HISTOPATHOLOGY OSPE
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
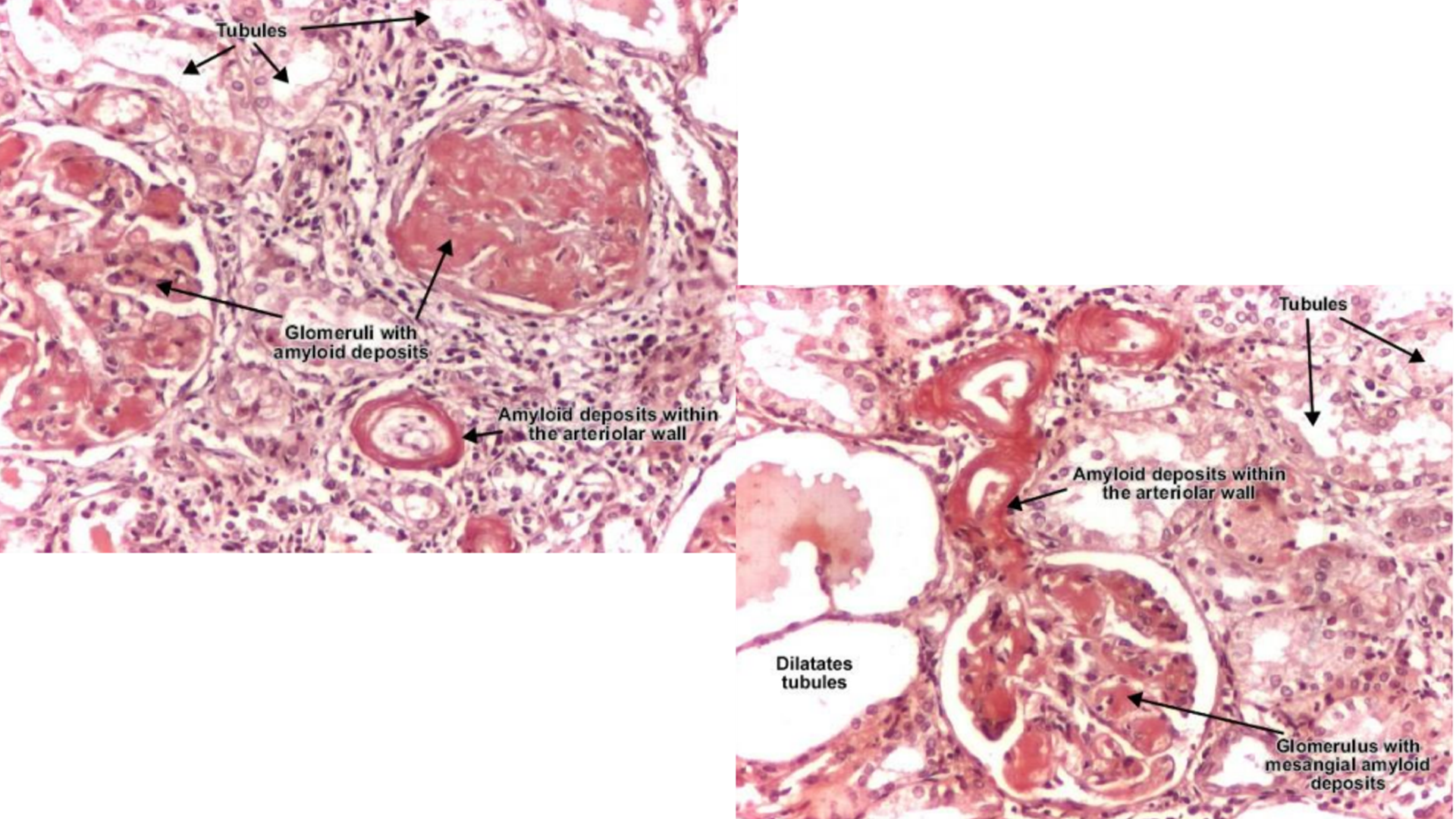
Renal Amyloidosis
Amorphous amyloid material occupying mesangium of glomerulus and walls of arterioles
Thickening of glomerular basement membrane (amyloid deposition)
Deposits can be nodular/diffused
No inflammation (acellular)
Thinning and dilated tubule walls
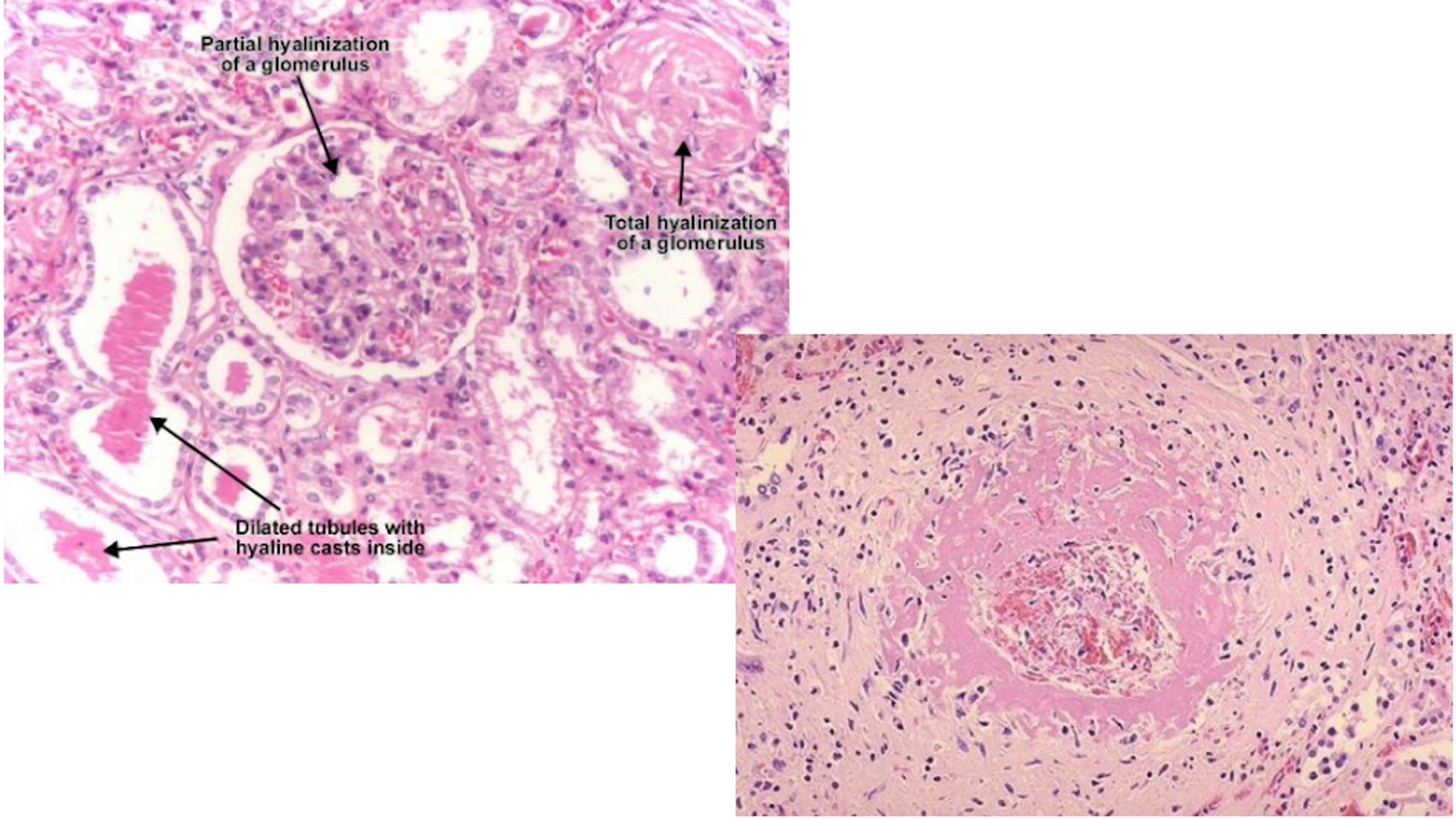
Hyaline Arteriosclerosis
Hyalinization of arteries first then may affect glomerulus
Narrowing artery lumen, thickening of artery walls
Deposits can be nodular/diffused
Tubular atrophy
Interstitial fibrosis (interstitial deposits)
Fibrinoid necrosis of small renal arteries
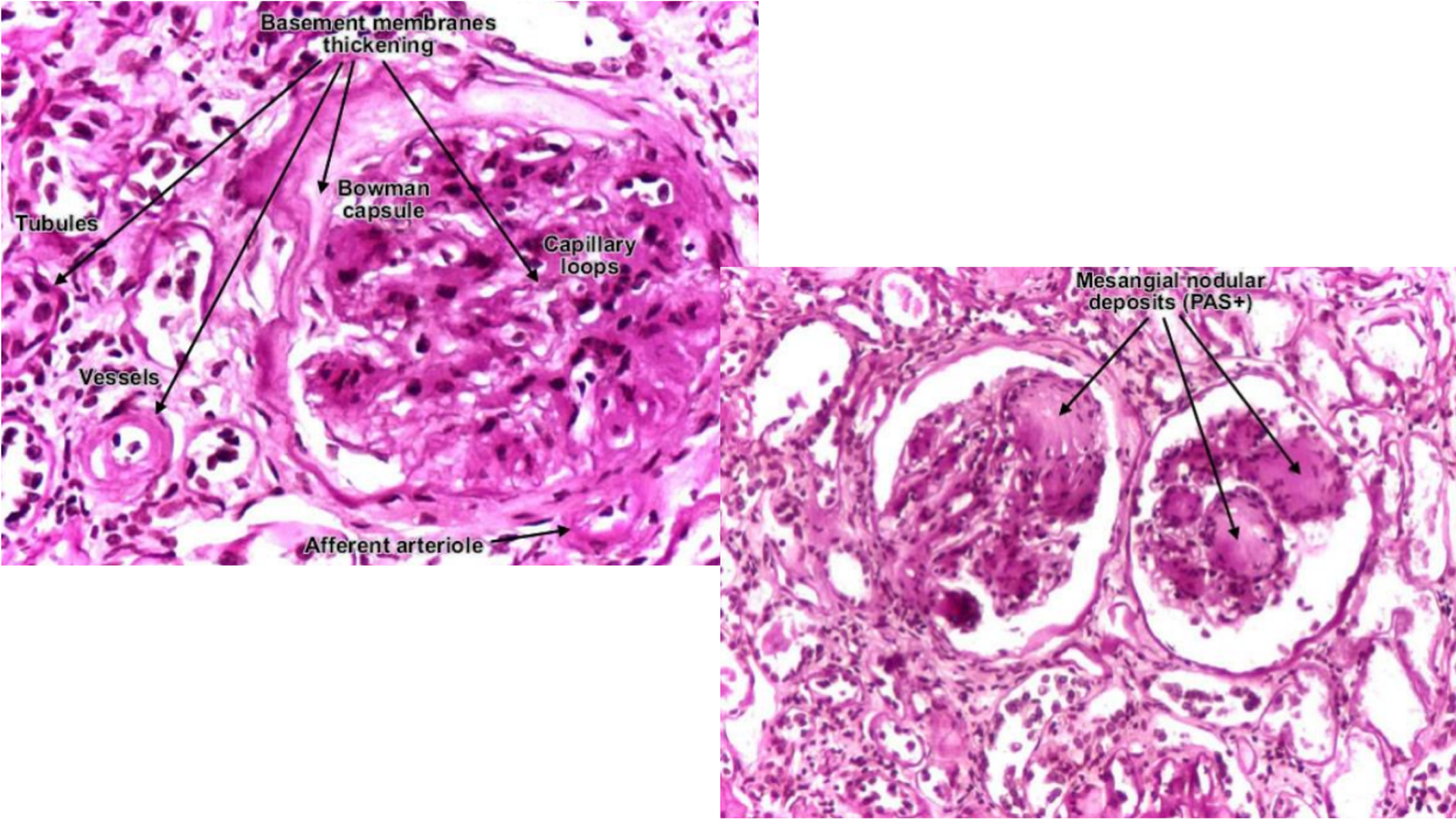
Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
Pink hyaline material in glomerular capillary loops
Increase in mesangial matrix (damage as result of non-enzymatic glycosylation of proteins)
Nodular = Kimmelstiel-Wilson lesion (usually focal, not entirely affects glomerulus)
Diffuse = Basement of membrane of capillary loops, may affect arteries and tubules
Differentiate between 3 deposits
Look at clinical findings:
If high immunoglobulin, renal amyloidosis
If patient has hypertension and arteries are affected mainly, hyaline arteriosclerosis
If patient is diabetic and glomerulus is affected mainly, diabetic glomerulosclerosis
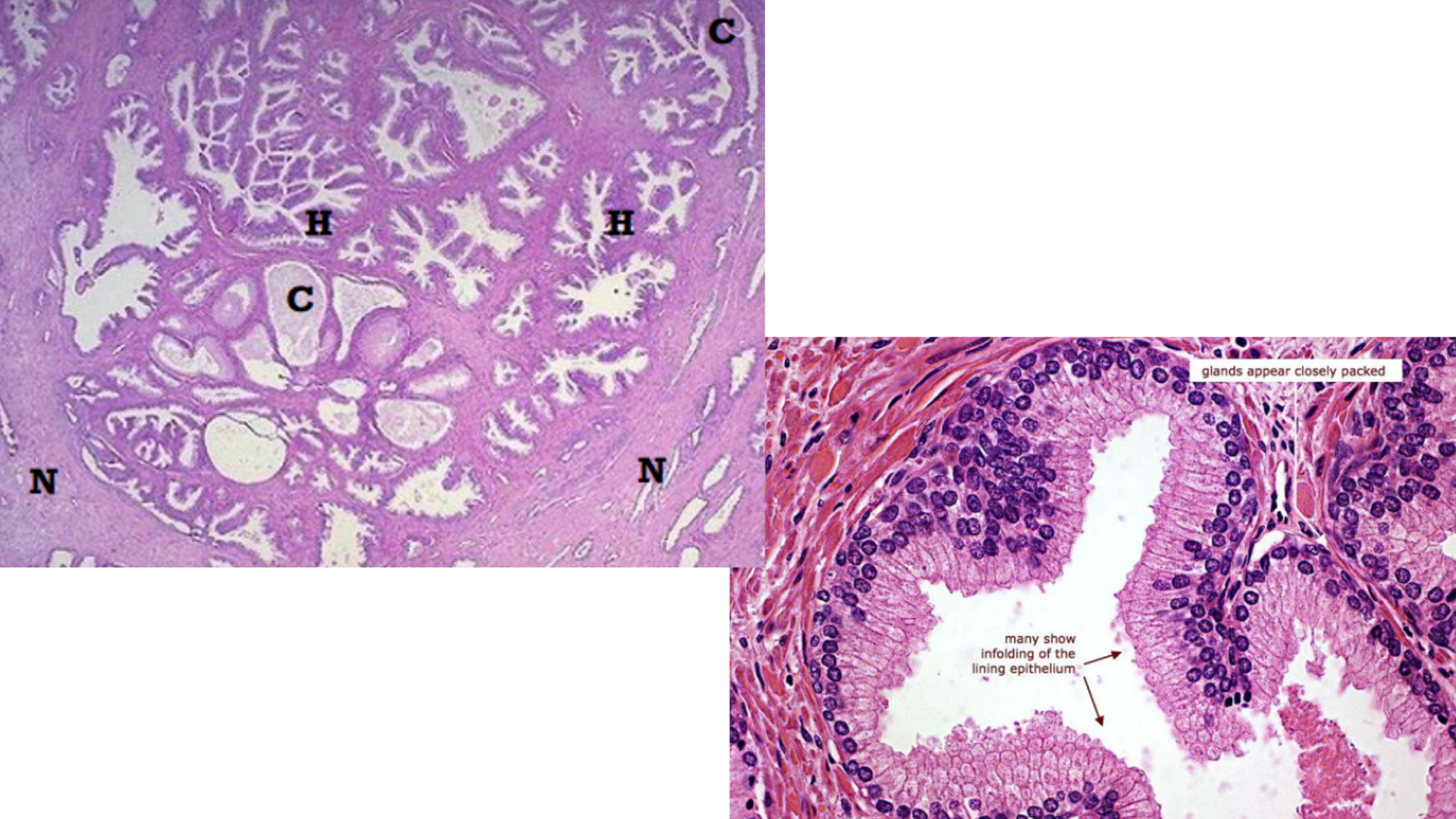
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Rounded nodules of hyperplastic prostatic tissue
Dilated hyperplastic glandular acini lined with tall columnar prostatic epithelial cells
Papillary folds of hyperplastic cells
Hypertrophy of fibromuscular tissues in bladder neck
Corpora amylacea
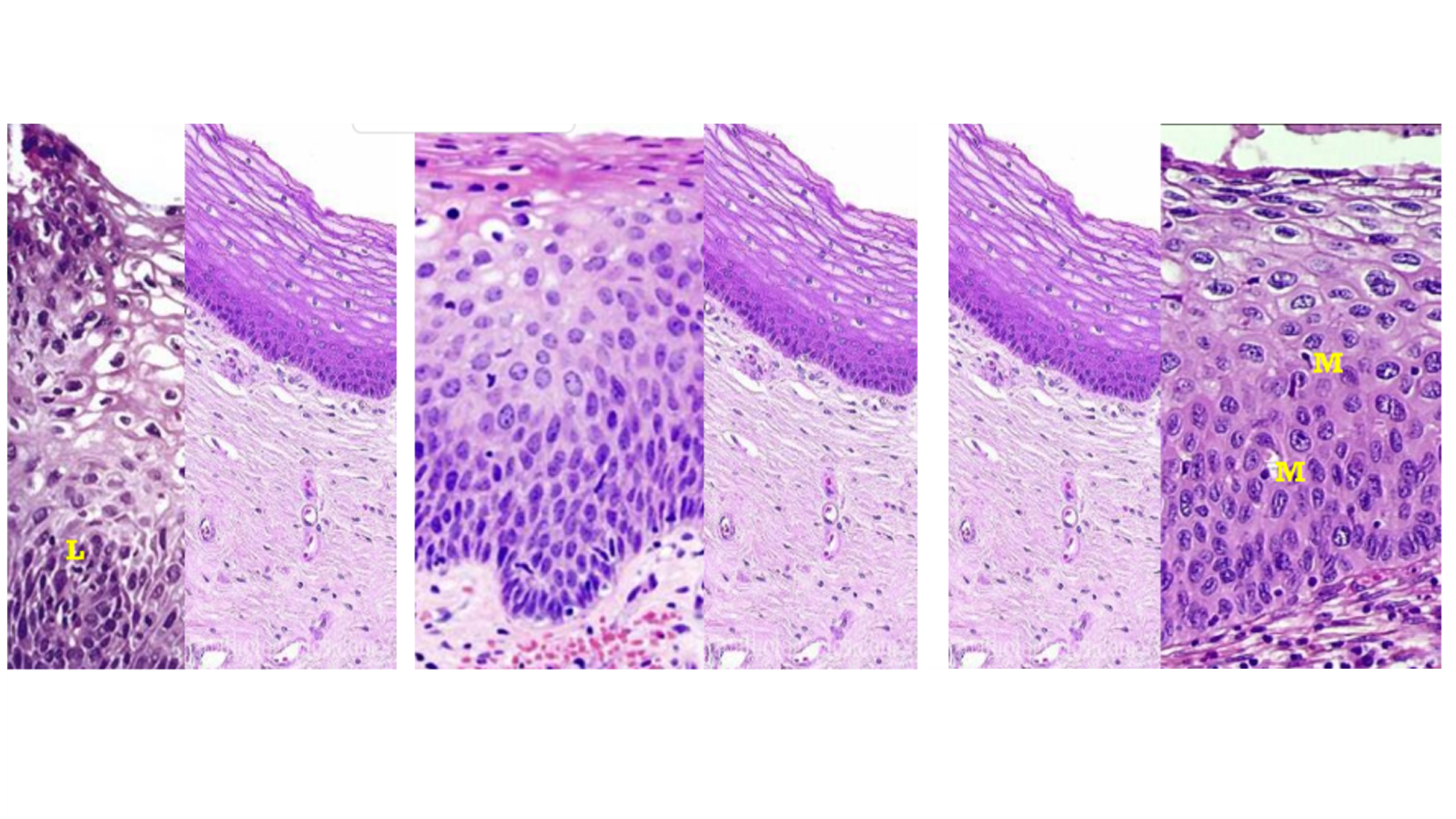
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Enlarged, hyperchromatic, increased mitotic activity
Koilocytes (enlarged irregular nuclei with clear cytoplasm)
Stages:
1: Lower epithelium only (most, confined to cervix)
2: 2/3 of lower epithelium
3: Entire epithelium, above basal cells
Invasive: Surface epithelium
Nest of carcinoma within supporting stroma
Surface of tumor is ulcerated alongside normal portion
Keratin pearls (well differentiated)
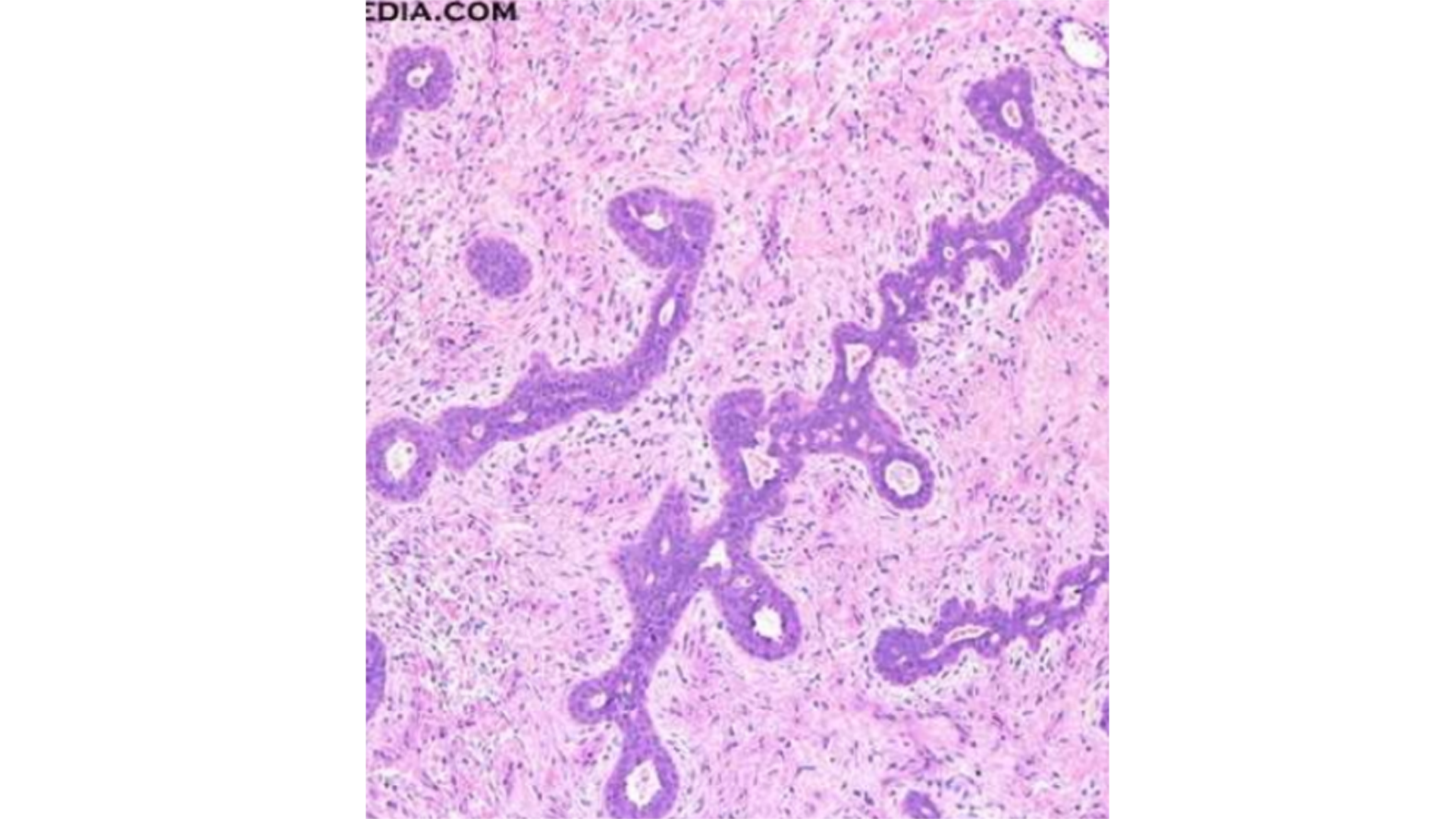
Fibroadenoma of Breast
Compressed ducts (glandular/cystic spaces lined by epithelium and enclosed by fibroelastic stromal component)
Loose cellular stroma (with fibroblasts and pale collagen)
Proliferation of both ducts (epithelium) and stroma
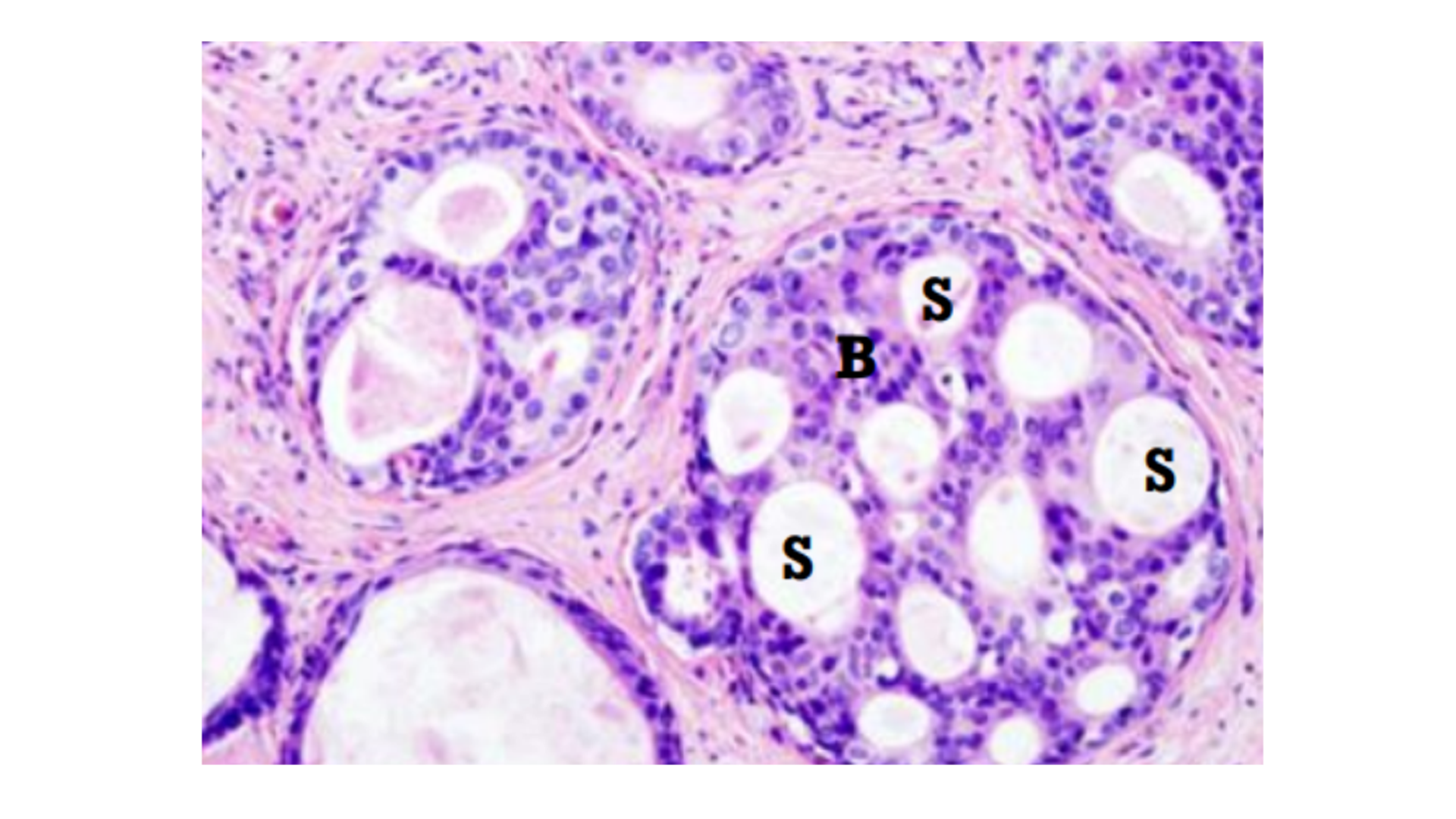
Ductal Carcinoma of Breast
Epithelial cells fill and expand tubules
Sharply defined glandular space
Bridges of cells between space
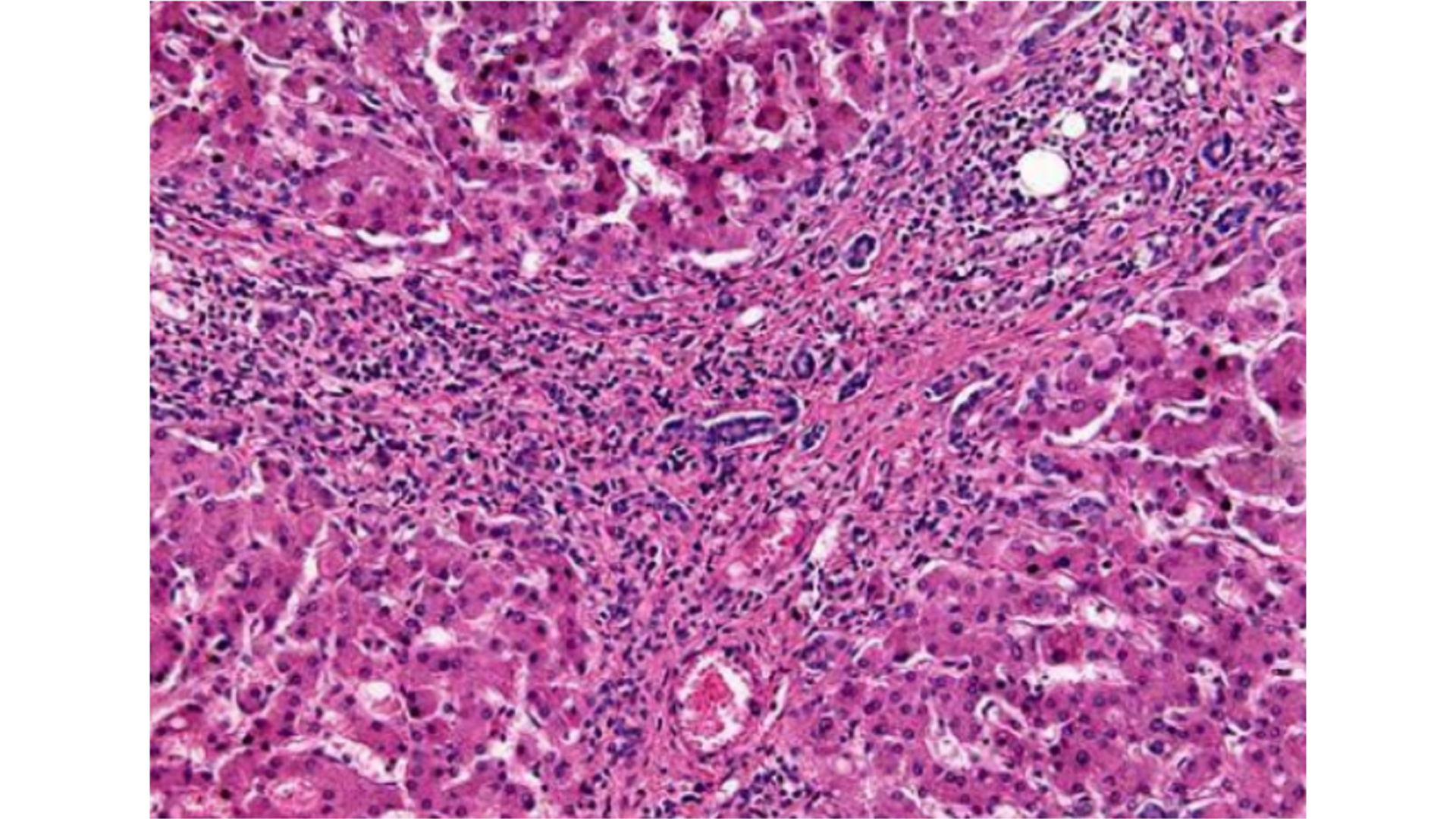
Cirrhosis
Regenerating nodules of liver cells between fibrous tissue bands
Chronic inflammatory cells in fibrous tissue
Bile duct proliferation
Portal tracts separated by fibrous connective tissue proliferation
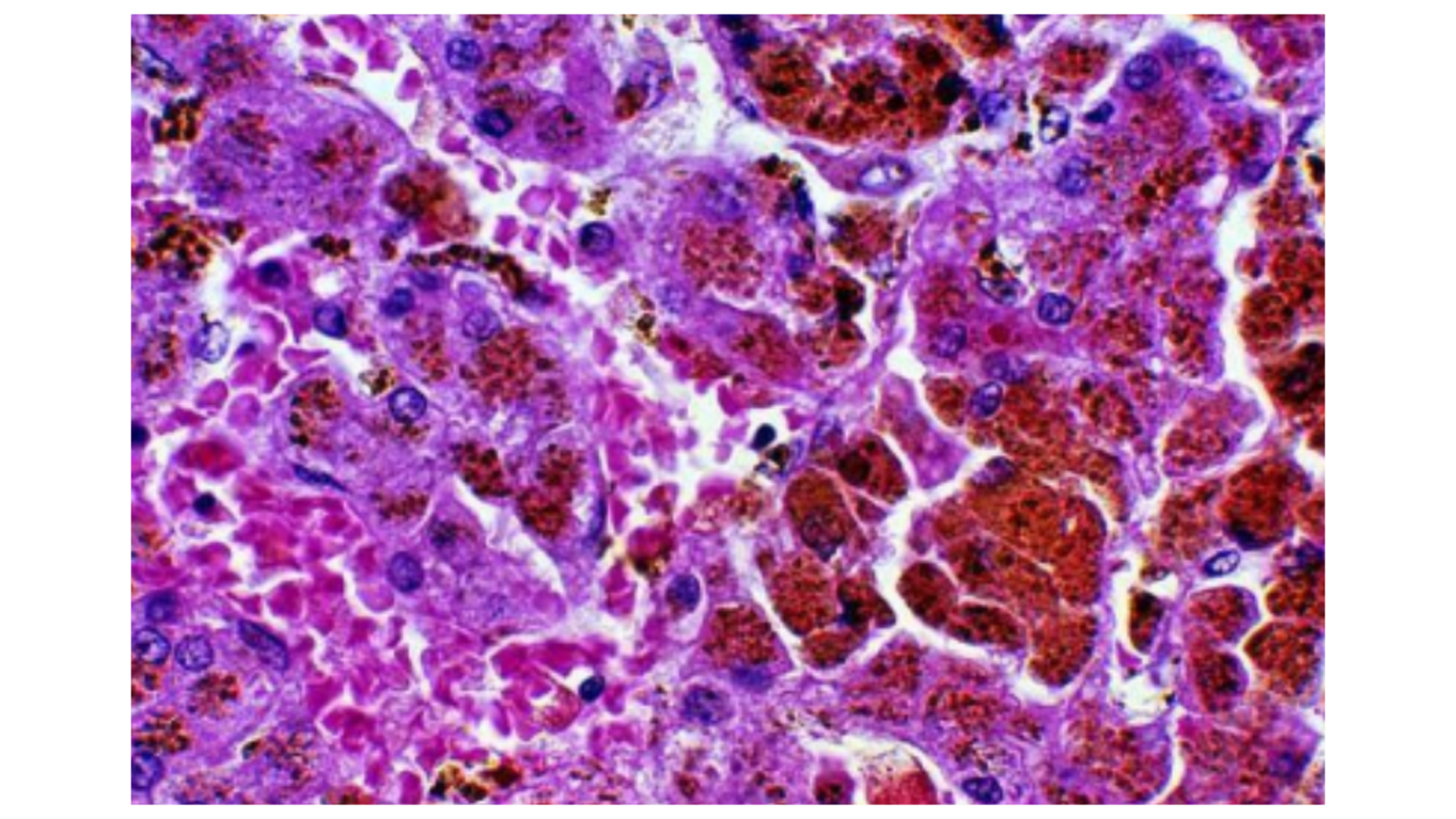
Hemochromatosis
Some fibrosis due to inflammatory injury
Some inflammatory cells
Brown pigment accumulation especially in periportal area
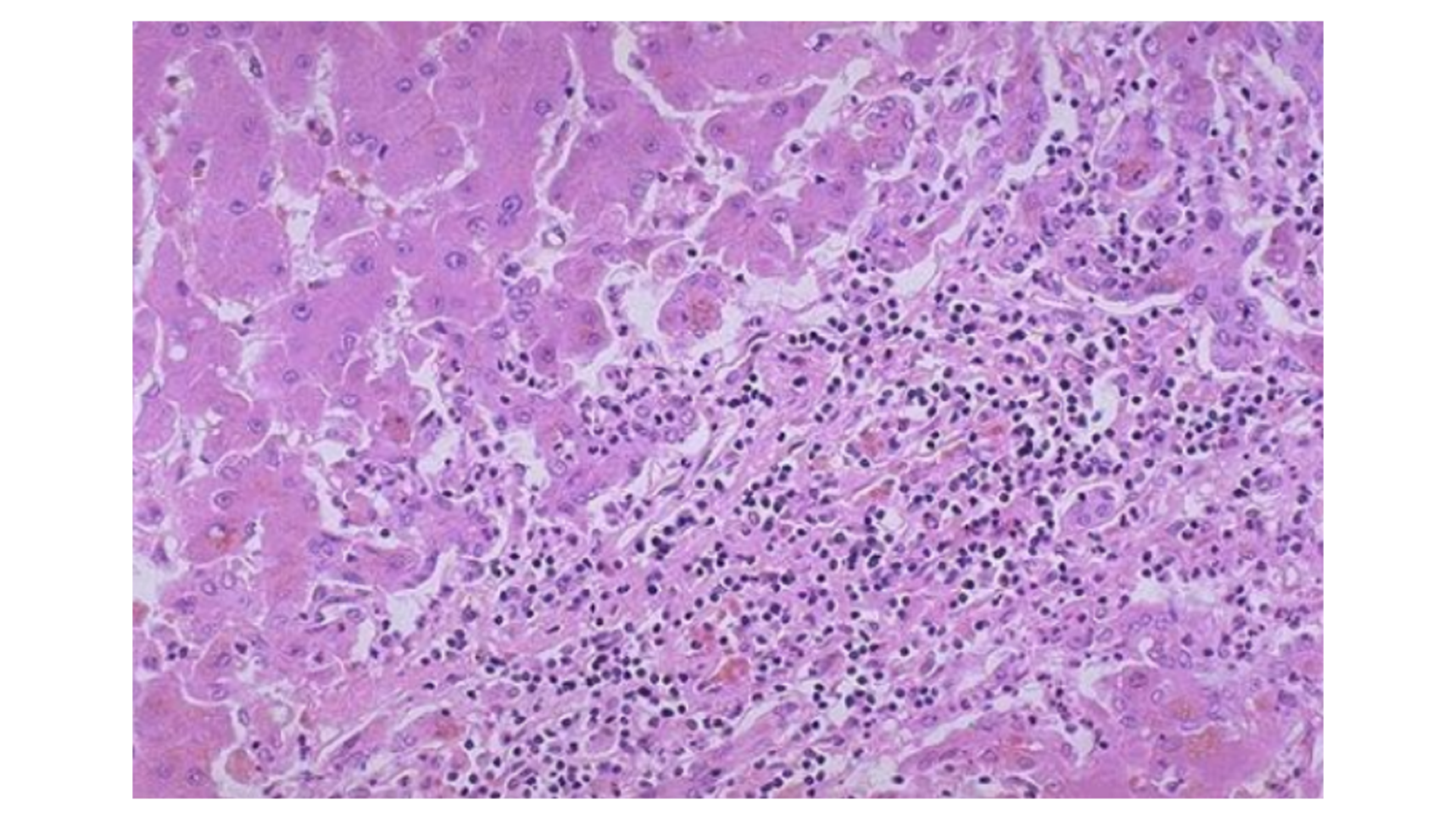
Viral Hepatitis
Inflammatory cell infiltrate, but not extended to other lobules (lymphocytic)
Councilman bodies (apoptosis)
Ballooning degeneration (apoptosis)
Kuffer cell hyperplasia
Caniculi cholestasis
For chronic: Extends to the other lobules, and is much much worse with fibrosis.
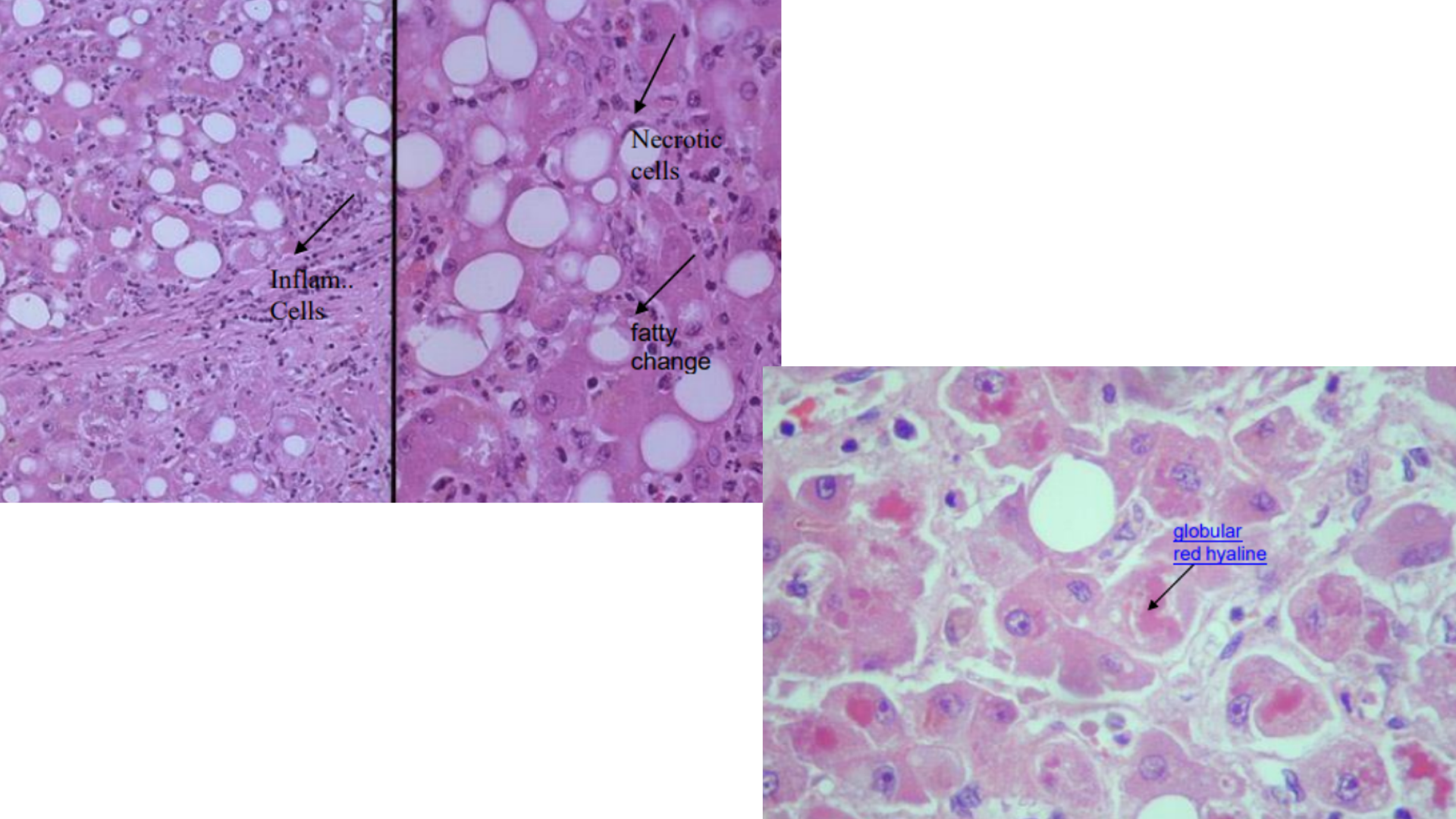
Alcoholic Hepatitis/Fatty Liver Disease
Inflammatory cell infiltrate (neutrophilic)
Mallory bodies (red hyaline within hepatocytes)
Fatty deposits (steatosis) in hepatocytes (micro/macrovesicular, push nucleus to the periphery)
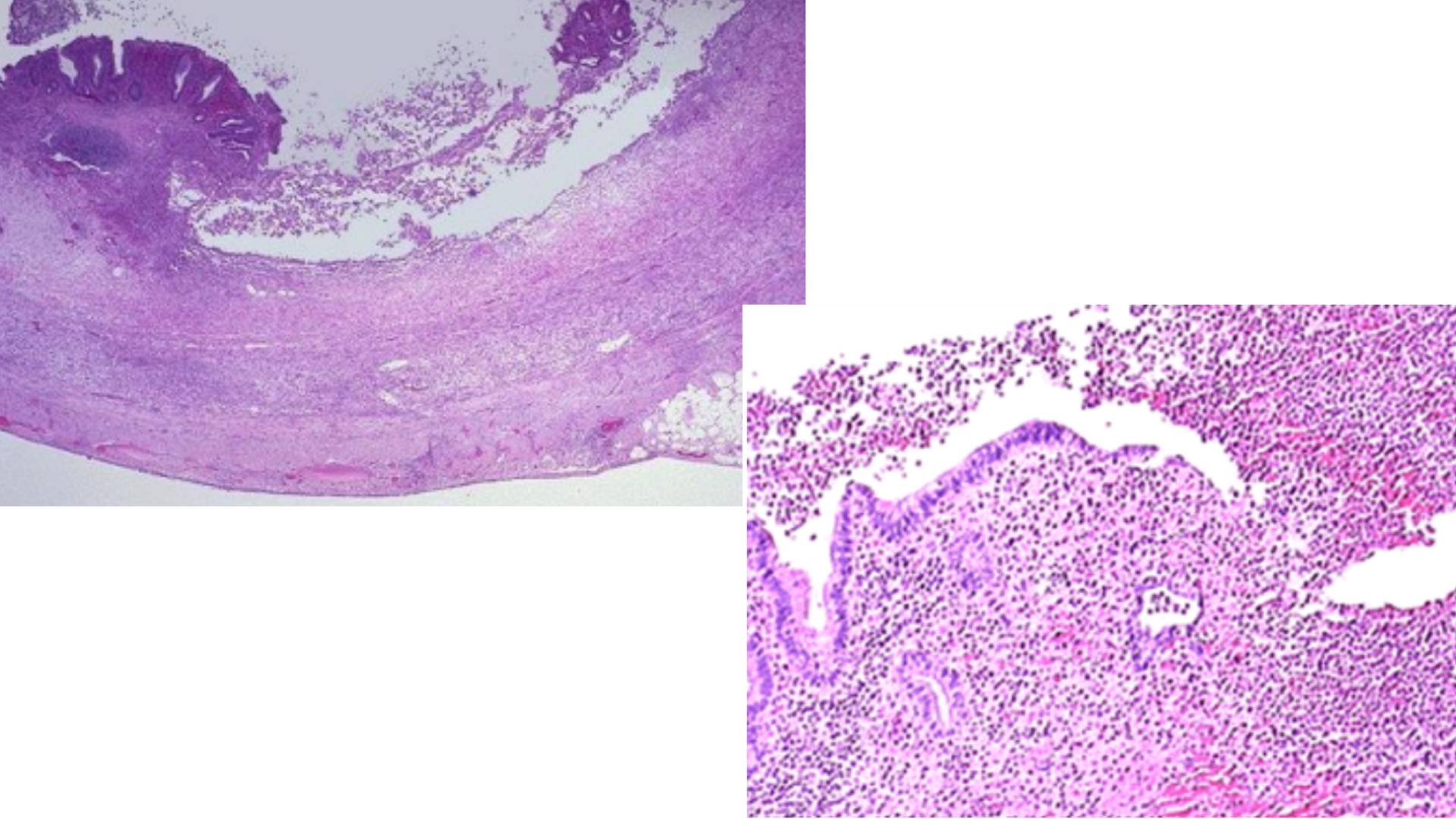
Acute Appendicitis
Inflammatory cell infiltrate (lumen, mucosa, muscularis, all by neutrophils)
Mucosal necrosis (ulceration: lining completely replaced by debris)
Fibrinopurulent exudate
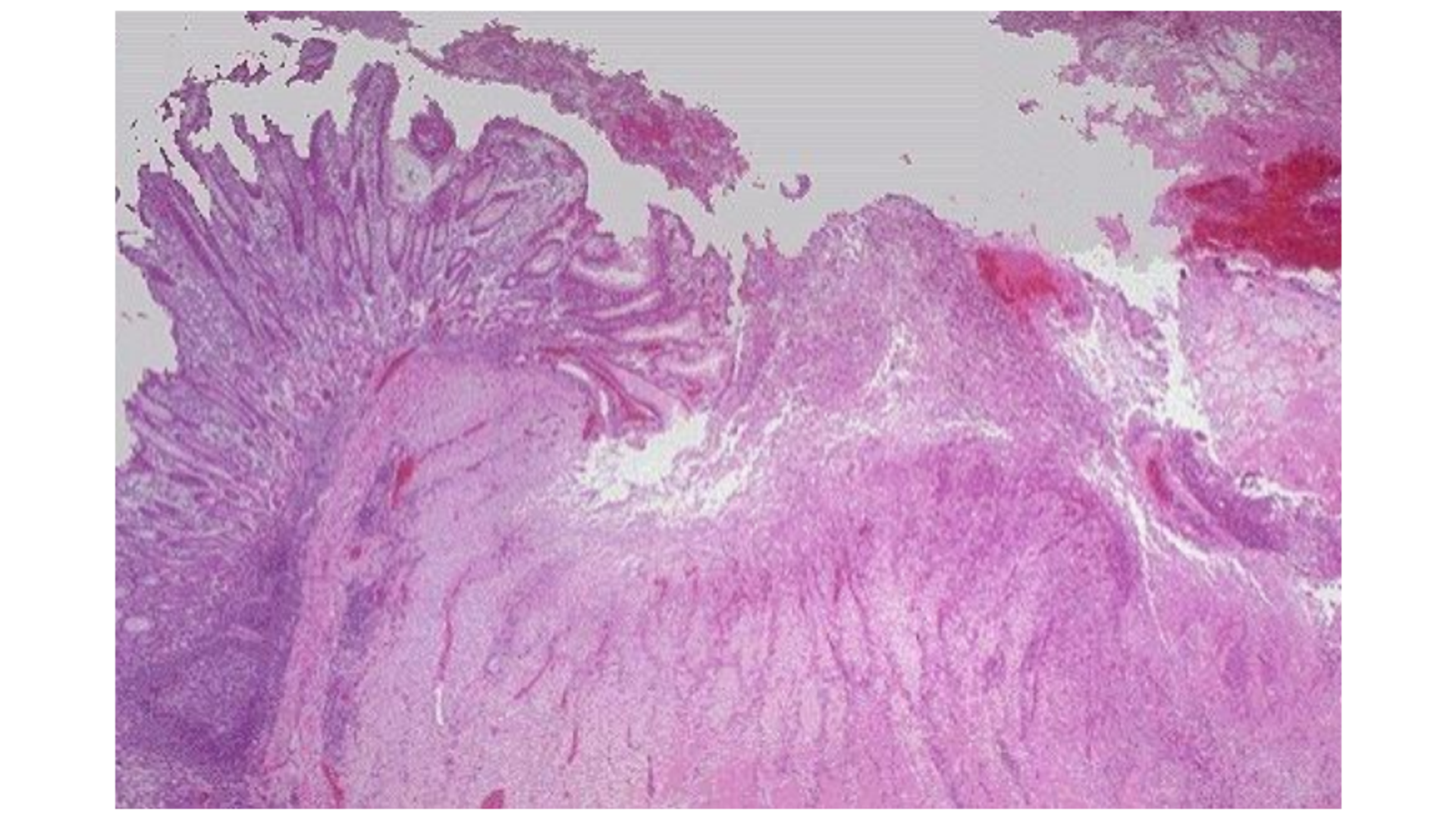
Peptic Ulcer
Coagulative necrosis of mucosa
Infiltration of PMN (neutrophil, macrophage)
Granulation tissue formation
Chronic: Fibrous tissue beneath the ulcer
Erosion: In NSAID use: Haemorrhage at ulcer base
Extends into submucosa, loss of tissue
Some mucosa not affected so can see normal mucosa beside the loss of lining
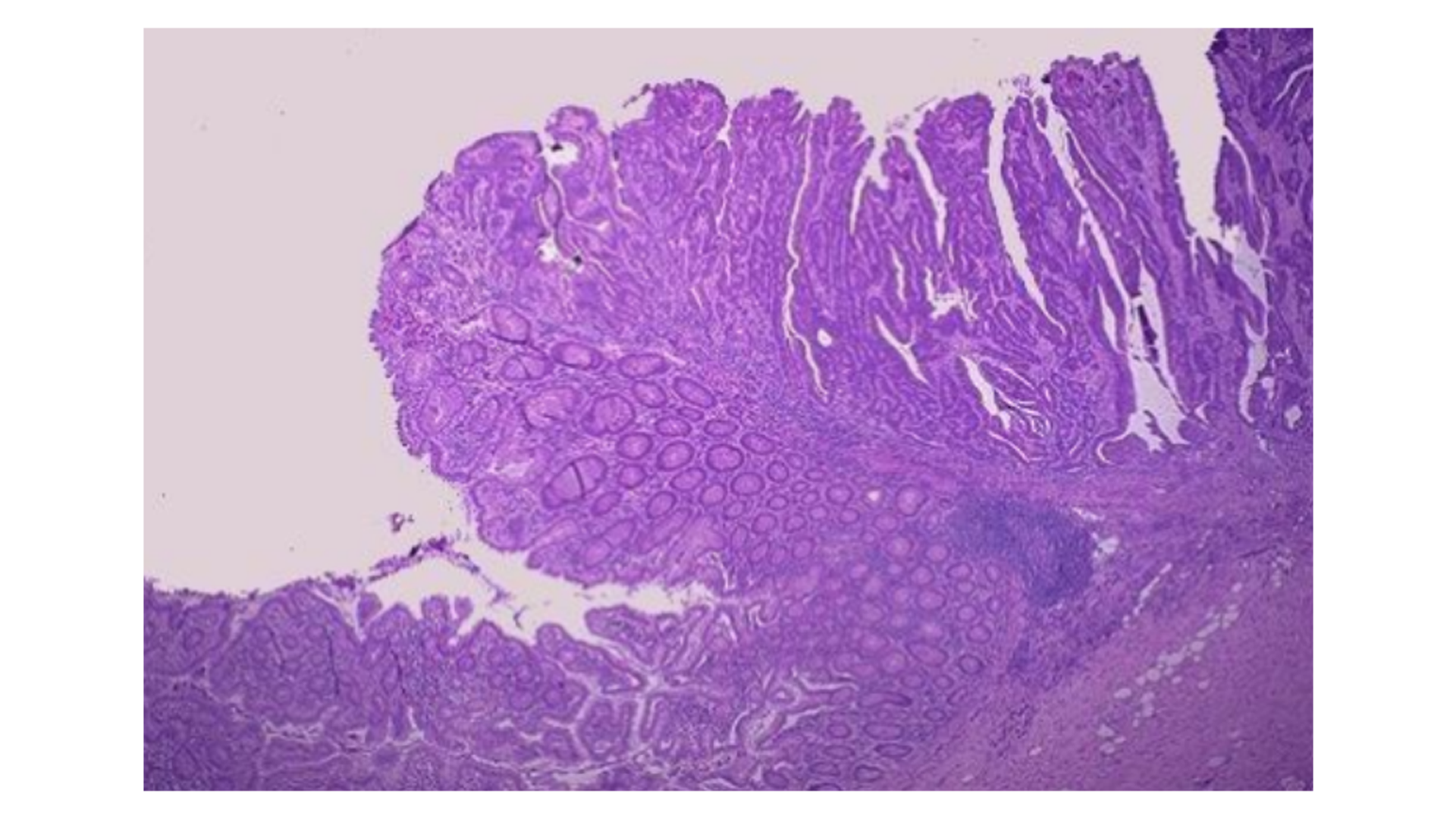
Colon Adenocarcinoma
Irregular gland formation, lined with columnar cells
Neoplastic glands are long, frond-like, exophytic growth
May infiltrate submucosa, muscularis and fat layer
Pleomorphic, hyperchromatism
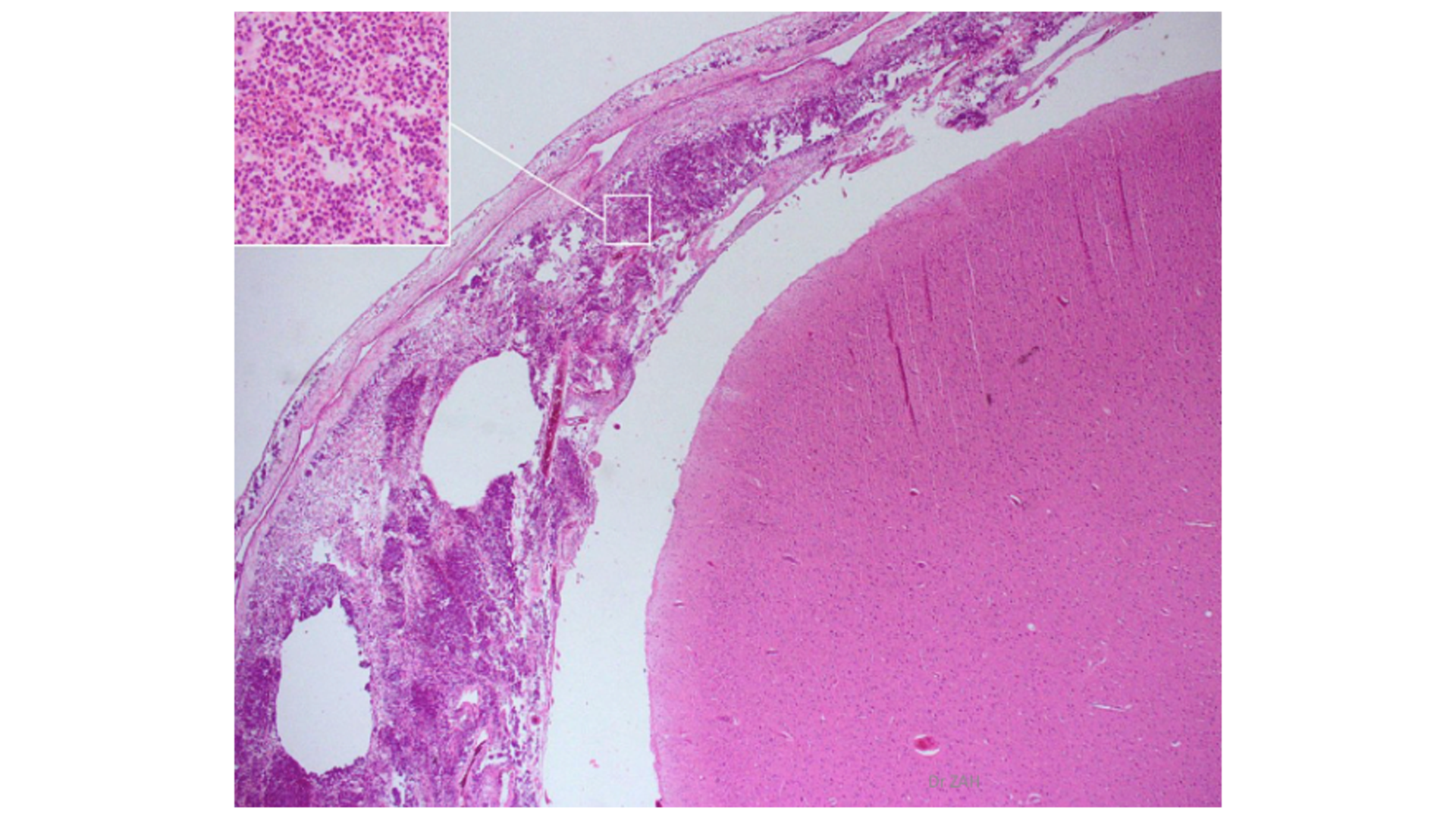
Acute Purulent Meningitis
Inflammatory cell infiltrate at meninges (Neutrophilic + Macrophages)
Purulent exudate (neutrophil and bacteria) in subarachnoid space/leptomeninges
Swelling of meninges
Phlebitis (inflammation of blood vessels and thrombus)
Blood vessels marginated with neutrophils, vasodilated
Cortex and white matter may be spongy due to edema
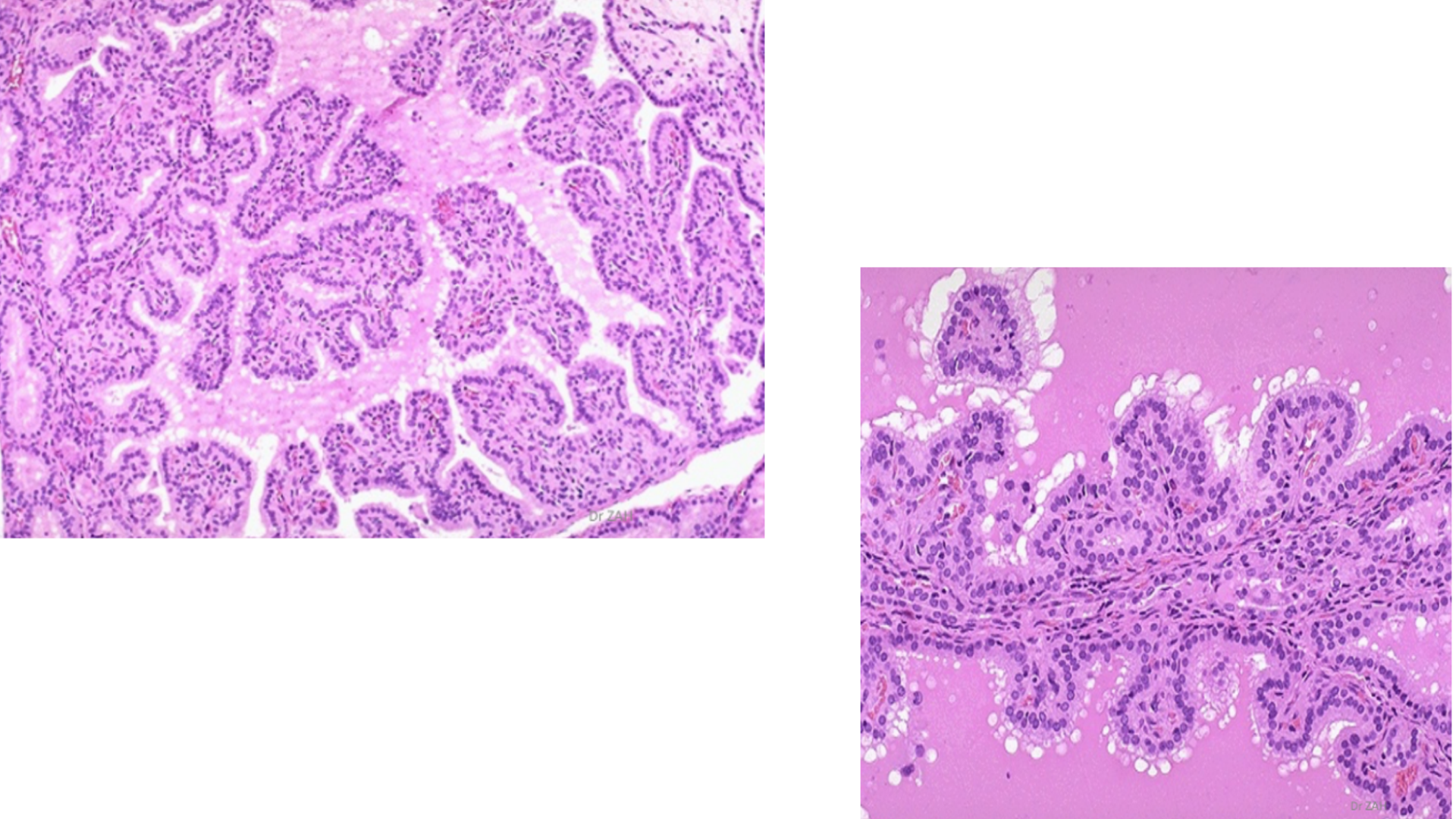
Graves’ Disease
Hyperplastia of follicular cells, causing papillary infolding into colloid with multiple layers
Tall columnar epithelial cells
Scalloping of colloid (clear vacuoles due to increased thyroid hormone production)
Watery and depleted colloid
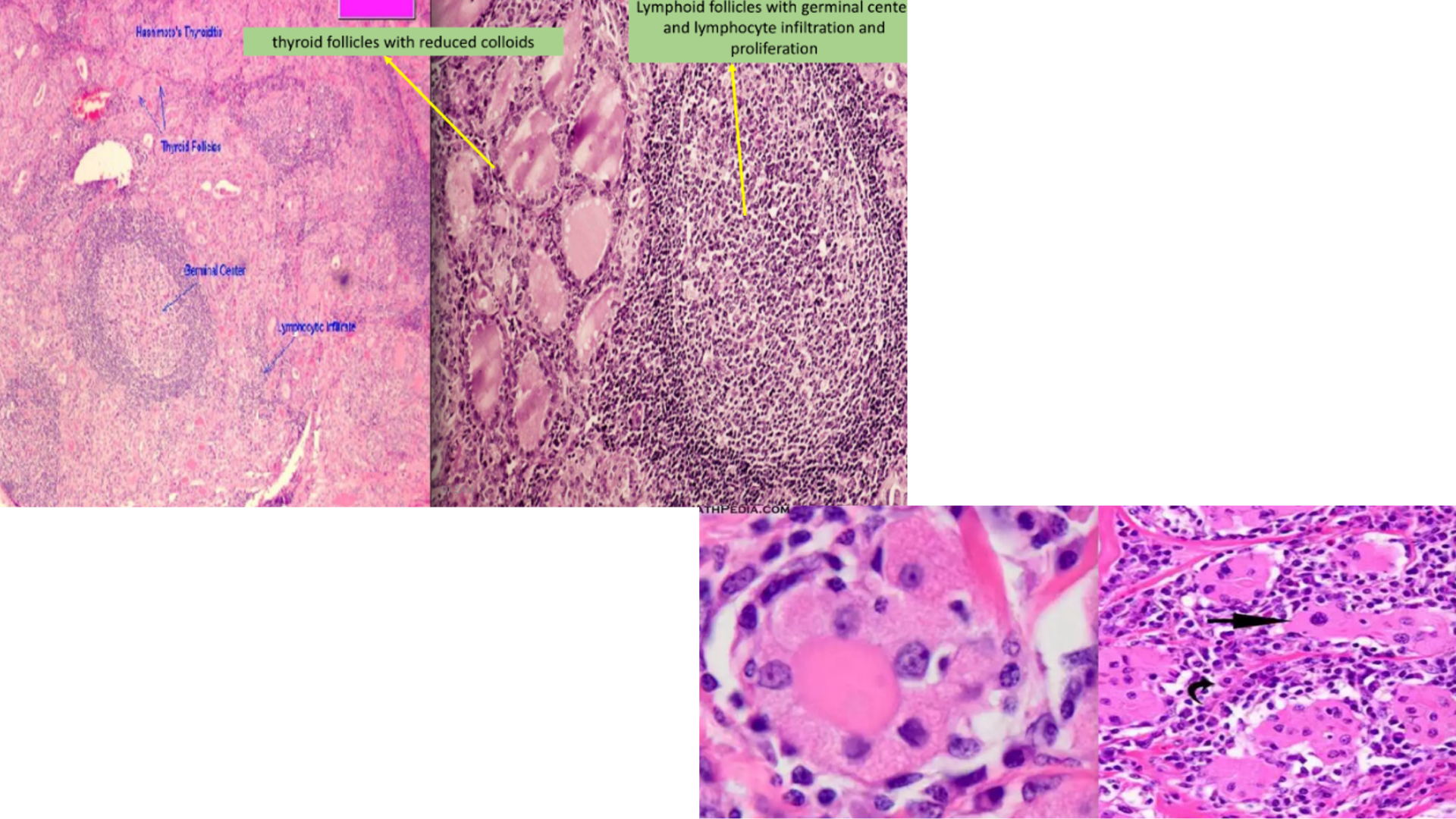
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Prominent lymphoid follicles with large, active germinal centers
Lymphocyte infiltration
Thyroid tissue replaced with lymphoid tissue
May progress into scar tissue formation
Reduced colloid
Thyroid follicular cell metaplasia form Hurthle/Oxyphil cell (finely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and enlarged nuclei)
Indication of progression to cancer due to constant inflammatory (stress)
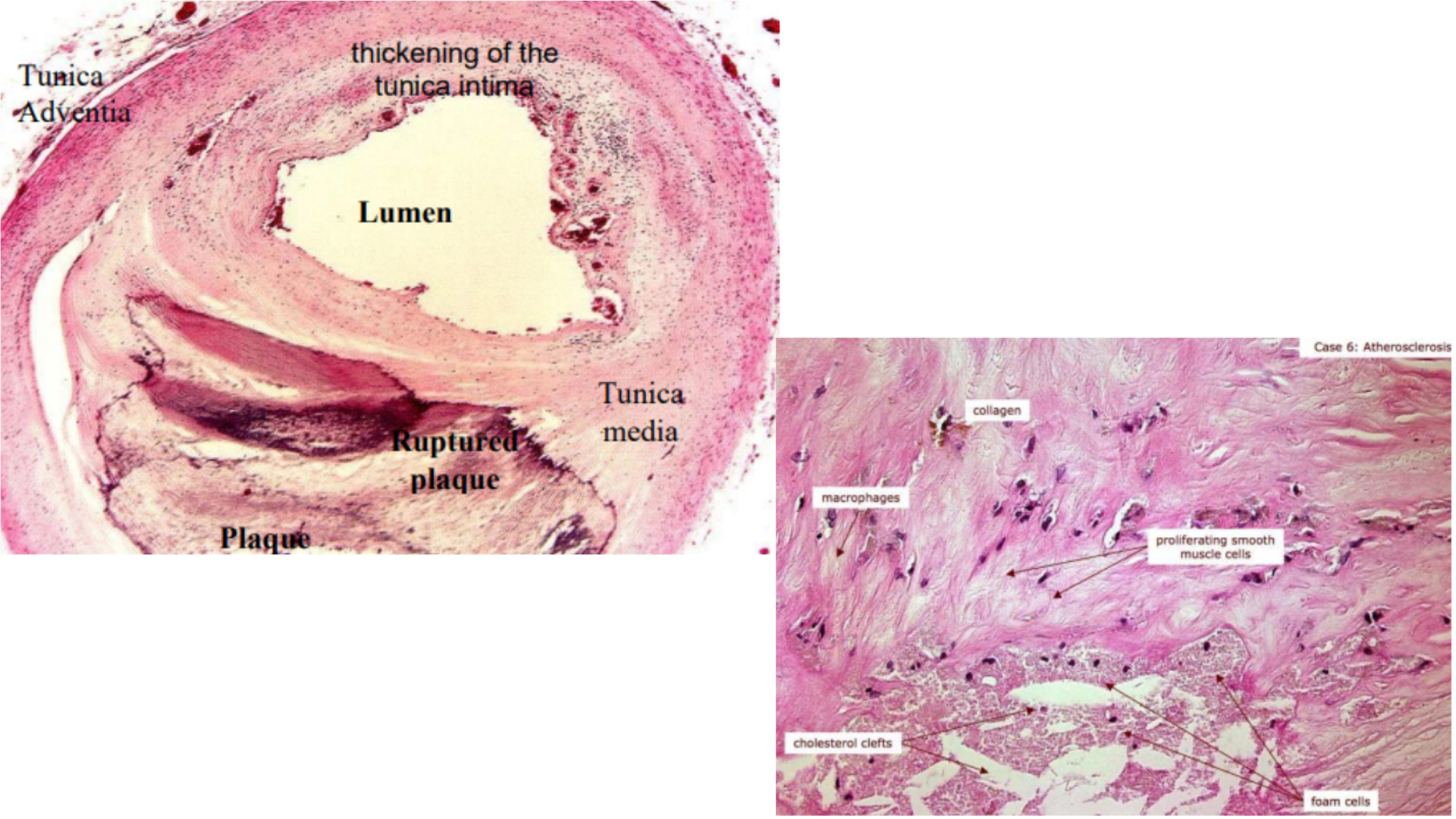
Artherosclerosis
Foam cell lesion with inflammatory cells (monocyte and lymphocyte)
Cholesterol clefts
Plaque formartion in artery, may/may not have recanalization, causing narrowing lumen
May have thrombus (with hemorrhage)
Lipid pools and lipid core in wall of artery
Fibrous cap
Intima thickening
Smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration to tunica intima
Proliferation of fibroblasts
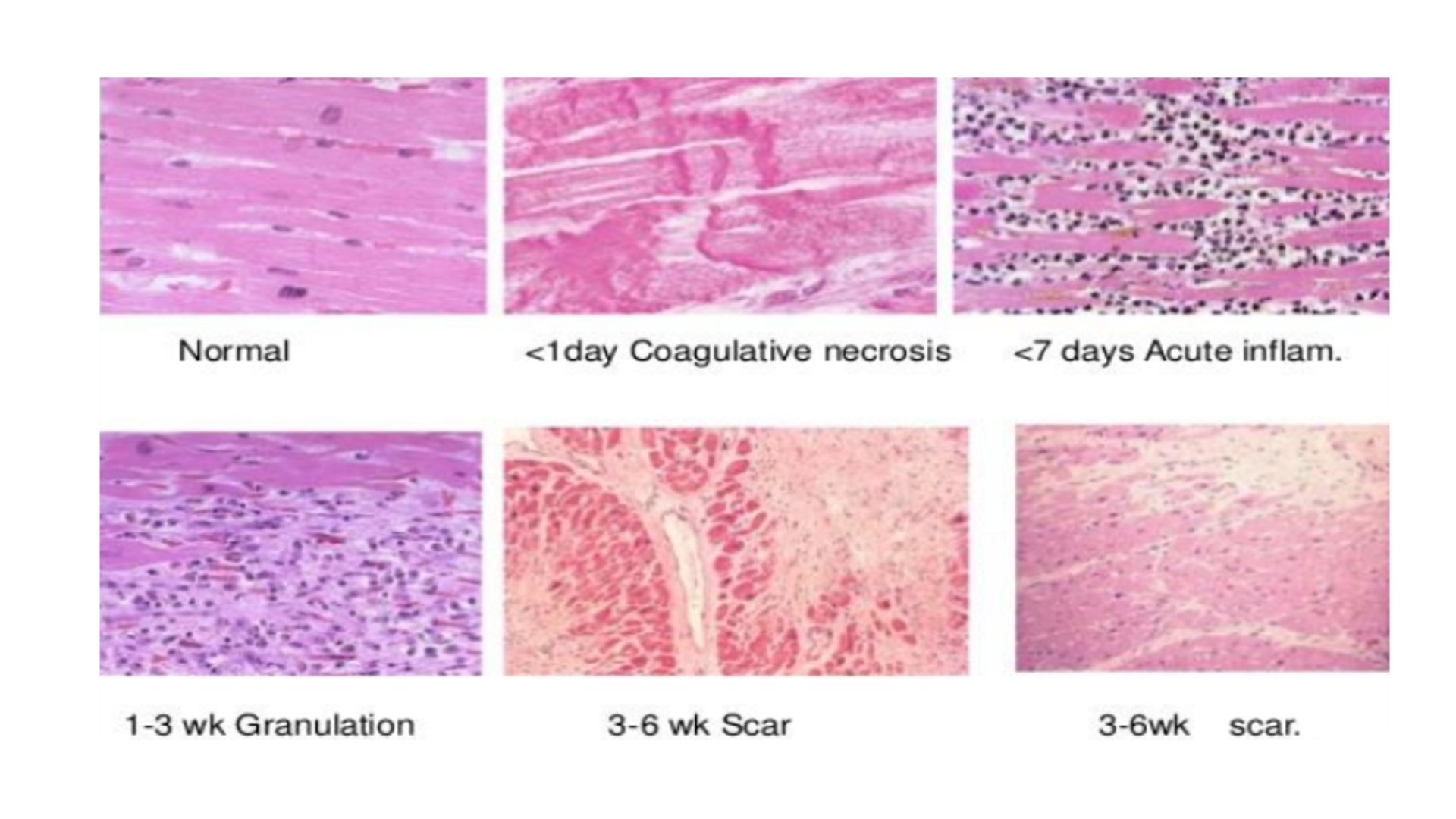
Myocardial Infarction
2 – 24 hours: Contraction bands, edema, acute inflammation (few)
3 – 7 days: Coagulative necrosis (due to no lysosomal enzymes, decreased staining), neutrophilic infiltrate
1 – 3 weeks: Granulation tissue formation, myocytes replaced by tissue, macrophages prominent
3 – 6 weeks: Fibrosis slowly replaces granulation tissue
2 months: Dense fibrosis
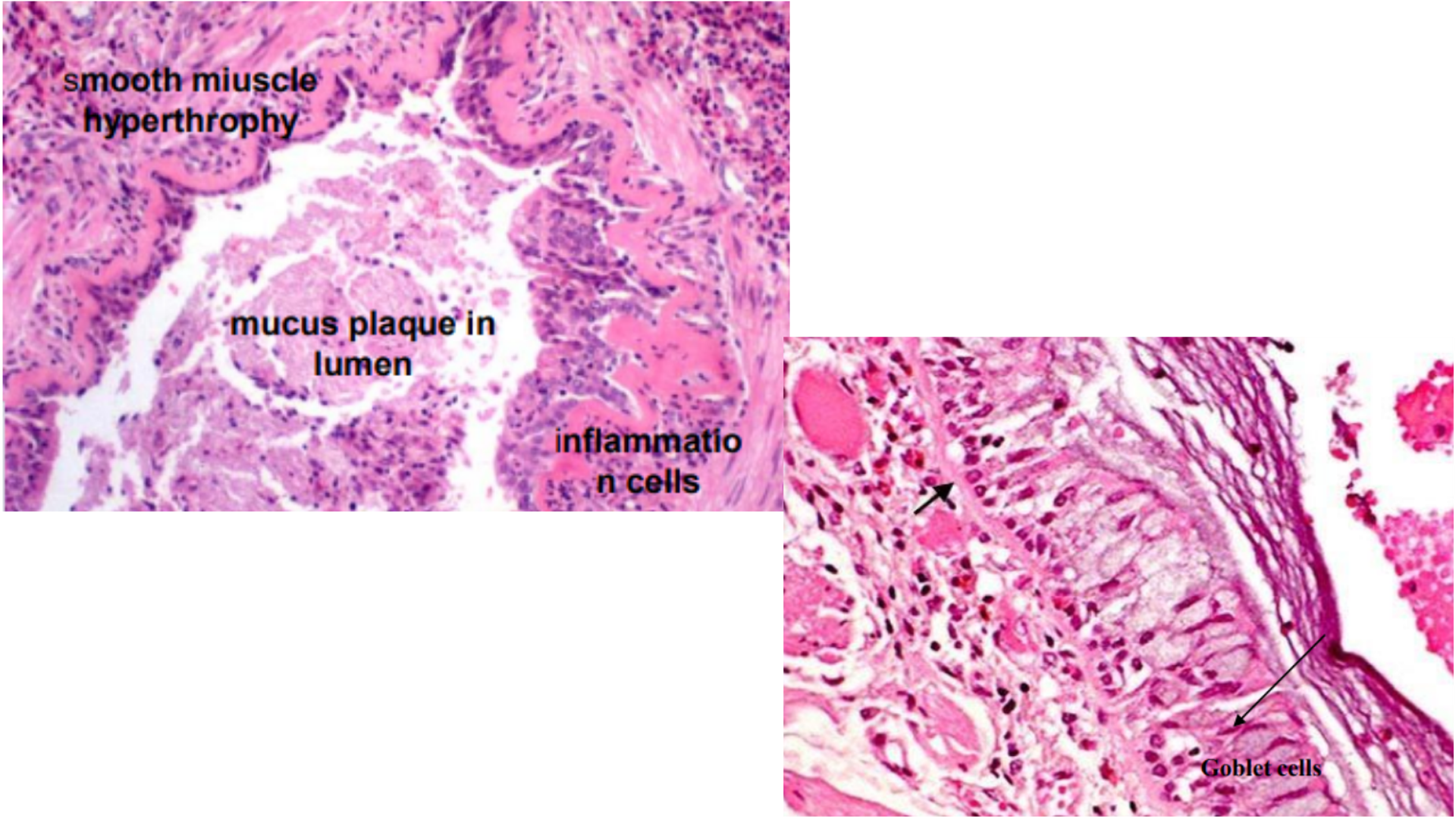
Asthma
Bronchiole lumen narrowing with mucus plug
Exudate with nucleus and serous components
Infiltration of eosinophils
Hyperplasia and increased submucosal mucinous glands (basement membrane thicken) and smooth muscle (bronchial wall)
Folded mucosa, thickened air walls
Charcot-Leyden crystals
Goblet cell hyperplasia
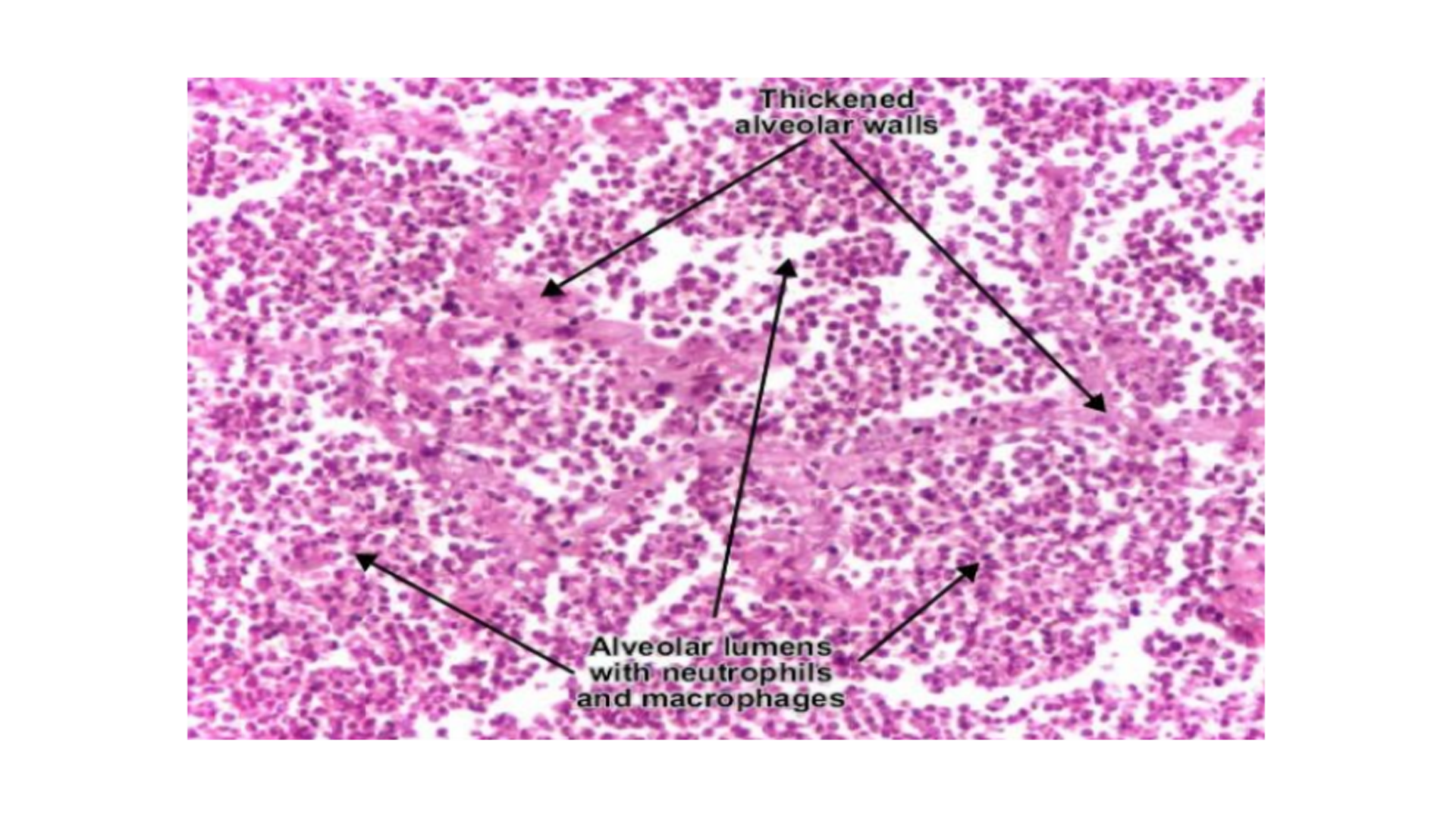
Lobar Pneumonia
Inflammatory cell infiltrate in one lobule (Mainly neutrophils)
Congested capillaries (dilated)
Congestion of alveolar spaces filled with exudate:
Congestion: Bacteria (Serous exudate)
Red Hepatization: Fibrin, neutrophils, RBC
Grey Hepatization: Neutrophils, macrophage, digesting fibrin
Resolution: Cleared, enzymes digested exudate
Edema of lungs
Alveolar walls are thickened due to capillary congestion and edema
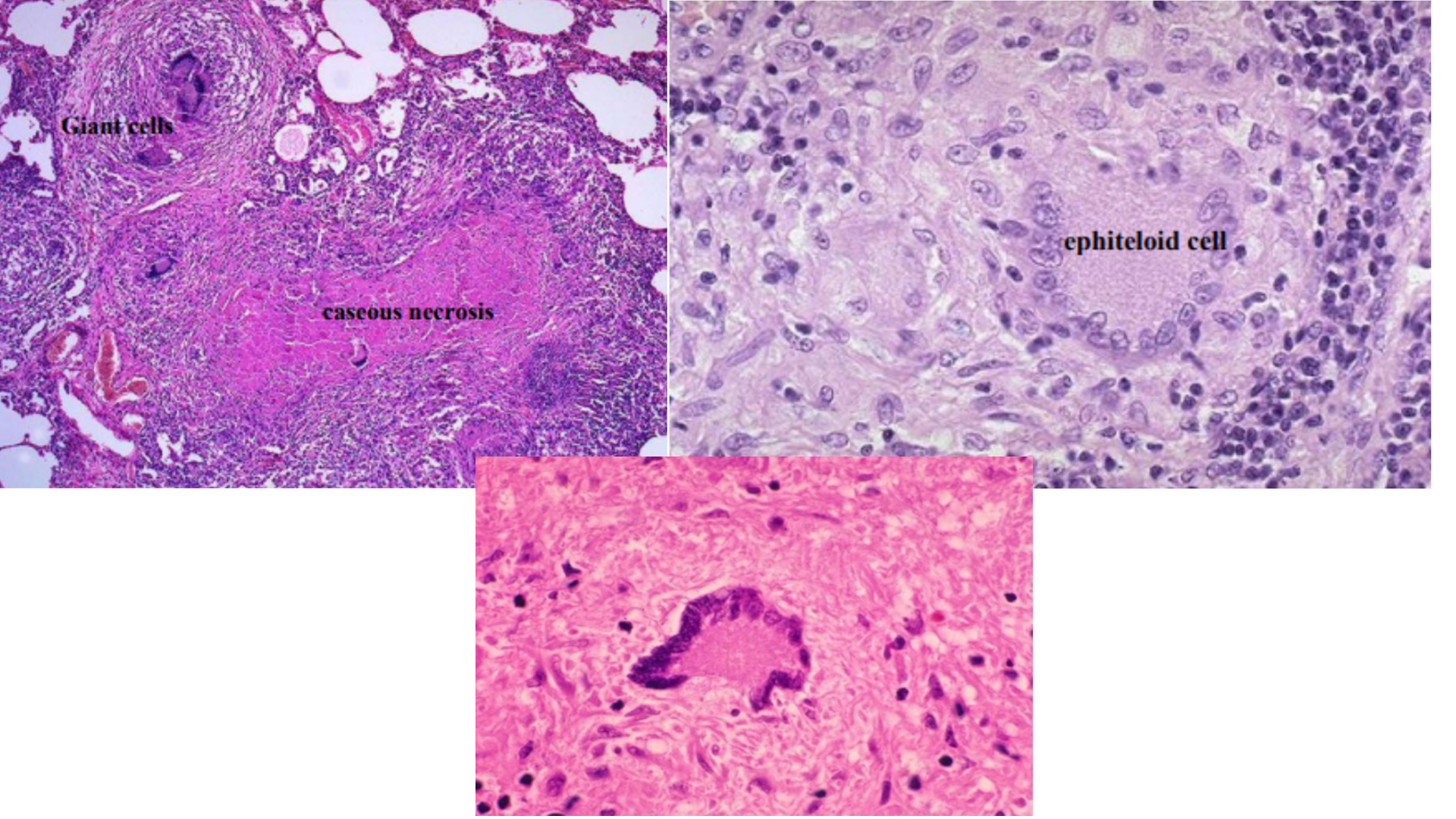
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Granulomatous inflammation (fibroblasts and mononuclear cells)
Caseous necrosis (amorphous and eosinophilic)
Langhan’s Giant Cell (horseshoe shape, macrophages fused together)
Epitheloid histiocytes, lymphocytes and macrophages
Tubercles with rounded outlines
Ghonn’s focus/lesion = all of the above
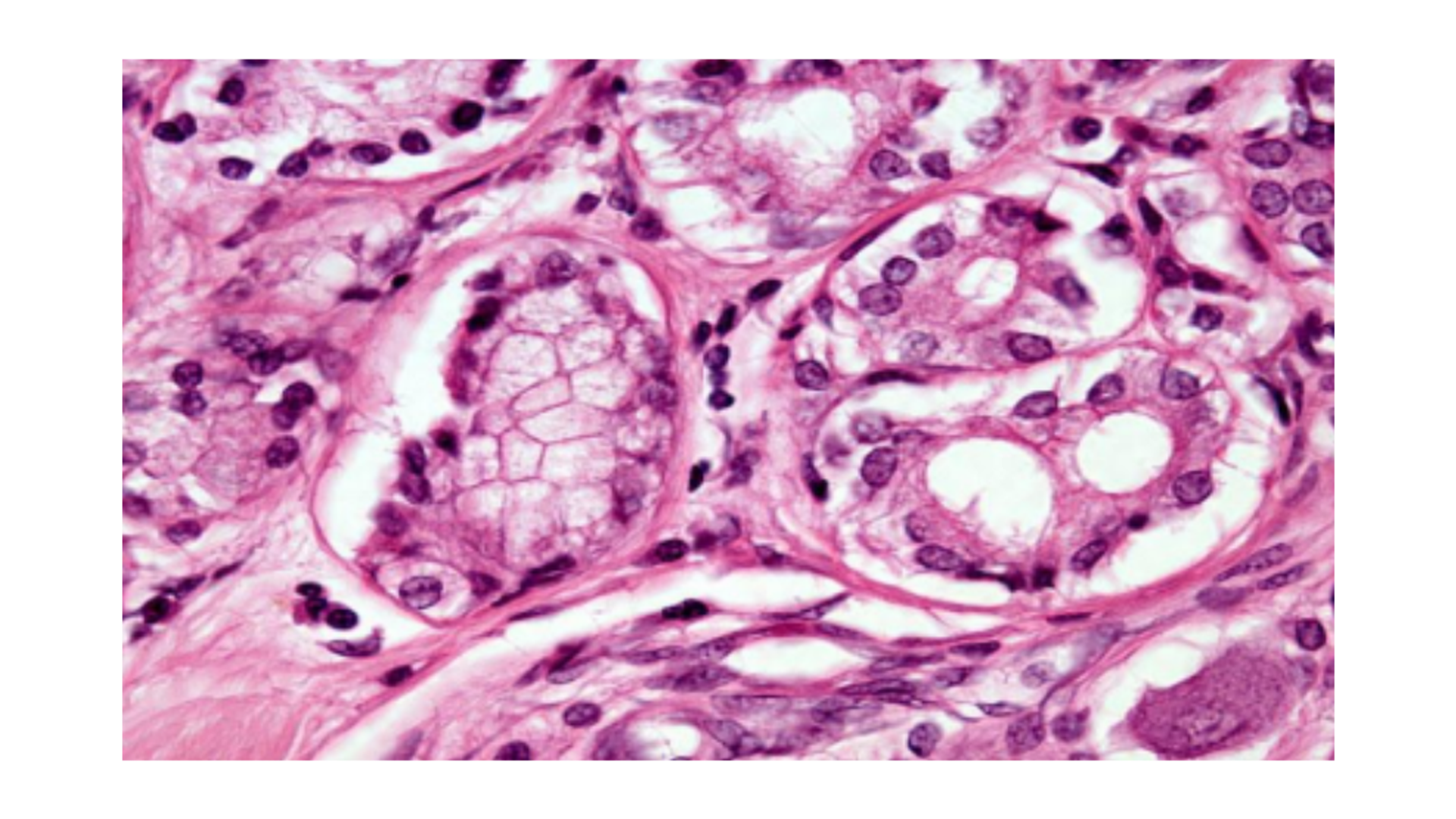
Lung Adenocarcinoma
Starts from peripheral of lungs
Glandular formation and origin
Mucin production, mucus glands stain positive
Columnar cell proliferation
Fibroblastic and inflammatory response
Lepidic growth pattern (along alveolar septae)
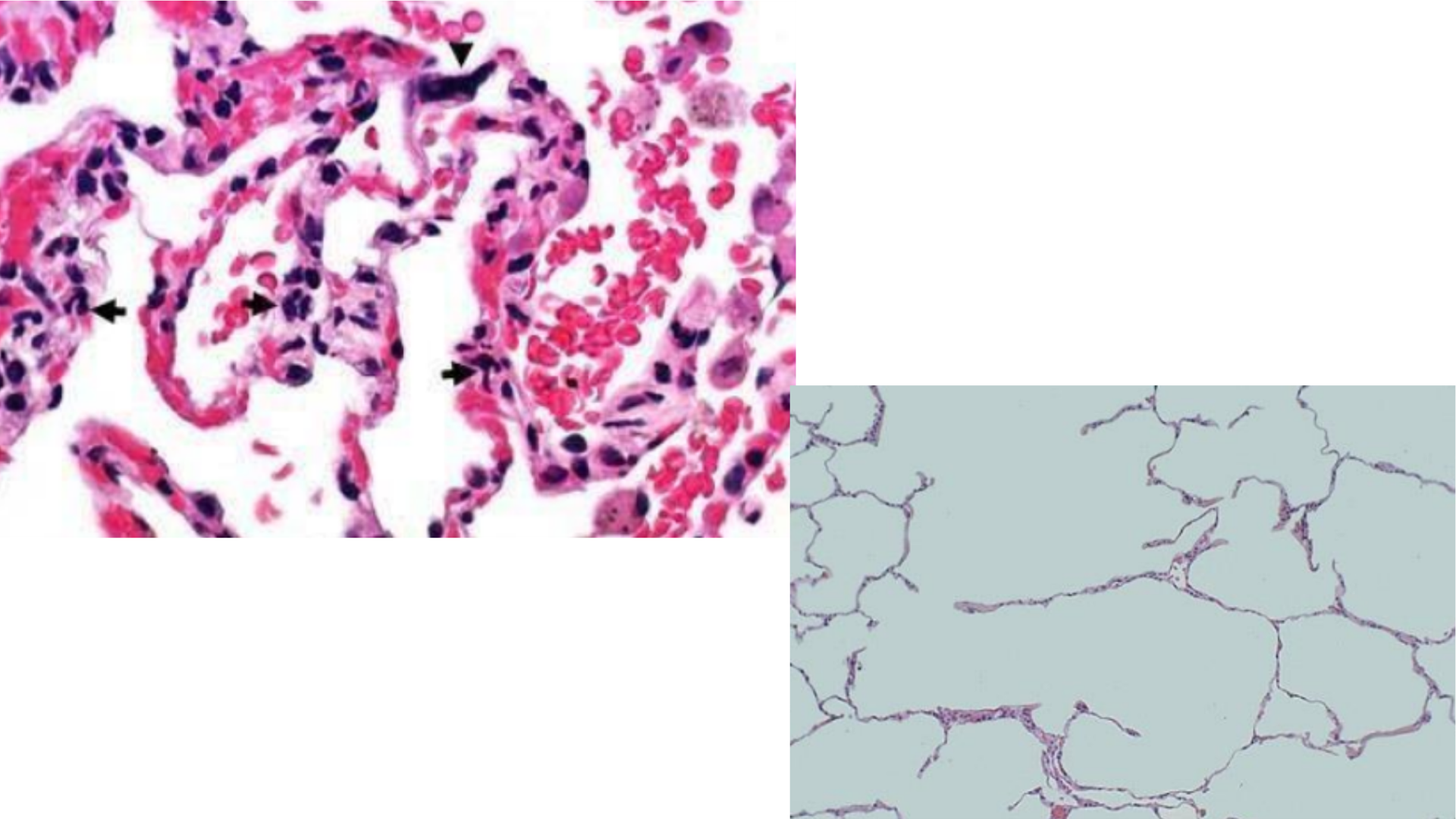
Emphysema
Wide and dilated alveolar spaces = formation of bullae
Destruction of alveolar walls and septums due to proteolysis of elastic fibers
Thick-walled capillaries
Inflammatory cell infiltrate (neutrophilic)
Test for Renal Amyloidosis
Congo Red staining – Red pigment deposited on amyloid deposits. Apple green under birefringence fluorescence.
Thioflavine T – Fluorescence under UV light
Test for Hyaline Arteriosclerosis/Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
PAS staining of hyaline – Dark pink pigment
Test for Peptic Ulcer
Urea Breath Test - Positive if H. pylori causes
Test for Meningitis
CSF Analysis – culture for bacteria and check WBC count
Test for Pneumonia
Blood tests for bacteria – S. pneumoniae, S. aureus
Test for Tuberculosis
Sputum culture – Positive for M. tuberculosis
Mantoux Test - Positive if there is a bump on skin