Oral Microbiology Flashcards
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering vocabulary terms from an Oral Microbiology lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Oral Microbiology
The study of the bacteria that are natural inhabitants of the oral cavity.
Dental Plaque
Bacteria found on human tooth surfaces in microbial communities.
Biofilms
Microorganisms immobilized at a surface and frequently embedded in an organic layer.
Dental Caries
Bacteria in dental plaque are the etiological agents.
Gingivitis
Specific bacteria growing at the margin of the tooth and the soft tissue or gingiva (gums) are responsible for inflammation and bleeding of the gums.
Periodontal Disease
Failure to remove the bacteria at the gingival margin can lead to destruction of the tissue adjacent to the tooth, creating periodontal pockets.
Destructive periodontitis
Pockets are 8-10mm and filled with variety of anaerobic bacteria.
Interactions between microbial species
Can be physical:
Non-specific: electrostatic and hydrophobic
Specific (protein-protein):
Co-aggregation: between suspended cells
Co-adhesion: between a suspended cell and a biofilm cell
Example: corn-cobb-like structures between Candida albicans and Streptococcus sp.
Chemical-metabolical
Quorum sensing: release of signal molecules
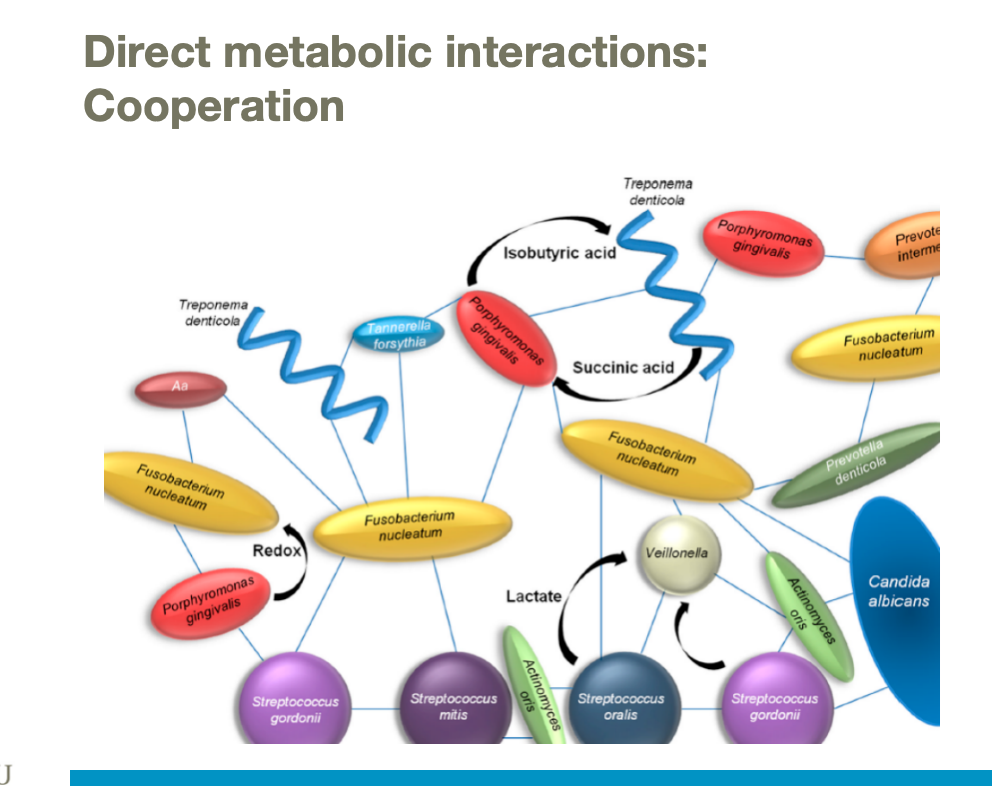
Direct metabolic interactions: production of substrates that are useful for other microbes. Usually related to central carbón metabolism.
Quorum sensing competition
Mutacin 1140, produced by S. mutans with activity anti Gram positive
Salivaricin: produced by S. salivarius, inhibits the growth of S. pyogenes and S. pneumonia
Competence-stimulating peptide produced by S. mutans inhibits filamentation of Candida albicans.
Quorum sensing
Release of signal molecules in microbial species.
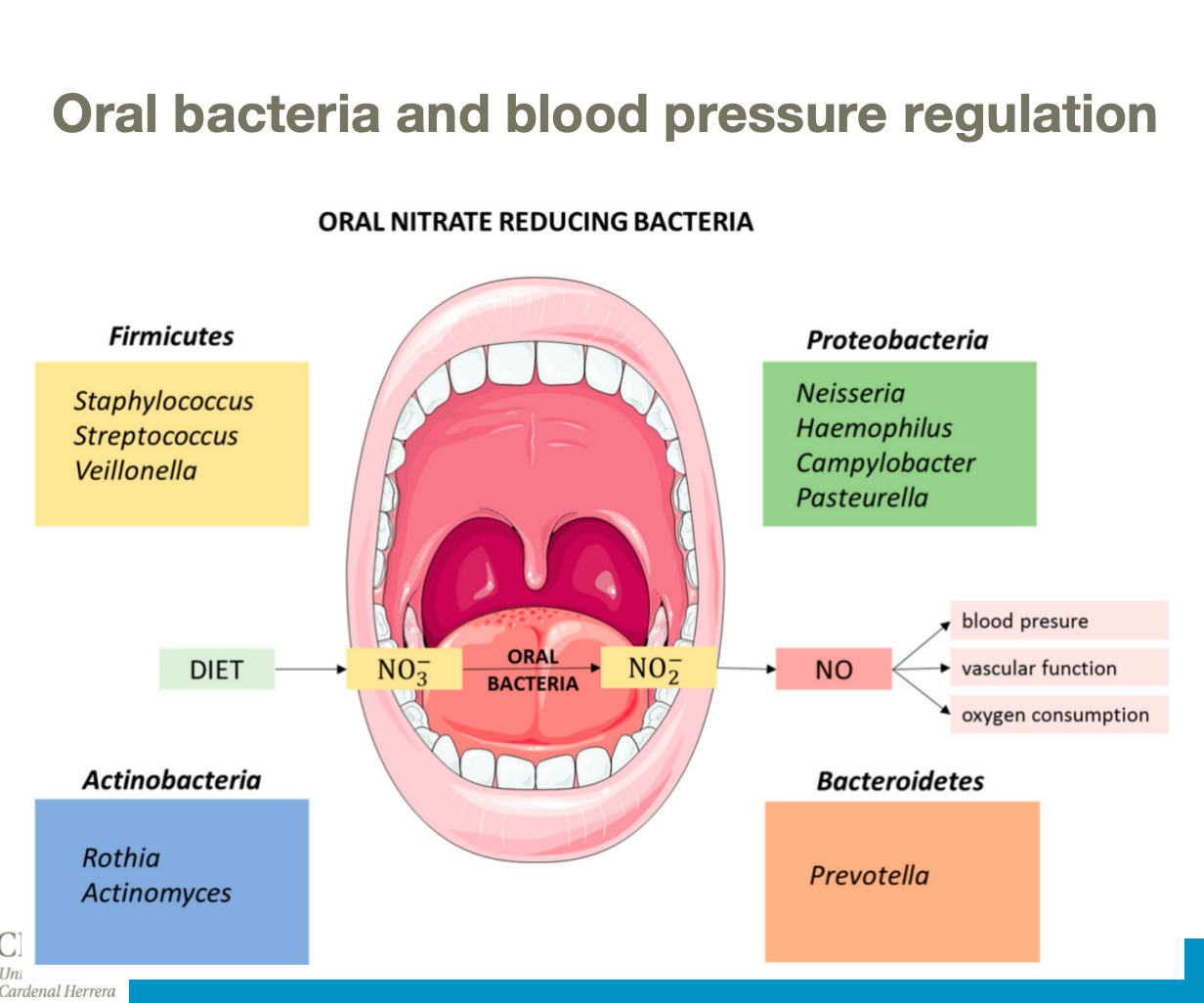
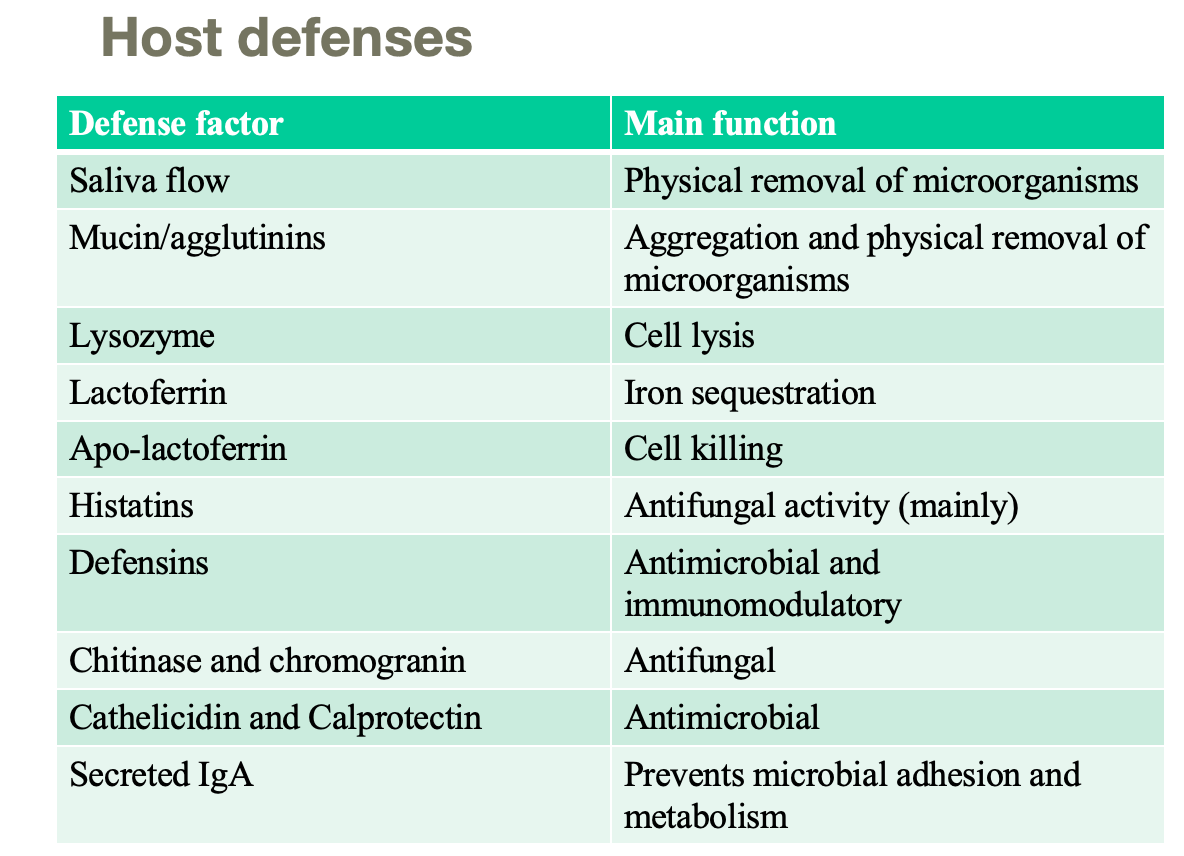
Saliva
Secreted into the mouth each day, flushes the epithelial surfaces and lubricates and protects tissues. Hypotonic with pH 6.7.
Major functions:
Physic-mechanical flushing
Tissue coating: lubrication and permeability barrier
Modulation of oral microbiota
Antiacid and neutralization of deleterious materials
Regulation of calcium and phosphate equilibrium
digestion
Normal Oral Flora
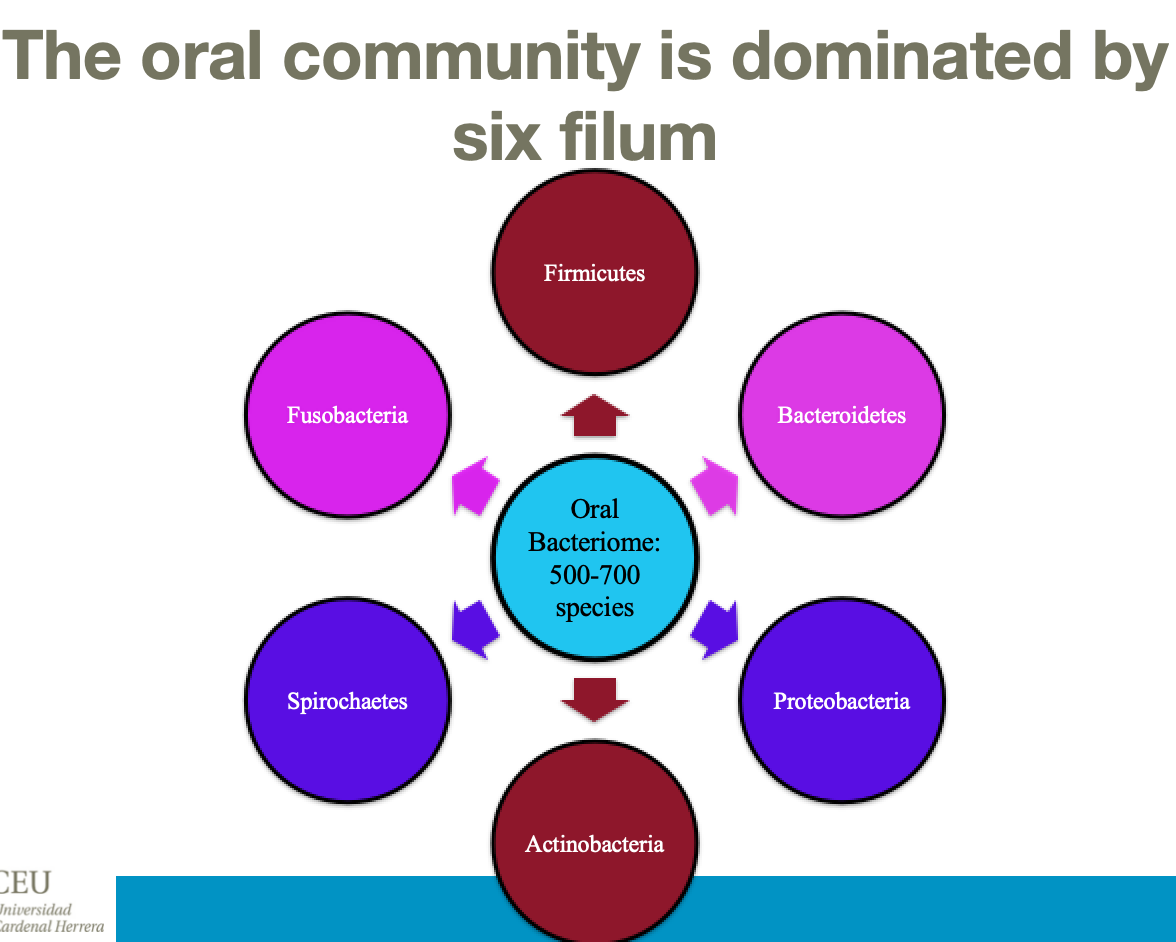
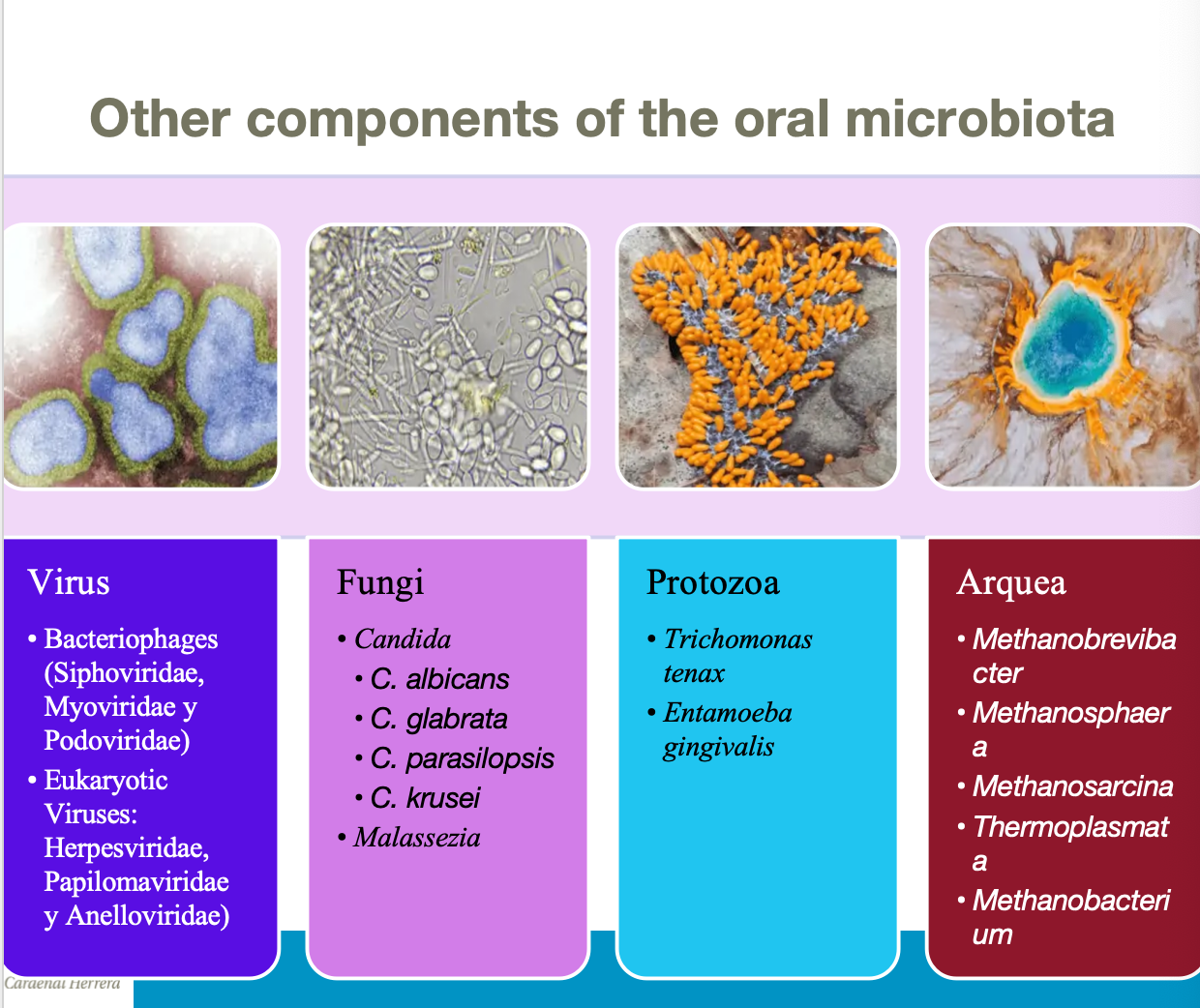
Diverse organisms, including bacteria, fungi, mycoplasmas, protozoa and viruses.
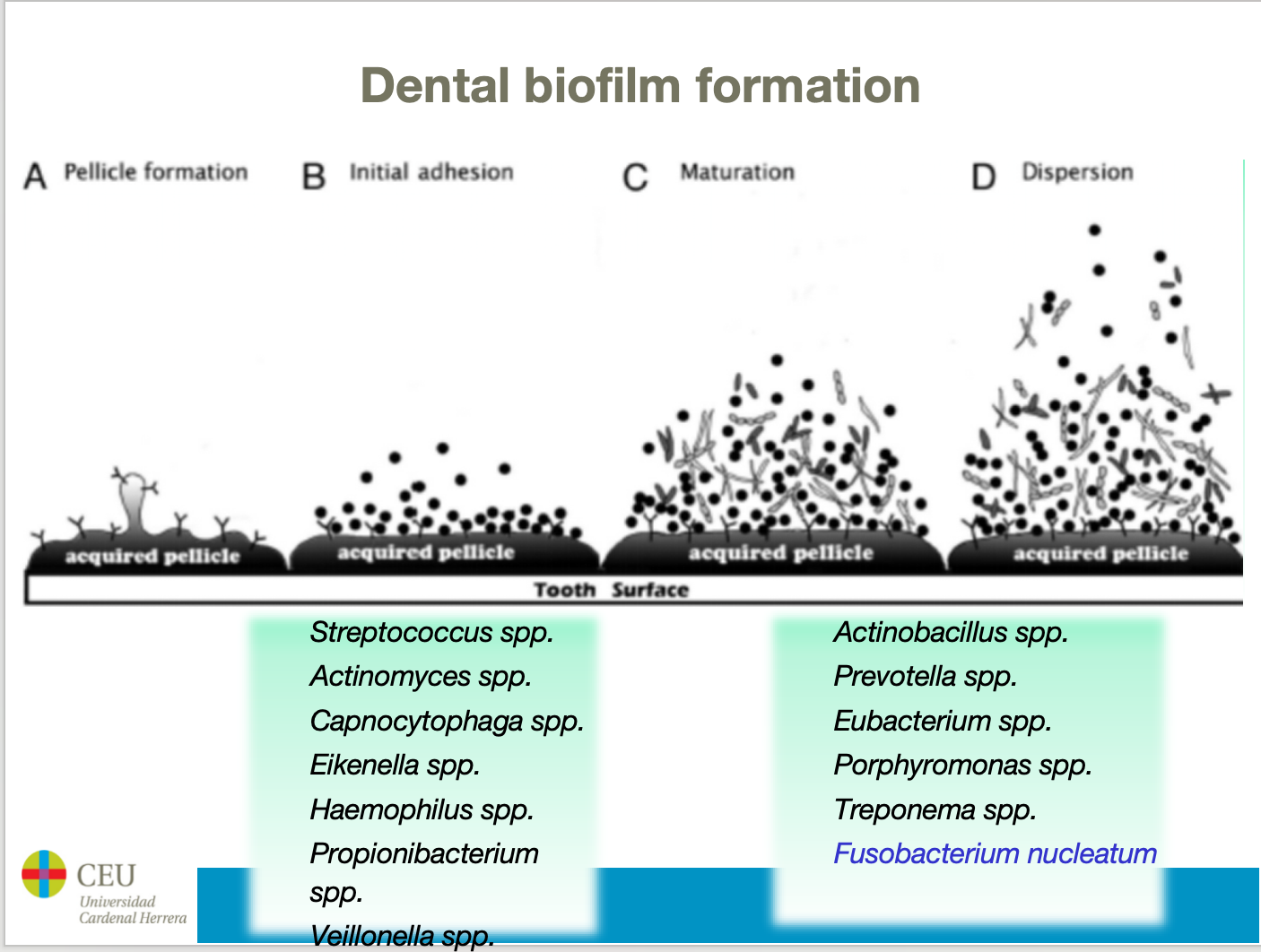
Pellicle
A layer of salivary proteins coating the teeth surface which allows bacteria to adhere. It is the first step in plaque formation.
The pellicle coated tooth is colonised by gram-positive bacteria, which are early colonisers. These include streptococcus, acintomyces…
Late colonisers like aggregator bacteria, eubacterium in plaque after 1 to 3 days.
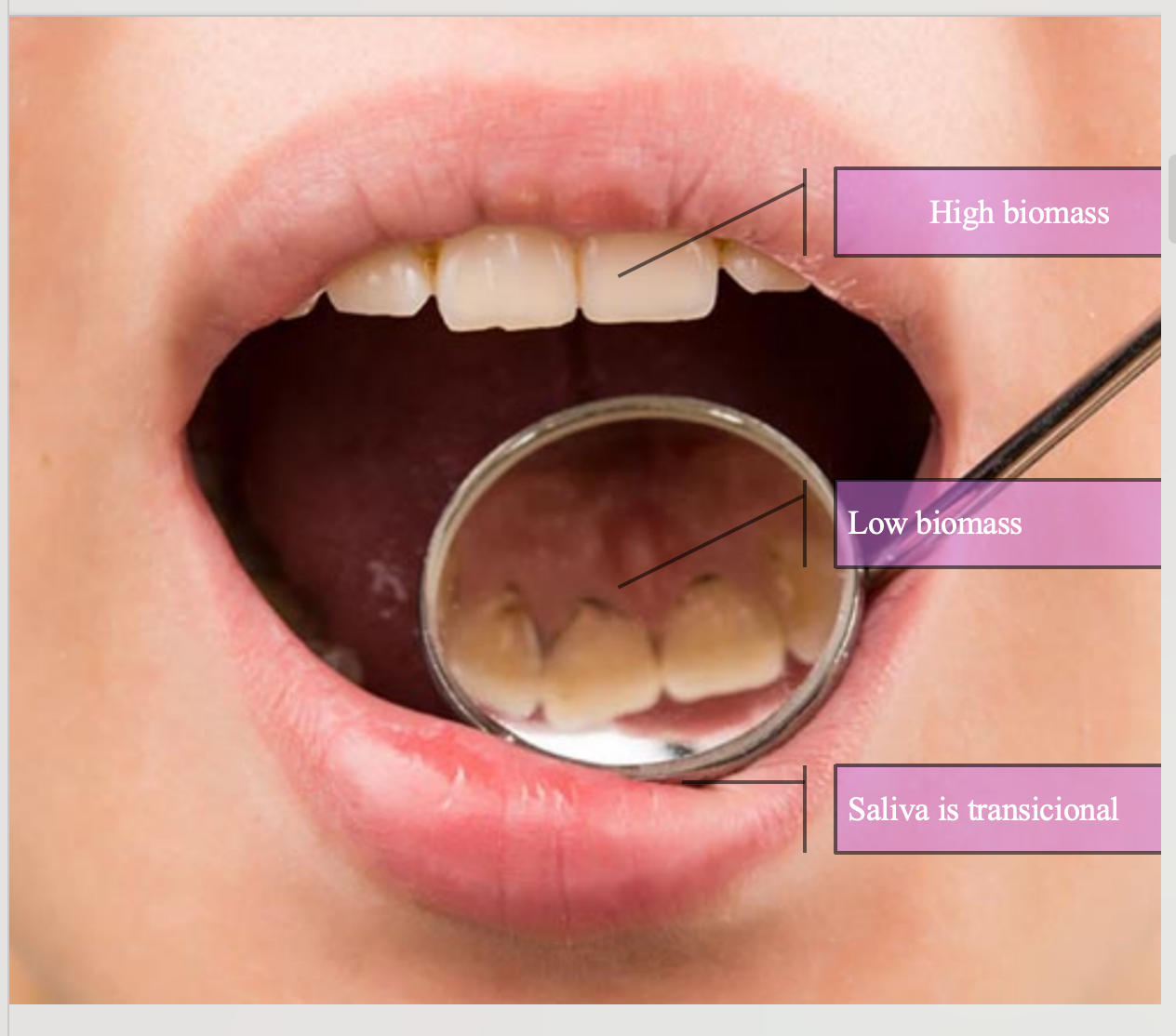
Oral ecological zones
High biomass sites
Non-shedding surfaces
Supragingival tooth surfaces
Subgingival tooth surfaces
Shedding surface
The tongue: reservoir for anaerobic bacteria
Low biomass sites
Shedding oral mucosa surfaces
Saliva as a transitional zone
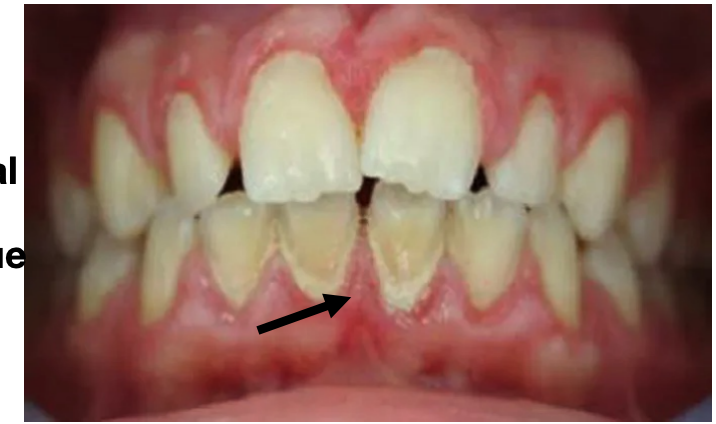
Materia alba
Exfoliated epithelial cells and food debris on the superficial surface of dental plaque.
Non-specific plaque hypothesis
Oral diseases are caused by the activity of all bacteria in plaque that accumulates on teeth and gingival crevices.The amount of plaque, instead of the composition, is considered to be the decisive factor in the development of oral disease. Founded in 1890 by miller
Specific plaque hypothesis
From the various components of the microflora found in the oral cavity, only some specific species are responsible for the initiation and progression of oral disease. Loesche in 1976
Ecological plaque hypothesis
Oral disease occurs when the host microbe balance is disrupted at the cellular or molecular level. Many oral diseases are polymicrobial in origin and both microbial and host factors contribute to the initiation and progression of disease Marsh in 1994
Keystone-pathogen hypothesis
Certain low-abundance microbial pathogens can trigger inflammatory disease that causes benign remodeling normal microbiota to a dysbiotic microbiota. 2012 by haji.
Oral Dysbiosis
Imbalance in the oral microbiome that can lead to oral and systemic diseases.
S.mutans, Candida, lactobacillus, scardovia and acintomyces thrive.
Causes caries and periodontists.
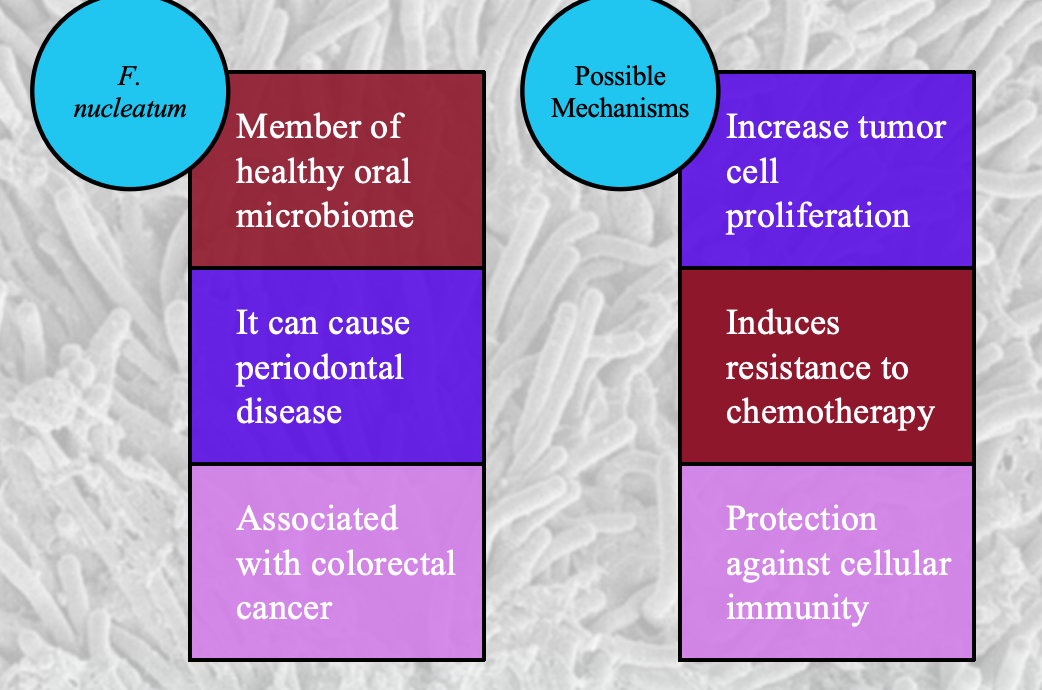
Fusobacterium necleatum
Present in plaque and linked to colorectal cancers.
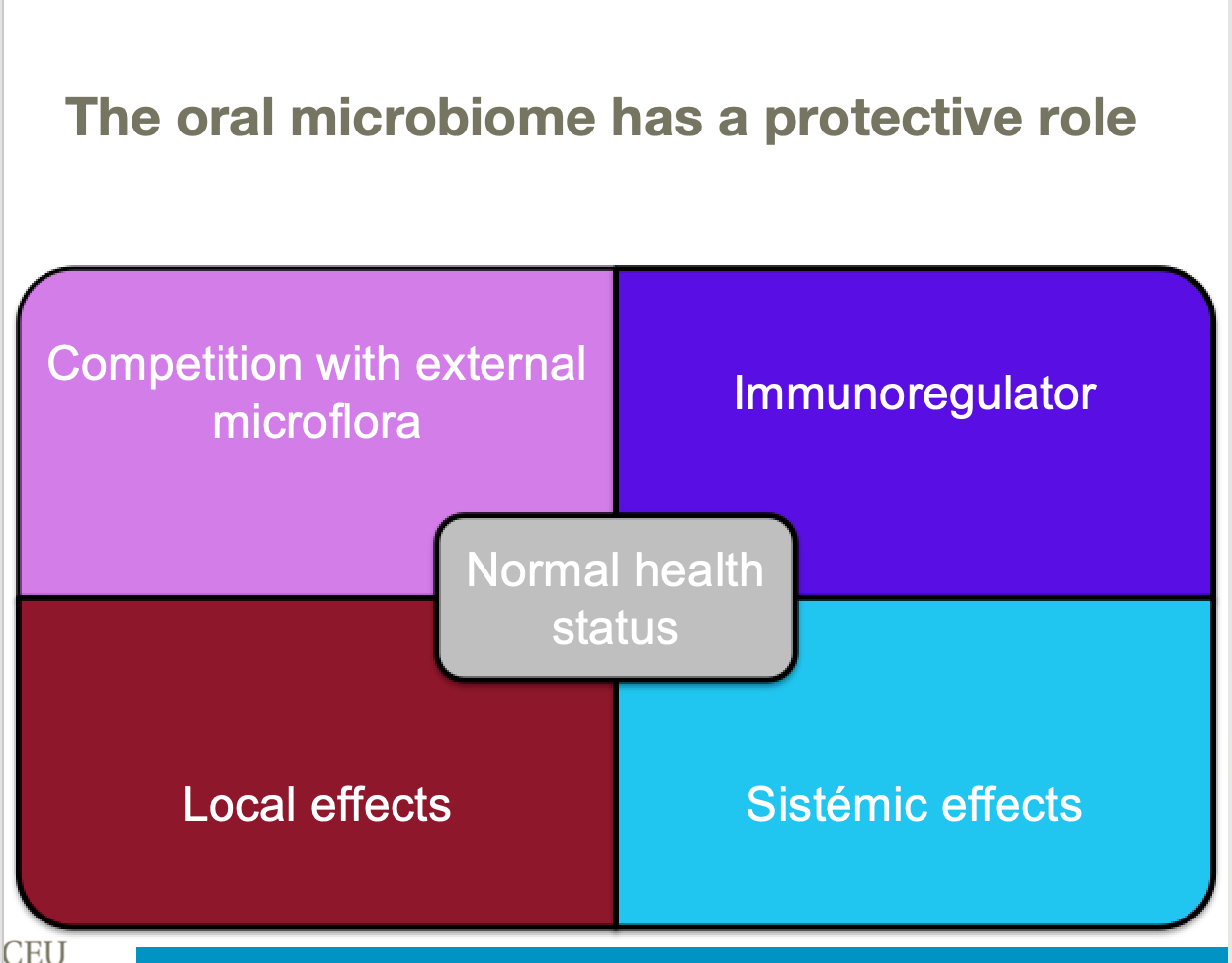
Defence against caries
Caries
Enamel deminarilised by microbial acid, mainly due to strep mutant.
Factors include diet, saliva and teeth.
Occurs when normally low populations of acidogenic and aciduric bacterial species increase, following high-frequency carbohydrate exposure- carcinogenic plaque

Periodontal diseases
Gingivitis overgrowth of supra gingival plaque. Exacerbated by systemic conditions.
Periodontitis- inflammatory infection which causes destruction of ppl and alveolar bone. Chronic/aggressive.
Necrotizing necrosis and painful of ppl and alveolar bone.
Agressive perio is strongly associated with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, either alone or synergistically with:
Capnocytophaga species
Porphyromonas gingivalis
Necrotizing is a specific, anaerobic, polymicrobial infection due to the combined activity of fusobacteria (Fusobacterium nucleatum), and oral spirochetes (Treponema spp.), called the Fusospirochaetal complex
Endodontic infections
Infections that occur within the tooth pulp in the root system or root apex.
Probiotics
Foods or supplements with live microorganisms to correct oral dysbiosis.