Chapter 23: Wiring the Brain: Development and Synaptic Plasticity
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Neurons
85 billion cells interconnecting in the brain.
Neurogenesis
Formation of new neurons during development.
Synaptogenesis
Creation of synapses between neurons.
Pathway Formation
Establishing neural pathways for communication.
Cell Proliferation
Radial glial cells produce neurons and astrocytes.
Transcription Factors
Proteins determining cell fate during division.
Cell Migration
Movement of cells to their final locations.
Pyramidal Cells
Neurons that migrate vertically along glial fibers.
Inhibitory Interneurons
Cells migrating laterally from different origins.
Subplate Layer
Initial residence of first migrating cells.
Cortical Plate
Destination for migrating neurons in the cortex.
Layer VI Neurons
First cortical layer formed during migration.
Cell Differentiation
Neurons acquire specific characteristics at destination.
Cortical Protomap
Blueprint for cortical area development.
Radial Unit Hypothesis
Neurons follow radial glial guides during migration.
Thalamic Input
Influences cortical differentiation during development.
LGN Input
Essential for monkey striate cortex differentiation.
Pathway Selection
First phase in forming neural pathways.
Target Selection
Second phase determining pathway endpoints.
Address Selection
Final phase ensuring precise connectivity.
Growth Cone
Tip of a growing axon.
Axon Guidance
Mechanisms directing axon growth to targets.
Pioneer Neurons
Neurons that lead axon growth directionally.
Chemoattractant
Substance that attracts growing axons, e.g., netrin.
Chemorepellent
Substance that repels growing axons, e.g., slit.
Optic Chiasm
Site where optic nerve fibers cross over.
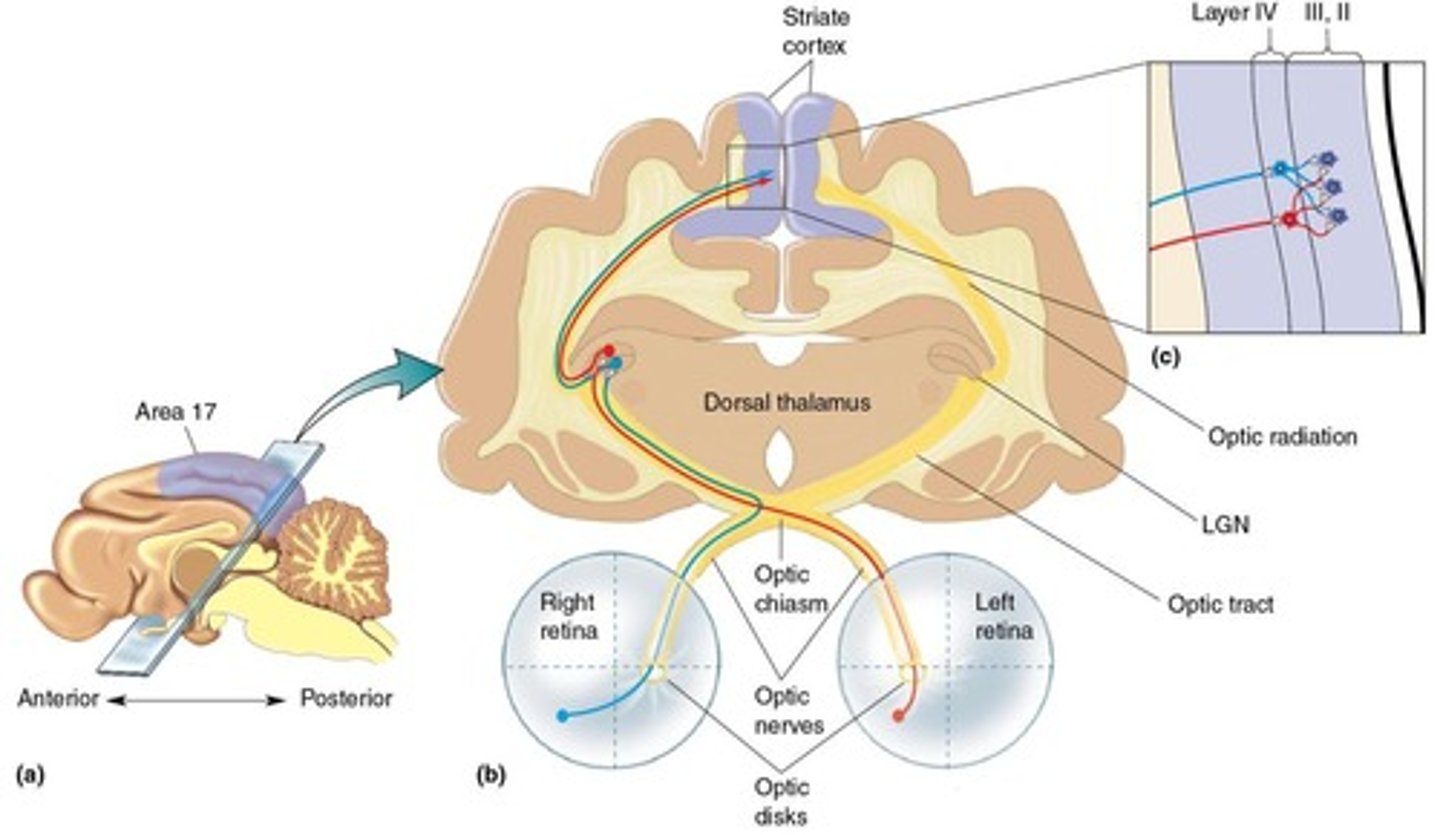
Topographic Maps
Organized neural connections based on spatial information.
Chemoaffinity Hypothesis
Theory that axons connect based on chemical signals.
CNS Regeneration
Ability of axons to regenerate in amphibians, not mammals.
Ephrins
Repulsive signals guiding retinal axon direction.
Retinotectal Projection
Mapping of retinal inputs to tectum.
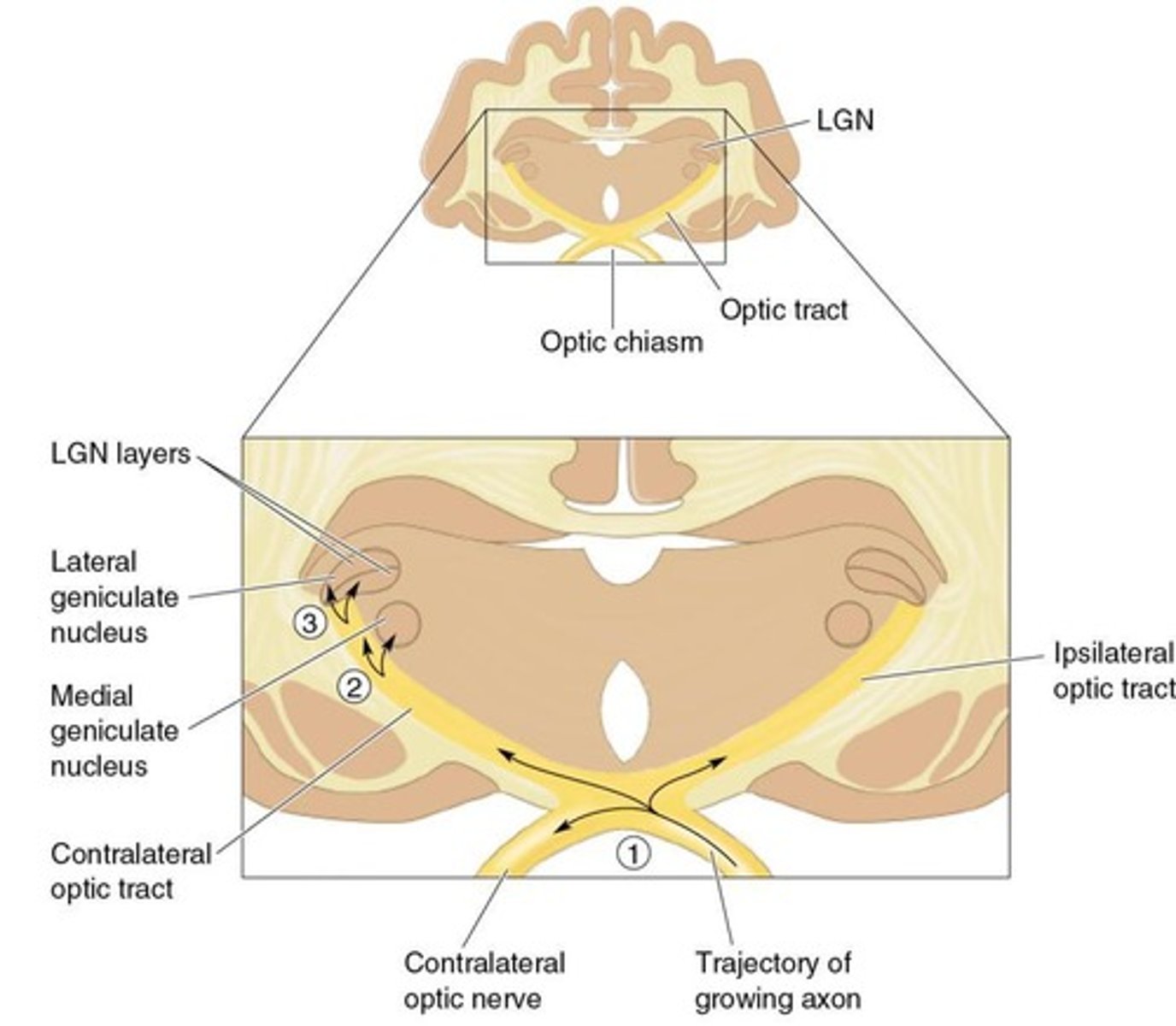
Neuromuscular Synapse Formation
Process of synapse development at muscle junctions.
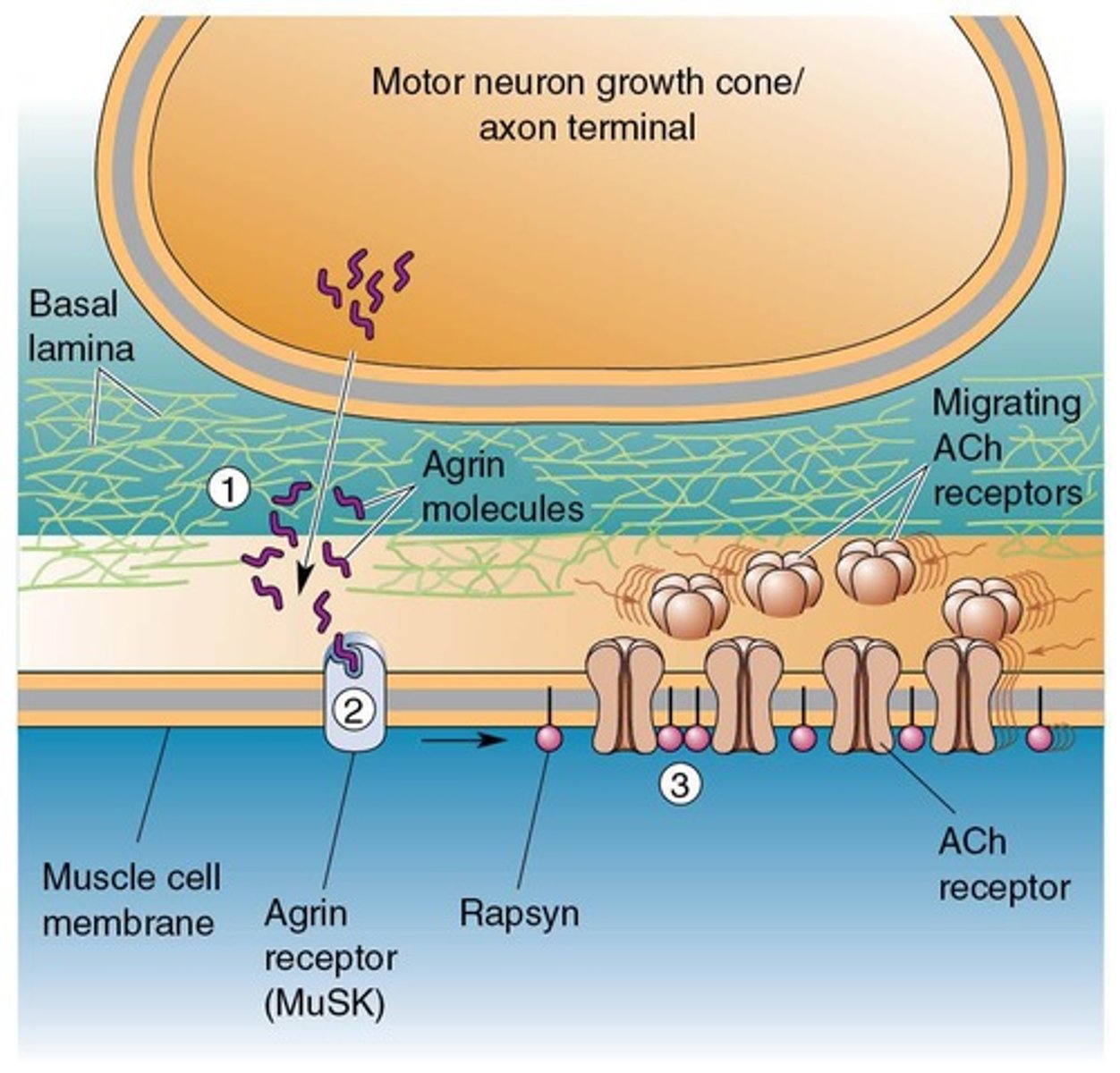
CNS Synapse Formation
Steps for establishing synapses in the central nervous system.
Dendritic Filopodium
Protrusion that contacts axons during synapse formation.
Synaptic Vesicles
Contain neurotransmitters at presynaptic membrane.
Postsynaptic Receptors
Proteins accumulating on postsynaptic membrane for signaling.
Cell and Synapse Elimination
Reduction of neurons and synapses for brain function.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death crucial for development.
Trophic Factors
Supportive proteins like nerve growth factor.
Synapse Elimination
Removal of synapses at neuromuscular junction.
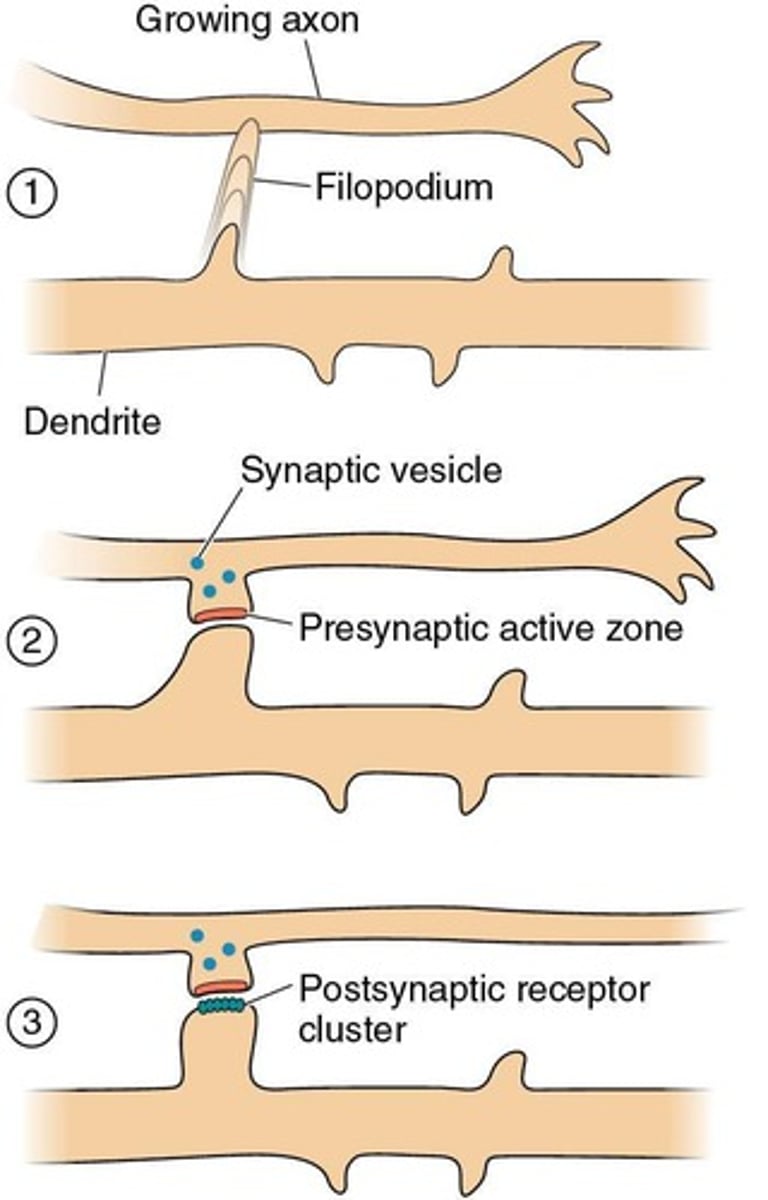
Activity-Dependent Synaptic Rearrangement
Changes in synaptic patterns due to neural activity.
Critical Period
Time frame for significant synaptic plasticity.
Synaptic Segregation
Refinement of synaptic connections in visual pathways.
Retinal Waves
In utero activity influencing synaptic segregation.
Hebbian Modifications
Synaptic changes based on correlated activity.
Ocular Dominance Columns
Visual cortex structures for segregated eye input.
Synaptic Rearrangement
Changes in synaptic connections due to experience.
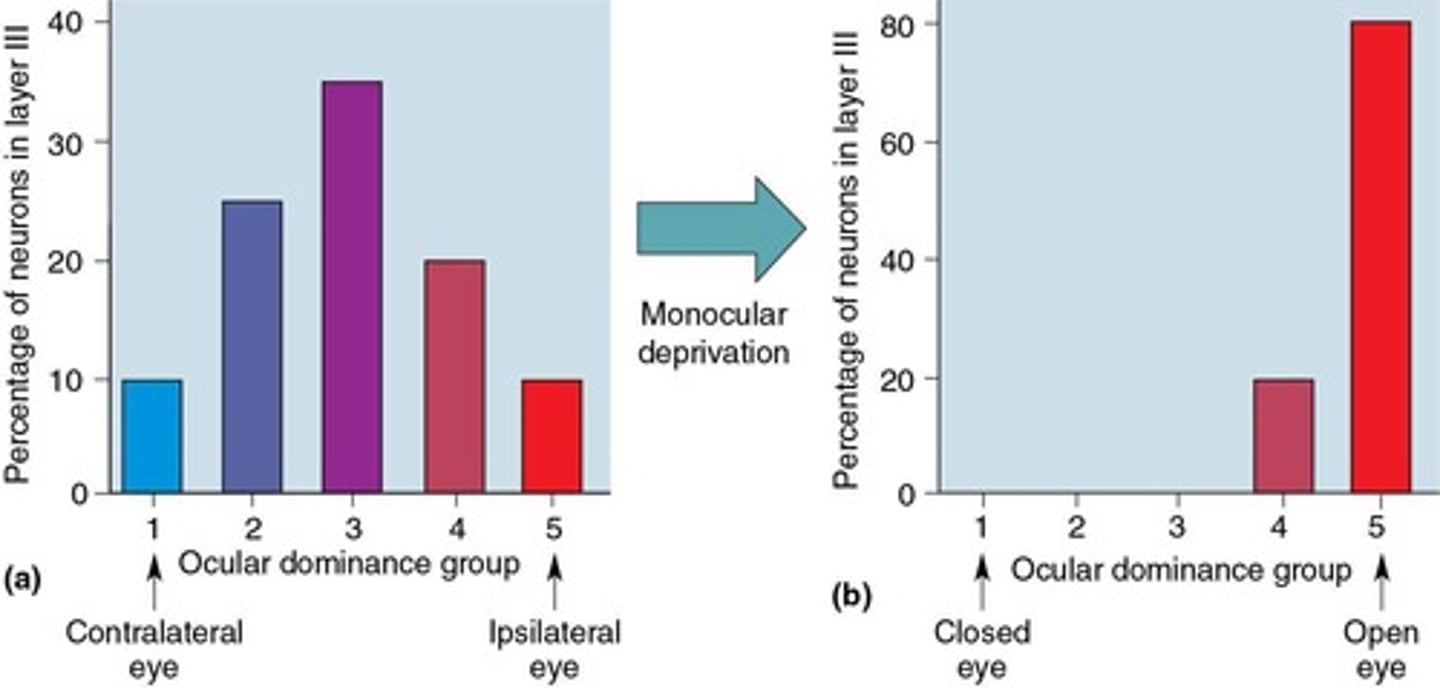
Monocular Deprivation
Experiment affecting ocular dominance and synaptic competition.
Ocular Dominance Shift
Change in visual processing due to eye activity.
Cortical Binocularity
Ability to process inputs from both eyes.
Cortical Synaptic Plasticity
Mechanisms for modifying synaptic strength and connections.
Synapse Activity
Correlates with multiple inputs on postsynaptic neuron.
Excitatory Synaptic Transmission
Involves glutamate receptors for signal transmission.
AMPA Receptors
Glutamate-gated ion channels facilitating synaptic transmission.
NMDA Receptors
Unique receptors with voltage-gated and calcium-conducting properties.
Calcium Flux
Signals pre- and postsynaptic coactivation levels.
Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
Strengthening of synaptic transmission due to NMDA activation.
Hebbian Detectors
NMDA receptors detect simultaneous presynaptic and postsynaptic activity.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Triggered by Ca2+ entry, modifying synaptic effectiveness.
Testing LTP
Monitor synaptic strength before and after NMDA activation.
Long-Term Depression (LTD)
Opposite of LTP, involves loss of synaptic AMPA receptors.
Monocular Deprivation Consequences
Leads to loss of synaptic influence on cortical neurons.
Critical Periods
Times when synaptic plasticity is heightened during development.
Axon Growth Cessation
Hypothesis for the end of plasticity in the brain.
Mature Synaptic Transmission
When synaptic connections stabilize and plasticity diminishes.
Cortical Activation Constraints
Limits on activation may affect synaptic plasticity.
Intrinsic Inhibitory Circuitry
Matures later, influencing plasticity and recovery.
Brain Development Circuitry
Formation and refinement of neural connections during growth.
Environmental Influence
Affects brain modification throughout an individual's life.
Visual System Plasticity
Critical periods observed in sensory and motor systems.
Reduced Visual Responsiveness
Result of brief monocular deprivation on visual processing.