1: Hematopoiesis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:23 AM on 8/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
Hematopoiesis
\
Cell division = 2 identical daughter cells
\*1 of these cells remains as a hematopoietic stem cell → proliferate and differentiate → progenitor cells (influenced by growth facotrs, production is based on necessity) → precursor cells
\
Cell division = 2 identical daughter cells
\*1 of these cells remains as a hematopoietic stem cell → proliferate and differentiate → progenitor cells (influenced by growth facotrs, production is based on necessity) → precursor cells
* continuous, regulated process of renewal, proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of all blood cell lines
* Prenatal and postnatal hematopoiesis
* Prenatal and postnatal hematopoiesis
2
New cards
RBC production
Erythropoiesis
3
New cards
WBC production
Leukopoiesis
4
New cards
granulocytic (neutrophil, basophil, eosinophil)
Myelopoiesis (under Leukopoiesis)
5
New cards
lymphocyte production
Lymphopoiesis
6
New cards
megakaryocyte
* thrombocyte / platelets
* thrombocyte / platelets
Megakaryopoiesis
7
New cards
1. Mesoblastic period
2. Hepatic period
3. Myeloid / Medullary period
3 stages of PRENATAL Hematopoiesis
8
New cards
Primitive Erythropoiesis
Mesoblastic period is AKA?
9
New cards
nineteenth (embryonic hemoglobin)
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* begins as early as the (?) day after fertilization
* begins as early as the (?) day after fertilization
10
New cards
erythrocytes
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* only (?) are made (primitive erythroblasts)
* only (?) are made (primitive erythroblasts)
11
New cards
1. Gower-1
2. Gower-2
3. Portland
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* the RBCs contain unique fetal hemoglobins
* the RBCs contain unique fetal hemoglobins
12
New cards
1. Gower-1
2. Gower-2
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* which fetal hemoglobin/s would disappear and be replaced eventually
* which fetal hemoglobin/s would disappear and be replaced eventually
13
New cards
intravascularly
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* occurs (?)
* occurs (?)
14
New cards
yolk sac of the embryo
**Prenatal: Mesoblastic**
* location
* location
15
New cards
fetal liver
**Prenatal: Hepatic**
* location
* location
16
New cards
* thymus
* spleen
* lymph nodes
* spleen
* lymph nodes
**Prenatal: Hepatic**
* what other organs are involved besides the liver
* what other organs are involved besides the liver
17
New cards
5-7
**Prenatal: Hepatic**
* Begins around (?) gestational weeks
* Begins around (?) gestational weeks
18
New cards
extravascularly
**Prenatal: Hepatic**
* occurs (?)
* occurs (?)
19
New cards
Hgb F and adult hemoglobins
**Prenatal: Hepatic**
* what *substances* replaced the Gower-1 and -2 from the Mesoblastic period?
* what *substances* replaced the Gower-1 and -2 from the Mesoblastic period?
20
New cards
Prenatal: Hepatic
* Beginning of definitive hematopoiesis
* Megakaryopoiesis begins
* Megakaryopoiesis begins
21
New cards
4th to 5th
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
* Begins at (?) month of fetal development
* Begins at (?) month of fetal development
22
New cards
medulla of BM
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
* location
* location
23
New cards
24th
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
* By the end of (?) weeks of gestation: BM becomes the primary site
* By the end of (?) weeks of gestation: BM becomes the primary site
24
New cards
Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary
* Detectable levels of EPO, G-CSF, GM-CSF
* Fetal Hgb, adult Hgb
* Fetal Hgb, adult Hgb
25
New cards
erythropoietin
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
Meaning of EPO
Meaning of EPO
26
New cards
granulocyte - colony stimulating factor
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
Meaning of G-CSF
Meaning of G-CSF
27
New cards
granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
Meaning of GM-CSF
Meaning of GM-CSF
28
New cards
hypoxia
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
stimulus of RBC production
stimulus of RBC production
29
New cards
bone marrow, RBC precursors
**Prenatal: Myeloid/Medullary**
Target EPO
Target EPO
30
New cards
delivery / birth
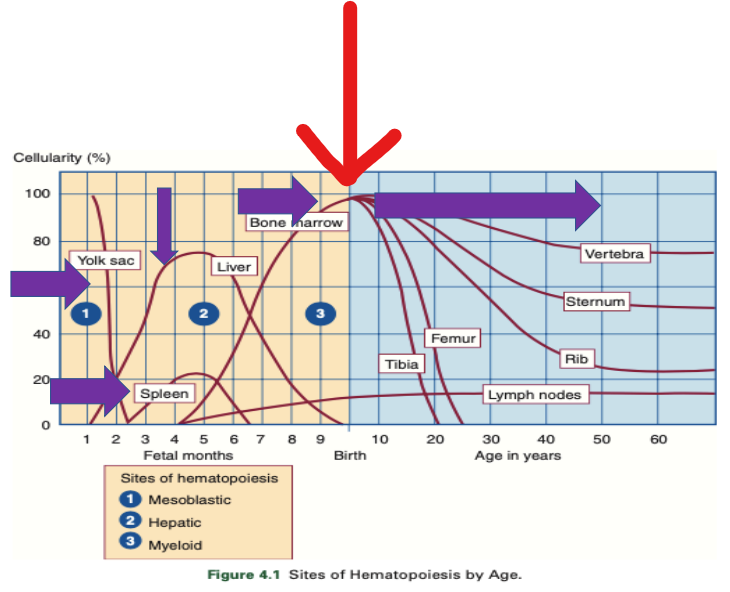
31
New cards
red marrow
32
New cards
childhood
at what age: all red marrow
33
New cards
adulthood
at what age: red marrow only in flatbones, cranium, sternum, pelvis, proximal ends of long bones
34
New cards
medullary hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis in the bone marrow
35
New cards
extramedullary hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis in areas other than the bone marrow
36
New cards
bone marrow, thymus
**Extramedullary Hematopoiesis**
2 primary lymphoid organs
2 primary lymphoid organs
37
New cards
spleen, lymph nodes
**Extramedullary Hematopoiesis**
2 secondary lymphoid organs
2 secondary lymphoid organs
38
New cards
medullary hematopoiesis
* sometimes occur, even in adulthood
* damage
* diseases associated w/ hematopoiesis
* damage
* diseases associated w/ hematopoiesis
39
New cards
1. Bone marrow
2. Liver
3. Lymph nodes
4. Spleen
5. Thymus
Name the 5 Hematopoietic tissues
40
New cards
inside the spongy bone
**Bone Marrow**
Located?
Located?
41
New cards
red; yellow
**Bone Marrow**
In a normal adult, ½ of the bone marrow is hematopoietically active (? marrow) and ½ is inactive, fatty marrow (? marrow).
In a normal adult, ½ of the bone marrow is hematopoietically active (? marrow) and ½ is inactive, fatty marrow (? marrow).
42
New cards
* Erythroid (RBC) precursors
* Leukocyte (WBC) precursors
* Platelet precursors
* Leukocyte (WBC) precursors
* Platelet precursors
**Bone Marrow**
Components (precursors)
Components (precursors)
43
New cards
50
**Bone Marrow**
Early in life most of the marrow is red marrow and it gradually decreases with age to the adult level of how many percent?
Early in life most of the marrow is red marrow and it gradually decreases with age to the adult level of how many percent?
44
New cards
adipose
**Bone Marrow**
We can find the yellow marrow in the (?) cells
We can find the yellow marrow in the (?) cells
45
New cards
5-10X
**Bone Marrow**
In certain pathologic states the bone marrow can increase its activity to (?) its normal rate
In certain pathologic states the bone marrow can increase its activity to (?) its normal rate
46
New cards
hyperplastic
**Bone Marrow**
In certain pathologic states the bone marrow can increase its activity to 5-10X its normal rate. When this happens, the bone marrow is said to be?
In certain pathologic states the bone marrow can increase its activity to 5-10X its normal rate. When this happens, the bone marrow is said to be?
47
New cards
hyperplastic
**Bone Marrow**
what do you call it when the hematopoietic stem cells exceed 70%
what do you call it when the hematopoietic stem cells exceed 70%
48
New cards
hyperplasia, hypercellularity
**Bone Marrow**
other terms for hyperlastic
other terms for hyperlastic
49
New cards
yellow; red
**Bone Marrow**
When in hyperplastic state, the (?) marrow replaces the (?) marrow
When in hyperplastic state, the (?) marrow replaces the (?) marrow
50
New cards
increased or ineffective
**Bone Marrow**
Hyperplastic conditions occur where there is (?) hematopoiesis
Hyperplastic conditions occur where there is (?) hematopoiesis
51
New cards
Acute blood loss
**Bone Marrow**
a temporary replacement of the yellow marrow
a temporary replacement of the yellow marrow
52
New cards
Severe chronic anemia
**Bone Marrow**
erythropoiesis (RBC production) may increase to the extent that the marrow starts to erode the bone itself
erythropoiesis (RBC production) may increase to the extent that the marrow starts to erode the bone itself
53
New cards
Malignant disease
**Bone Marrow**
both normal red marrow and fatty marrow may be replaced by proliferating abnormal cells
both normal red marrow and fatty marrow may be replaced by proliferating abnormal cells
54
New cards
Vitamin B
**Bone Marrow**
Vitamin crucial in the production of the DNA
Vitamin crucial in the production of the DNA
55
New cards
hypoplastic
**Bone Marrow**
this can also become inactive or (?)
this can also become inactive or (?)
56
New cards
hypoplasia, hypocellularity
**Bone Marrow**
other terms for hypoplastic
other terms for hypoplastic
57
New cards
* chemicals
* genetics
* Myeloproliferative disease that replaces hematopoietic tissue with fibrous tissue
* genetics
* Myeloproliferative disease that replaces hematopoietic tissue with fibrous tissue
**Bone Marrow**
becomes hypoplastic due to:
becomes hypoplastic due to:
58
New cards
insecticides
**Bone Marrow**
example of chemical that can induce hypocellularity
example of chemical that can induce hypocellularity
59
New cards
CELLULARITY
**Bone Marrow**
ratio of marrow cells to fat
ratio of marrow cells to fat
60
New cards
NORMOCELLULAR
**Bone Marrow**
30-70% HSCs
30-70% HSCs
61
New cards
HYPERCELLULAR/HYPERPLASTIC
**Bone Marrow**
>70% HSCs
>70% HSCs
62
New cards
HYPOCELLULAR/HYPOPLASTIC
**Bone Marrow**
63
New cards
APLASTIC
**Bone Marrow**
few or no HSCs
few or no HSCs
64
New cards
Normal
**Bone Marrow**
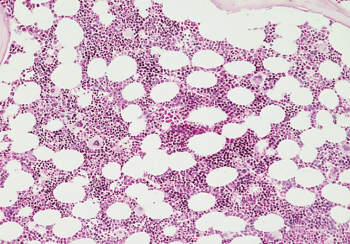
65
New cards
Hyperplastic
**Bone Marrow**
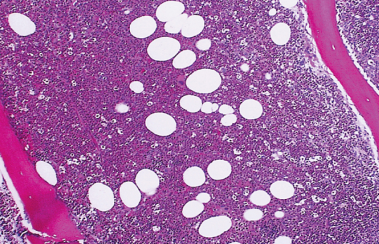
66
New cards
Hypoplastic
**Bone Marrow**
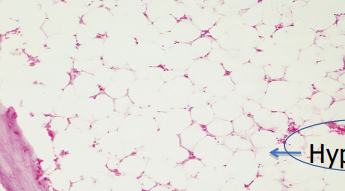
67
New cards
Pancytopenia
**Bone Marrow**
* deficiency of all three cellular components of the blood (red cells, white cells, and platelets)
* bone marrow doesn't produce enough healthy blood cells
* deficiency of all three cellular components of the blood (red cells, white cells, and platelets)
* bone marrow doesn't produce enough healthy blood cells
68
New cards
M:E (myleloid:erythroid) ratio
**Bone Marrow**
ratio of granulocytes & their precursors to nucleated erythroid precursors
ratio of granulocytes & their precursors to nucleated erythroid precursors
69
New cards
2:1 and 4:1 (average of 3:1)
**Bone Marrow**
Normal M:E (myleloid:erythroid) ratio
Normal M:E (myleloid:erythroid) ratio
70
New cards
Granulocytes; erythrocytes
**Bone Marrow**
(?) are numerous because of their short survival (1-2 days) as compared to (?) of 120 days
(?) are numerous because of their short survival (1-2 days) as compared to (?) of 120 days
71
New cards
Infection
**Bone Marrow**
6:1
6:1
72
New cards
neutrophils
**Bone Marrow**
(?) phagocytize bacteria and die after
(?) phagocytize bacteria and die after
73
New cards
neutropenia
**Bone Marrow**
low neutrophil count
low neutrophil count
74
New cards
neutrophilia
**Bone Marrow**
high neutrophil count
high neutrophil count
75
New cards
Leukemia
**Bone Marrow**
25:1
25:1
76
New cards
Myeloid hyperplasia
**Bone Marrow**
20:1 (high WBC count)
20:1 (high WBC count)
77
New cards
Myeloid hypoplasia
**Bone Marrow**
3:20 (low WBC count)
3:20 (low WBC count)
78
New cards
hepatocytes
**Liver**
cells in the liver
cells in the liver
79
New cards
protein synthesis and degradation, coagulation factor synthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, drug and toxin clearance, iron recycling and storage, and hemoglobin degradation
**Liver**
functions of hepatocytes
functions of hepatocytes
80
New cards
hemoglobin degradation
**Liver**
function of hepatocytes in which bilirubin is conjugated and transported to the small intestine for eventual excretion
function of hepatocytes in which bilirubin is conjugated and transported to the small intestine for eventual excretion
81
New cards
Kupffer cells
**Liver**
Contains phagocytic cells known as
Contains phagocytic cells known as
82
New cards
Kupffer cells
**Liver**
act as a filter for damaged or aged cells in a manner similar to, but less efficient than the phagocytic cells in the spleen
act as a filter for damaged or aged cells in a manner similar to, but less efficient than the phagocytic cells in the spleen
83
New cards
splenic macrophages
**Liver**
which cell is more efficient than the Kupffer cells
which cell is more efficient than the Kupffer cells
84
New cards
bilirubin
**Liver**
degradation product of protoporphyrin
degradation product of protoporphyrin
85
New cards
* lymph nodes
* lymphatic vessels
* drain into the left and right lymphatic duct
* lymphatic vessels
* drain into the left and right lymphatic duct
Composition of lymphatic system
86
New cards
Lymph
**Lymph Nodes**
formed from blood fluid that escapes into the connective tissue
formed from blood fluid that escapes into the connective tissue
87
New cards
It is because these lymph nodes are more superficial. However, lymph nodes can still be found all over the body.
**Lymph Nodes**
Why are the axillary, inguinal, and cervical lymph nodes easily found/palpated?
Why are the axillary, inguinal, and cervical lymph nodes easily found/palpated?
88
New cards
lymphoma
**Lymph Nodes**
cancer of lymph nodes
cancer of lymph nodes
89
New cards
lymph nodes
**Lymph Nodes**
* very significant in the development of lymphocytes and macrophages
* filter the lymphatic fluid.
* very significant in the development of lymphocytes and macrophages
* filter the lymphatic fluid.
90
New cards
lymphatic fluid
**Lymph Nodes**
plasma outside the cardiovascular system
plasma outside the cardiovascular system
91
New cards
plasma
**Lymph Nodes**
the composition of lymphatic fluid is similar to (?)
the composition of lymphatic fluid is similar to (?)
92
New cards
3%
**Lymph Nodes**
Every time our heart beats, blood is distributed all throughout and around how many percent of our plasma leaks out and enters the connective tissues?
Every time our heart beats, blood is distributed all throughout and around how many percent of our plasma leaks out and enters the connective tissues?
93
New cards
lymphocytes, macrophages, and a reticular network
**Lymph Nodes**
composition
composition
94
New cards
medulla
**Lymph Node**
Structure
* inner area
* plasma cells
Structure
* inner area
* plasma cells
95
New cards
plasma cells
**Lymph Nodes**
Structure
* these cells are derived from B lymphocytes
* involved in antibody producion
Structure
* these cells are derived from B lymphocytes
* involved in antibody producion
96
New cards
cortex
Lymph Node
Structure
* outer area
* follicles, B lymphocytes
Structure
* outer area
* follicles, B lymphocytes
97
New cards
B lymphocytes
**Lymph Nodes**
Structure
* these cells are involved in humoral immunity
Structure
* these cells are involved in humoral immunity
98
New cards
plasma cells, memory cells
**Lymph Nodes**
Stucture
* B lymphocytes can develop into what 2 types of cells?
Stucture
* B lymphocytes can develop into what 2 types of cells?
99
New cards
memory cells
**Lymph Nodes**
Structure
* cells for recognition
Structure
* cells for recognition
100
New cards
paracortex
Lymph Node
Structure
* T lymphocytes
* macrophages
Structure
* T lymphocytes
* macrophages