lecture exam 2 (chapters 4-6)
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
3 cartilage types
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage location
ends of bones, nose, and rings in walls of respiratory passages
elastic cartilage location
external ear, epiglottis
fibrocartilage location
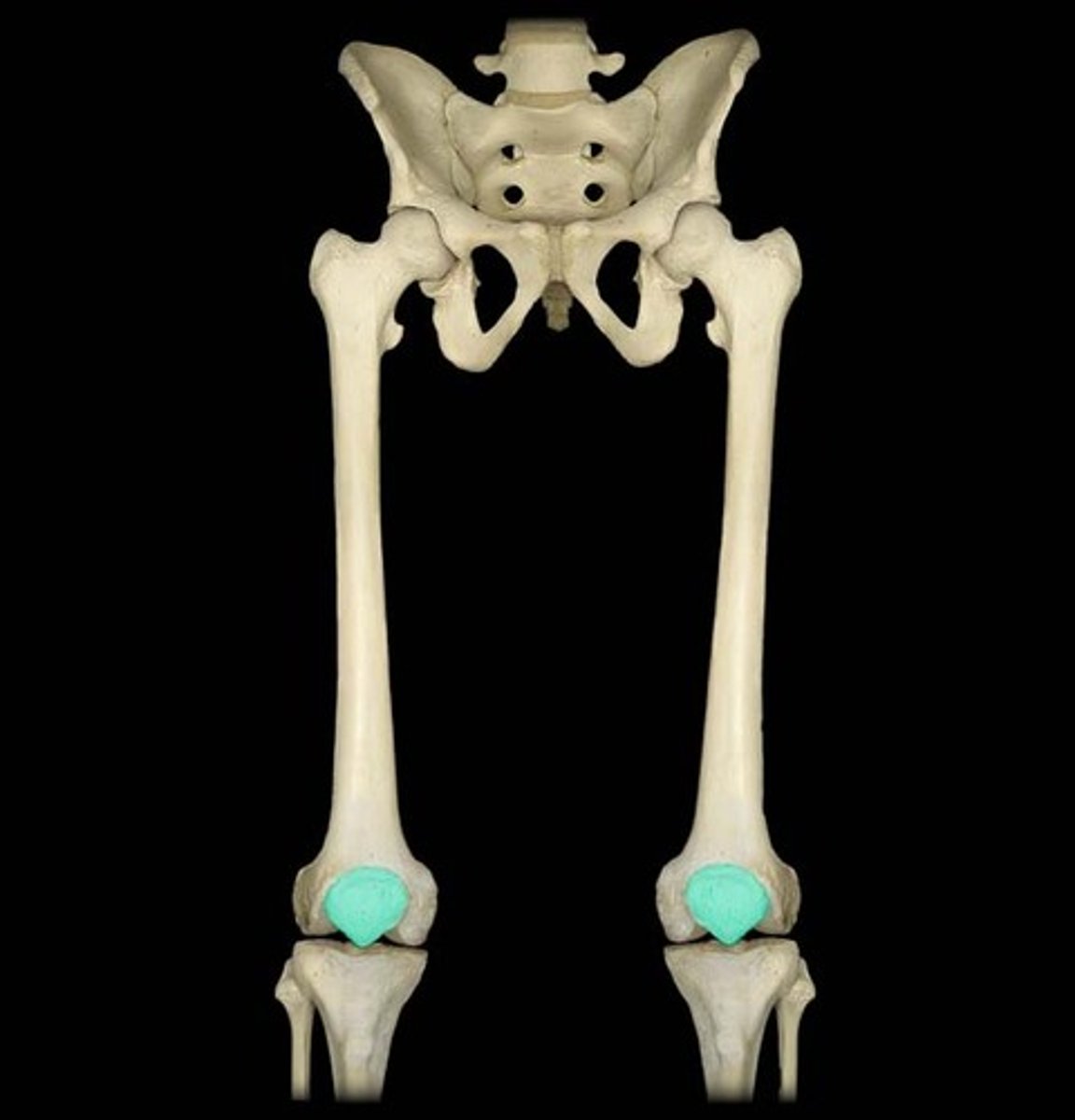
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint
periosteum function
covers outer surfaces of bones
Periosteum consists of
outer fibrous and inner cellular layers
interstitial growth
growth in length
appositional growth
growth in width
osteogenesis and ossification
bone formation
-the process of replacing other tissues with bone
Endochondral ossification
Process of transforming cartilage into bone.
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from a fibrous membrane
- (flat bone) (clavicle)
chondral
cartilage
two hormones in blood regulation of Ca++
-Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
-Calcitonin
parathyroid hormone (main regulatory hormone)
-stimulation of osteoclast
-increase in bone formation, small intestine Ca++ absorption, and kidney Ca++ reabsorption
Calcitonin
- stimulation of osteoblast
-increase of bone formation, decrease in small intestine Ca++ absorption, decrease in kidney Ca++ reabsorption
bone healing (four stages)
1. hematoma
2. Fibrocartilaginous callus formation
3. Boney Callus formation
4. Bone Remodeling
hematoma
a solid swelling of clotted blood within the tissues.
fibrocartilaginous callus formation
- Phagocytic cells clear debris
- Osteoblasts begin forming spongy bone within 1 week
-Fibroblasts secrete collagen fibers to connect bone ends
-Mass of repair tissue now called fibrocartilaginous callus
Boney callus formation
cartilage is replaced with bone material and bone strengthens
bone remodeling
ongoing replacement of old bone tissue by new bone tissue
factors that affect bone healing
age, bone type, severity of break, bone health
compact bone
dense, hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the periosteum
spongy bone
The layer of bone tissue that has many small spaces and is found just inside the layer of compact bone.
Osteoporosis
low-density bone
-osteoclast > osteoblast
underlining causes
1. low calcium ion
2. low vitamin D
bone growth depends on
1. minerals (calcium ion, phosphate)
2. vitamins (A, C, D, B12, K)
vitamin A
stimulates osteoblast activity
vitamin C
needed for synthesis of collagen
vitamin D
helps absorb calcium
Vitamin B12 and K
required for synthesis of bone proteins
red bone marrow
(in spongy bone)
-blood vessels
-supplies nutrients to osteocyte
yellow bone marrow
(in spongy bone)
-stores fat
Osteocytes
mature bone cells, maintain the protein and mineral content of the matrix
osteoblast
bone building cell
osteoclasts
break down bone
osteoprogenitor cells
bone stem cells, divides to produce osteoblast
assist in fracture repair
Structure of Long Bone: Diaphysis
Tubular shaft that forms the axis of long bones
Composed of compact bone that surrounds the medullary cavity
Structure of Long Bone: Epiphysis
Wide part at each end
Articulation with other bones
Mostly spongy (cancellous) bone
Covered with compact bone (cortex)
Structure of Long Bone: Metaphysis
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet
Structure of Flat Bone
resembles a sandwich of spongy bone between two layers of compact bone
Bone Matrix
2/3 calcium phosphate, 1/3 collagen fibers
osteon
structural unit of compact bone
central canal (haversian canal)
canal that houses blood vessels located at the center of the osteon
lamellae
rings around the central canal, sites of lacunae
Lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
Function and components of skeletal system
Supports and protects tissues; stores minerals; forms blood cells
Bones, Cartilages, and Joints, Ligaments, Bone Marrow
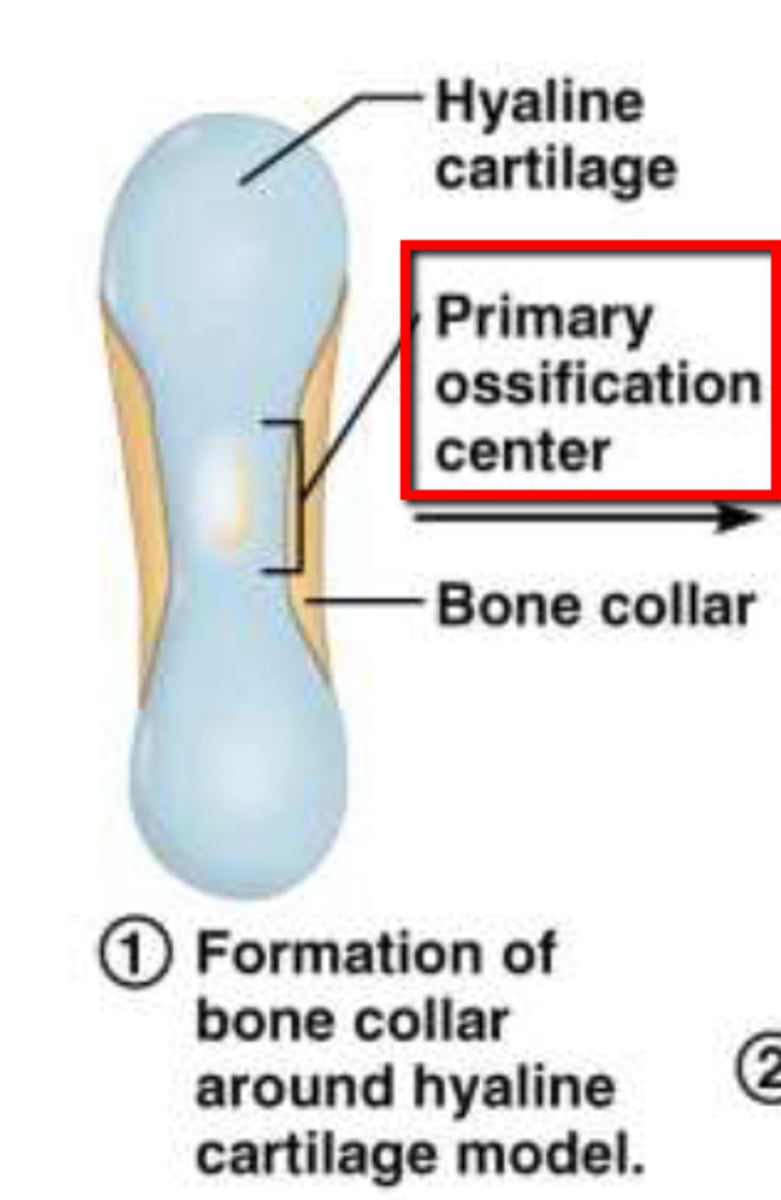
primary ossification center
region, deep in the periosteal collar, where bone development starts during endochondral ossification
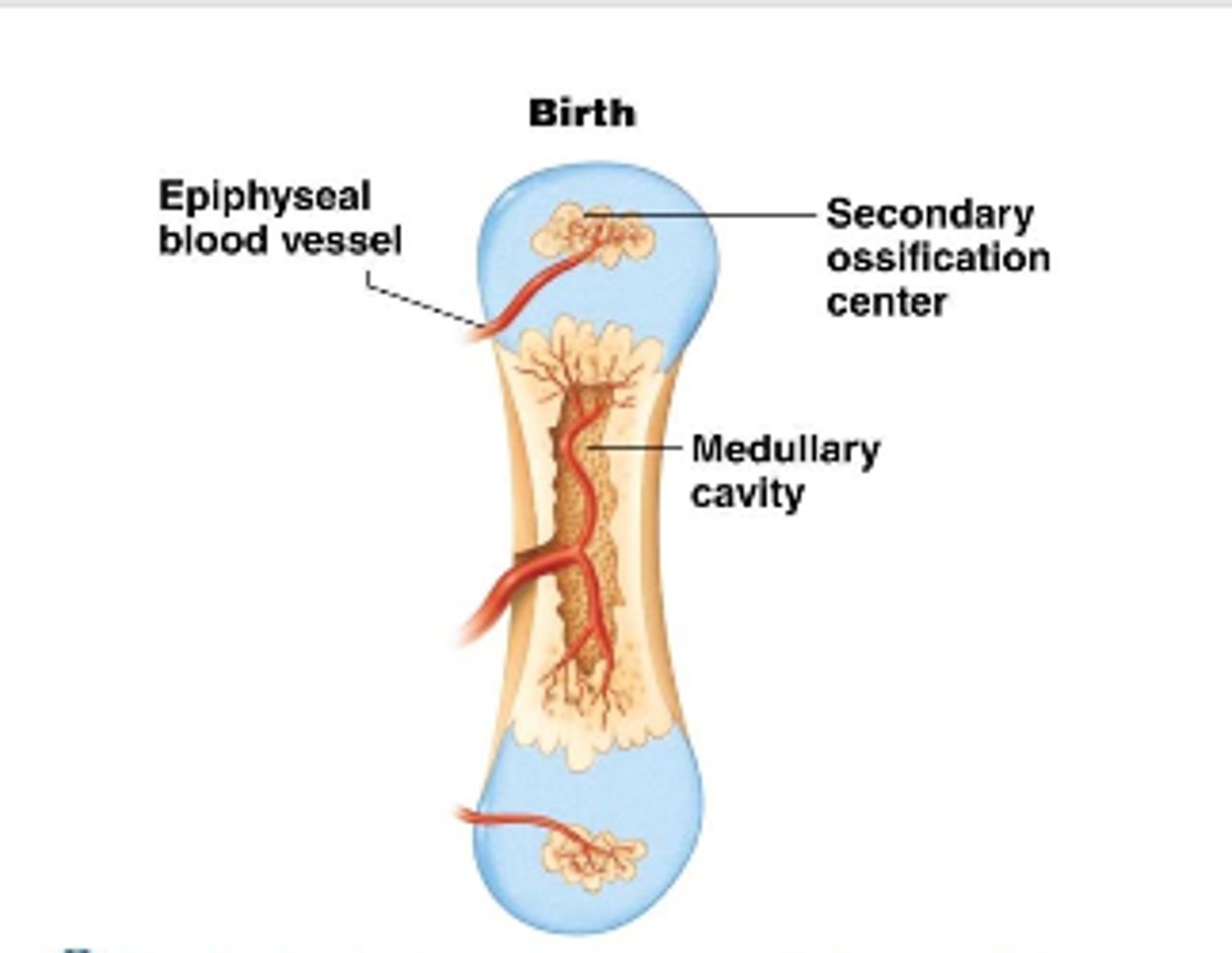
secondary ossification center
this develops in the epiphyses of bone during endochondral ossification
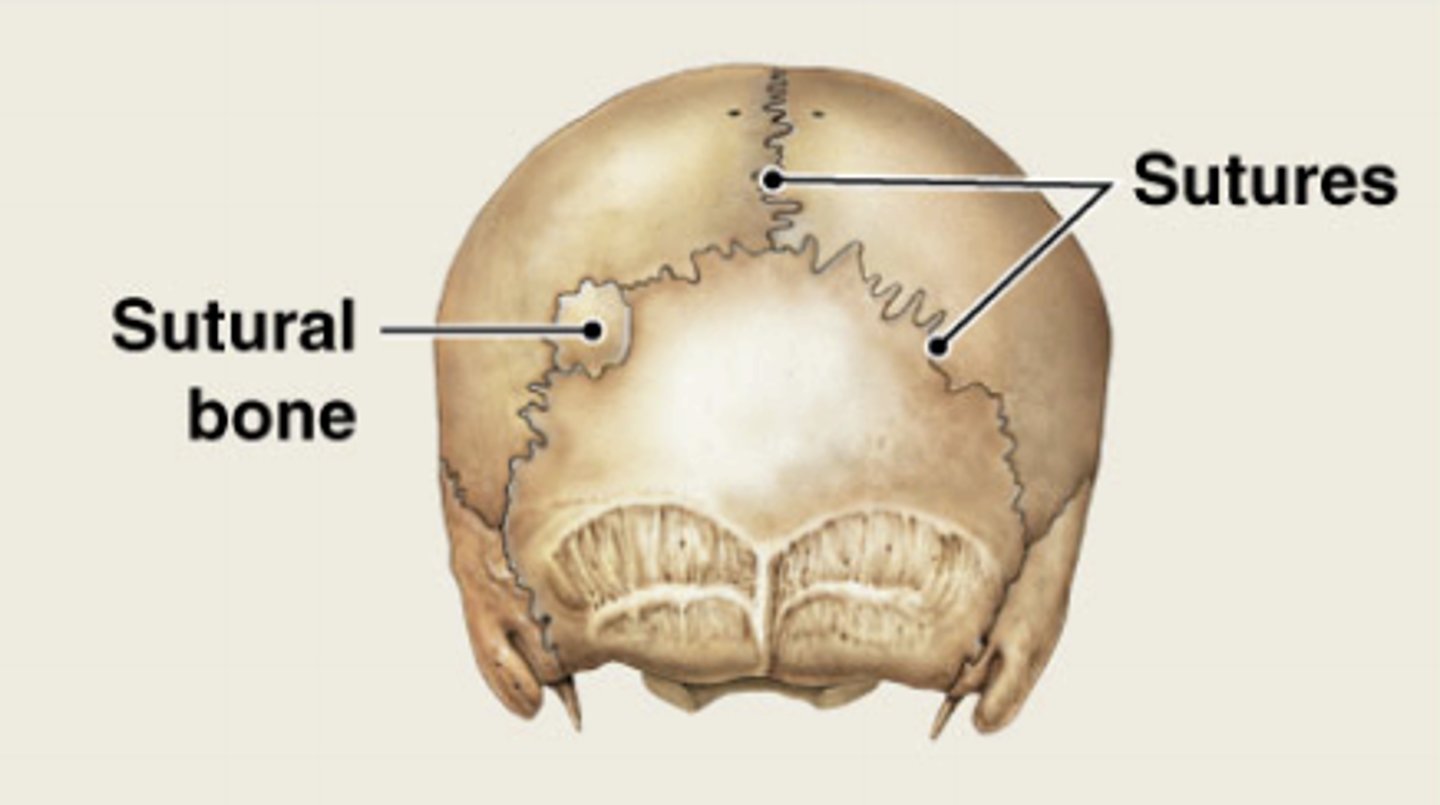
sutral bones
small, flat, oddly shaped bones found between the flat bones of the skull
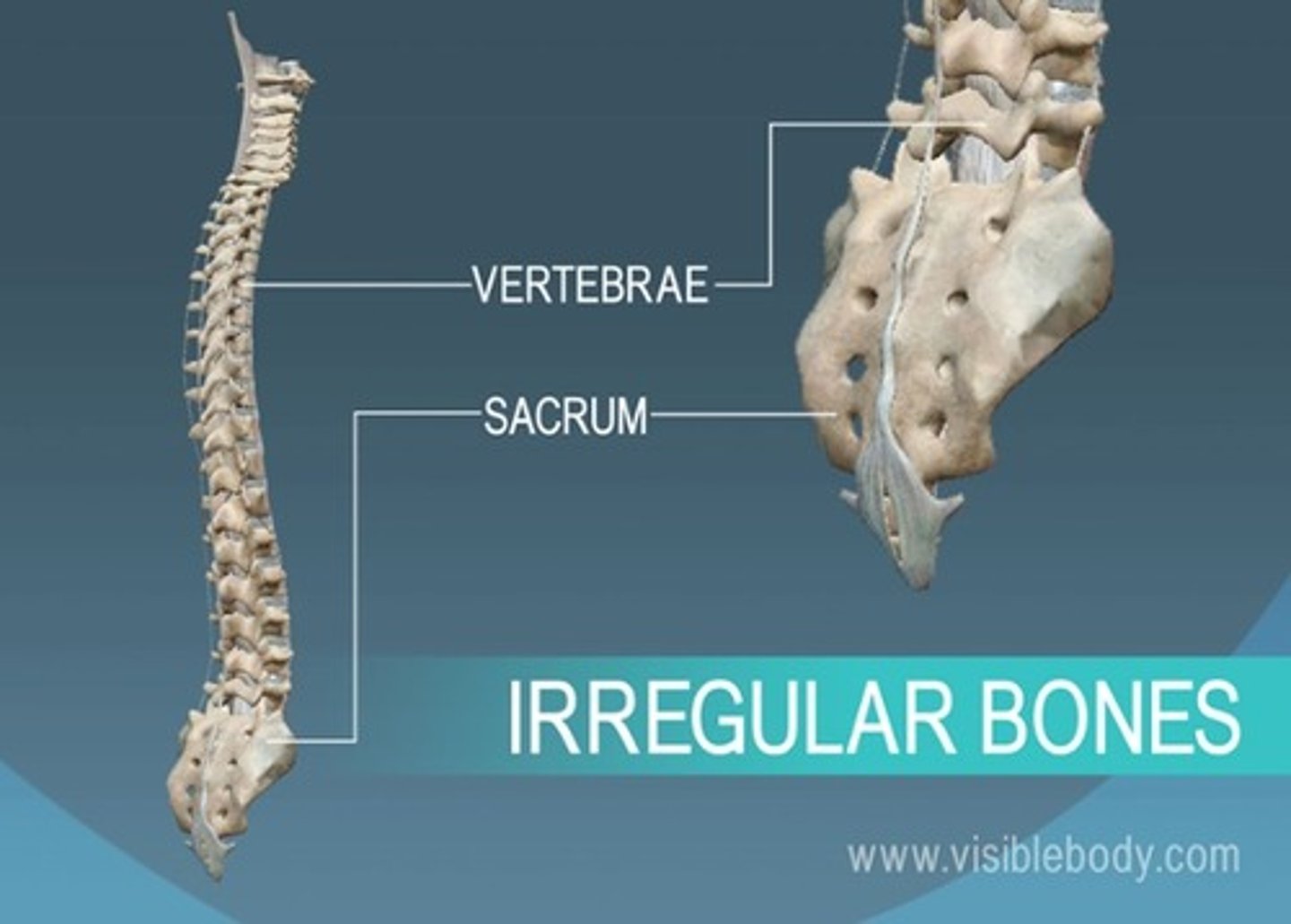
irregular bones
vertebrae and facial bones
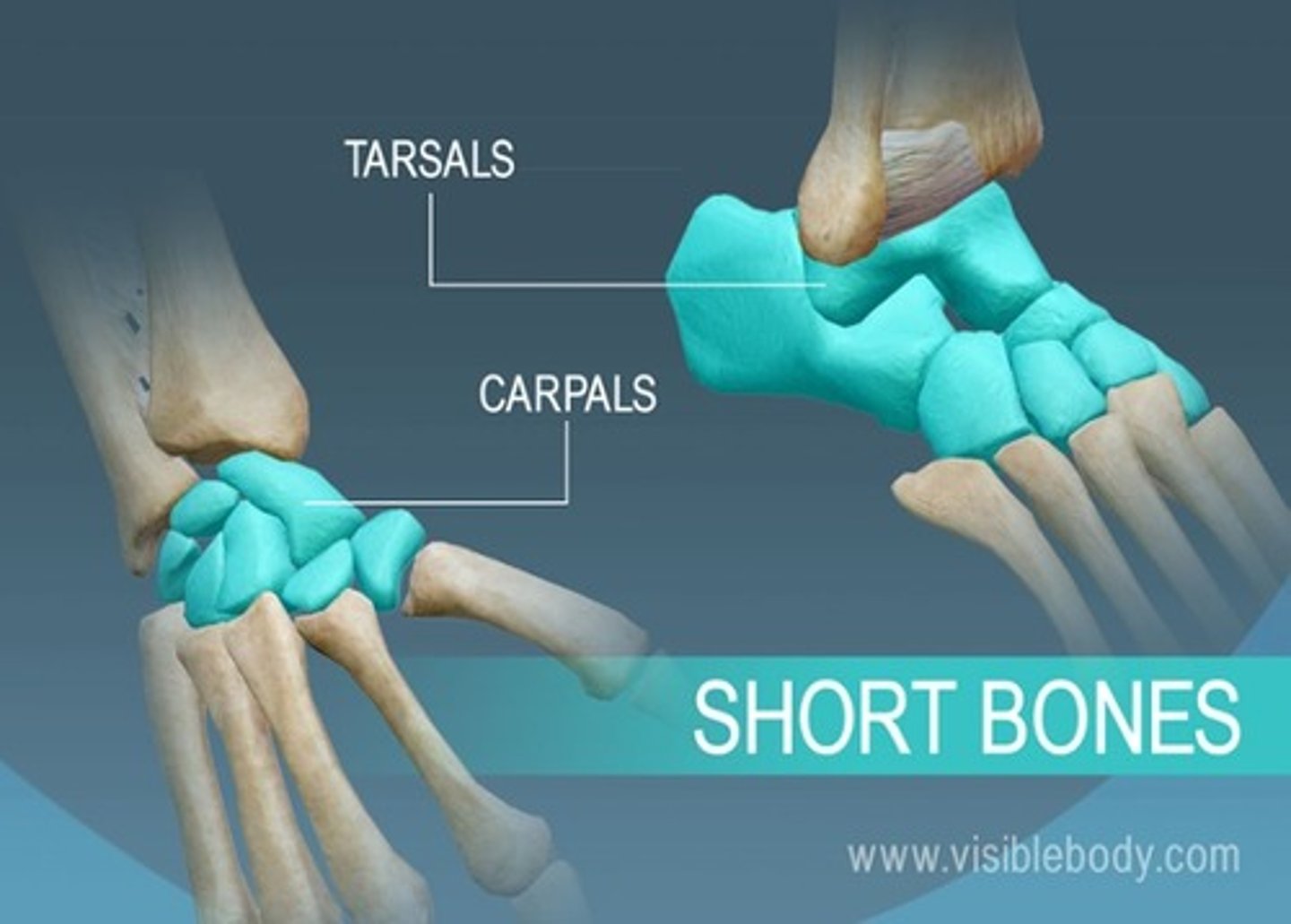
short bones
carpals and tarsals
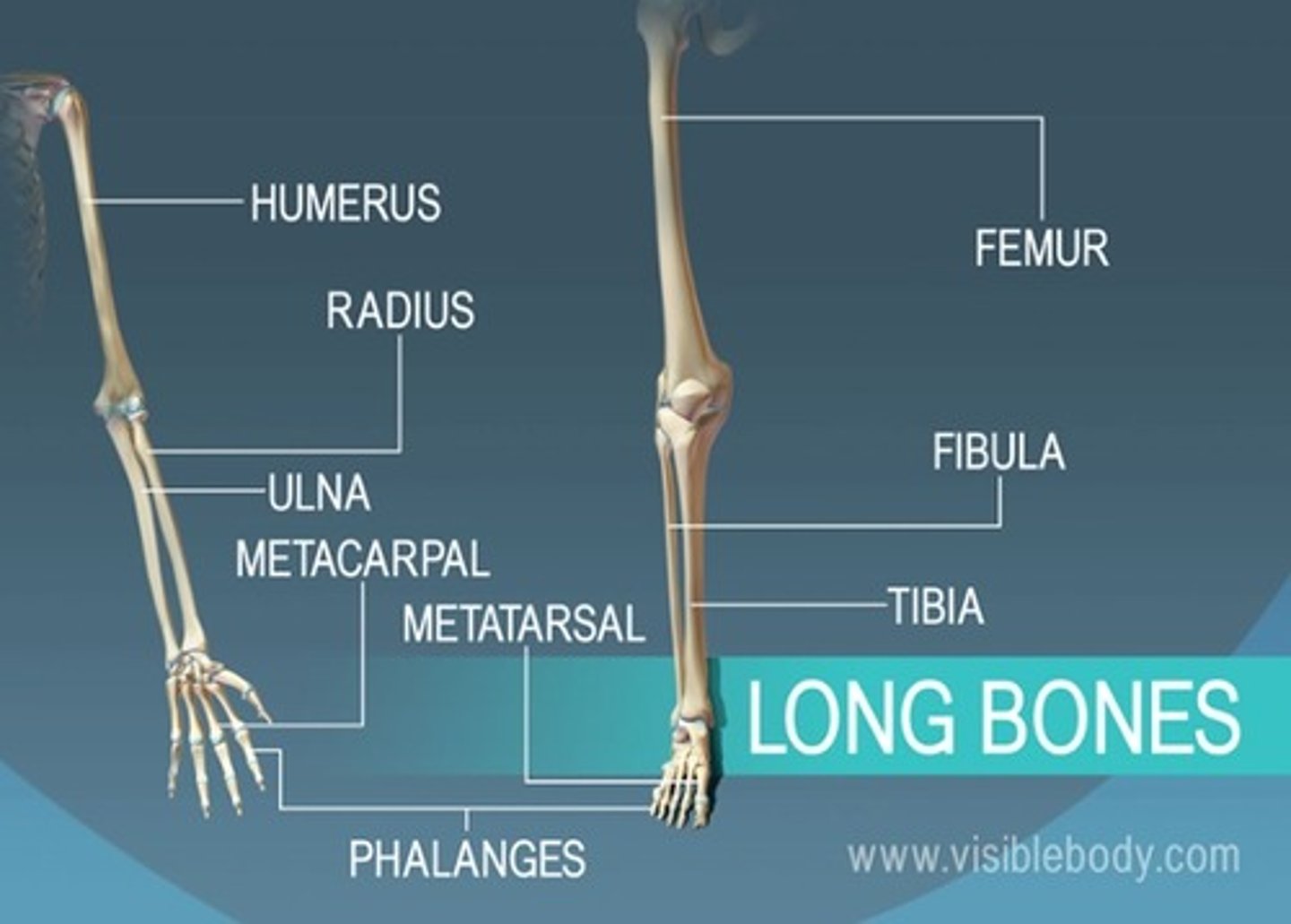
long bones
bones of the arms and legs
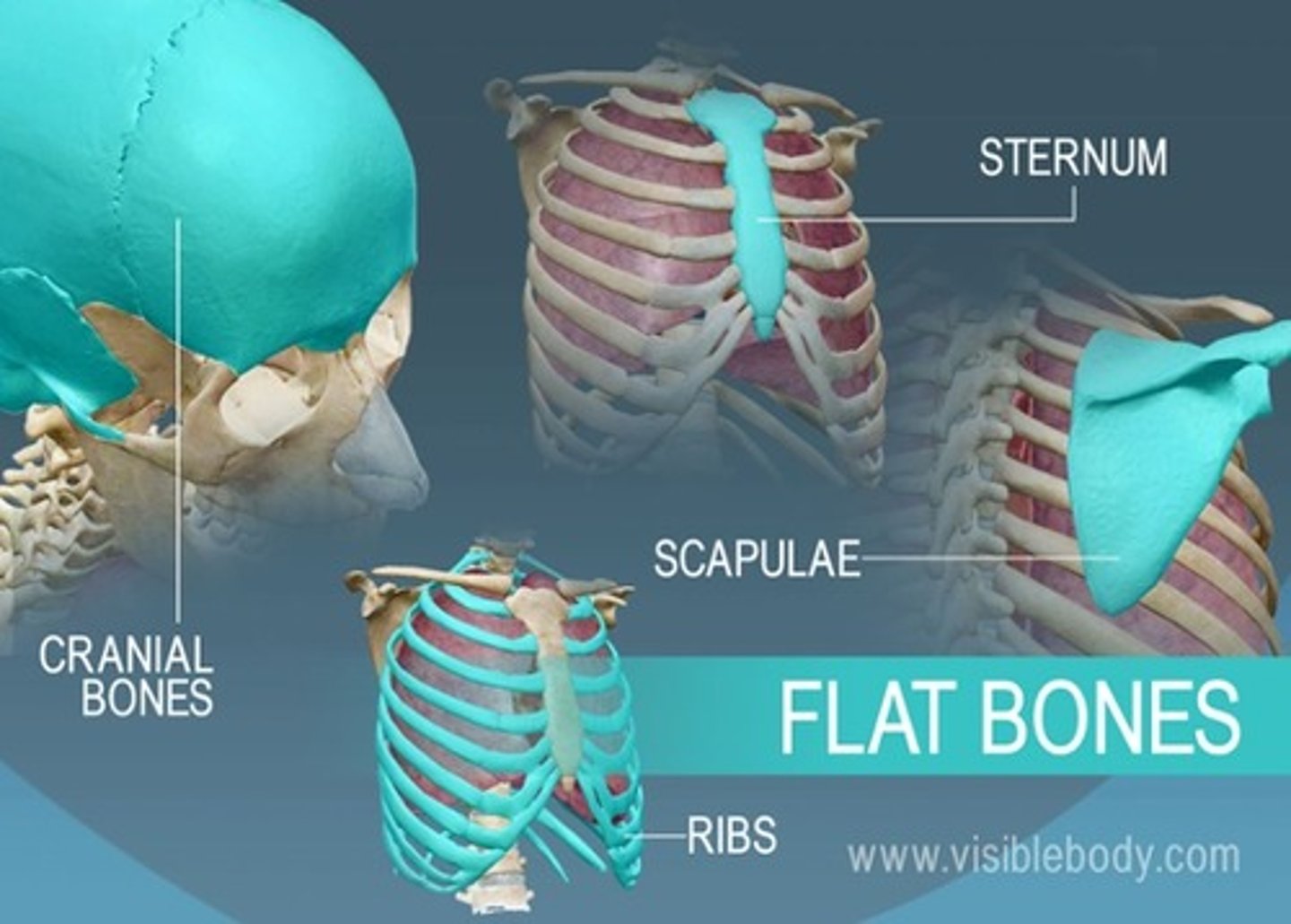
flat bones
bones of the ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull
sesamoid bones
patella
thin skin vs thick skin
Thin Skin
-cover most of body
-has glands & hair follicles
- 4 layers in epidermis
Thick Skin
-only on palmar or plantar skin
-no hair follicles
-abundant eccrine sweat glands
-5 layers in epidermis(extra layer stratum lucidum)
-epidermal ridges
stratum basal
Cells undergo rapid mitosis; the Deepest layer of the epidermis.
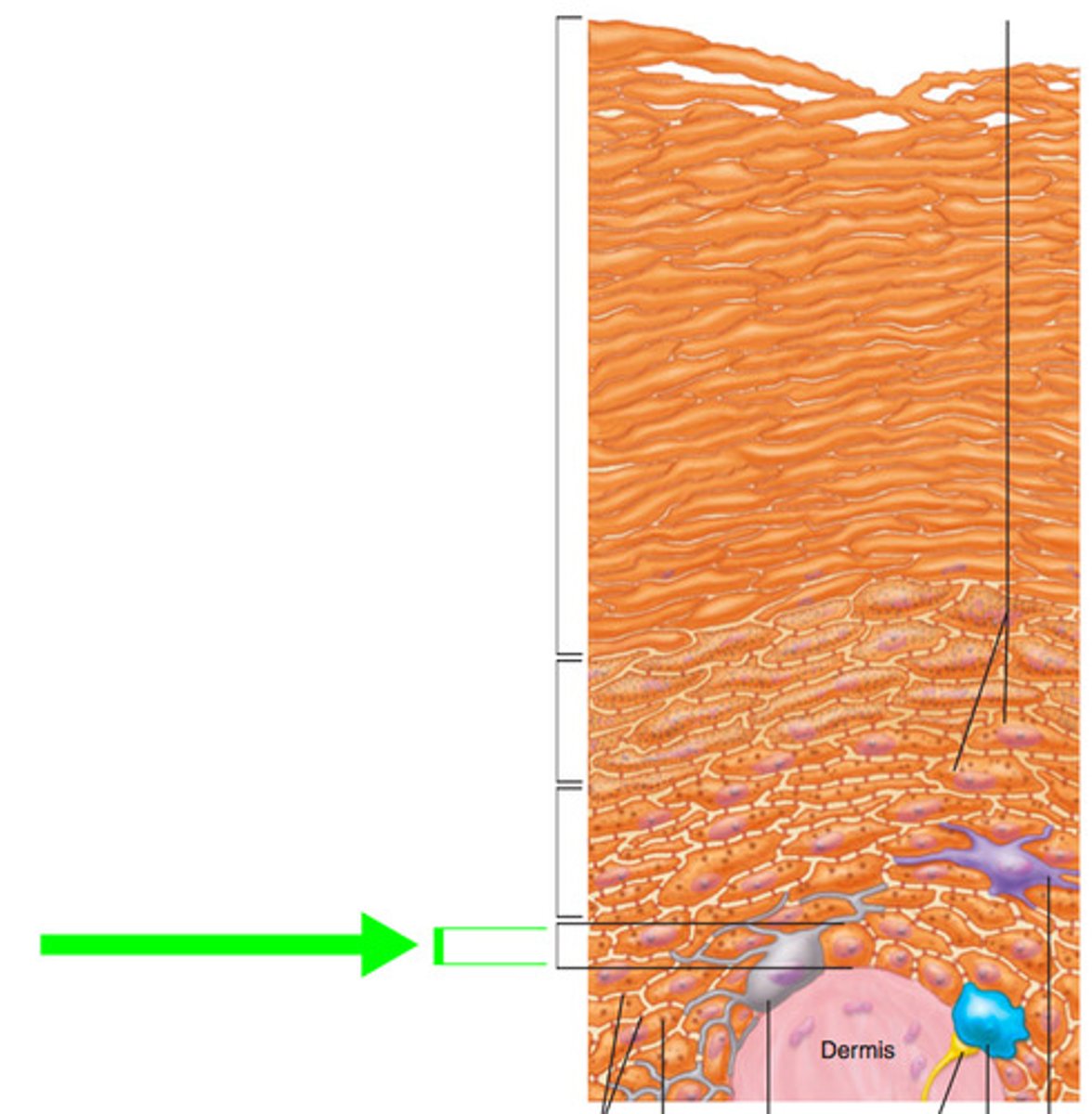
stratum spinosum
(little bit of mitosis) some cell division
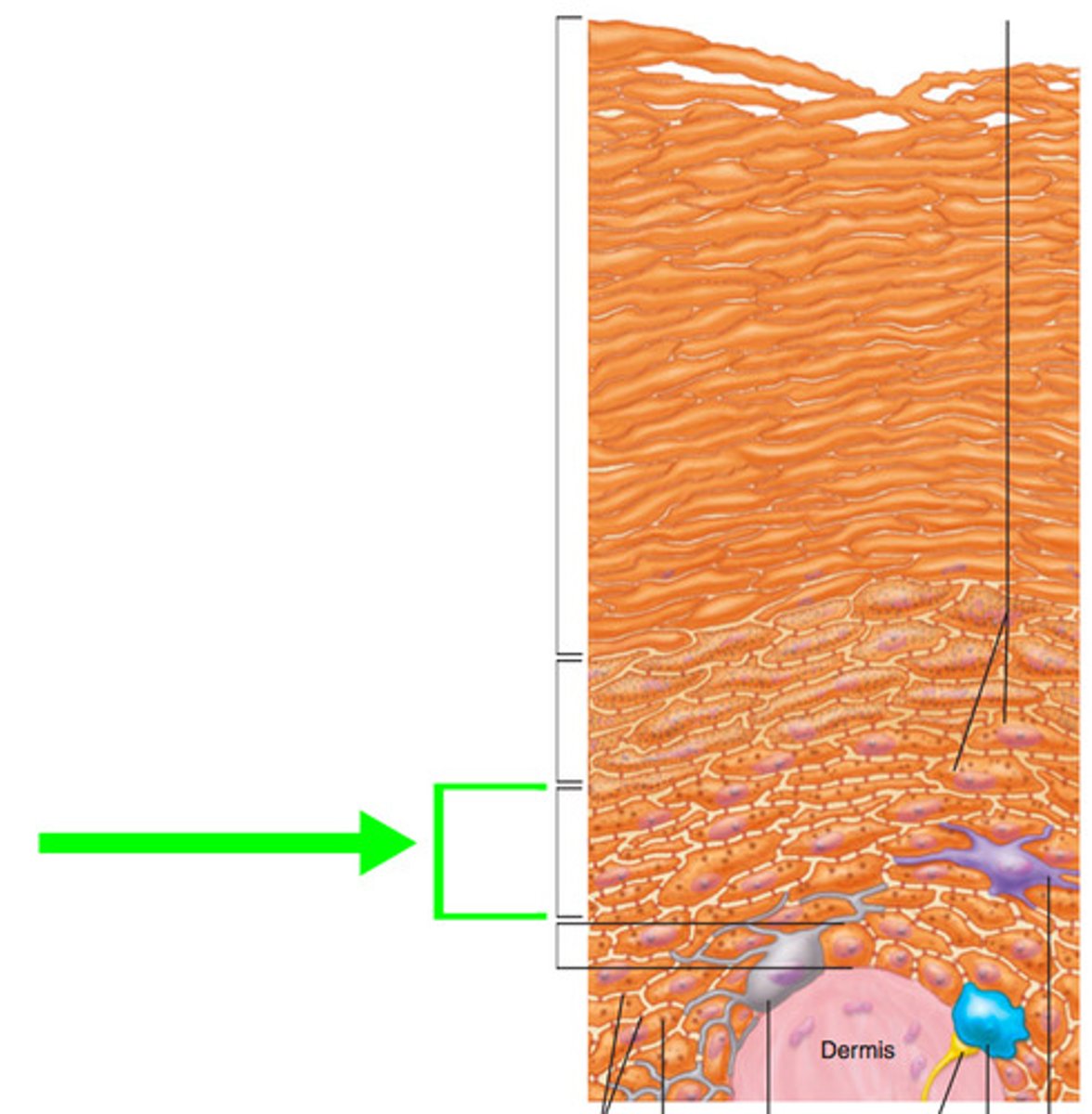
stratum granulosum
apoptosis (program cell death) becomes denucleated
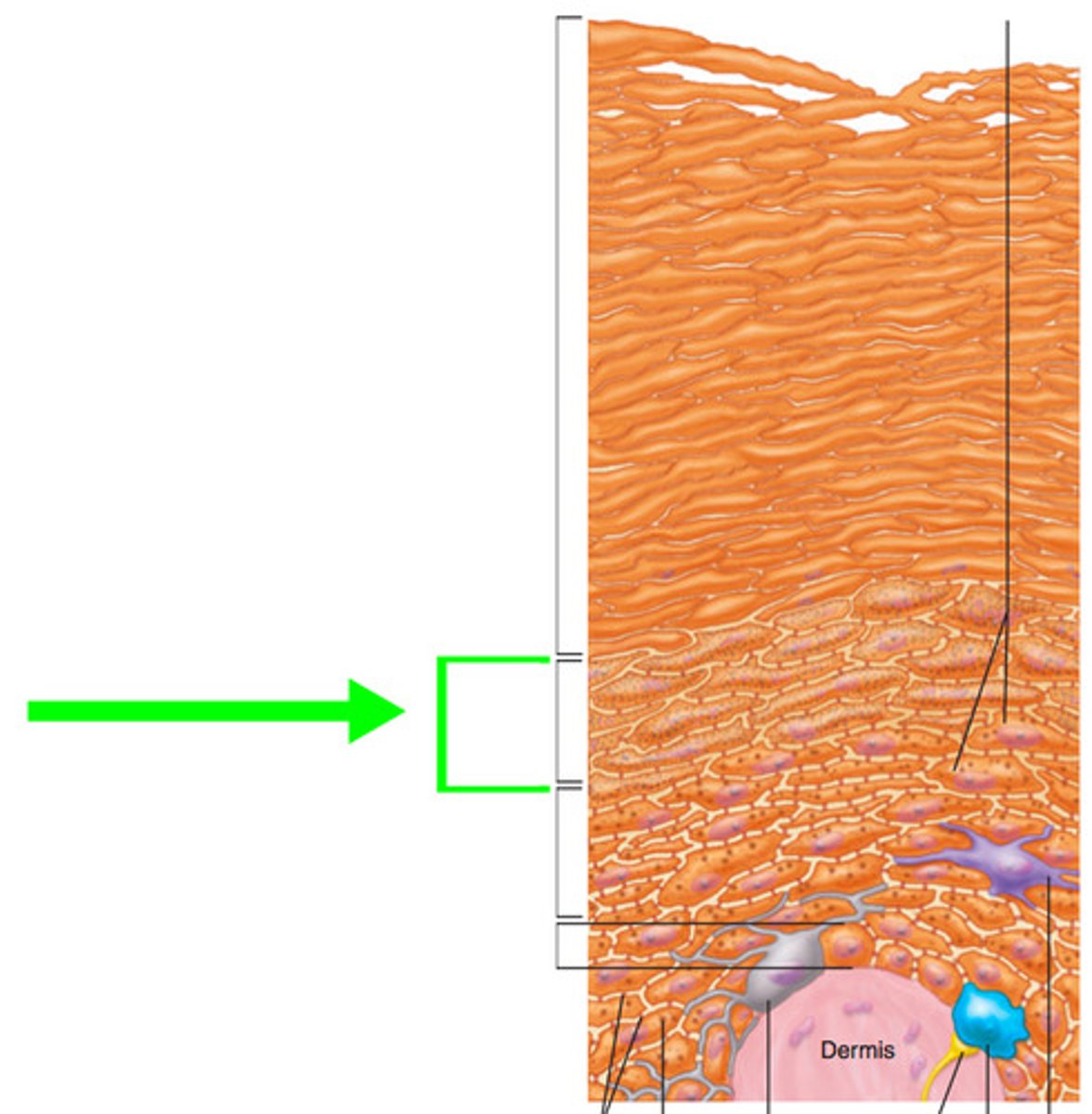
Statum Lucidum
(luci=clear) only in palms, fingertips, soles, dead, flat, clear cells
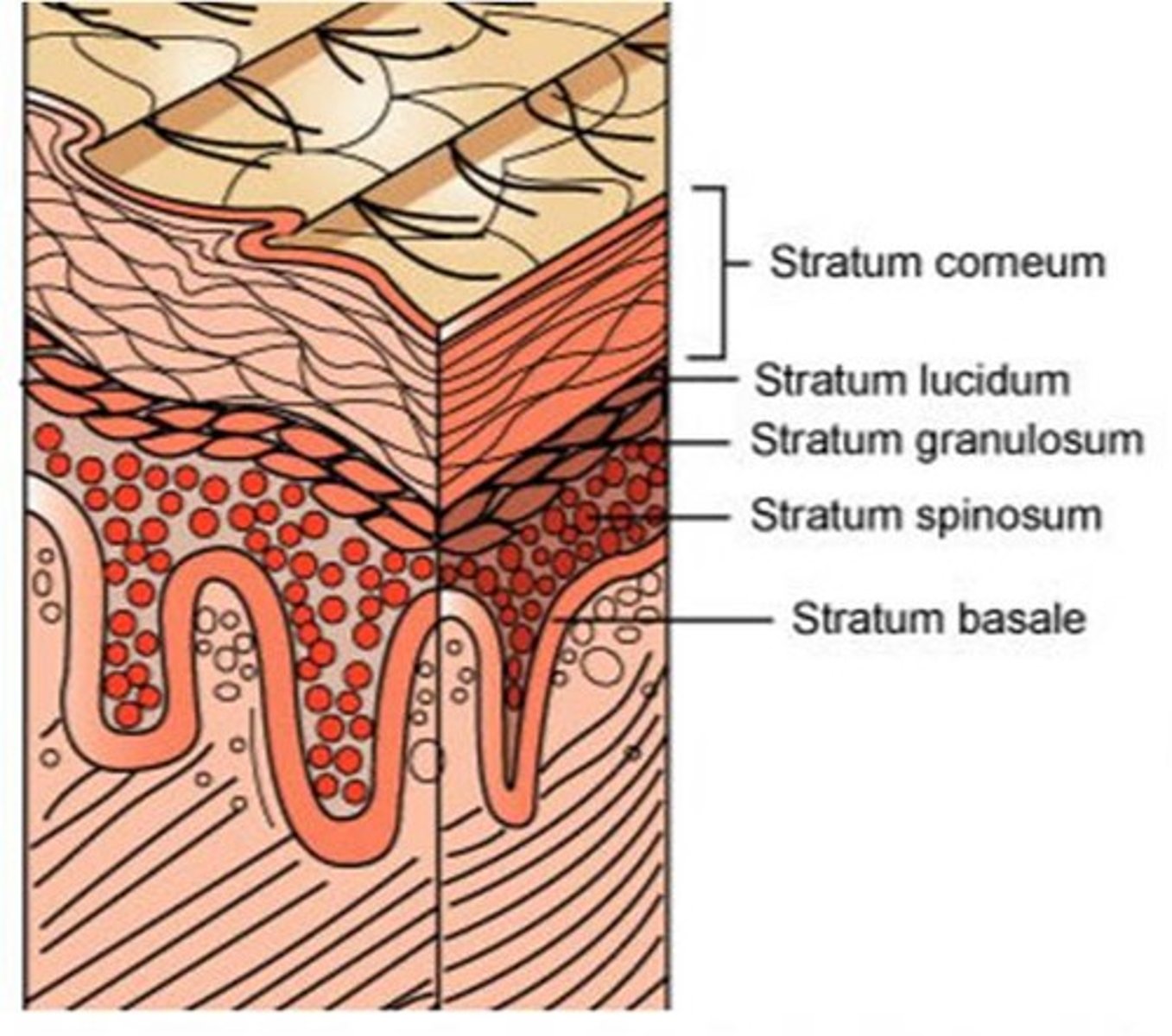
stratum corneum
toughest layer (most superficial layer) least protected layer by melanin
1st degree burn
Only the epidermis (red, painful, and edema)
2nd degree burn
epidermis and part of dermis (blistered)
3rd degree burn
Full thickness damage through skin into nerves and muscles
function and components of skin
-resistance to trauma, infections, waterproofing, uv radiation
(keratin, acid mantle)
two principle parts:
-epidermis, and dermis
ceruminous glands
modified sweat glands, located in external ear canal, secretes cerumen (earwax)
-protects eardrum
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
eccrine sweat glands
-all over the body
-aid in temperature control (Vitamin C)
-secrets water, salt, wastes such as urea and uric acid
Appcrine sweat glands
-anywhere with hair growth
-produce an odor in response to stress
-groin, anal, axilla, areola regions
basal cell carcinoma
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer; stratum basal cells proliferate and invade the dermis and hypodermis
squamous cell carcinoma
(prolong sunlight exposure)
-arises from keratinocytes of um
-most common in ears, scalp, and lower lip
-rapid growth, metastasizes
-radiation therapy
melanoma
The most serious form of skin cancer
-highly metastatic
-resistant to chemotherapy
Carotene
the yellow pigment of the skin
Oxyhemoglobin
reddish pigment of the skin
(100% saturated by oxygen)
Melanin
a dark brown to black pigment occurring in the hair, skin, and iris of the eye in people and animals. It is responsible for tanning of skin exposed to sunlight.
Keratinocytes
The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin.
(makes glycoprotein)
Macrophages
immune cells
Merkel cells
touch receptors in the skin
-located in the deepest layer of epidermis
Pacinian corpuscles
respond to deep pressure and vibration
Meissher's corpuscles
respond to light touch
Ruffini
respond to heat
Bulbs of Krause
respond to cold
keratinocyte, melanocyte, Langerhans cell, Merkel cell
four types of cells within epidermis
ground substance
unstructured material that fills the space between the cells and contains the fibers
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities.
(GI tract, kidney, glands)
connective tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
(bones, tendons, flat and other soft padding tissue)
muscle tissue
A body tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move.
(skeletal, cardiac, smooth)
nervous tissue
A body tissue that carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body.
(brain, spinal card, and nerves)
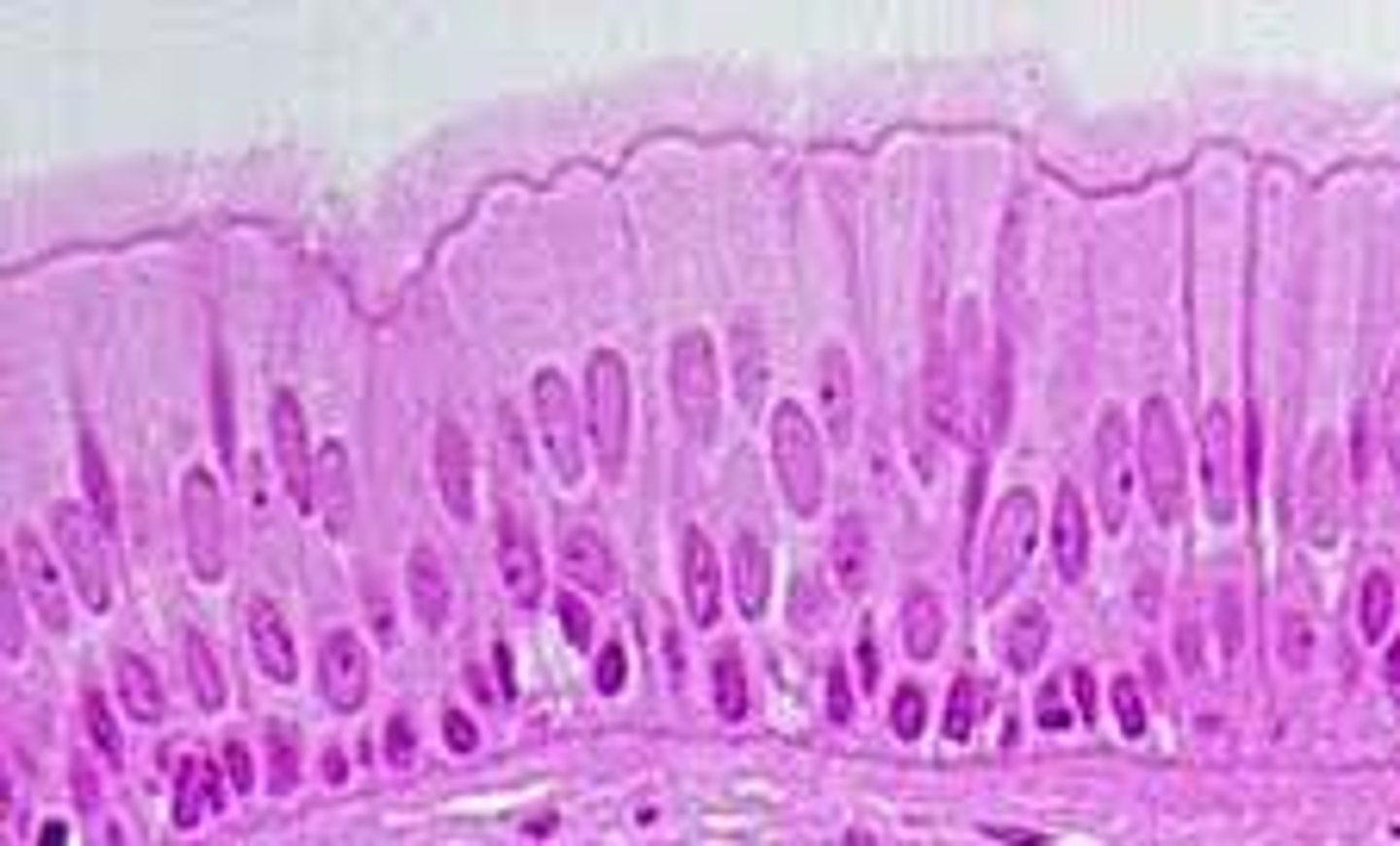
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
number of layers: single layer
location: respiratory system
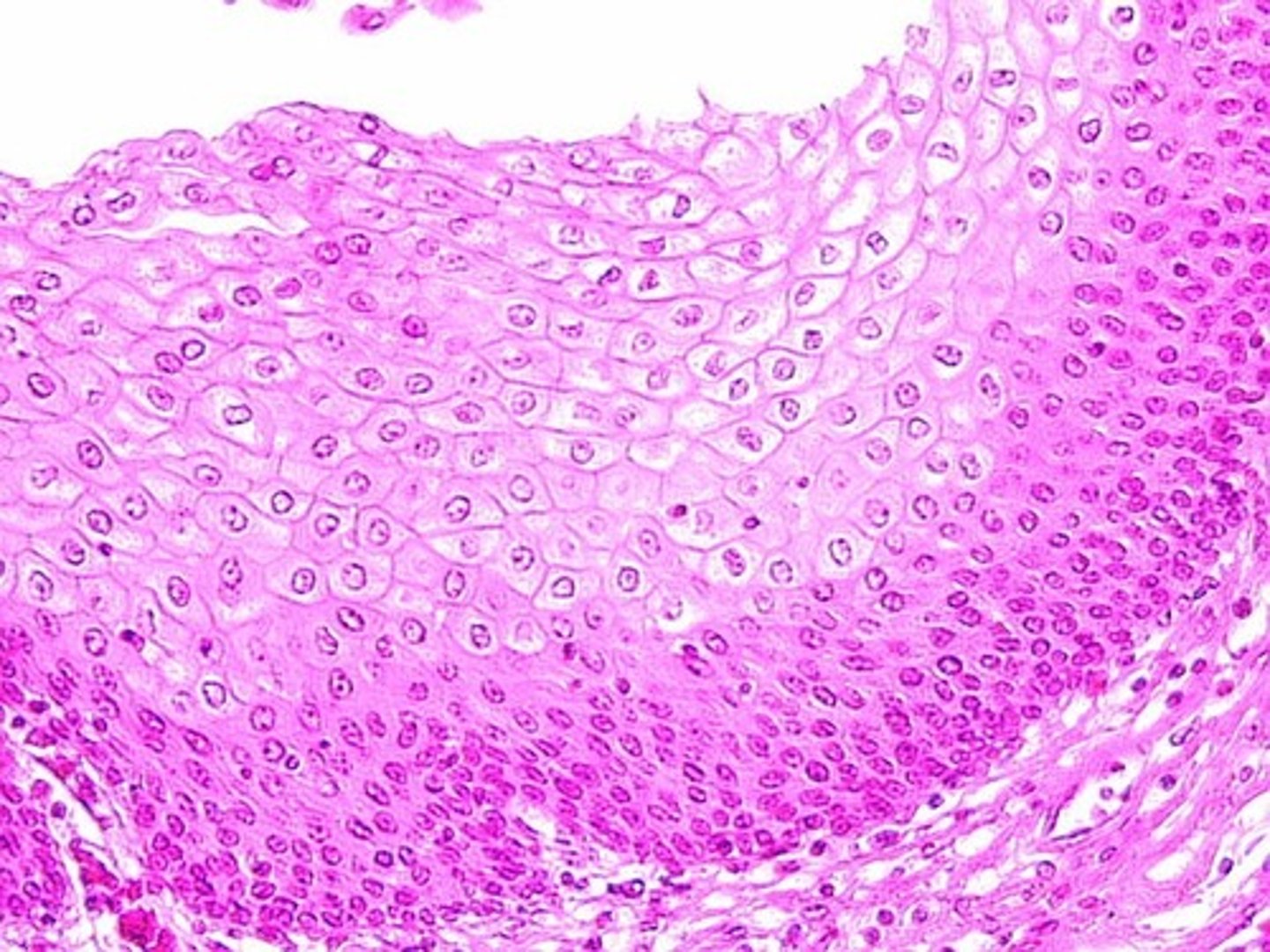
stratified squamous epithelium
number of layers: two or more layers
location: esophagus, mouth, and vagina
stratified columnar epithelium
number of layers: multiple
location: some sweat and mammary glands
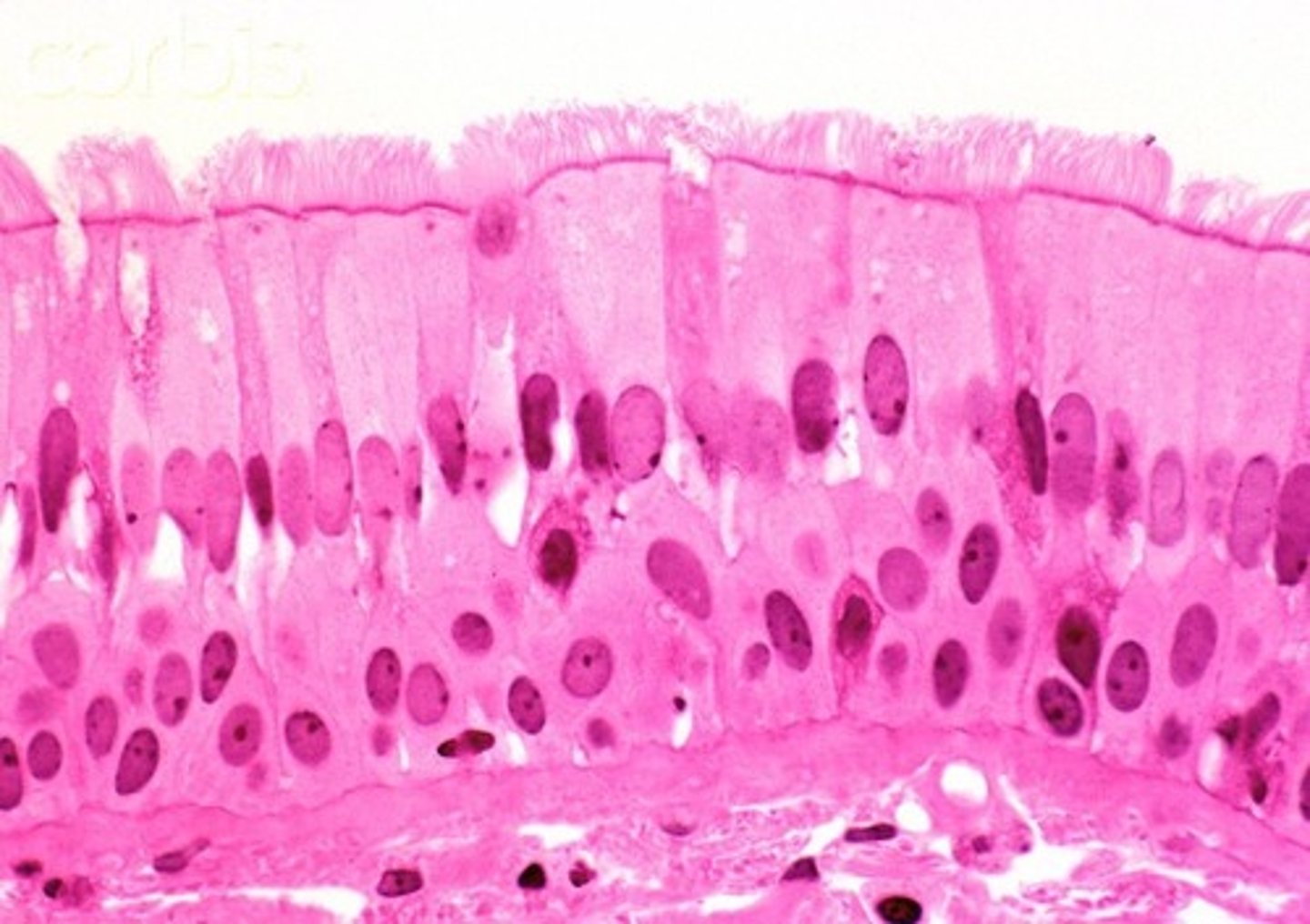
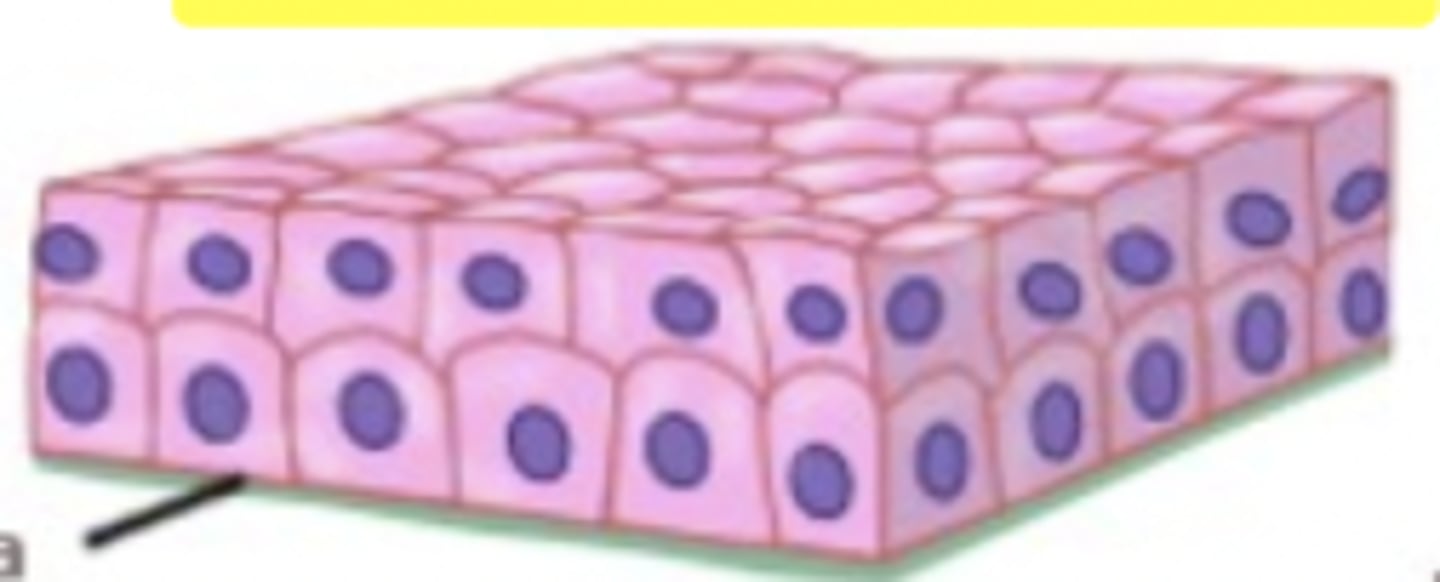
stratified cuboidal epithelium
number of layers: 2-3
location: Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
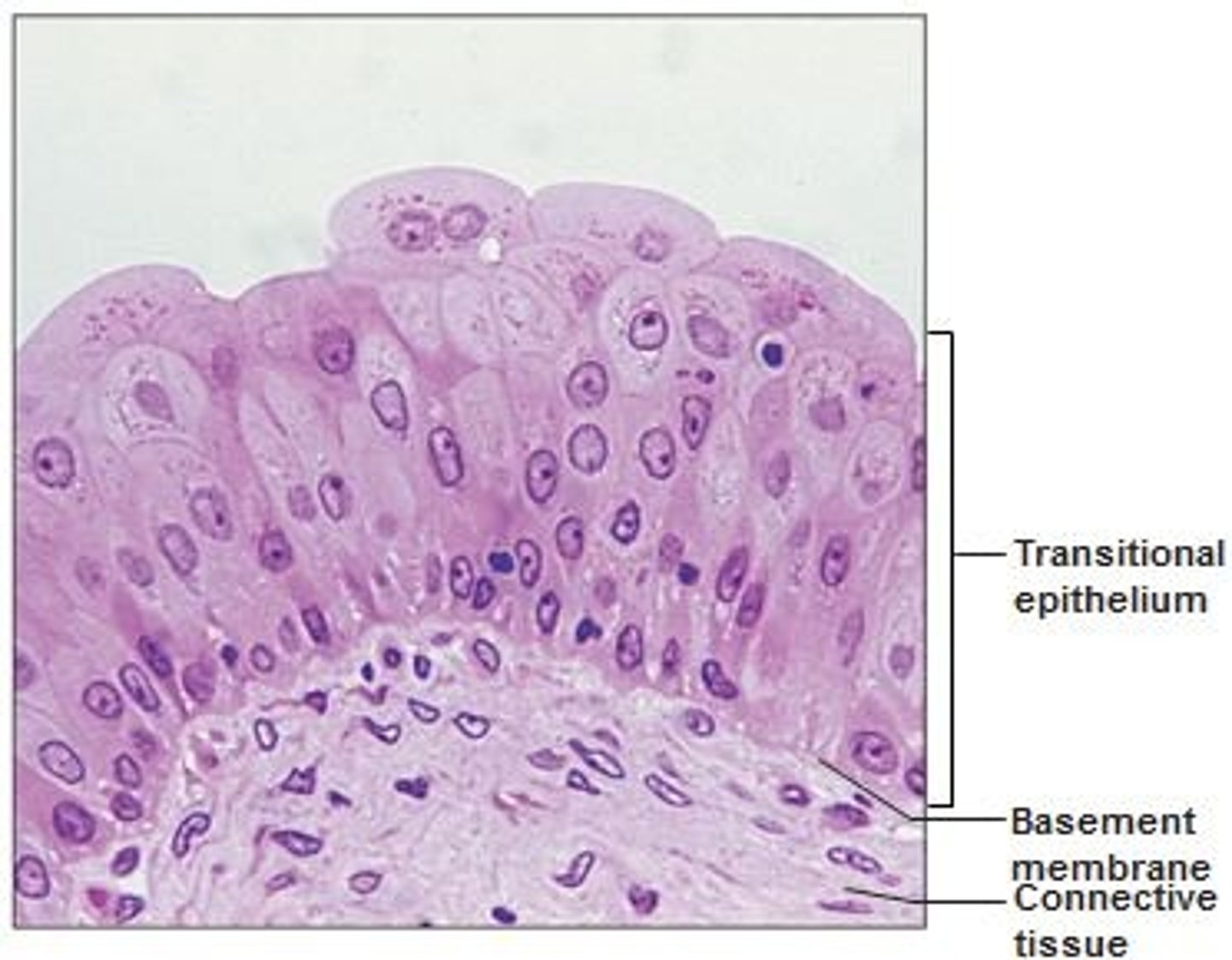
transitional epithelium
number of layers: 3-4
location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
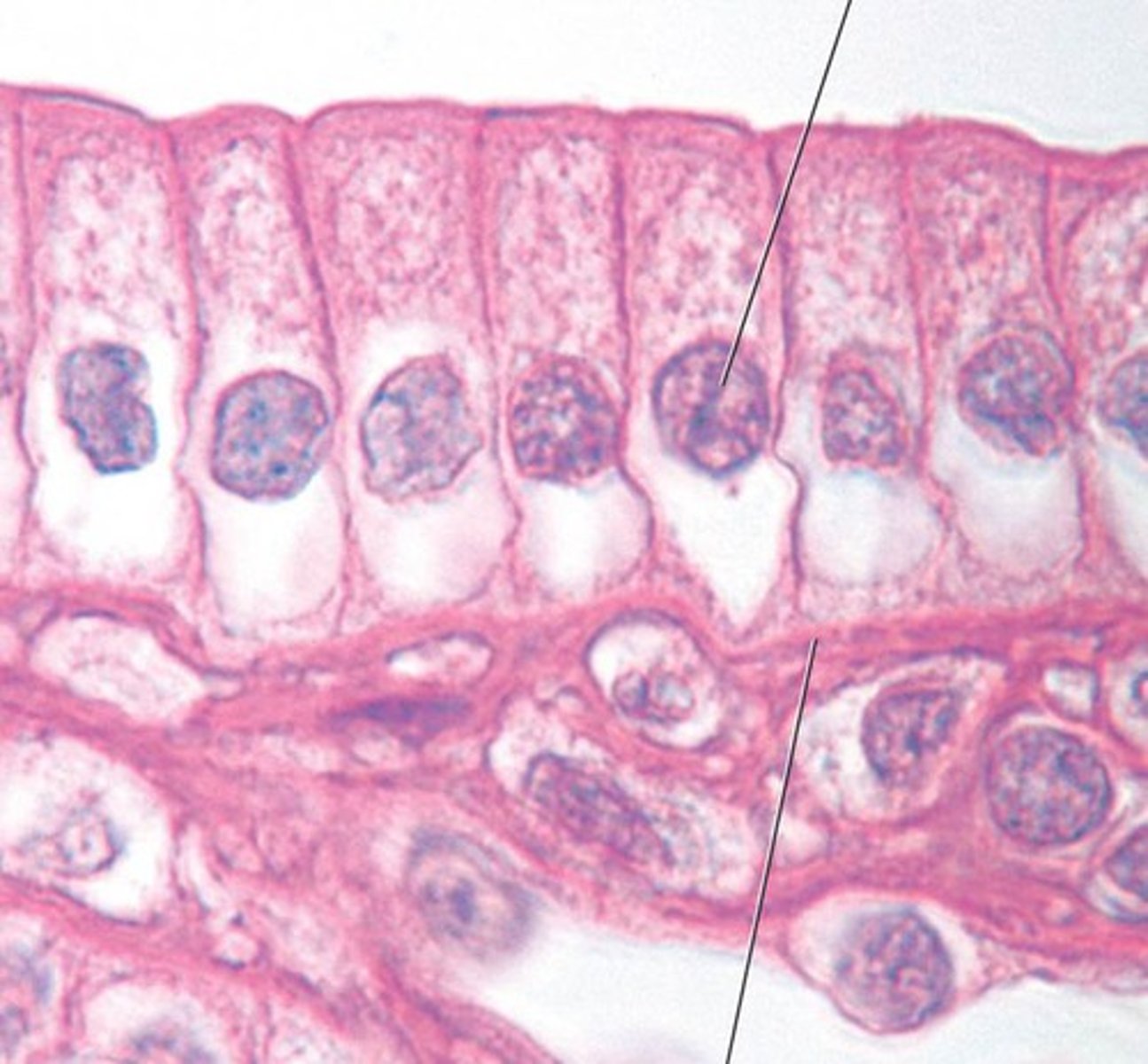
simple columnar epithelium
number of layers: single (1)
Location: digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), gallbladder, small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
simple cuboidal epithelium
number of layers: single (1)
location: Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface.
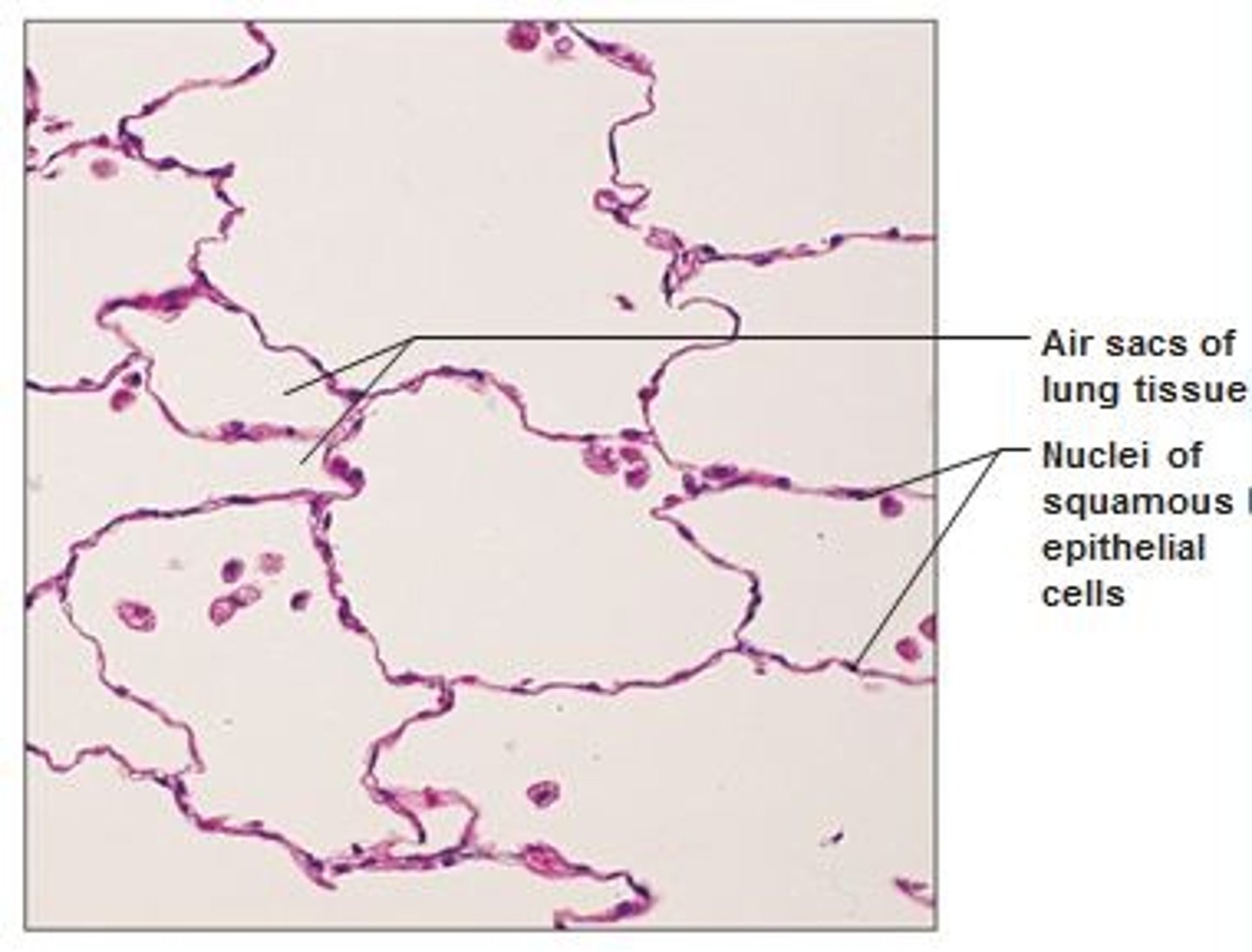
simple squamous epithelium
number of layers: single (1)
Location: Kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels; lining of ventral body cavity(serosae)
collagen fibers
cable like, resist to stretching
elastic fibers
Flexible and "stretchy" fibers that add elasticity to tissue
reticular fibers
tough but flexible
-lymph nodes, spleen, liver
ground substance of connective tissue
unstructured material that fills the space between cells
Ground substance + protein fibers = extracellular matrix
Fibroblast (connective tissue)
always present. Produce collagen, reticular and elastic fibers, in addition to ground substance
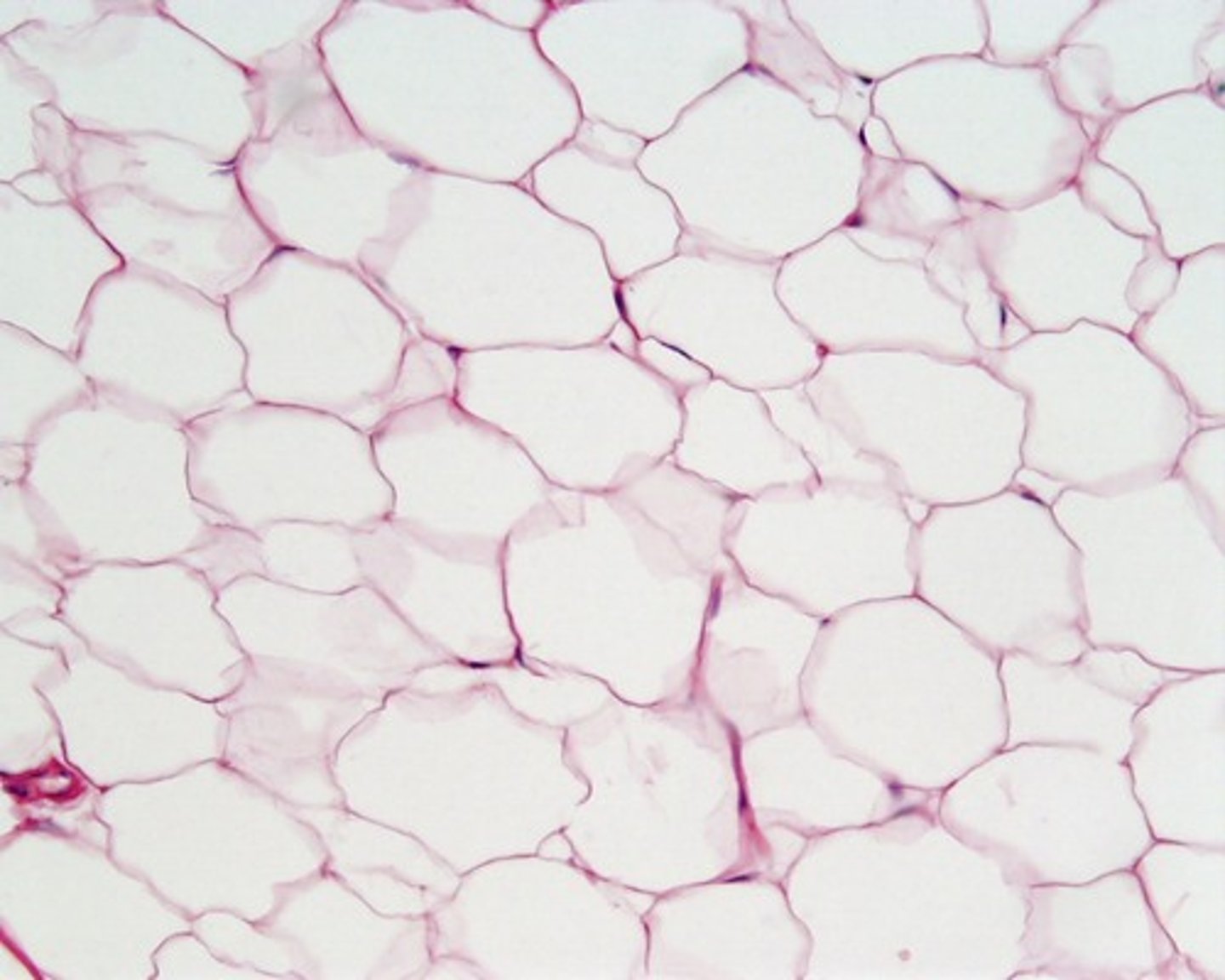
loose connective tissue
(adipose tissue)
-reduces heat loss
-loose areolar