of the auditory association cortex
middle temporal gurus
Processing and interpretation of auditory information
Wernicke’s area – comprehension of language
Location and function of the primary olfactory cortex/ association cortex
inferior temporal gyrus
Awareness and processing of smell
Function of the hippocampus and amygdala
Learning, memory, emotional regulation
What do Lateral geniculate bodies do?
Take part of the raw information from the outer part of the retina to the visual cortex
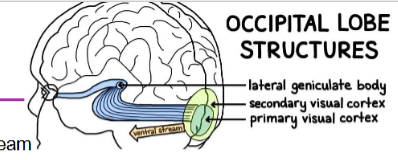
What do lingula bodies do?
Gathers general info about the field of vision from the inside half of the retina → depth perception
What does the Primary and secondary visual cortex do?
Primary visual cortex:
Visual perception – receives images from the retina → interprets and transmits the info via the ventral and dorsal streams
→ Ventral stream: takes info to the temporal lobe to interpret the image → object recognition
→ Dorsal stream: takes info about an object’s location to the parietal lobe → interprets the space and shape of objects in the field of vision
Secondary Visual Cortex:
receives information from the primary visual cortex
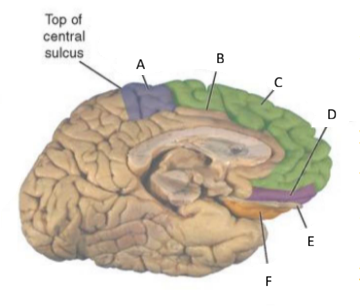
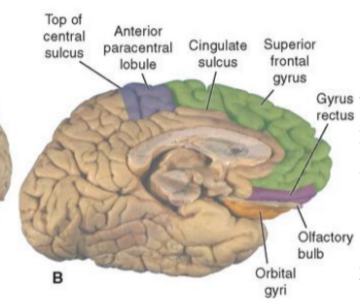
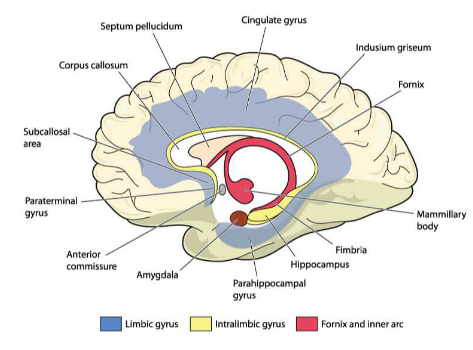
What is part of the limbic system?
hippocampus, fornix, amygdala
What are some surface contributors to the limbic lobe?
cingulate and parahippocampal gyri
What is the Insula and what does it do?
Forms the floor of the lateral sulcus
Has connections with the neocortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, and limbic system
The anterior insula is a cortical centre for pain
The central region is continuous with the frontoparietal and temporal opercular cortex → language function
The posterior insula is interconnected with the entorhinal cortex, and the amygdala → emotional processes
What are the different cortical connections and what do they do?
Association fibres: interconnect cortical sites lying within one cerebral hemisphere
Commissural fibres: run from one cerebral hemisphere to another
Projection fibres: pass between the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures
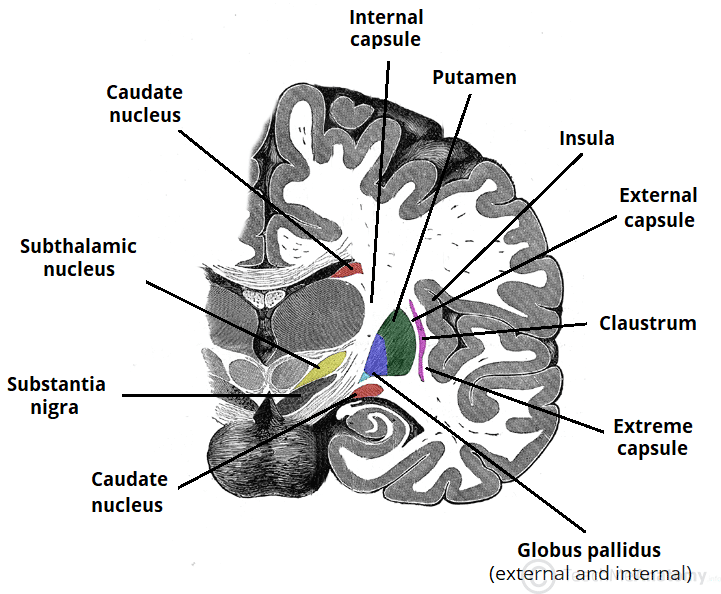
What are basal Ganglia and what is their function?
a group of deep, interconnected subcortical nuclei
Function: fine-tune voluntary movements via the thalamus
also involved in higher cortical function: planning and modulation of movement, memory, motivation, reward
what are the 5 pairs of basal nuclei?
Caudate nucleus
Putamen
Globus pallidus: External (GPe) and internal (GPi) segments
Subthalamic nucleus
Substantia nigra
– Substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr)
– Substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc)
What is the lentiform nucleus composed of?
lateral putamen and medial globus pallidus
What is the striatum composed of?
caudate nucleus, putamen
Describe the basal ganglia blood supply
mainly from the striate branches of the middle cerebral artery
The main branches of the middle cerebral arteries are the lenticulostriate arteries (medial and lateral)
The recurrent artery of Heubner is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery and supplies some of the more anterior aspects of the basal ganglia
Posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries supply the substantia nigra and the subthalamic nucleus
What can happen if you have a blockage in one of the arteries supplying the basal ganglia?
lacunar strokes
What causes huntington’s and what are some symptoms?
Hereditary loss of basal ganglia and cortical neurons leads to hyperactive state of involuntary movements called chorea
uncontrolled movements
slurred speech
impaired coordination
balance problems
What causes Parkinson’s and what are some symptoms?
Degeneration of dopamine secreting neurone on the substantia nigra – progressive and results in slower movement.
tremor (pill rolling)
rigidity
stooped posture
shuffling gait
mask face
Function of the amygdala
• Regulates fear and anxiety responses
• Response to acute stress
• Modulates the acquisition and formation of memories that invoke an emotional response
Location of the amygdala
Located medial to the hypothalamus, anterosuperior to the inferior horn of the Lateral ventricle
Location of the hippocampus
Located in the floor and medial wall of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle
Function of the hippocampus
Crucial in learning and memory, including the storage of long-term memories
Spatial navigation
Function of the hypothalamus
Endocrine control
Regulation of the autonomic nervous system
Regulation of thirst, hunger, body temperature, sleep/wakefulness, fluid balance, memory, reproductive drive
Location of the hypothalamus
Forms the floor and the inferolateral walls of the third ventricle
Separated from the thalamus by the hypothalamic sulcus
What is the Epithalamus made up of and what are their functions?
pineal gland, habenular complex and stria medullaris
Pineal gland – produces melatonin, regulates circadian rhythm
Habenula receives information from the limbic system via the stria medullaris fibres – involved in modulation of the reward system and responses to aversive stimuli
How is the thalamus split into three principal nuclear masses?
Divided by the internal medullary lamina into:
Anterior, medial and lateral thalamic groups
Further divided into ventral and dorsal groups
Function of the thalamus
Acts as a relay station for the processing of sensory information
** Every sensory modality (except for olfaction) will be received and processed by the thalamus, then relayed to the associated area of the cortex
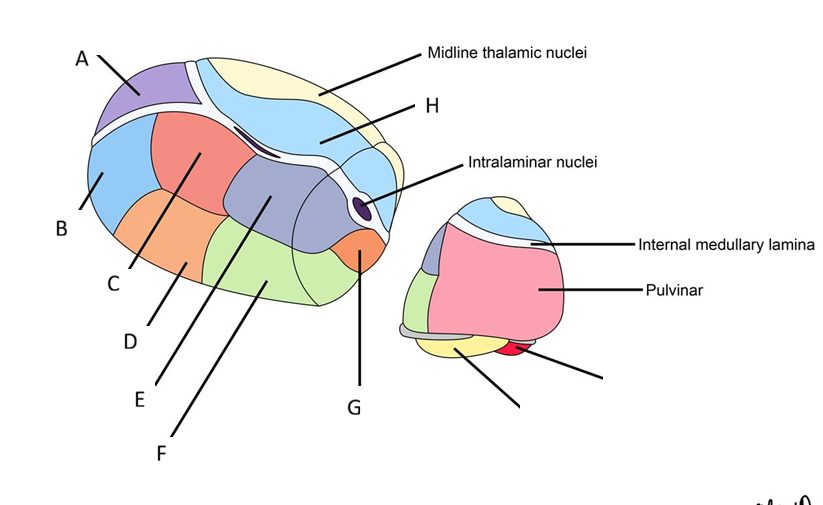
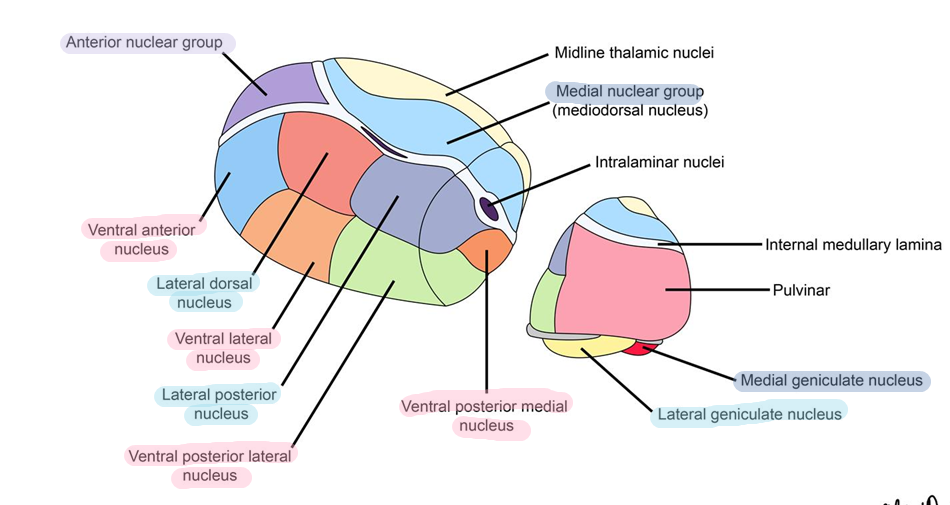
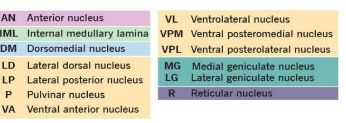
Thalamic nuclei project to the what cortical areas?
VPL: Primary sensory cortex (post central gyrus)
VPM : Primary sensory cortex (precentral gyrus)
VL: Primary motor
VA: Premotor and supplementary motor cortex
Anterior: Cingulate Gyrus
LD: Cingulate gyrus and precuneus
LP: Percuneus and superior parietal lobe
MD: Prefrontal cortex and frontal lobe
Pulvinar: Association areas of partial, temporal and occipital lobes
Location of the internal capsule
lateral to the thalamus and caudate nucleus, and medial to the lentiform nucleus
Divisions of the internal capsule
anterior limb, genu, posterior limb, retrolenticular segment, sublenticular segment
Blood supply to the internal capsule
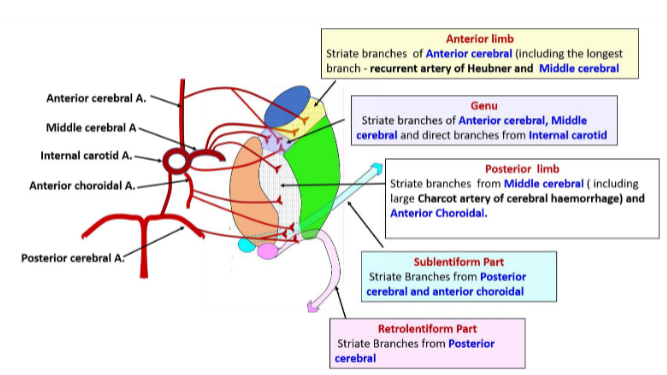
What can lesions in the anterior limb of the internal capsule cause?
contains frontopontine fibres and anterior thalamic radiation fibres
Lesions can manifest as confusion, impaired attention, agitation, and dysarthria
What can lesions in the genu of the internal capsule cause?
Contains corticobulbar tract fibres
Lesions can cause face and tongue weakness and dysarthria
What can lesions in the posterior limb of the internal capsule cause?
Contains fibres of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts and posterior thalamic radiations
Damage to anterior portion can cause contralateral motor hemiparesis
Damage to the posterior portion can cause contralateral hemisensory deficits
What can lesions in the retrolenticular segment of the internal capsule cause?
contains fibres of the optic pathway
Lesions can cause visual field deficits
What can lesions in the sublenticular segment of the internal capsule cause?
Contains fibres of the auditory pathway
Lesions can cause auditory deficits
Location of the midbrain
Most rostral part of the brainstem, sits in the posterior cranial fossa
What is the midbrain divided into?
Tectum (dorsal/posterior surface) → split into 4 tubercles: L/R superior and inferior colliculi
Cerebral peduncles (ventral/anterior surface) → crus cerebri and tegmentum, separated by the substantia nigra
Substantia Nigra → Pars compacta (dorsal), Pars reticulata (ventral)
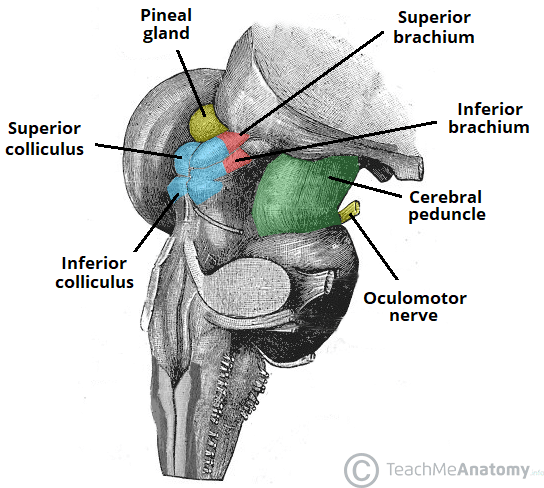
Function of the Tectum (part of midbrain)
Involved in visual and auditory pathways
Function of the Cerebral peduncles (part of midbrain)
Provide pathways between the cerebral cortex and spinal cord
Tegmentum contains cranial nerve nuclei (III, IV, Edinger,Westpahl)
Function of the Substantia Nigra (part of midbrain)
Functional component of the basal ganglia
Dorsal: Pars compacta
• Produces dopamine, connects with the striatum
Ventral: Pars reticulata
• Produces GABA, receives information from striatum, projects it to the thalamus
** Pigmented with neuromelanin
What is the pons made up of?
comprised of two major components:
The ventral pons contains the pontine nuclei → responsible for coordinating movement
** Fibres from the pontine nuclei cross the midline and form the middle cerebellar peduncles on their way to the cerebellum
The tegmentum forms part of the reticular formation → responsible for arousal and attentiveness
The rest of the pons is made up of tracts passing through the pons
Location of the cerebellum
Originates from the dorsal aspect of the brainstem and overlies the fourth ventricle
Connected to the brainstem by the inferior, middle and superior cerebellar peduncles
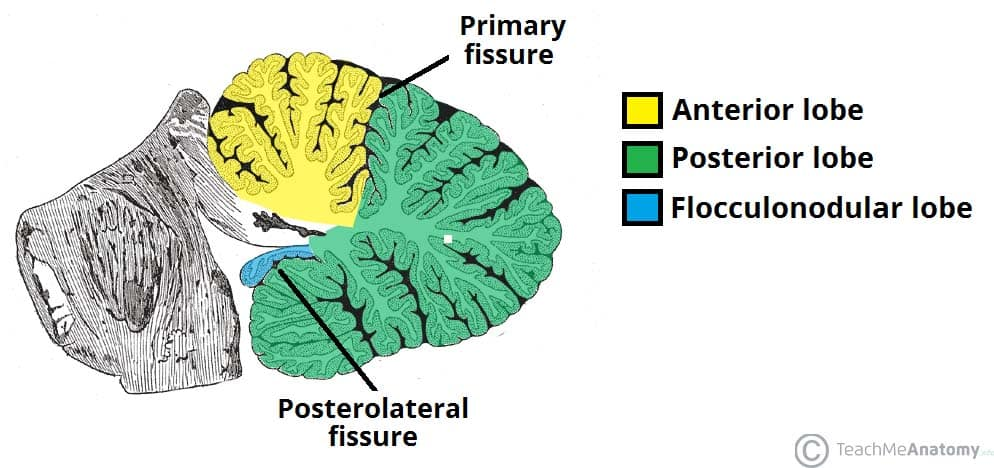
Structure of the cerebellum
Two hemispheres, joined in the midline by the vermis
Divided into anterior, posterior and flocculonodular lobes
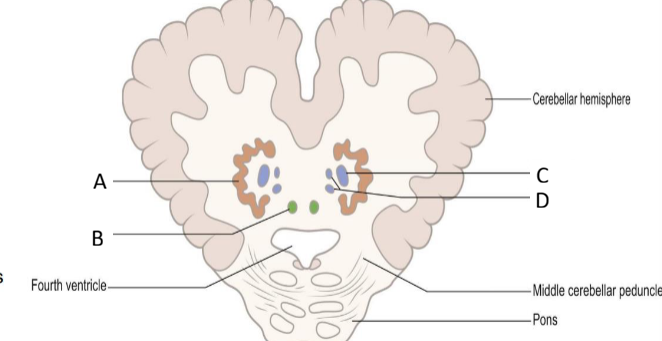
Name the different parts of the functional zone and their functions
Vermal zone - responsible for maintaining balance; major nucleus: fastigial nucleus
Paravermal zone - involved with skilled, volitional movements; major muclei: interposed nuclei
Lateral zones - responsible for regulating entire motor activity; major nucleus: dentate nucleus
Flocculonodular zone - coordinates eye movements and balance
Layers of the cerebellum from superficial to deep
Molecular layer contains: dendritic trees of the Purkinje cells, axons of granule cells, outer stellate cells, inner stellate cells
Purkinje cells layer contains: Purkinje cells that emerge inhibitory efferent pathway to the vestibular and cerebellar nuclei
Granular layer contains: granule cells and Golgi cells
** cerebellum efferent fibres
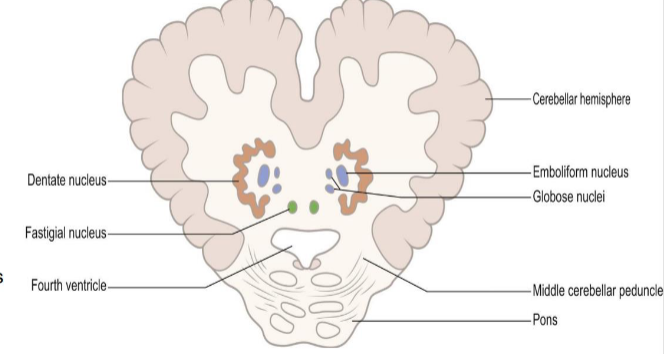
Function of Cerebellar nuceli
Fastigial nuclei:
receive spinocerebellar and labyrinthine afferents
project to the spinal cord and ventral thalamic nucleus
Globose & Emboliform nuclei (interposed nucleus)
sends interpositiorubrothalamic tract to the lateral thalamic nucleus and red nuclus
Dentate nucleus
receives corticopontocerebellar fibers
sends dentatorubrothalamic and dentatoolivary tracts
** Mnemonic: Don't Eat Greasy Food (Dentate, Embolform, Globose, Fastigial)
How does the cerebellum influence motor activity?
Via Cerebellar Loops:
Cerebrocerebellum (Dentatothalamic tract)
Vestibulocerebellum (Cerebellovestibular tract)
Spinocerebellum (Cerebellorubral tract (rubro=red))
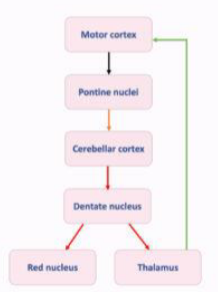
What does the Cerebrocerebellum (Dentatothalamic tract) do?
Carries information from the dentate nucleus through the superior cerebellar peduncle to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus
Planning of motor activity
Movements then executed via the corticospinal tract
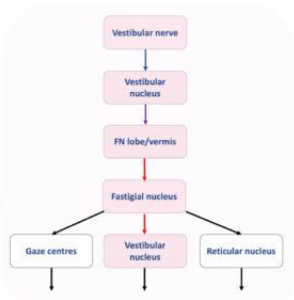
What does the Vestibulocerebellum (Cerebellovestibular tract) do?
Carries information from the fastigial nucleus to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus
Also sends fibres via the inferior cerebellar peduncle to the vestibular nuclei
Relayed to the periphery via the vestibulospinal tracts → posture
What does the Spinocerebellum (Cerebellorubral tract) do?
Carries information to the red nucleus which then transmits information to the inferior olive and then back again to the cerebellum → creating a feedback loop
** Red nucleus also communicated with the periphery via the rubrospinal tract
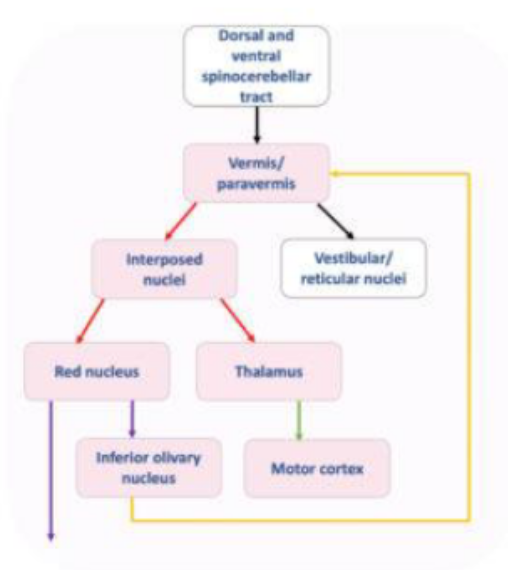
What does the Olivocerebellar (afferent) fibres join?
Arise from the olivary nucleus and decussate to reach the fibres of the opposite Raphe nucleus.
From here they pass onwards as internal arcuate fibres, through the inferior peduncle, and to the opposite cerebellar hemisphere
What does the Vestibulocerebellar (afferent) fibres join?
Joins the pontine tegmentum to the cerebellar cortex
What does the Reticulocerebellar (afferent) fibres join?
Originate at various levels of the reticular formation and mainly terminate in the vermis (which lies in the midline)
What does the Corticopontocerebellar tract (afferent) fibres join?
Connects the premotor areas to the contralateral cerebellar hemisphere via the pontocerebellar tract
What does the Trigeminocerebellar (afferent) fibres join?
Ascend via the inferior cerebellar peduncles and transmit proprioceptive information from the face to the cerebellum.
What does the Cerebellovestibular tract (efferent) fibres join?
This is an output from the cerebellum to the extensor muscles of the axial muscles which coordinate muscle tone adjustment
What does the Cerebelloreticular tract (efferent) fibres join?
This tract sends information to the motor circuits of the brain stems
What does the Corticonuclear tract (efferent) fibres join?
This connects the cerebral cortex to the brainstem and is functions for the motor function of the oculomotor nerve
What does the Cerebellothalamic tract (efferent) fibres join?
Arises from the superior cerebellar peduncle, arises from the cerebellar nuclei and decussates to terminate in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus
What does the Cerebellorubral tract (efferent) fibres join?
Sends information from the cerebellum to motor systems of the brainstem
Movement of information from the superior cerebral peduncle
Dentate nucleus part of cerebrocerebellar tract
Axons go to red nucleus or thalamus (contralateral) Dentothalamic pathway
Red nucleus can then connect to the thalamus (dentorubrothalamic pathway)
Thalamus to the motor cortex
Activate red nucleus can cross to contralateral side and activate flexor muscles (rubrospinal pathway)
Globose and emboliform nuclei → contralateral red nucleus then decussates activate LMN → muscles
Cerebellovestibular pathway = Purkinje fibres → directly stimulate vestibular nuclei – vestibular spinal tract (extensor) and medical longitudinal fasciculus → eye movements
Movement of information to the superior cerebral peduncle
Ventral spinocerebellar tract (proprioceptors below L2/3)
Rostral cerebellar tract cerevical spine and upper region
Tectocerebellar tract: visual and auditory → coordinate eye and head movements
Movement of information to the middle cerebral peduncle
Corticopontocerebellar fibres
Cortex→ pontine nuclei → cross over to other side → cerebellar cortex
The denothalamic or dentorubic pathway (superior cerebellar peduncle)
** biggest peduncle with only afferent fibres
Movement of information from the inferior cerebral peduncle
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract
Cuneocerebellar tract
Vestibularcerebellar tract
Oliovocerebellar tract
Reticulocerebellar tract
Movement of information to the inferior cerebral peduncle
Cerebellreticular
Cerebellovestibular
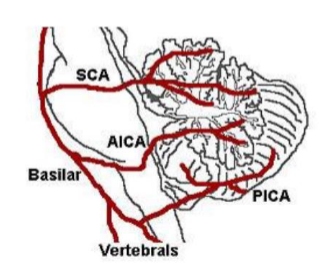
Blood supply to the cerebellum
Superior cerebellar artery (SCA), Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) → Branches of the basilar artery
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) → Branch of the vertebral artery
Movement of information by the Dorsal Spinocerebellar Tracts
C8→ L1/2
Periphery Goes into the spinal cord → dorsal root ganglion → lateral white column upwards → inferior peduncle → cerebellar cortex
Movement of information by the Ventral Spinocerebellar Tract
Below L1/2
Periphery → Dorsal root ganglion→ dorsal grey horn → crosses to contralateral side and ascends upwards → superior cerebellar pedicles → crossed to other cerebellum
Movement of information by the Cutancerebellar tract
C1-C8
Periphery → posterior grey horn → moves upwards ipsilaterally → accessory cuneate nucleus → inferior cerebellar peduncles (extremal arcuate fibres) → cerebellar cortex
Movement of information by the Spino-olivary tract
Periphery → dorsal root ganglion→ crosses over → moves upwards → Inferior olivary nuclei in medulla → cross over again → inferior cerebellar peduncle → cerebellar cortex
Symptoms of cerebellar disease
Vertigo
Ataxia
Nystagmus
Intention tremor
Speech (Slurred, scanning, staccato)
Hypotonia
Exaggerated broad based gait
Dysdiadochokinesia/Dysmetria
(impaired ability to perform rapid, alternating muscle movements/ brain can't accurately judge the distance, speed, or force for coordinated movements)