AP Bio Unit 3 - Cellular Energetics
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is an enzyme?
biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions
most are proteins
What must be maintained in an enzyme to retain functionality?
the tertiary shape
Active Site
the empty space in an enzyme that the substrate goes into
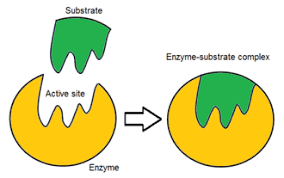
Substrate
a molecule that can interact with an enzyme
What are the characteristics of an active site?
unique shape an size specific to the substrate
sometimes charged, sometimes not
slight changes occur to make the substrate fit
What do enzyme names often end in?
-ase
(eg. sucrase, lactase)
Are enzymes reusable? Why or why not?
Yes!
They aren’t chemically changed by their reaction
What types of reactions of enzymes facilitate?
synthesis
digestion
(only one reaction type per enzyme tho!)
What kind of energy do all biochemical reactions require?
activation energy (an initial kick-start)
What are the two ways energy goes in a reaction (net)?
net release
net absorption
Which kind of reaction requires less activation energy?
those resulting a net release of energy
(they require more than one resulting in a net absorption)
How to enzymes accelerate the rate of reactions?
they lower the activation energy required
What are the two types of tests in a controlled experiment?
control group (generates data for normal, non-manipulated conditions)
experimental group (generates data for abnormal, manipulated/treated conditions)
Negative Control
not exposed to the experimental treatment
not exposed to anything that has a known effect
Positive Control
not exposed the experimental treatment
exposed to something that has a known effect
What is the difference between a control group and controlled variables?
controlled variables
aspects that could be changed, but aren’t
variables that are the same within the control group and the experimental group
kept the same to identify the impact of the tested variable
control group
a group not exposed to the experimental variable/treatment
Denaturation
changes in the tertiary structure/conformational shape of an enzyme
What causes leads to denaturation?
changes in temperature
changes in pH
What is the effect of denaturation? Is it reversible?
it can no longer catalyze the reaction
usually no, but sometimes it can regain the ability to catalyze
Optimum Temperature
the range at which an enzyme speeds up a reaction the best
What happens when there is an environmental increase in temperature? Why?
reaction rate increases at first
faster molecular movement causes more collisions with the enzymes and substrate
if its too high, it will go through denaturation
What happens when there is a decrease in environmental temperature? Why?
reaction rate slows down
slower molecular movement = less frequent enzyme+substrate collisions
Does denaturation occur when temperature decreases?
no, only if the temperature gets too hot
What does pH measure?
concentration of hydrogen ion concentration
What happens when the environmental pH changes?
decrease = slow down
increase = speed up
Under what changes in pH does an enzyme denature? Why?
increase in pH
decrease in pH
changes disrupt the hydrogen bonds in the enzyme’s structure
What happens to the reaction rate when there is a increase in substrate concentration?
initially increases
substrate saturation happens (rate reaches a plateau)
What is a product in terms of enzymes?
the end result of an enzyme catalyzed reaction after it interactions with the substrate
What happens to the reaction rate when there is an increase in concentration of products? Why?
it decreases
there is more matter which takes up more space, so there is a smaller chance of enzymes colliding with substrate
What happens to reaction rate when there is less enzyme? When there is more?
less enzyme = lower reaction rate
more enzyme = higher reaction rate (but will plateau if substrate is limited)
What is a Competitive Inhibitor? What is its function?
molecules that bind to the active side of an enzyme
It slows down the reaction rate (if there are more inhibitors than substrate)
What happens to the enzyme if an inhibitor binding is irreversible?
enzyme function is prevented and can no longer happen
What happens to the enzyme when the inhibitor is reversible?
the enzyme can regain its function once its detaches
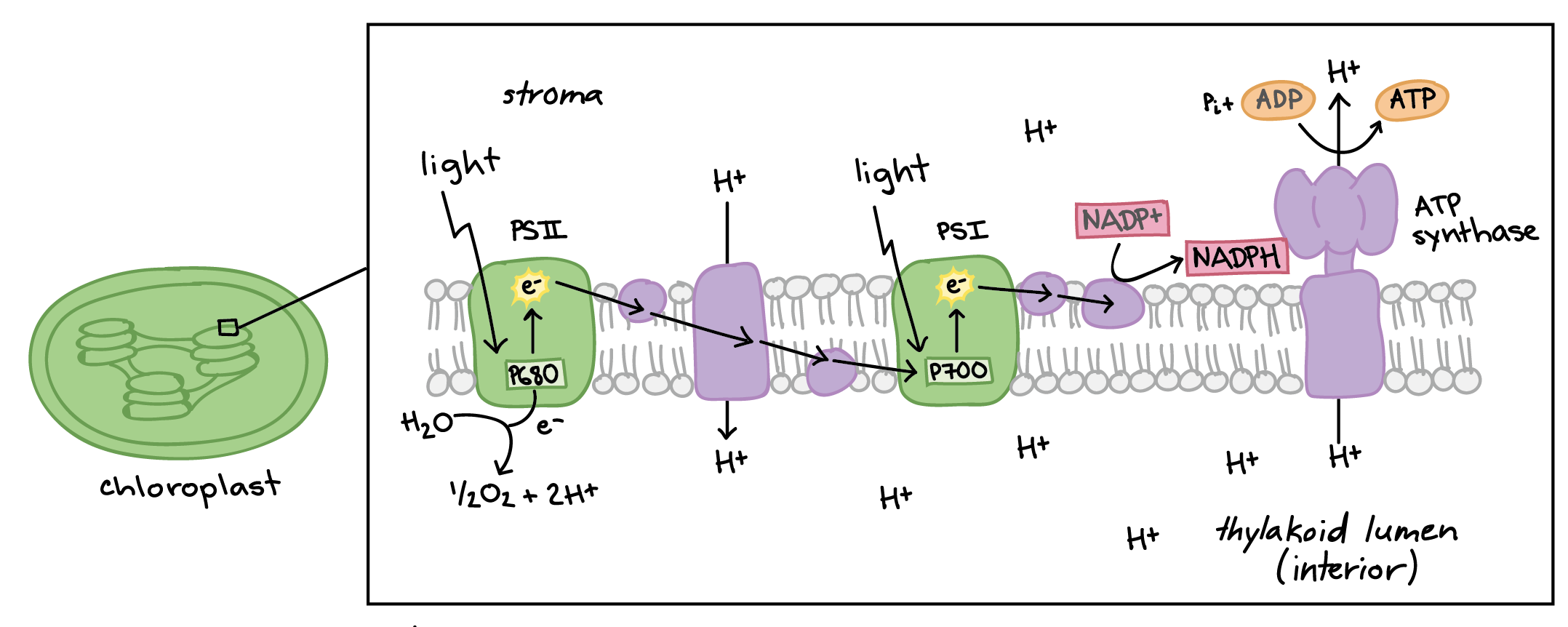
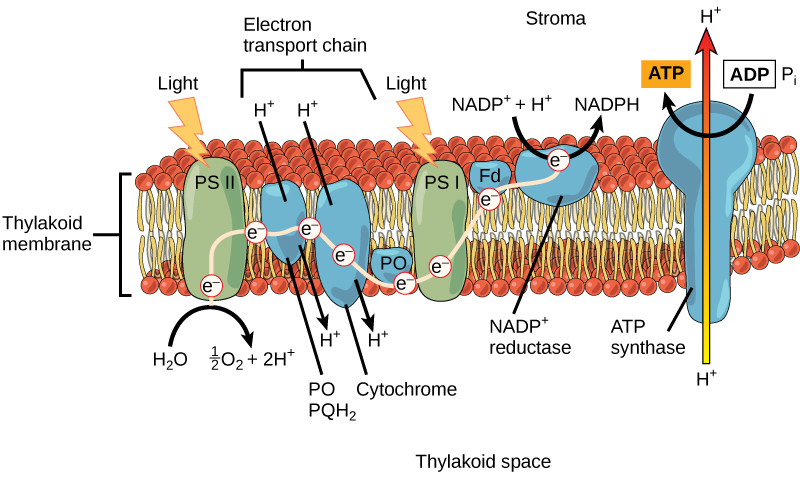
What is required across the thylakoid membrane in order for ATP to be produced? What does this mean for the pH on both sides?
proton gradient
lots of protons inside of thylakoid (low pH)
less protons outside of the thylakoid/in the stroma (high pH)
What is the order of the photosystems in light reaction?
Photosystem II (PSII) is first
Photosystem I (PSI) is second
What are antenna pigments? Where are there located? What is their function?
pigments surrounding the reaction center
they capture light energy for the light reaction in photosynthesis
What is cyclic electron flow? What does it produce? Which photosystem does it use?
produces ATP without producing NADPH
PSI
How much ATP compared to NADPH does the Calvin Cycle require?
it requires more ATP than NADPH
What method creates the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane (which drive ATP synthesis)?
chemiosmosis
What is the organelle where photosynthesis takes place?
chloroplast
What is the organelle where cellular respiration takes place?
mitochondria
What is the light absorbing pigment? What light does it absorb? What light to it reflect?
chlorophyll
absorbs red and blue light
reflects green light (why plants are green)
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
light dependent reaction
light independent reaction (Calvin Cycle)
Where does the light reaction take place? What about Calvin Cycle?
light reaction → in the thylakoid inside the chlorophyll
calvin cycle → in the stroma of the chloroplast
What are the four main things that happen in the light dependent reaction?
Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen
Electrons are lost through the splitting of water
NADP+ picks up lost electrons and turns into NADPH (reduction reaction)
Some light energy converts ADP and a phosphate group to make ATP
Is the splitting of water a reduction or oxidation reaction?
oxidation because it looses the hydrogen ions
What are the reactants in the light dependent reaction? products?
reactants = light energy, water, NADP+, ADP, and phosphate
products = oxygen, ATP, NADPH
What is a reduction reaction? What is an oxidation reaction?
reduction = adding electrons (adding hydrogen)
oxidation = losing electrons (losing hydrogen)
What must happen if there is a reduction reaction and vice versa?
there must be an oxidation reaction somewhere
What is the main function of the Calvin Cycle?
take CO2 and reduce it into simple sugars such as glucose
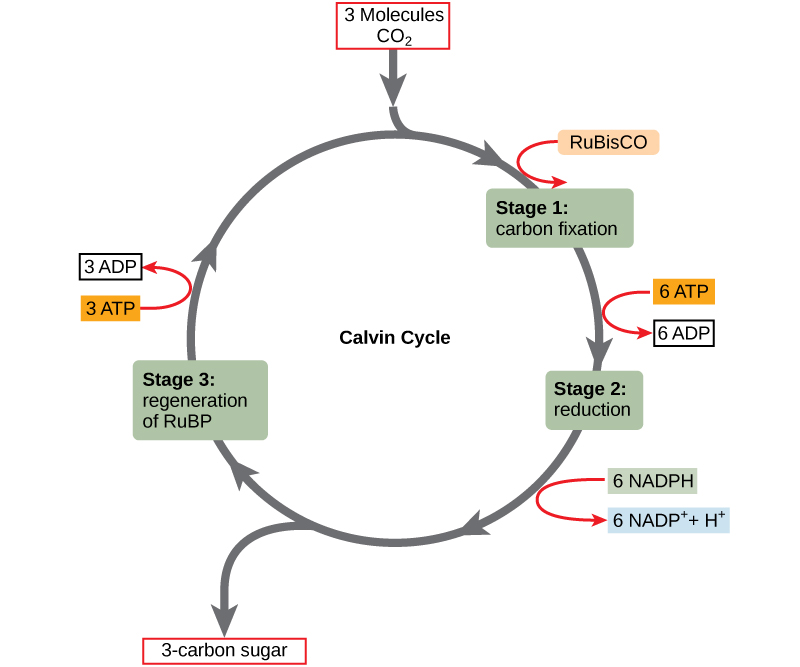
What are the two main things that happen in the Calvin Cycle?
NADPH is oxidized to give its electrons to CO2 and turns back into NADP+
ATP converts back into ADP + Phosphate, which gives energy to convert CO2 into glucose
What are the reactants in the Calvin Cycle? products?
Reactants
CO2
NADPH
ATP
Products
ADP
Phosphate
NADP+
Glucose or other sugar
What happens in Photosystem II (P680)? Where do the electrons go when they leave it?
light particle strikes it, exciting the electrons in chlorophyll
electrons from chlorophyll flow into electron carrier PQ
chlorophyll takes electrons from water (oxidation) to replenish itself
H2O becomes O + 2H+
electron character PQ carries electrons from the 2H to Cytochrome B6-f complex
Why is PSII called P680 and PSI called P700?
that is the wavelength of light (in nanometers) that has the highest absorption
What is the function of cytochrome B6-f complex? What happens there?
PQ carries electrons from PSII to it
protons are pumped from outside of the thylakoid (stroma) to inside of the thylakoid (lumen)
creates a electrochemical concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane
Where to electrons go after they enter the Cytochrome B6-f?
peripheral protein PC
they are then transferred to PSI
How do electrons gain more energy once they enter PSI?
they are struck by another photon of light
What is the main thing that happens in PSI?
electrons are excited
they are then transferred to peripheral protein Fd
Where does the peripheral protein Fd carry electrons to? What happens then?
NADP reductase enzyme (also a peripheral protein)
NADP+ is reduced to create NADPH
What does the reaction in NADP reductase do to the hydrogen ion concentration in the stroma?
It reduces the concentration, making the difference larger, supporting the later synthesis of ATP
What happens to the hydrogen ions after the NADP reductase reaction? What does it create?
they flow from the inner thylakoid through ATP synthase
ATP is created
Where are there more hydrogen ions during photosynthesis just before ATP is made, thylakoid space or stroma?
more hydrogens in thylakoid space so they can flow through ATP Synthase and release ATP into the stroma
What was responsible for the early production of oxygen in the atmosphere?
photosynthetic prokaryotic organisms such as cyanobacteria
What type of energy does photosynthesis convert light energy into?
chemical energy
What reaction in photosynthesis produces the oxygen released in the end?
splitting of water
What products of the light-dependent reaction are used in the Calvin Cycle?
ATP and NADPH
Photophosphorelation
using light energy to turn ADP into ATP
In which bonds is the chemical energy created from light energy in the light-dependent cycle temporarily stored before the Calvin Cycle?
chemical bonds of NADPH and ATP
What do chlorophyll pigments convert light energy to? What does the create and therefore allows the reduction of what?
high energy electrons
creates proton gradient
NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
What colors of light are best absorbed in photosynthesis?
red and blue
What do electrons pass through when they are transferred between molecules in the light-dependent reaction?
electron transport chain
What is the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
all of the photosystems, carrier proteins, etc. that work to use the electrons to create ATP and NADPH and convert light energy into chemical energy
What are the three parts of the Calvin Cycle?
Fixation of carbon dioxide
Reduction of PGA (3-phosphoglycerate) to G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate)
Regejneration of RuBP (Ribulose 1,5-biphosphate) from G3P
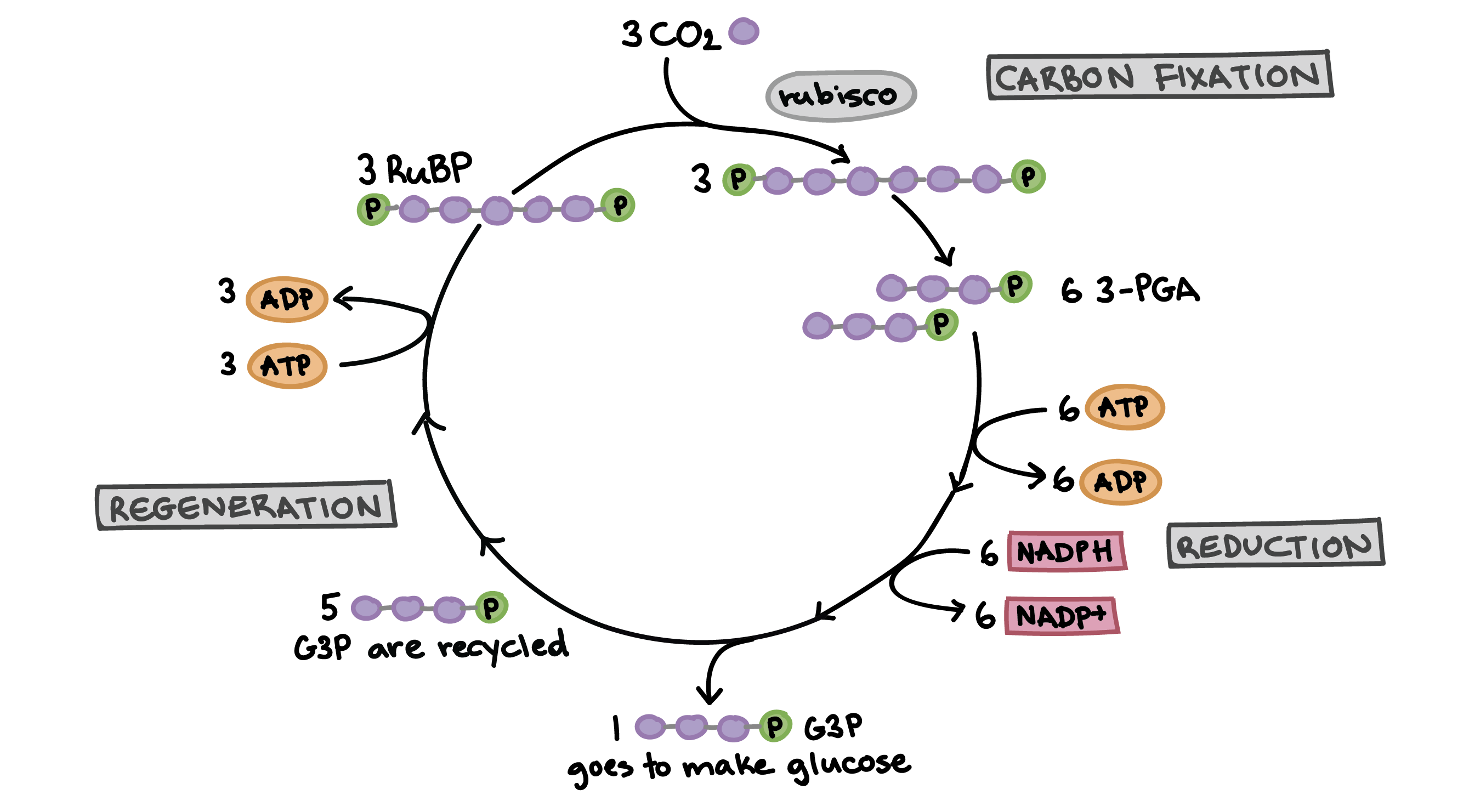
What happens during carbon fixation (step 1) of the Calvin Cycle? What catalyzes this? What is the product?
3 CO2 enters the cycle
3 CO2 reacts with 3 RuBP
Catalyzed by Rubisco enzyme
End up with 6 PGA (3-phosphoglycerate)
What is RuBP?
Ribulose 1,5-biphosphate
5 carbon atoms
phosphate groups attached to carbon 1 and carbon 5 (2 in total)
How many PGA are created during carbon fixation in the Calvin Cycle? Why?
6
3 CO2
3 RuBP
3 6-carbon molecules
splits into 6 3-carbon molecules (PGA)
What happens to reduce PGA to G3P? (two main steps, the reactants from the light reaction are used)
ATP gives a phosphate group to PGA, becoming ADP
1,3-biphosphoglycerate is created
NADPH donates hydrogen to 1,3-biphosphoglycerate, becoming NADP+
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) is created
How does G3P regernerate RuBP?
1 G3P is used in sugar production
The other 5 regenerate (make new ones of) RuBP
What is the primary product of the Calvin Cycle? (hint: it is not simply glucose or sugar)
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
What are the two methods that organisms use to get energy from macromolecules?
cellular respiration
fermentation
What type of energy is released when organisms use macromolecules for their energy?
chemical energy
What is the main difference between fermentation and cellular respiration?
cellular respiration uses oxygen
fermentation doesn’t use oxygen
What is the energy used by all cells to do work?
ATP
What are the four steps in cellular respiration in eukaryotes? Where in the cell do they occur?
Glycolysis - cytoplasm
Pyruvate Oxidation - mitochondria matrix
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) - occurs in mitochondria matrix
Electron Transport Chain - inner mitochondrial membrane
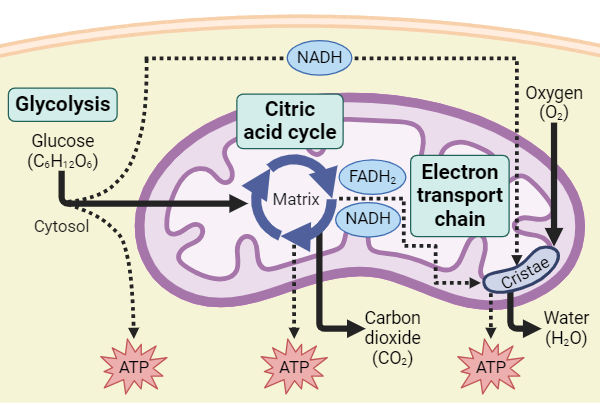
What does the ETC in cellular respiration do? What does it establish across the membrane?
it splits up the movement of electrons into a few, smaller steps
this makes it more efficient
establishes electrochemical/proton gradient
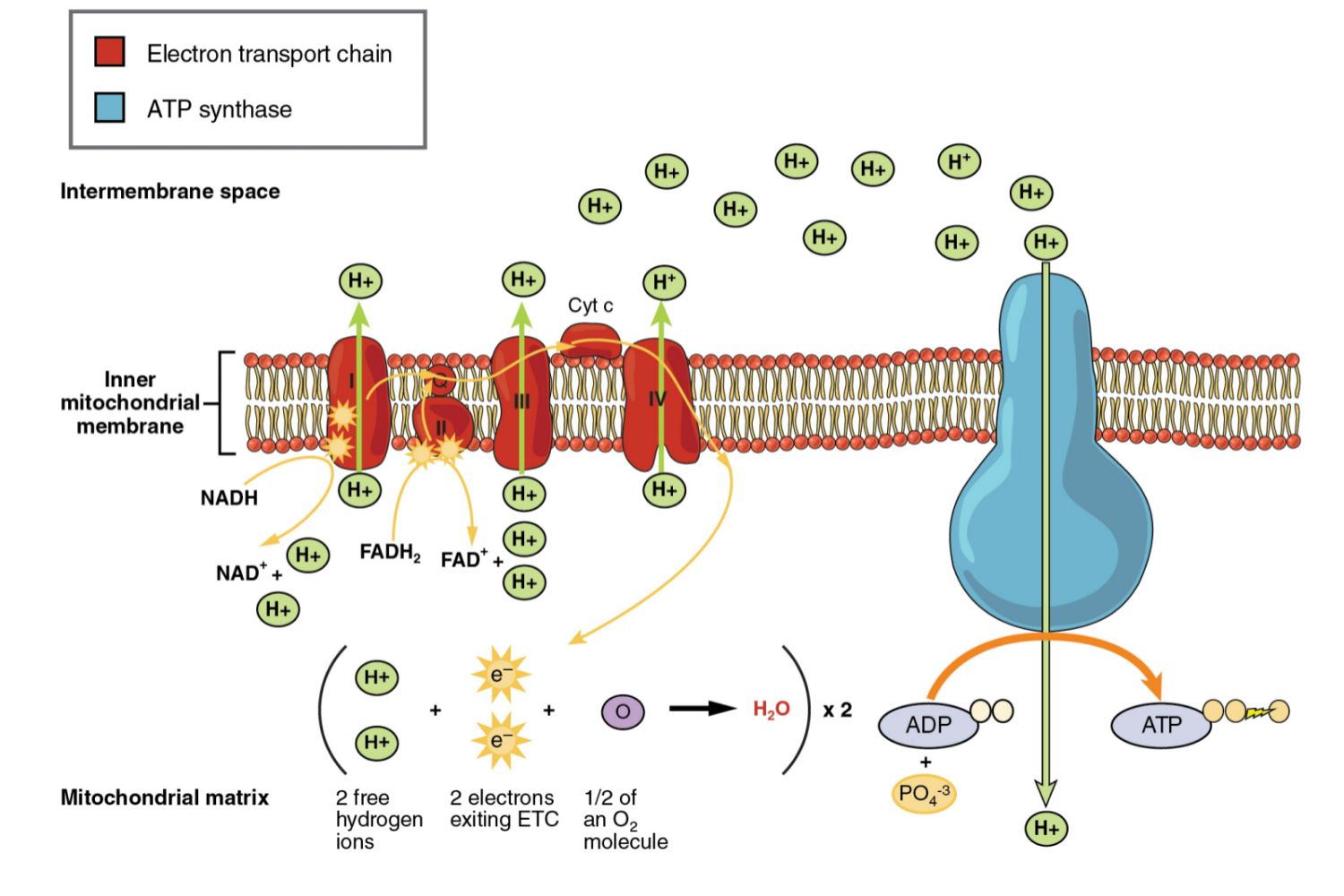
What is the product that comes out of the ETC in cellular respiration? Where do electrons flow through to make this happen?
ATP by electrons flowing through ATP Synthase
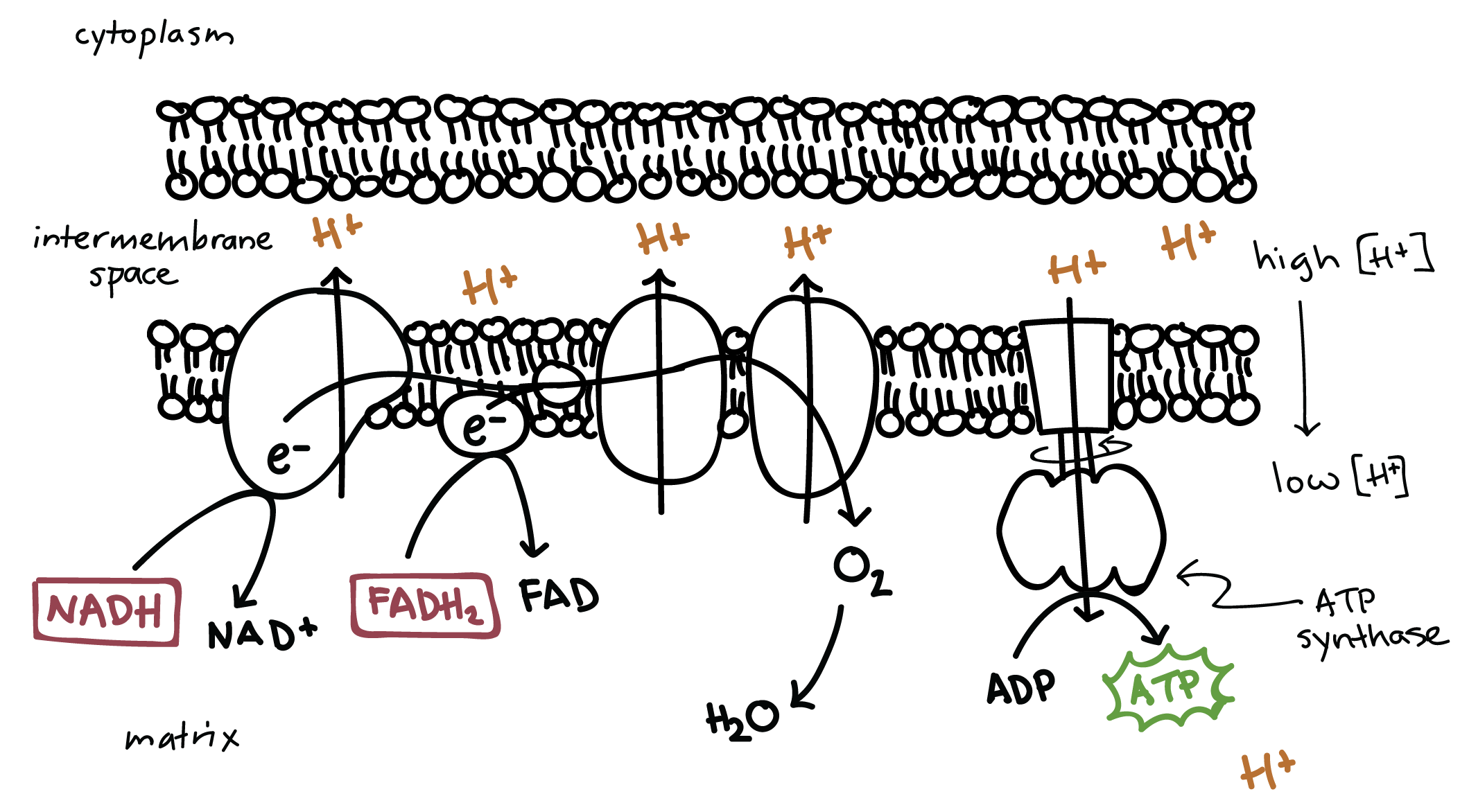
What are the electron carriers in the ETC of the mitochondria (cellular respiration)?
NADH
FADH2
Where is the ETC in eukaryotic cells?
inner mitochindrial membrane and internal membrane of chloroplasts (thylakoid)
Where is the ETC in prokaryotic cells?
main plasma membrane
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
in cellular respiration, when the energy achieved from breaking down food molecules is used to create ATP
oxidative = NADH and FADH2 lose electrons in the ETC
phosphorylation = ATP synthase adds a phosphate to ADP
What is an allosteric inhibitor, what kind of site does it bind to, what can it do? What about non-competitive?
allosteric = binds at a site other than the active site
binds to the allosteric site
either speeds up or slows down reaction
non-competitive = type of allosteric inhibitor
can only slow it down
doesn’t entirely prevent substrate from binding
The flow of protons by [what process] through ATP synthase drive the production of ATP synthesis?
chemisosmosis
What is decoupling oxidative phosphorylation?
the proton gradient not being used by ATP synthase to make ATP
decoupling = taking the process apart
What product of decoupling can be used in endothermic organisms?
the heat produced can be used to regulate body temperature
What are the products of glycolysis?
NADH
ATP
Pyruvate
Where does pyruvate go once it is produced through glycolysis? Then, what happens to it?
it is actively transported through the membranes of the mitochondria into the mitochondrial matrix
it is oxidized
it enters the Krebs cycle
What are the 3 steps in the Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle?
carbon dioxide is released
high energy electrons are transferred to create NADH and FADH2
ADP turns into ATP
What happens to the electrons that are extracted in the glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle?
transferred to the electron transport chain
What is fermentation?
It is how glycolysis proceeds in the absence of oxygen
What are the byproducts of fermentation?
lactic acid
ethanol