Bio Cell Transport Quiz
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Function of cell membrane, structure of cell membrane, cellular transport, passive transport, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, solutions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the function of Cell membrane (All cells)?
Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance and provides protection and support for the cell.
What is the structure of cell membrane?
Lipid Bilayer - 2 layers of phospholipids
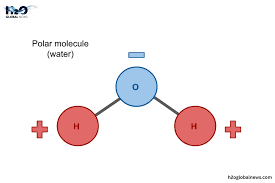
Phosphate head is polar
Fatty acid tail is non-polar
Proteins embedded in membrane
Selectively Permeable
What does polar mean?
Water loving
What does non-polar mean?
Water fearing
What is Selectively Permeable?
Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out.
What is Equilibrium?
The concentration of water is the same inside and outside of the cell.
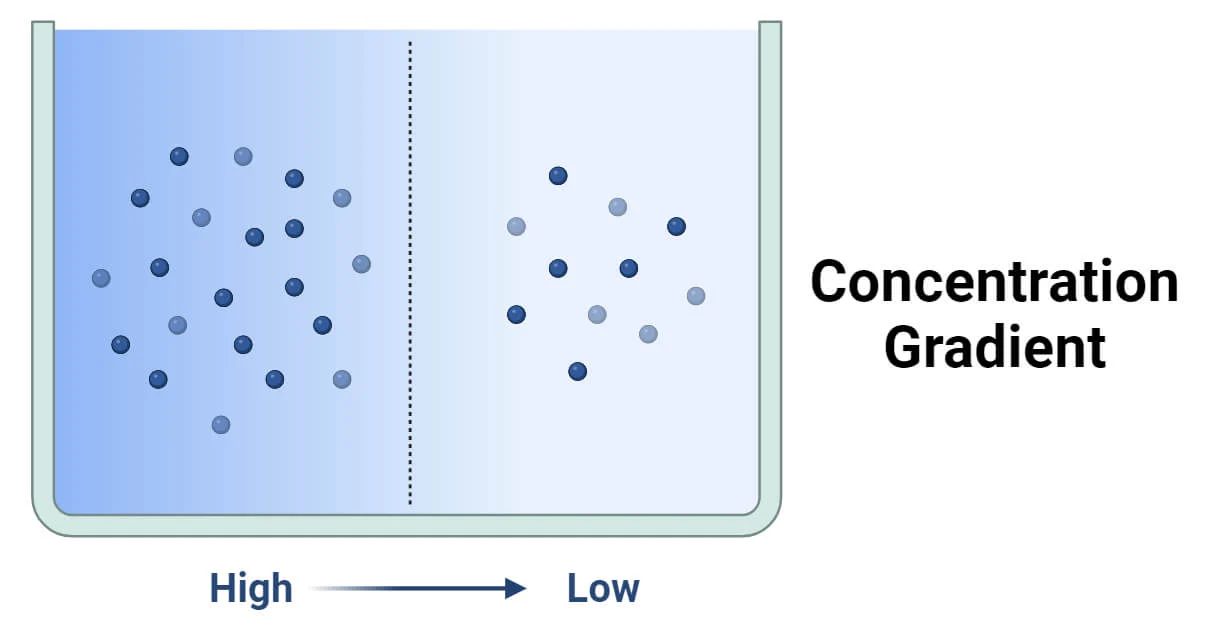
What is a Concentration Gradient?
A difference in the concentration of a substance (high or low concentration).
What is the difference between Passive Transport and Active Transport?
Passive doesn’t use energy while Active Transport does.
What are the 3 types of Passive Transport?
Diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, and Osmosis.
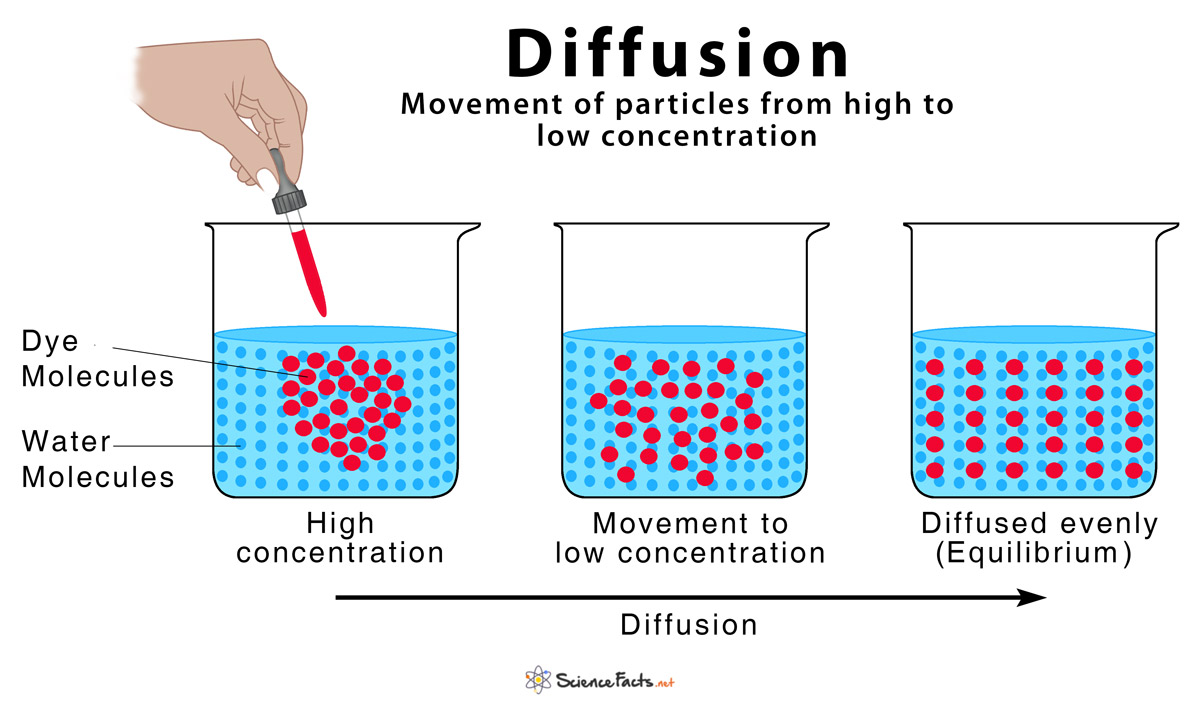
What is Diffusion?
Random movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration and continues until an equilibrium is reached.
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
A diffusion of specific particles through transport found in the membrane.
Transports larger or charged molecules
Ex : Ion Channel and Carrier Protein
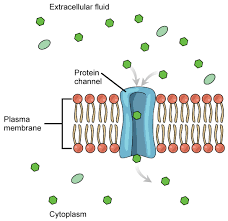
What is Ion Channel
A transport proteins with a polar pore; ions pass through
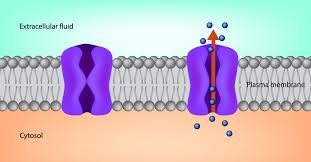
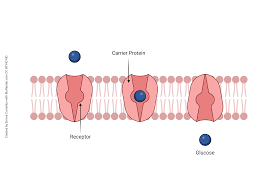
What is a Carrier Protein
Attached to a molecule on the outside of the cell, transport it across the membrane, release it on the other side.
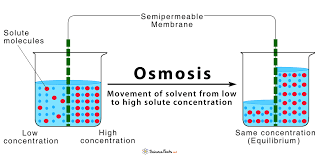
What is osmosis
A diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Water moves from high to low concentrations
Example of Active Transport
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
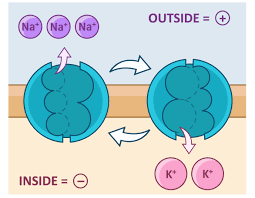
What is Sodium-Potassium Pump?
Transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell.
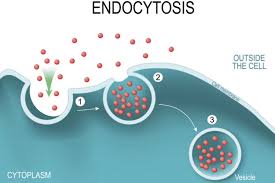
What is Endocytosis
Taking material into a cell
Uses energy
Cell membrane in-folds around particle
‘cell eating’
How white blood cells eat bacteria
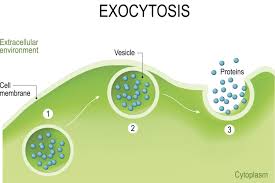
What is Exocytosis?
Forces material out of a cell in bulk
Vesicles in the cell fuse with cell membrane and release their content
Ex : Hormones or wastes released from cell
What is Hypotonic Solution?
Solution that has low solute : high water concentration (prominently water) than a cell.
Result : Water goes inside the cell →Cell grows (Cytolysis)

What is Hypertonic Solution?
A solution that has high solute : low water concentration (more solute) than a cell.
Result : Water moves into the solution → Cell shrinks (Plasmolysis)

What is Isotonic Solution?
The concentration of solute : water is equal.
Result : Water moves in and out → cell remains the same size (Dynamic Equilibrium).

What do all cells have?
A cell membrane.

What is homeostasis?
An internal balance.

How do organisms deal with osmotic pressure?
Cell walls keeps bacteria and plants from over-expanding
Contractile vacuoles collect water flowing in and pump it out to keep them from over-expanding
Salt water fish pump salt out of gills so they don’t dehydrate
Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys remove excess salt and water to keep blood Isotonic.