Tectonic plates
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Crust
Made up of rocks and mineral
70% covered by oceans
Thin, brittle outer coating
Outer layer (7-50km thick)
Mantle
below the crust (1288km thick)
Temperature near the crust is 500 degree celsius and at the bottom of the mantle is 300 degree celsius
Top part is made out of clay and bottom part is solid
Semi liquid rock or molten rock
Outer core
made up of molten, metals, (iron and some nickels)
Very hot and liquid, temperature ranging from 4000 degree celsius to 6000 degree celsius
Inner core
temperature is almost 10 000 degree celsius and at
Doesn’t melt or boil because of the force of the Earth pushing down
Made up of soild metals (iron and nickel)
Tectonic plates
Large piece of the Earth’s outer layer that moves very slowly
Continental drift
Theory that states that Earth continents are moving away and towards one another.
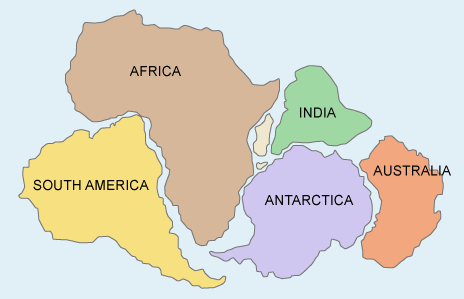
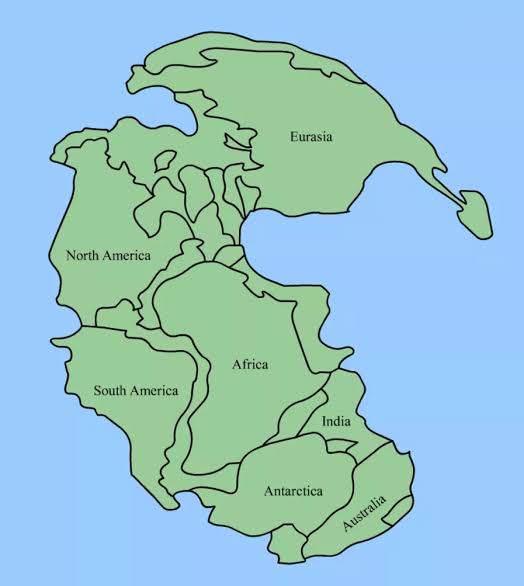
Pangea
When all continents combined together
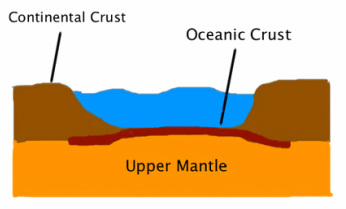
Continental crust/plate
Possess large land masses of them. Usually quite thick but lighter than oceanic plates
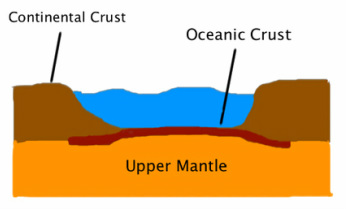
Oceanic crust/plate
Oceans lay on top of them. Usually quite thin but heavier than continental plates.
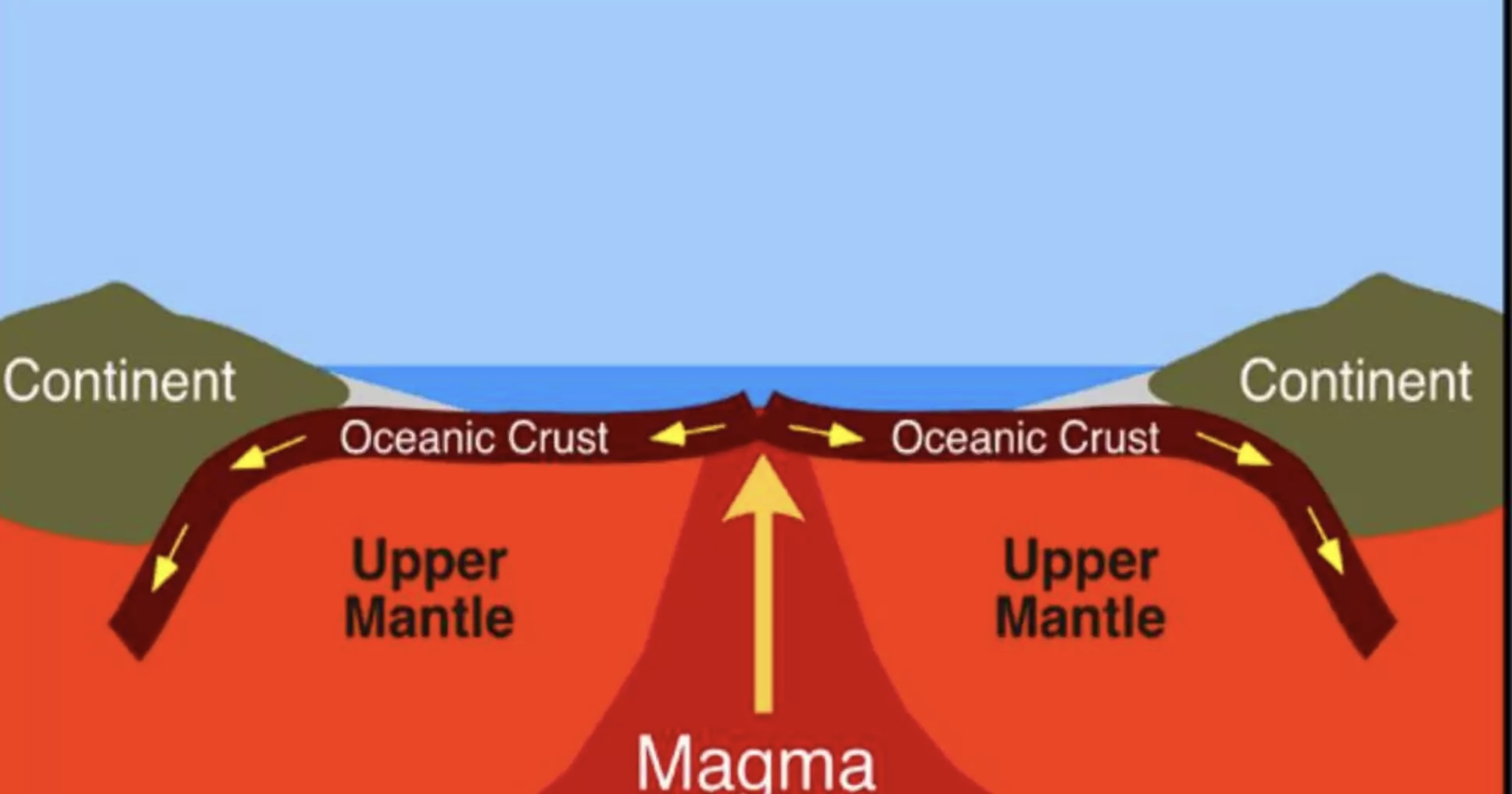
Sea floor spreading
When oceanic plates move away from each other.
New rocks is formed between the two plates as they appear
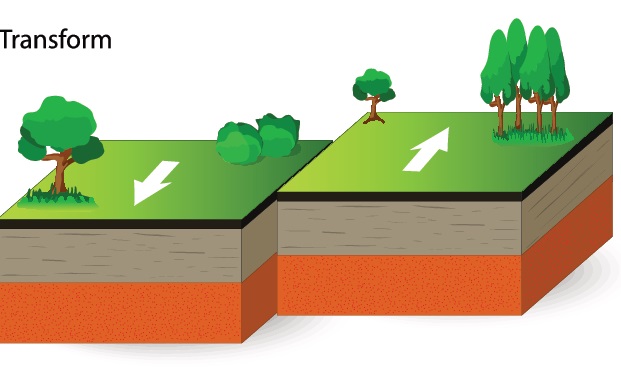
Transforming plate boundaries
Where two plates slide past each other
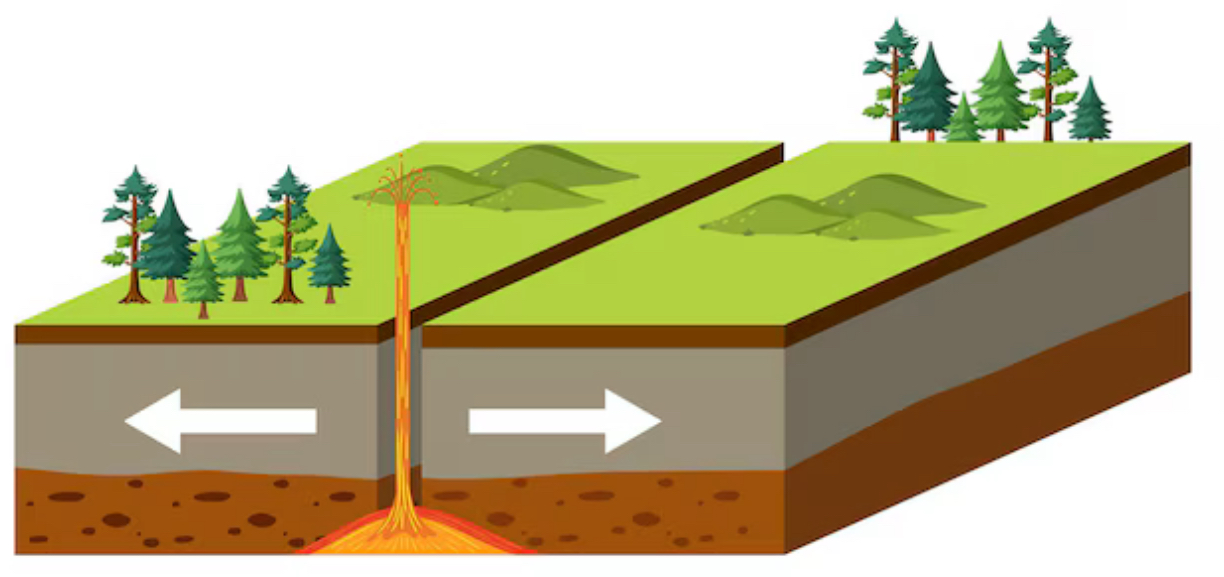
Diverging plate boundaries
Two plates moving away from each other
Converging plate boundaries
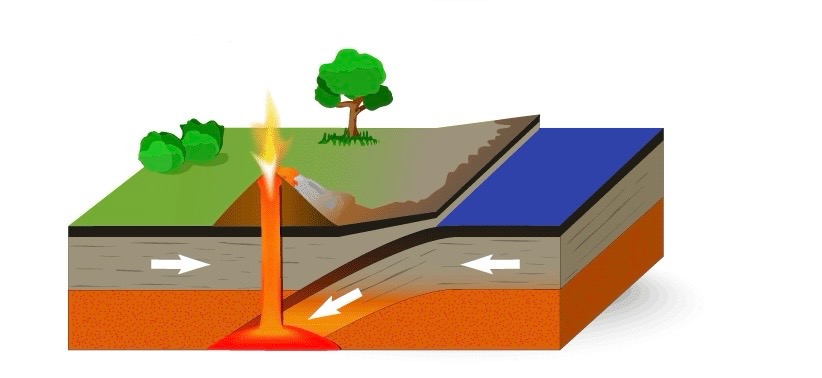
When two plates collide together.
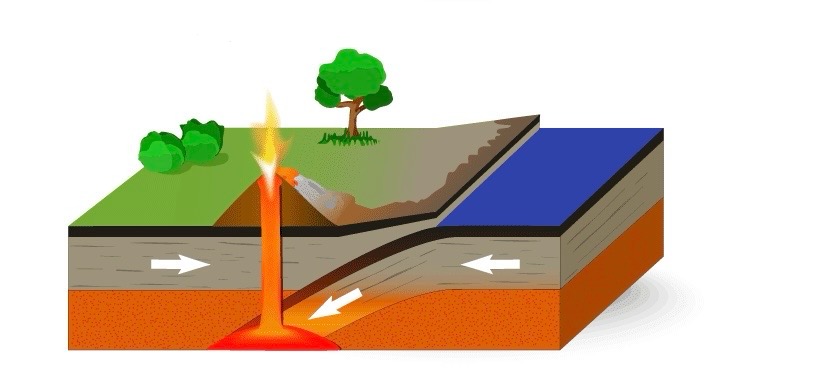
Convection currents
circular movements of fluid (liquid or gas) caused by the heating and cooling process, resulting in the transfer of heat energy.
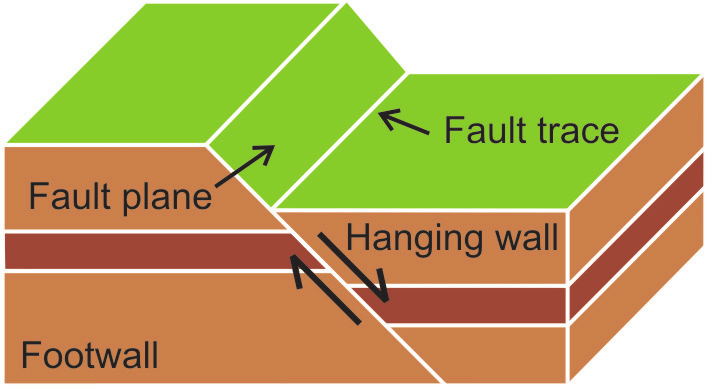
Fault
Fracture or break in the Earth’s crust. It occurs when shear stress on a rock overcomes the forces holding it together.
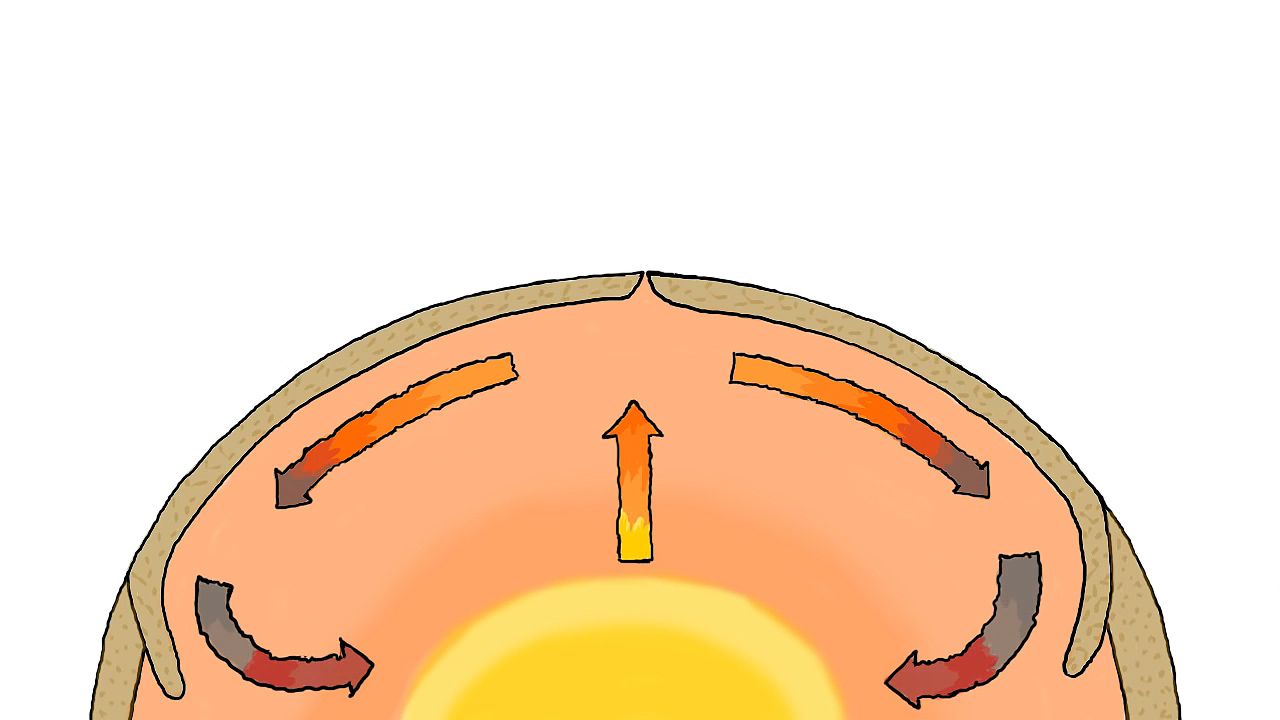
Hot spots
Regions deep within the Earth where unusually hot magma rises through the mantle to the surface, creating volcanic activity.
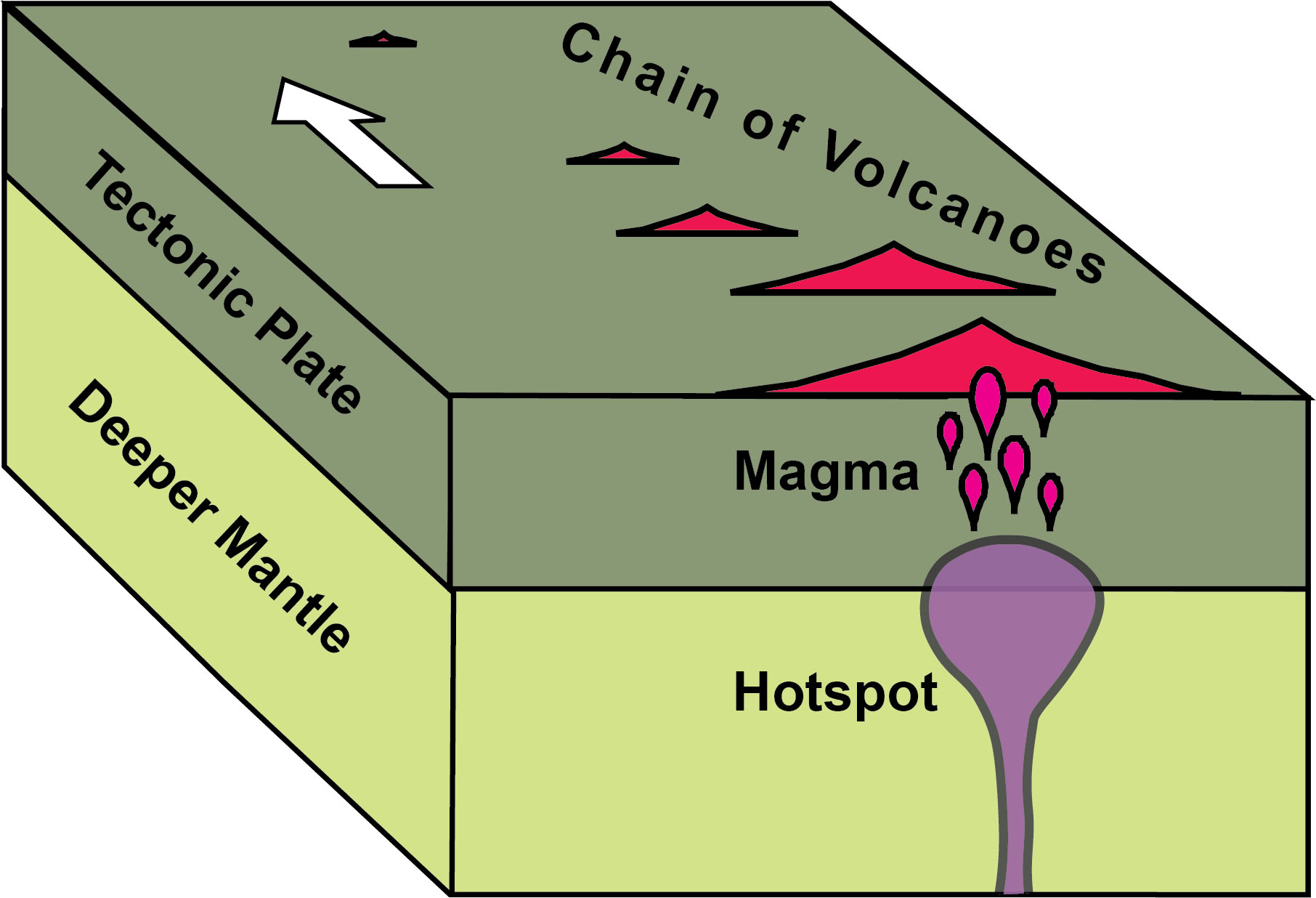
Subduction
One plate being forced beneath another.