Histological Stains and Pathology: Amyloid, Fibrosis, and Atherosclerosis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the molecular mechanism of the Congo Red stain?
It binds specifically to the beta-pleated sheet structure of amyloid proteins through hydrogen bonds.
What is the clinical use of the Congo Red stain?
To diagnose Amyloidosis.
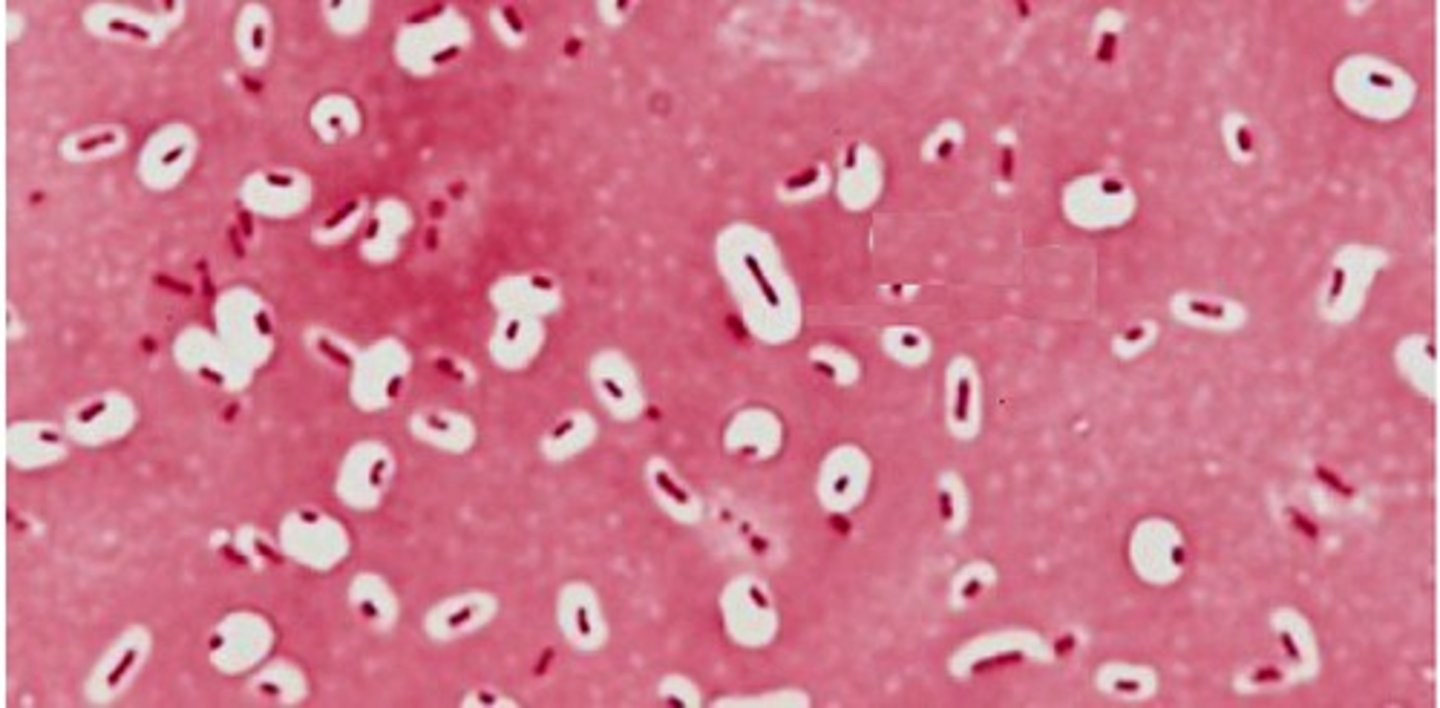
What is the chemistry behind Hematoxylin staining?
It is a basic (positively charged) dye. It requires a mordant (metal salt like aluminium) to bind to the negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA and RNA within the cell nucleus.

How does Alcian Blue identify specific mucins?
It binds to acidic mucopolysaccharides (negatively charged carboxyl and sulfate groups). Note: pH is critical; at pH 2.5, both sulfated and carboxylated mucins are stained..
What is the Verhoeff-Van Gieson (VVG) stain used for?
To visualise Elastic Fibres.
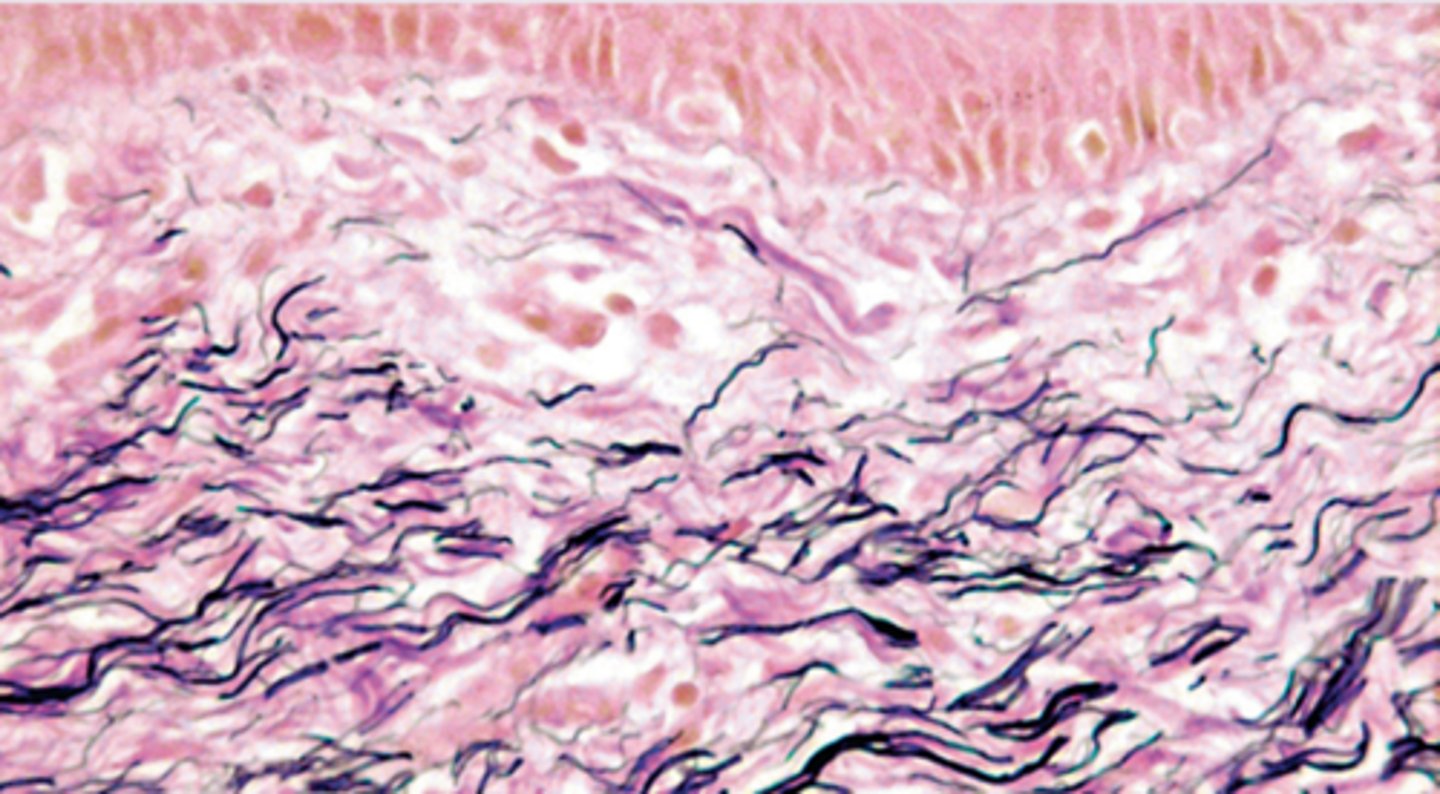
What is the appearance of elastin and collagen when stained with VVG?
Elastin stains black/blue-black, while collagen stains red.

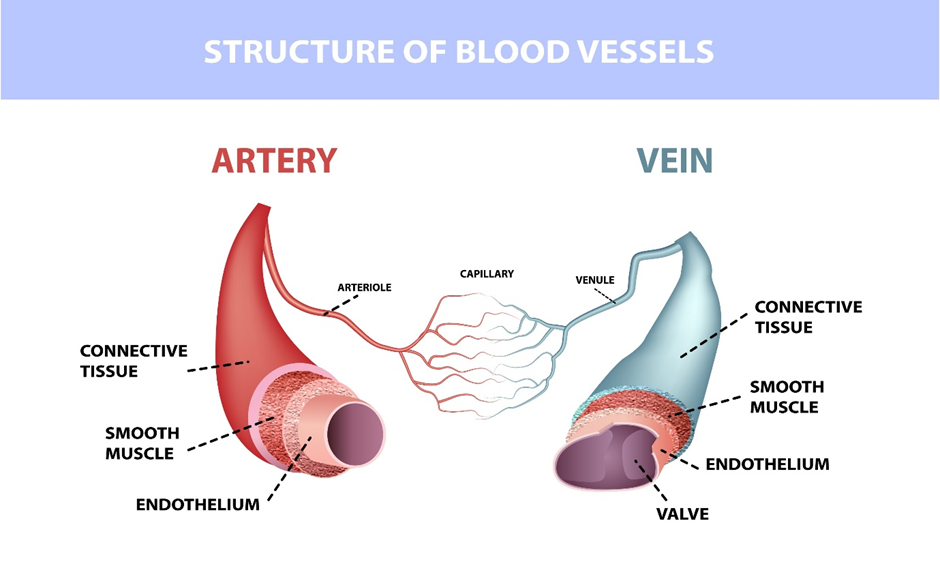
What is the difference between a Vein and an Artery on a slide?
Arteries have thick walls with a distinct elastic layer; veins have thin walls and a larger lumen.
How do you identify Early-stage Fibroatheroma?
Characterized by lipid accumulation and a thin fibrous cap.

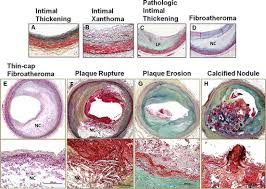
What features characterise Late-stage Fibroatheroma?
Presence of a large necrotic core, cholesterol crystals, and often calcification.
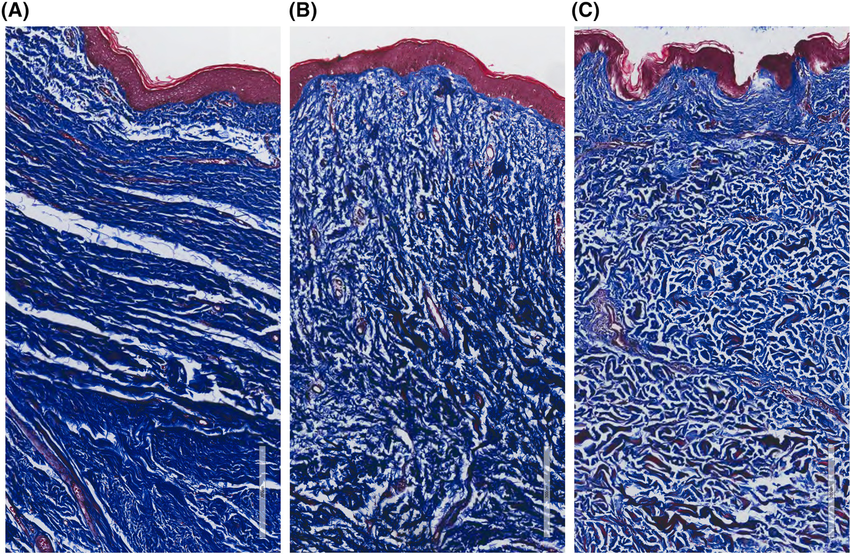
How do you confirm Fibrosis in a tissue section?
Use Masson's Trichrome; high-density blue/green staining indicates excessive collagen deposition.
What is the Volcano Lesion in C. diff pathology?
A histological feature of Pseudomembranous Colitis with a fountain of fibrin, mucus, and neutrophils.
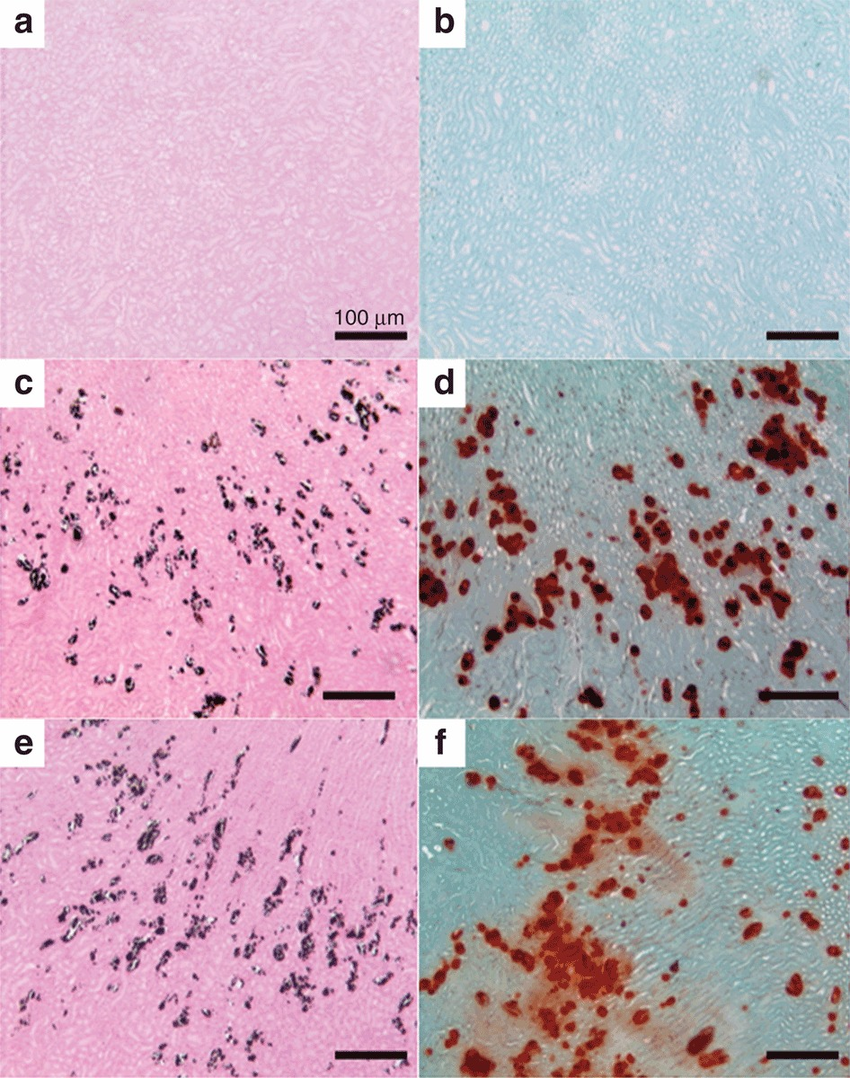
Which stain is used to detect Calcium in an artery?
Alizarin Red or Von Kossa.
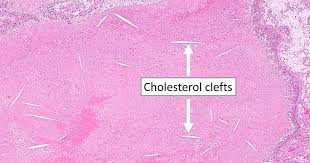
What are Cholesterol Clefts/Crystals?
Needle-shaped empty spaces in a tissue section where cholesterol was located.
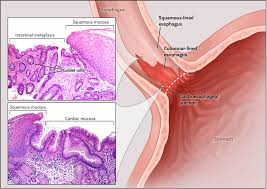
How do you identify Intestinal Metaplasia (Barrett's Oesophagus)?
Use Alcian Blue to look for Goblet cells (bright blue circles) in a tissue where they don't belong (like the oesophagus or stomach).
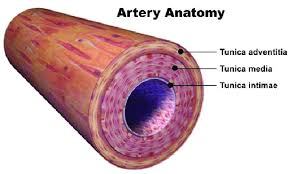
What are the three layers of an Artery wall (inside to out)?
1. Tunica Intima, 2. Tunica Media, 3. Tunica Externa/Adventitia.
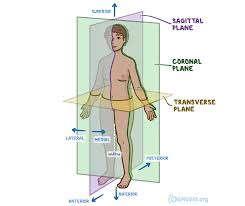
Why is sectioning orientation important?
Cross-sections show lumen and wall thickness; longitudinal sections show vessel length.
What does the PAS stain specifically?
It stains neutral polysaccharides and basement membranes magenta. It is used to identify fungal infections or thickening of the basement membrane in kidney disease.
What is the practical exam logic for staining Atherosclerosis?
Lipids: Oil Red O; Elastin: VVG; Collagen/Fibrosis: Masson's Trichrome; Calcium: Von Kossa.