Therapeutic Anticoagulation — 16 Exam-Ready Flashcards
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is the aim of anticoagulant therapy?
Prevents thrombus formation and prevents extension of thrombus, also most effectively in fibrin-rich venous clots.
Where anticoagulants work best
Why are anticoagulants more effective in venous than arterial thrombosis?
Venous clots are fibrin-rich, Arterial clots are platelet-rich and Anticoagulants target the coagulation cascade, not platelets
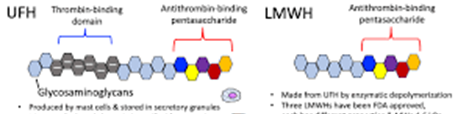
How does low molecular weight heparin differ from UFH?
More selective for Factor Xa, Less platelet interaction, Better bioavailability, Longer half-life
What are common clinical uses of UFH and LMWH?
UFH and LMWH are used to treat DVT and PE, manage atrial fibrillation, and provide peri-procedural anticoagulation.
What is fondaparinux and how does it work?
It is a synthetic pentasaccharide anticoagulant that works by binding to antithrombin, which then selectively inhibits Factor Xa, preventing clot formation.
Heparin adverse effect
What is the main adverse effect of heparin?
Bleeding, More common with UFH, Rapid reversal due to short half-life
How does warfarin exert its anticoagulant effect?
Inhibits vitamin K-dependent factor synthesis, Affects II, VII, IX, X Also affects protein C and S
Why does warfarin take several days to become effective?
Existing clotting factors persist
Prothrombin has long half-life
Anticoagulation effective after ~3 days
Monitoring warfarin
How is warfarin therapy monitored?
It is monitored with Prothrombin Time (PT), reported as INR, and allows dose adjustment
Warfarin limitations
Front: Why does warfarin require close monitoring?
Narrow therapeutic window
Many drug interactions
Affected by diet and liver function
Strong pharmacogenomic effects
Why is warfarin contraindicated in pregnancy?
Crosses placenta
Teratogenic
Causes fetal bleeding
Direct thrombin inhibitors
How do direct thrombin inhibitors work?
Direct thrombin inhibitors work by directly inhibiting thrombin and acting independently of antithrombin; an example is dabigatran.
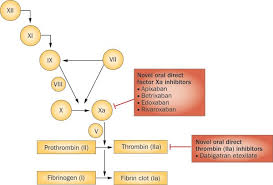
Direct Factor Xa inhibitors
How do direct Factor Xa inhibitors differ from warfarin?
Direct inhibition of Factor Xa
Predictable effect
Rapid onset
No routine monitoring required
Fibrinolytic agents
When are fibrinolytic agents used?
Breakdown of fresh thrombi and STEMI in cases where PCI is unavailable. Most effective within 6 hours