2 Diagnostic Imaging
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are the types of diagnostic imaging
conventional radiology
contrast-enhanced imaging
computerized tomography
magnetic resonance imaging
nuclear imaging
diagnostic ultrasound
fluoroscopy
what is an x-ray
invisible light beam (EM radiation, high energy/short wave length) that can penetrate deeply
radiograph
image is produced by the x-ray penetrating through the body. various structures absorb energy differently
what is radiodensity
thickness, anatomic weight of the structure
how does a more radiodense structure appear on film? less radiodense?
more radiodense will be white (contrast medium like barium or metal implant will appear white)
less radiodense will be darker
most radiographs have at least ___ projections at __º of separation
2, 90
position of the patient in relation to the x-ray beam
sagittal, frontal/coronal, axial/transverse
projection of x-ray across the sagittal plane
A-P/P-A
projection of x-ray across the frontal plane
lateral (left or right, named depending on side closest tot he film casette)
oblique x-ray projections
approximately 45º from the sagittal plane, named for the side closest to the film cassette
anterior or posterior and right or left
what types of radiological images exist? what is most commonly used now?
plain films - standard film image on hard copy
digital radiology - stores the diagnostic image in a computer and computer reproduces the image
most commonly used now is digital
analyzing radiographs
viewing - computer
A-P or P-A - views pt in anatomical position
lateral/oblique films - view in the same direction as x-ray
markers - name/side of the body
what is the systemized approach when viewing radiographs?
ABC’s - alignment, bone density, cartilage spaces
alignment in radiograph
general skeletal architecture, contour of bone, alignment of bone relative to adjacent bones
bone density in radiographs
general bone density, local bone density, texture abnormalities
cartilage spaces in radiographs
joint space width
subchondral bone
epiphyseal plates
soft tissues in radiographs
muscles, fat pads and fat lines, joint capsules
indications of conventional radiology
most frequently used and most commonly performed imaging
other imaging techniques are used to confirm or deny a diagnosis made with conventional radiology
primary indication is bone injury
what is a CT scan (computerized tomography)
radiographs taken in 360º
patient is placed on a table moving through a circular ring
radiographs are taken axially every 0.3-1.5 cm
originally only axial views were available but other planes are now available
pros of CT scan
complex fractures/tumors (wrist, face, pelvis, spine)
eliminates superimposition of one anatomical part on another
can look at blood flow
cons of CT scan
insufficient for visualization of articular cartilage, tendon rupture/tendonitis
what is fluoroscopy
similar to plain-films but can be static or dynamic
x-ray beam passes through the patient and interacts with an image intensifier tube
image is transferred to a screen
used during casting/splinting/surgery
fluoroscopy indications
open reduction for fracture reduction/fixation
observe abnormal movement of a jointf
fluoroscopy negative factors
increased radiation
poor quality image
what has the most radiation exposure?
CT scan
x-ray absorptiometry indications
bone density may be evaluated radiologically but plain-films are not very sensitive to changes in bone density. changes in bone density is called osteopenia
bone densitometry
name for all radiological studies of osteopenia. bone densitometry uses standard anatomical parts as a reference and compares them to a normative model
does a bone scan have high sensitivity or specificity?
high sensitivity
low specificity
dual x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
measures the changes of an x-ray beam from 2 levels of energy as it passes through the body
what is quantitative CT
takes a CT of 3 lumbar vertebrae
assesses bone density against a normative model
what is nuclear imaging aka bone scan?
nuclear medicine study that is very sensitive to changes in bony metabolism
bone scan procedure
radiopharmaceutical agent injected
pt placed under scintillation camera
entire body scanned simultaneously
side to side comparison possible
normal bone is lighter than pathologic bone
indications of bone scan
tumors, metastatic disease, infections, stress reactions, fractures, avascular necrosis
what is MRI
produced by the interaction of tissues with radio frequency within a magnetic field
each tissue type has a typical energy pattern that the computer reconstructs into an image
indications for MRI
ideal for bone, soft tissue lesions, surgical planning
stress fx
AVN/tumors
ligament injury
bone marrow edema
articular cartilage/meniscus cartilage
head trauma/spinal cord injured
T1 vs T2
T1 - bone, fat, subacute hemorrhage is bright
T2 - fluid and soft tissue are bright
when is T1 used vs T2
T1 for anatomy in detail
T2 for acute trauma
what is contrast enhanced imaging
contrast medium is injected into an anatomical part followed by a radiograph
helps with improved visualization of pathology
can be used with most diagnostic imaging modalities
types of contrast-enhanced radiology
arthrography - joint
myelography - spine
what is diagnostic ultrasound
most commonly used to image soft tissue lesions in tendon and muscle
does not use ionizing radiation
image quality is not as good as CT or MRI
becoming more popular
indications for ultrasound
prevalent in research and some PT practices
pre and post movement re-education - abdominal muscles, pelvic floor (urinary incontinence), lumbopelvic
who orders imaging?
MD’s, nurses, PT’s (in the military), outside the military PT’s cannot order but can recommend
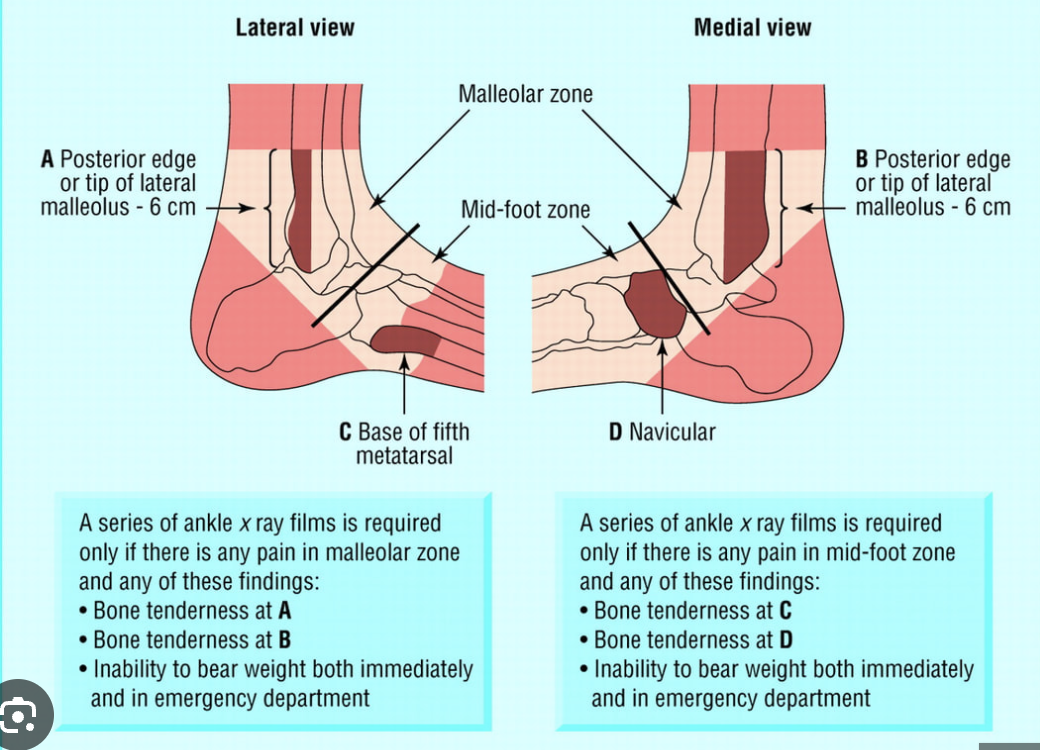
ottawa ankle rules
ottawa knee rules
an x-ray is indicated if the patient has any of the following features
age > 55
inability to bear weight both immediately and in the emergency department (4 step) **
isolated tenderness of the patella *
tenderness at head of fibula
inability to flex to 90º
*no bone tenderness of knee other than patella
**unable to bear weight wice onto each limb regardless of limping
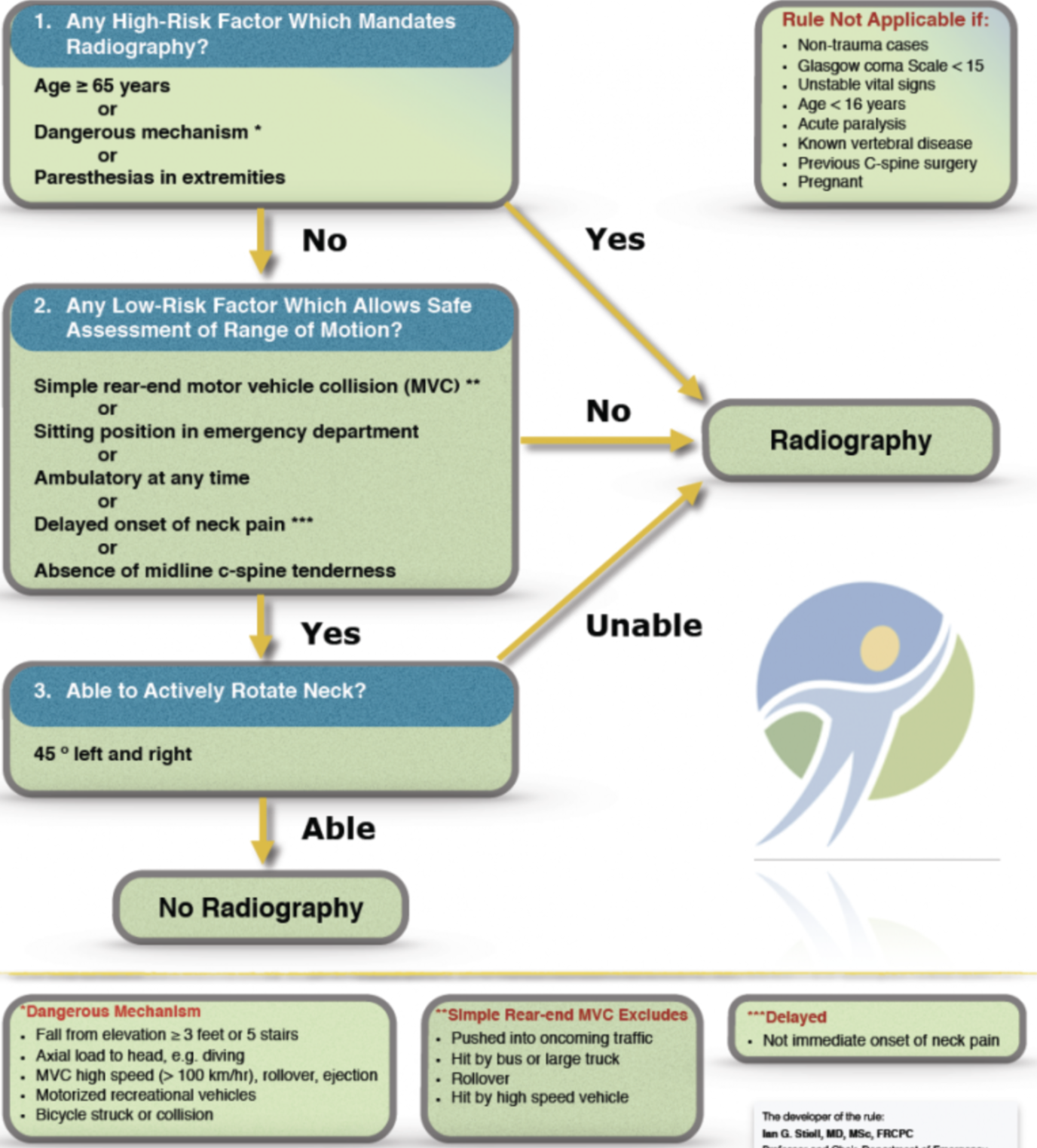
canadian c-spine rules