Chapter 35-- 2022 Fall BIOL 1002 for Adam Hrincevich
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:22 AM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
Fat cells
_____ helped our ancestors survive starvation periods
_____ produce leptin, a hormone that controls hunger
_____ produce leptin, a hormone that controls hunger
2
New cards
fattest
--adipose
--adipose
Americans are among the____ people in the world
--Estimated that 60% of adults are overweight
--Obesity is over-abundance of fat in_____ tissue
--Estimated that 60% of adults are overweight
--Obesity is over-abundance of fat in_____ tissue
3
New cards
leptin
Obese people do not have less___ than normal, but ___ receptors may not work properly
4
New cards
Gastric bypass
What type of surgery is used to close off part of stomach/intestine?
5
New cards
Cholecystokinin
What may promote appetite suppression?
6
New cards
cholecystokinin
Elderly tend to have low appetites that sometimes endanger health; new drugs that block____ may help
7
New cards
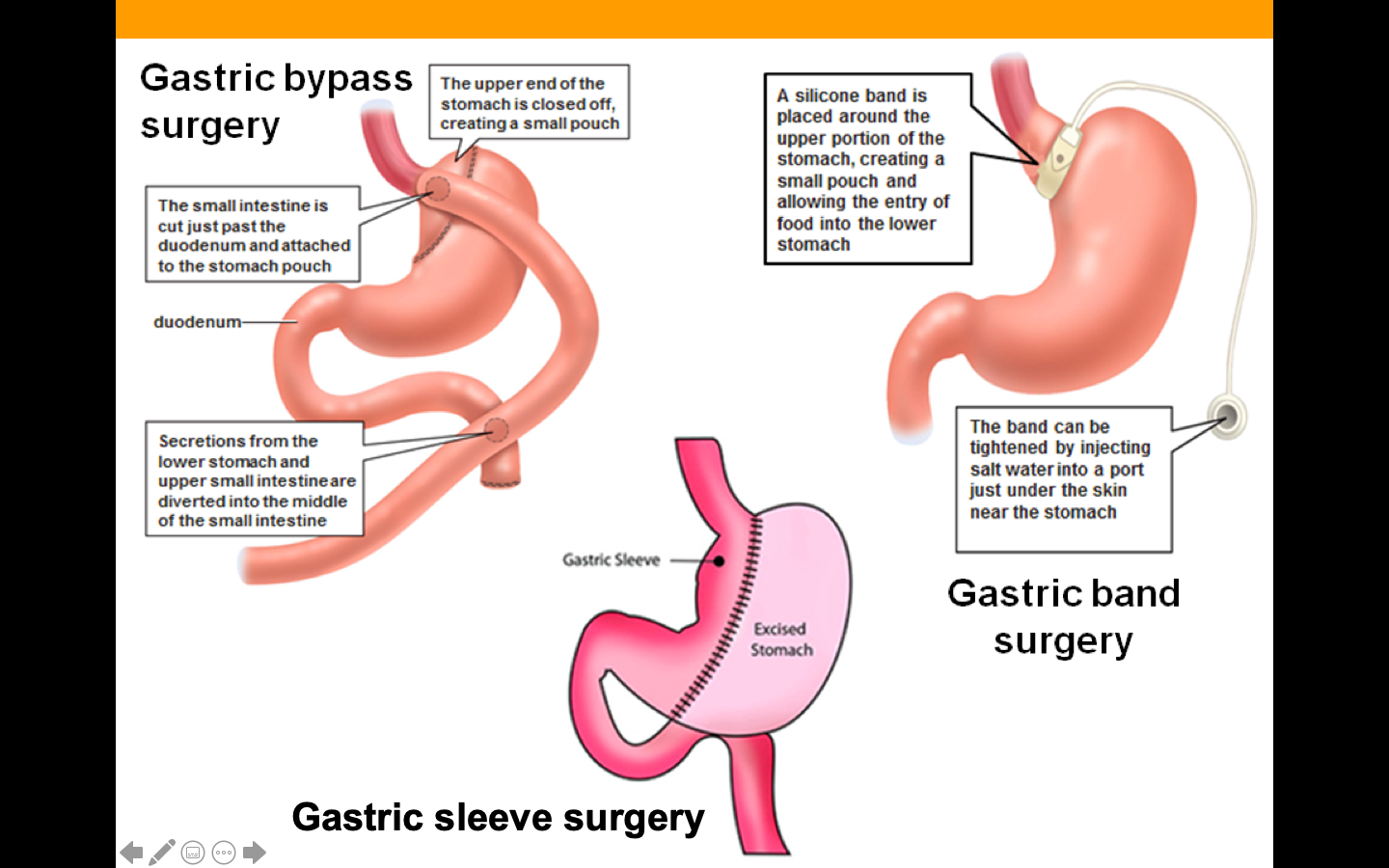
Gastric bypass – surgery to close off part of stomach/intestine
Benefits~ weight loss decreases a person's risk of coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral heart disease.
Changes~ Diet & exercise
False
The stomach will expand lager until it goes back to its original size. Must change lifestyle/diet
Benefits~ weight loss decreases a person's risk of coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral heart disease.
Changes~ Diet & exercise
False
The stomach will expand lager until it goes back to its original size. Must change lifestyle/diet
Benefits of this procedure? Lifestyle changes?
Individ who have gastric surgery loose weight permanently?
Individ who have gastric surgery loose weight permanently?
8
New cards
--
No
Complications of surgery include infection, blood clots, and internal bleeding.
No
Complications of surgery include infection, blood clots, and internal bleeding.
How does a gastric bypass work? Is it permanent? What are the risks?
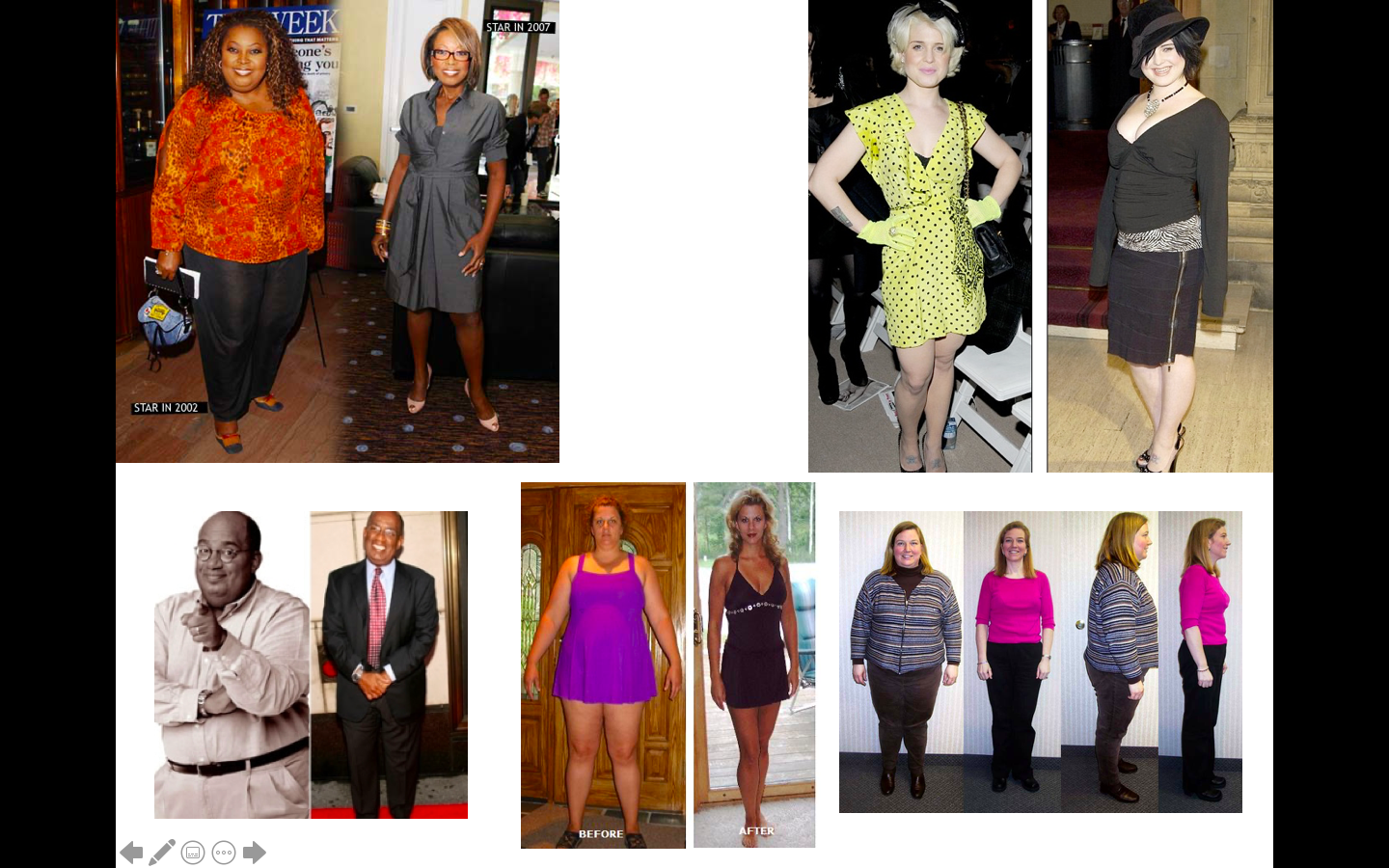

9
New cards
Nutrients
____are substances obtained from the environment that organisms need for their growth and survival
10
New cards
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Minerals
5. Vitamins
6. Water
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Minerals
5. Vitamins
6. Water
Nutrients fall into six major categories:
11
New cards
carbohydrates and fats
Most energy is provided by ___ & _______
--Without this energy, cells die within minutes
--Without this energy, cells die within minutes
12
New cards
lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins
Nutrients that supply energy are (3)____
--These molecules are broken down into subunits during digestion, which are then used during cellular respiration to generate ATP
--These molecules are broken down into subunits during digestion, which are then used during cellular respiration to generate ATP
13
New cards
calories
--calorie
--calorie
Energy from nutrients is measured in___
--A ___ is the amount of energy required to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius
--A ___ is the amount of energy required to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius
14
New cards
--70
--20
--20
The average human burns__ Calories per hour at rest, and up to___ Calories per minute during exercise
15
New cards
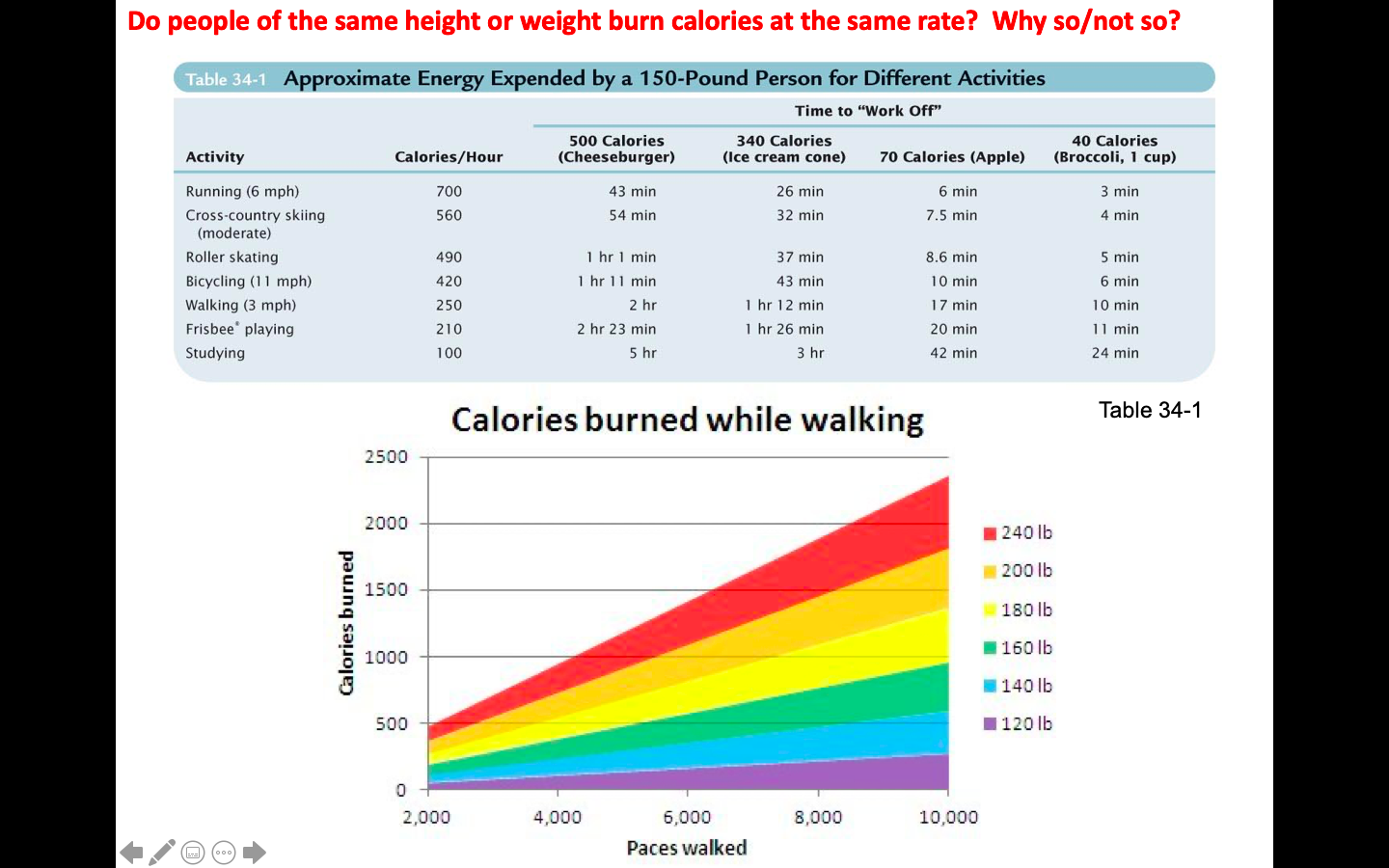
Do people of the same height or weight burn calories at the same rate? Why so/not so?
16
New cards
Carbohydrates
What is a source of quick energy?
17
New cards
Carbohydrates
Starch
Starch
--______include glucose, sucrose, and polysaccharides, long chains of sugar molecules
--What is the principle energy-storage material of plants?
--What is the principle energy-storage material of plants?
18
New cards
Glycogen
What is used by animals for short-term energy storage?
19
New cards
Fats/oils
_____ are the most concentrated energy source.
_____contain over twice as many Calories per unit weight as do carbohydrates or proteins
_____contain over twice as many Calories per unit weight as do carbohydrates or proteins
20
New cards
body fat
Fat deposits (body fat)
Fat deposits (body fat)
When an animal’s diet provides more energy than it expends, most of the excess carbohydrates and fats are stored as ____
____ also provide insulation for animals living in cold environments such as seals, walruses, ect.
____ also provide insulation for animals living in cold environments such as seals, walruses, ect.
21
New cards
Fat Provides Insulation
fats are essential for maintaining the health of your skin and preventing chronic disease, but consuming too much of the wrong type of fat can lead to weight gain or heart disease.
fats are essential for maintaining the health of your skin and preventing chronic disease, but consuming too much of the wrong type of fat can lead to weight gain or heart disease.
Why is fat used in the animal kingdom? What advantages or disadvantages does it have?
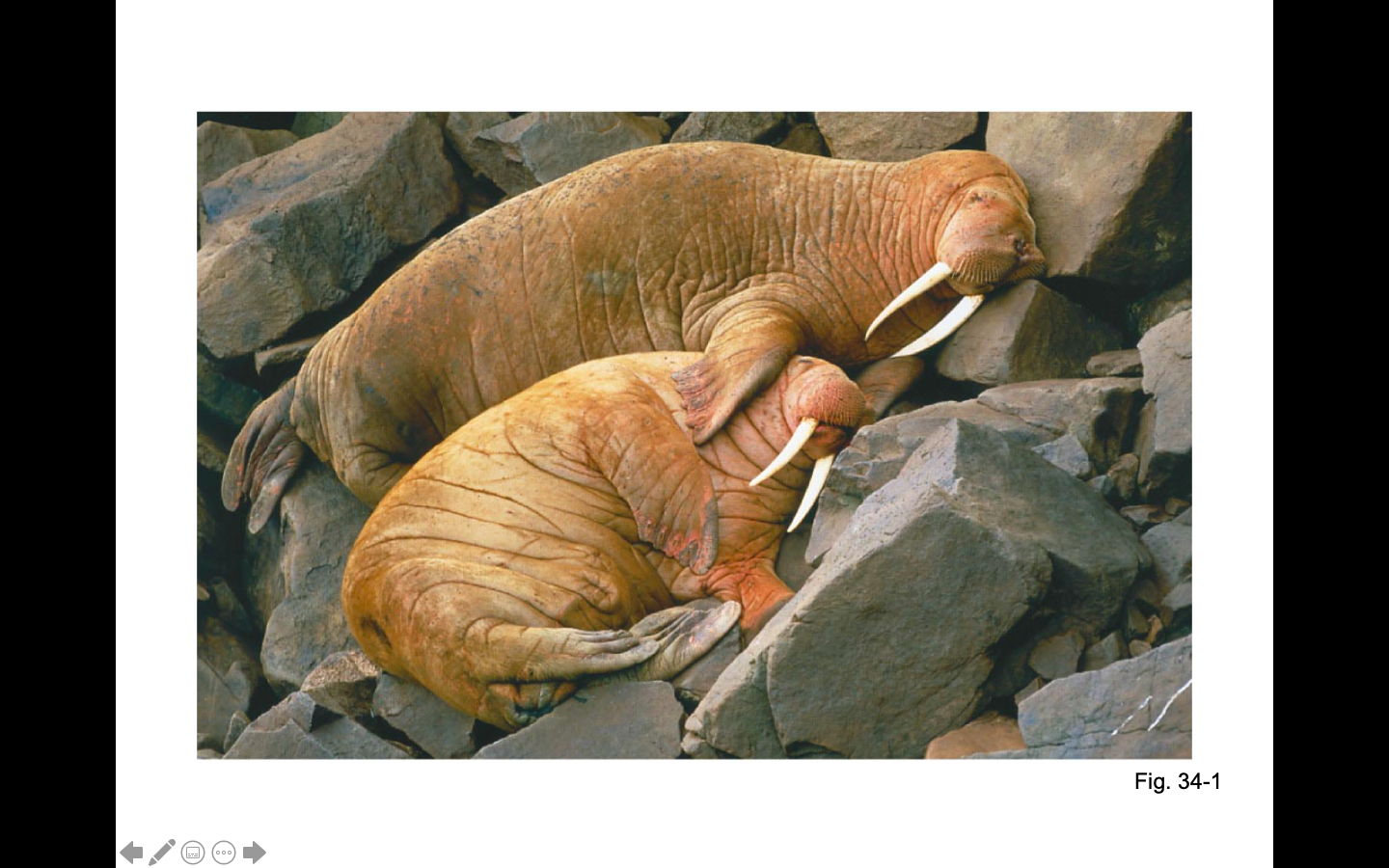

22
New cards
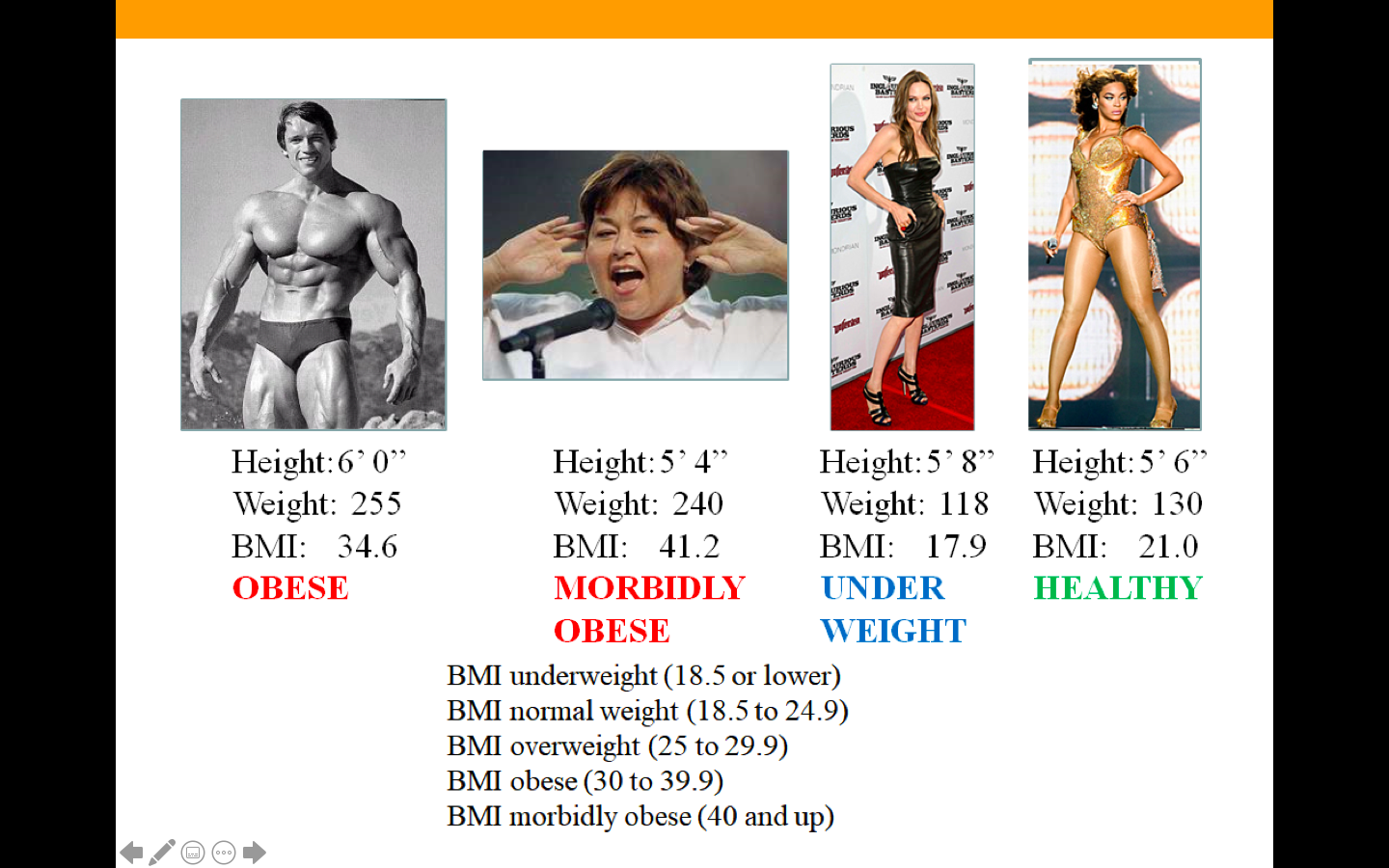
body mass index (BMI)
The_____ is a common tool for estimating a healthy weight
23
New cards
18.5 and 24.9
A BMI between __&___ is considered healthy
24
New cards
33%
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that about ___ of all U.S. adults are overweight (BMI between 25 and 29.9) and an additional ___ are obese
25
New cards
BMI= body mass index
M= mass (in kilograms)
H= height (in meters)
M= mass (in kilograms)
H= height (in meters)
BMI= m/ h^2
What do the letters mean?
What do the letters mean?
26
New cards

27
New cards
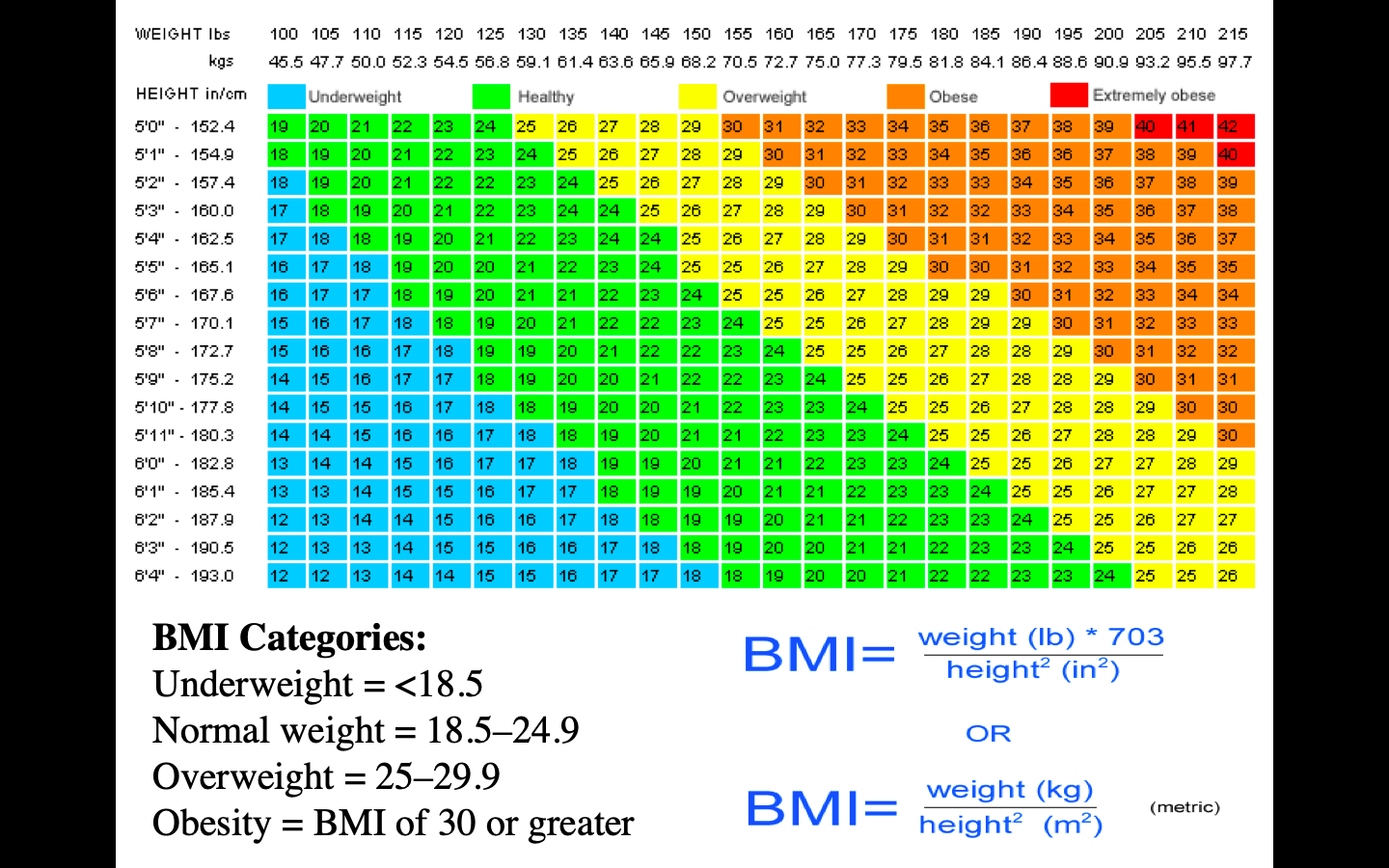
BMI= m(kg)/ h(m/)^2
How do you calculate a BMI? Is this number “exact” per se for determining overweight conditions? How does body frame factor in?
28
New cards
protein
Amino acids form the building blocks of ______
29
New cards
In the digestive tract, protein from food is broken down into its amino acid subunits, which can be used to synthesize new proteins
Simply explain protein break down
30
New cards
--9
--essential amino acids
Essential amino acids can be obtained from protein-rich foods such as meat, milk, eggs, corn, beans, and soybeans
--essential amino acids
Essential amino acids can be obtained from protein-rich foods such as meat, milk, eggs, corn, beans, and soybeans
Humans are unable to synthesize___ of the 20 amino acids needed to make proteins
Those amino acids that cannot be synthesized must be obtained in the diet are called _________, which are obtained from:
Those amino acids that cannot be synthesized must be obtained in the diet are called _________, which are obtained from:
31
New cards
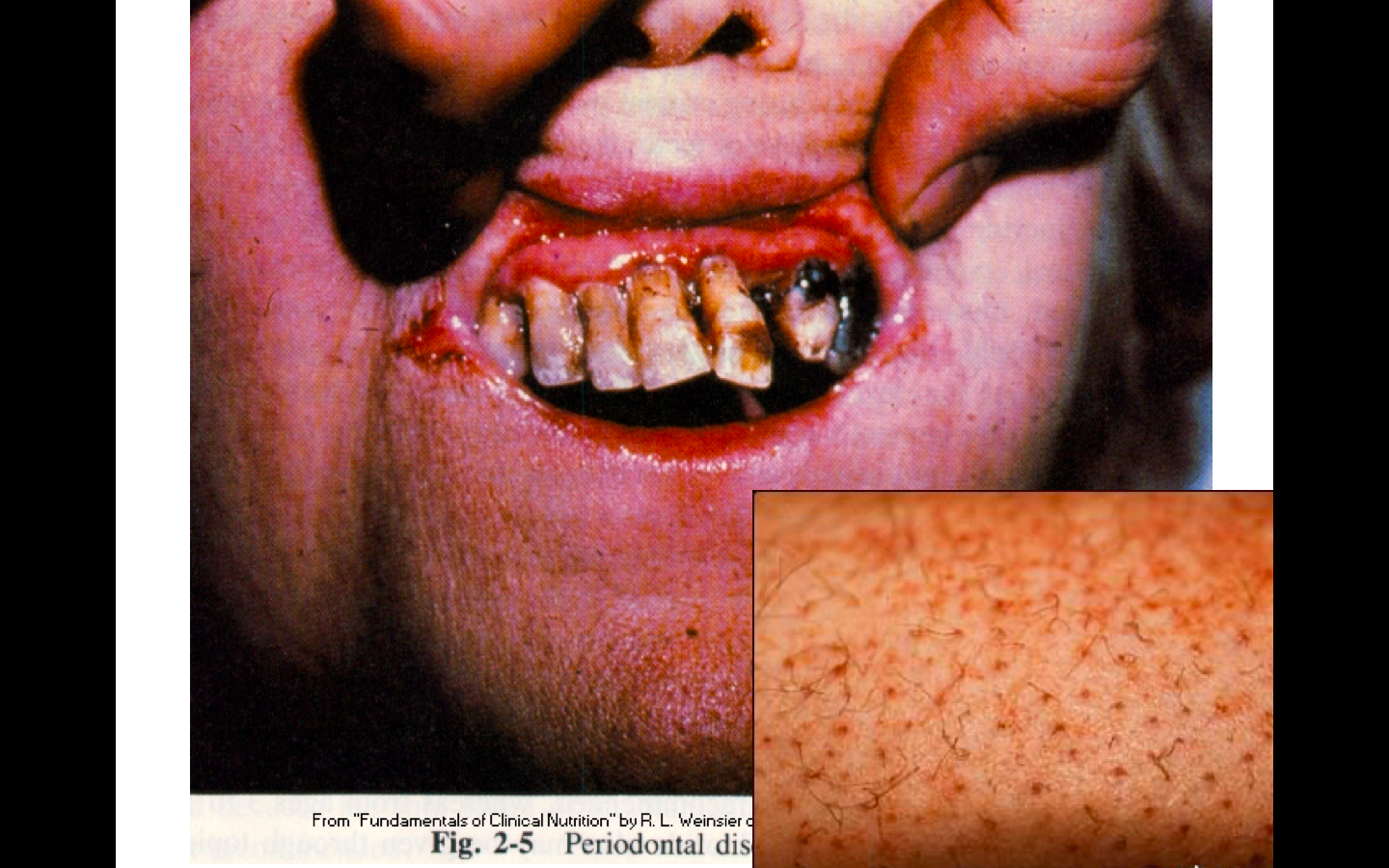
a number of debilitating conditions, including kwashiorkor
Protein deficiency can result in:
32
New cards
Protein Deficiency
What causes kwashiorkor?
33
New cards
~famine, limited food supply and/or low levels of education (when people do not understand how to eat a proper diet).
--Kwashiorkor is most common in areas where there is:
--More common in very poor countries. It often during a drought or other natural disaster, or during political unrest. These conditions are responsible for a lack of food, which leads to malnutrition
--More common in very poor countries. It often during a drought or other natural disaster, or during political unrest. These conditions are responsible for a lack of food, which leads to malnutrition
34
New cards
Anorexia is a mental health condition in which someone has fears about weight gain or body shape. It can involve a severely restricted diet or medications to purge calories. Anorexia affects every body system due to severe weight loss or nutritional deficiencies.
What is this? How does to affect the body?
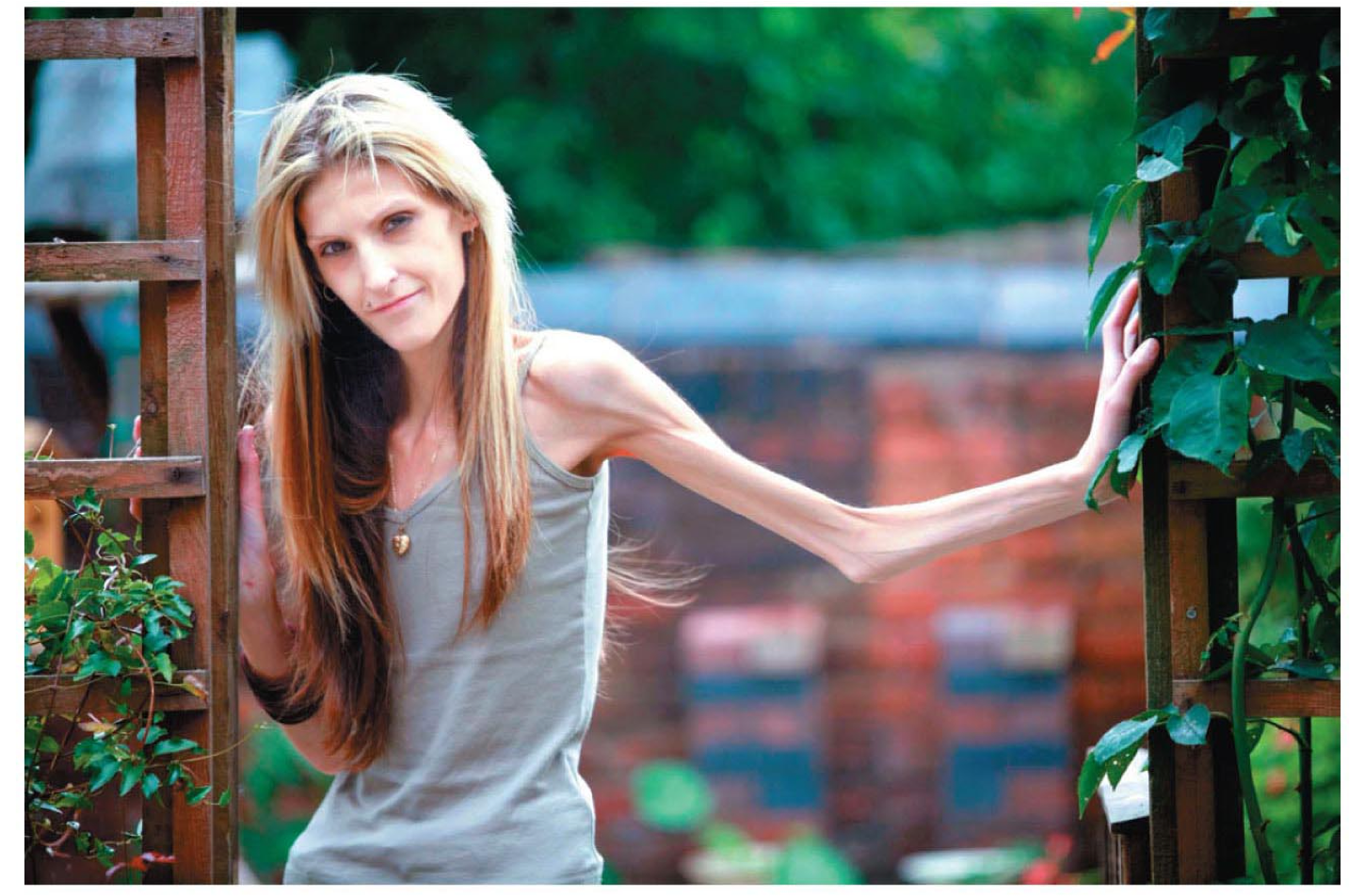

35
New cards
Minerals
____are elements required by the body
--can only be obtained in the diet or dissolved in drinking water
--can only be obtained in the diet or dissolved in drinking water
36
New cards
Calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and phosphorus (P)
Major minerals for bone and teeth:
37
New cards
Sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), and potassium (K)
minerals for muscle contraction and the conduction (movement) of nerve impulses:
38
New cards
Iron (Fe)
iodine (I)
iodine (I)
____ a central mineral of hemoglobin in the blood and ____is found in hormones produced by the thyroid gland
39
New cards
zinc (Zn), magnesium (Mg), copper (Cu), and chromium (Cr)
Animals also require trace amounts of these minerals:
40
New cards
Vitamins
____play many roles in metabolism
_____ are organic molecules that animals require in small amounts for normal cell function, growth, and development
_____ are organic molecules that animals require in small amounts for normal cell function, growth, and development
41
New cards
No; they must be obtained in the diet
Can the body synthesize Vitamins?
42
New cards
1. Water soluble
2. Fat soluble
2. Fat soluble
What are the two categories of vitamins?
43
New cards
vitamin C and the nine compounds that make-up the B-vitamin complex
Water-soluble vitamins include:
44
New cards
Dissolve in the blood plasma and are filtered out by the kidneys, they are not stored in appreciable amounts
How are water-soluble vitamins processed?
45
New cards
coenzymes
Most water-soluble vitamins act as_____ & work in conjunction with enzymes to promote chemical reactions.
46
New cards
a single
Because each vitamin participates in several metabolic processes, a deficiency of ____ vitamin(s) can have wide ranging effects
47
New cards
thymine
impairs cell division throughout the body
impairs cell division throughout the body
folic acid (a B vitamin) is required to synthesize____, a component of DNA; folic acid deficiency:
48
New cards
scurvy
pellagra
pellagra
--Low vitamin C levels can lead to____
-- Low niacin (a B vitamin) can lead to____
-- Low niacin (a B vitamin) can lead to____
49
New cards
A deficiency in niacin can cause pellagra
A deficiency in a Water-Soluble Vitamin; Niacin which is a B vitamin that's made and used by your body to turn food into energy.
A deficiency in a Water-Soluble Vitamin; Niacin which is a B vitamin that's made and used by your body to turn food into energy.
What is this and what is it caused by?
What nutrient deficiency can cause this?
What nutrient deficiency can cause this?
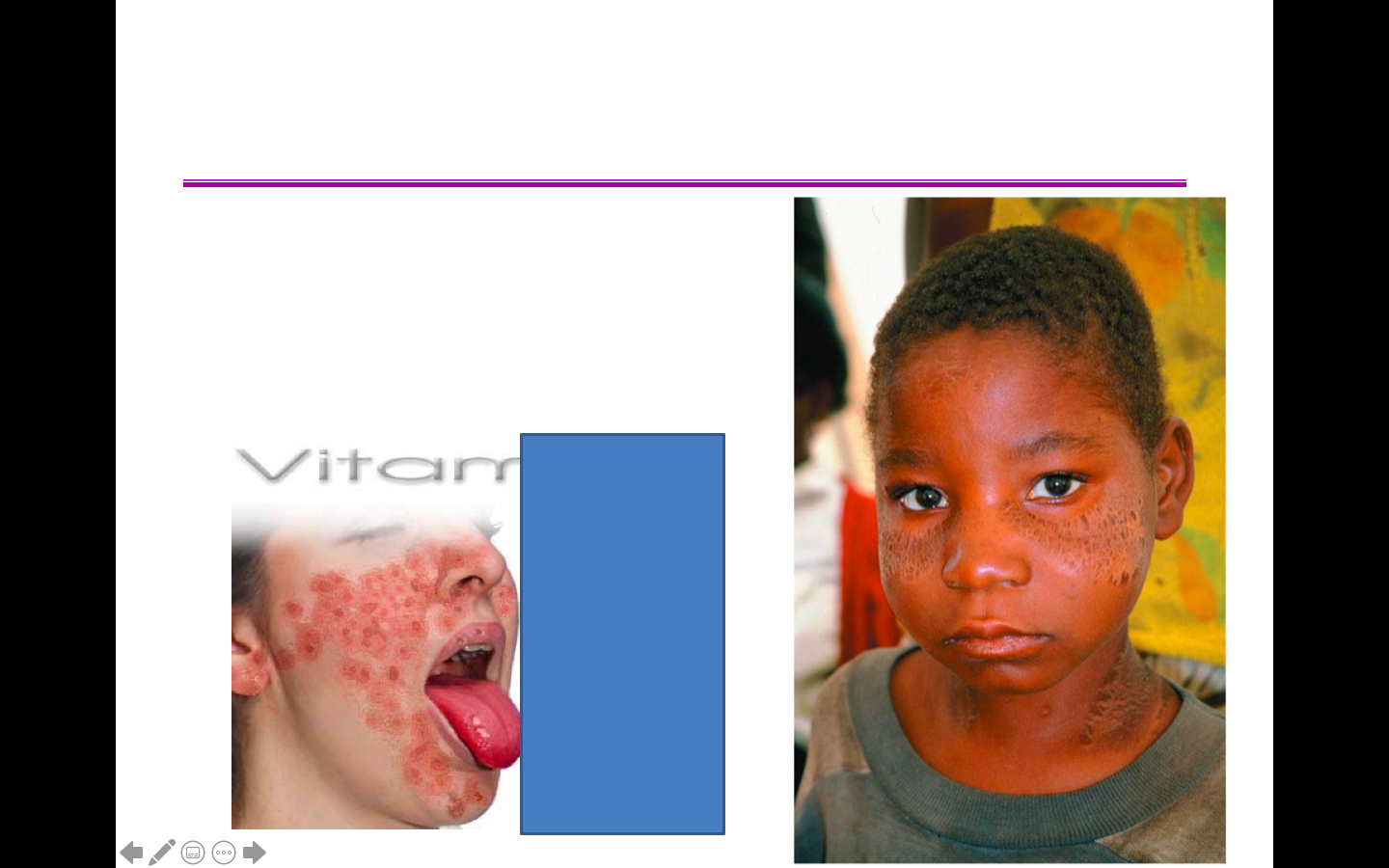
50
New cards
Low vitamin C (a water-soluble vitamin) levels lead to scurvy; included gradual weakening, pale skin, sunken eyes, tender gums, muscle pain, loss of teeth
The use of lemons and limes to combat scurvy
The use of lemons and limes to combat scurvy
What disease is shown here? How would you get it?
51
New cards
Fat-soluble vitamins
A, D, E, and K
A, D, E, and K
____ can be stored in body fat and may accumulate over time
The fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins:
The fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins:
52
New cards
1. A
2. D
3. E
4.K
Fat-soluble vitamins
2. D
3. E
4.K
Fat-soluble vitamins
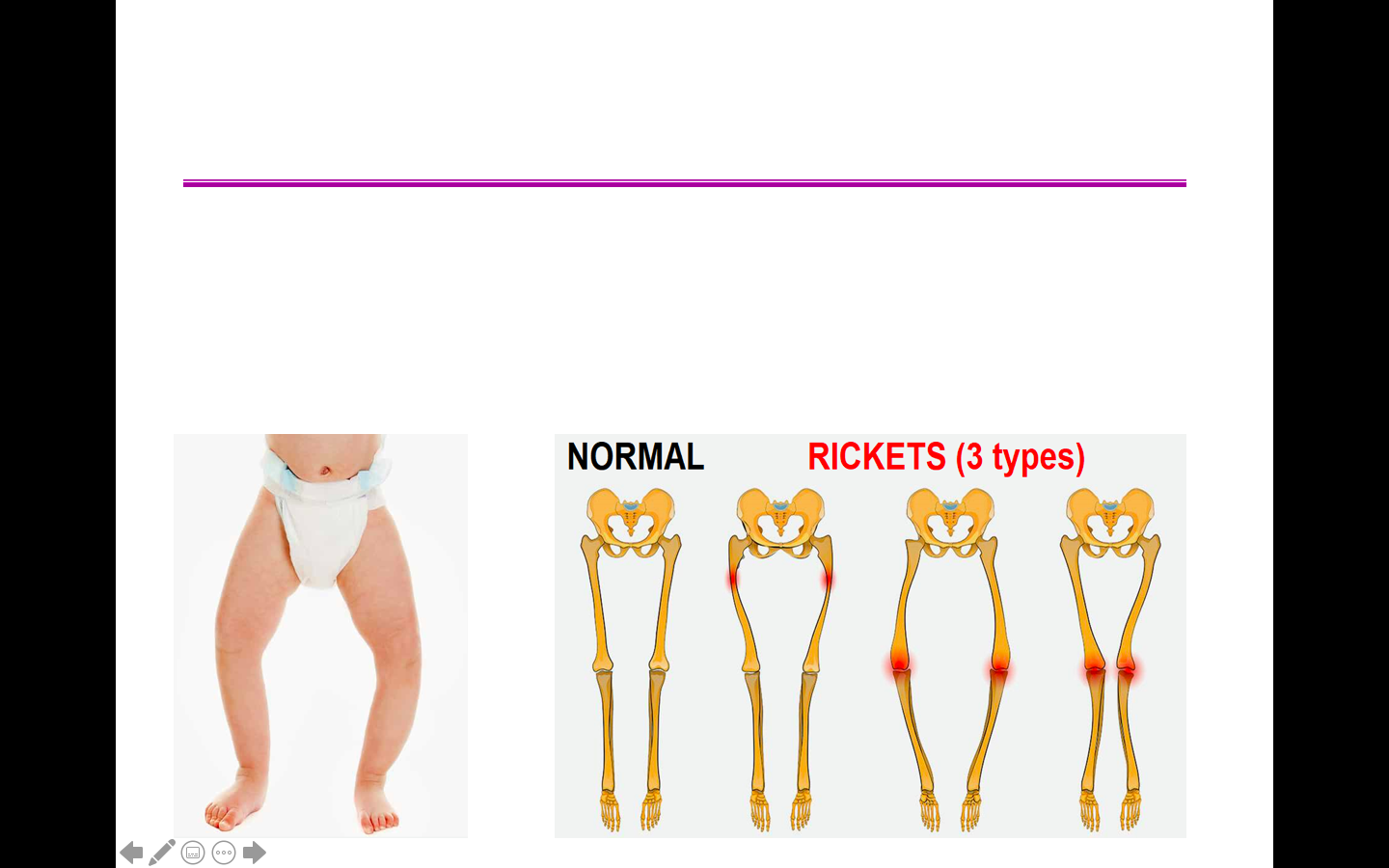
Vitamin ___: used to synthesize the light-capturing molecule in the retina of the eye
Vitamin____: required for bone formation; its deficiency can lead to bone deformities such as rickets
Vitamin ___: an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that form in the body
Vitamin ___: helps to regulate blood clotting
What type of vitamins are theses?
Vitamin____: required for bone formation; its deficiency can lead to bone deformities such as rickets
Vitamin ___: an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that form in the body
Vitamin ___: helps to regulate blood clotting
What type of vitamins are theses?
53
New cards
A deficiency in vitamin D (a Fat-soluble vitamin) can cause ricketts
What disease is shown here? How would you get it?
54
New cards
60% water
The human body is about ____
55
New cards
Food
Can a person survive longer without food or water?
56
New cards
watery solution
hydrolysis
hydrolysis
All metabolic reactions occur in a _____, and water participates directly in____ reactions that break down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats
57
New cards
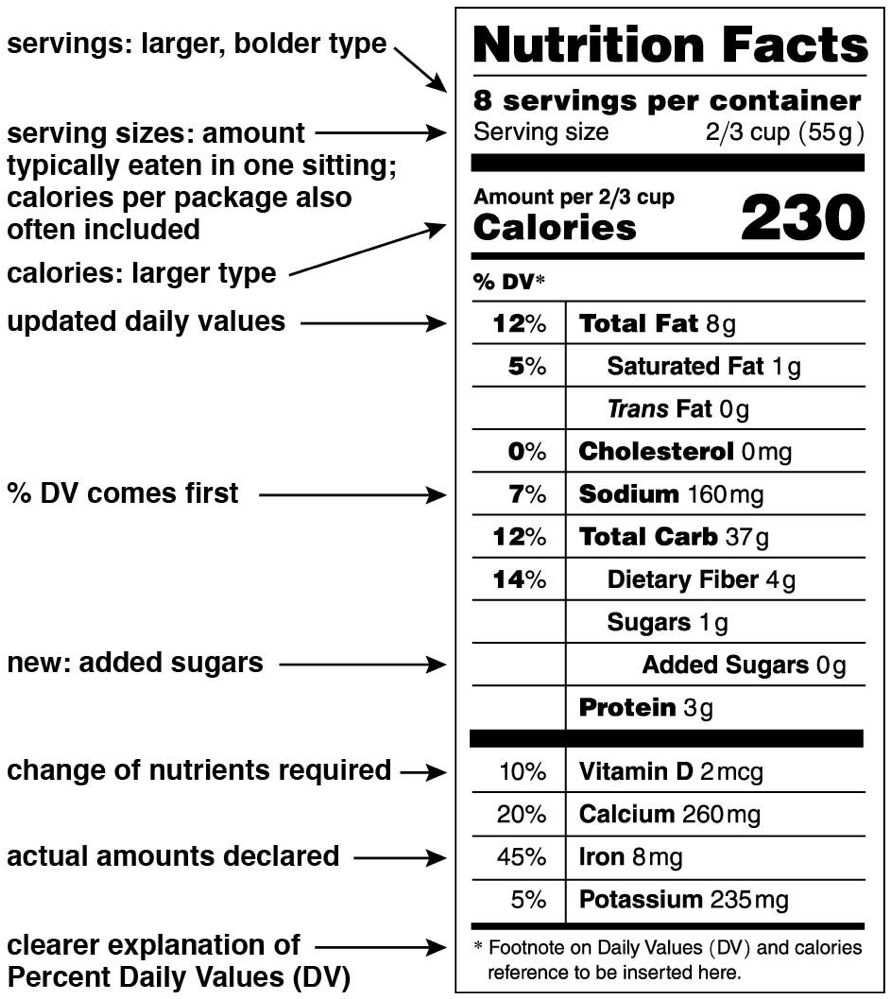
To guide informed nutritional choices
calories, fats,
calories, fats,
Why are food labels placed on products today? What do these labels actually list?

58
New cards

red= Bad
Green= Good
Green= Good
Good versus bad foods? Saturated fat (bad)

59
New cards
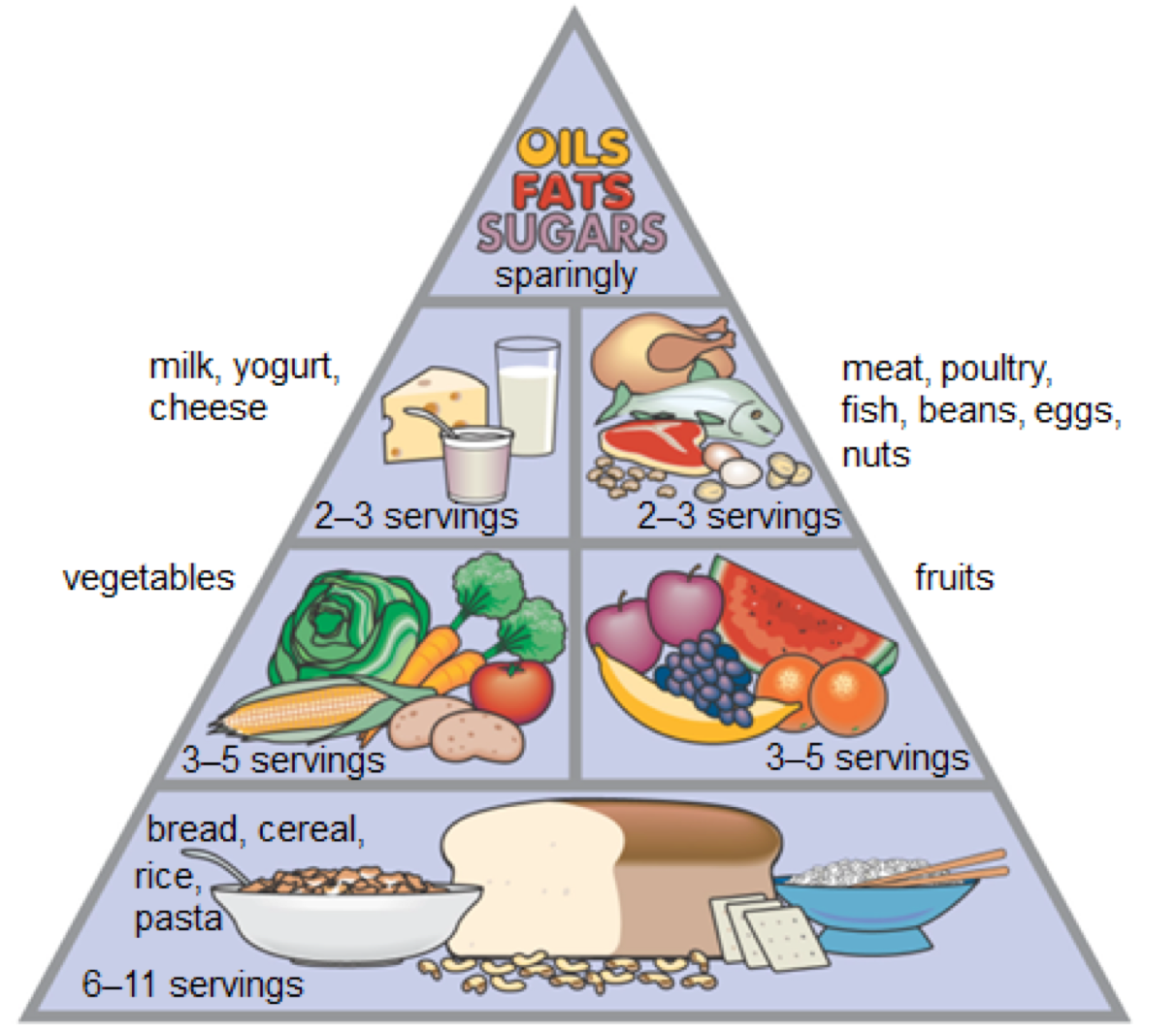
Can you place the
food groups in the
correct spaces in this triangle?
food groups in the
correct spaces in this triangle?
60
New cards
61
New cards
62
New cards
63
New cards
too much of anything is not healthy
How does a “healthy diet” keep you healthy? Are ALL natural foods healthy?

64
New cards
Digestion
____is the process that physically and chemically breaks down food
65
New cards
Takes food in, digests food into small pieces that can be absorbed by the body, pieces not absorbed are waste products
Describe the simple of digestion:
66
New cards
1. Ingestion
2. Mechanical digestion
3. Chemical digestion
4. Absorption
5. Elimination
2. Mechanical digestion
3. Chemical digestion
4. Absorption
5. Elimination
All digestive systems perform five tasks:
1. ____- Food is brought into the digestive tract through an opening, usually called a mouth
2.____-The food is physically broken down into smaller pieces that have a greater surface area than do larger particles, allowing digestive enzymes to attack them more efficiently
3.____- Digestive chemicals and enzymes break down large food molecules into smaller subunits
4.____- The small subunits are transported out of the digestive tract through cells lining the digestive tract to the blood for use by body cells
5.____- Indigestible materials are expelled from body
1. ____- Food is brought into the digestive tract through an opening, usually called a mouth
2.____-The food is physically broken down into smaller pieces that have a greater surface area than do larger particles, allowing digestive enzymes to attack them more efficiently
3.____- Digestive chemicals and enzymes break down large food molecules into smaller subunits
4.____- The small subunits are transported out of the digestive tract through cells lining the digestive tract to the blood for use by body cells
5.____- Indigestible materials are expelled from body
67
New cards
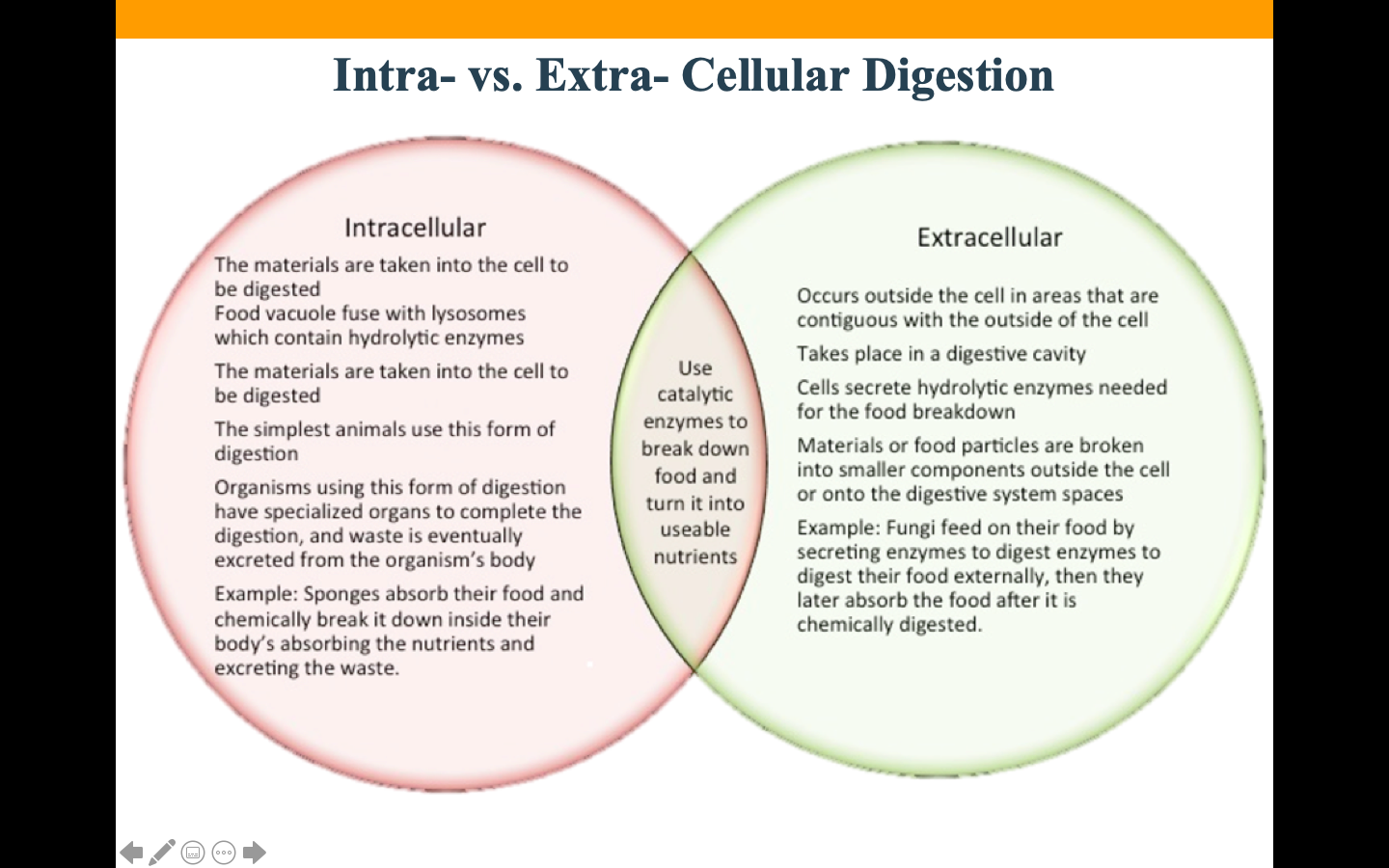
Differences between these 2 types of digestion?
68
New cards
intracellular digestion; digestion occurs within individual cells
What type of digestion do sponges do?
69
New cards
sedentary; chamber
Sponges are_____ filter-feeders that lack a digestive____
70
New cards
collar cells (line inside sponge)
phagocytosis
food vacuole
lysozome
phagocytosis
food vacuole
lysozome
Sponge Digestion takes place in _______ that engulf microscopic food particles and ingest them using______, forming a ______ which fuses with a______ (packet of digestive enzymes) within the cell that breaks down the food into smaller molecules
The smaller food molecules are absorbed into the cells cytoplasm
Indigestible material is expelled from the cell and sponge through a large opening in the body wall
The smaller food molecules are absorbed into the cells cytoplasm
Indigestible material is expelled from the cell and sponge through a large opening in the body wall
71
New cards
intracellular digestion: Collar cells engulf using phagocytosis--> forms food vacuole that fuses with lysozome to break down--> cells' cytoplasm absorbs--> Expel wastes thru opening in body wall
Describe sponge digestion--
72
New cards
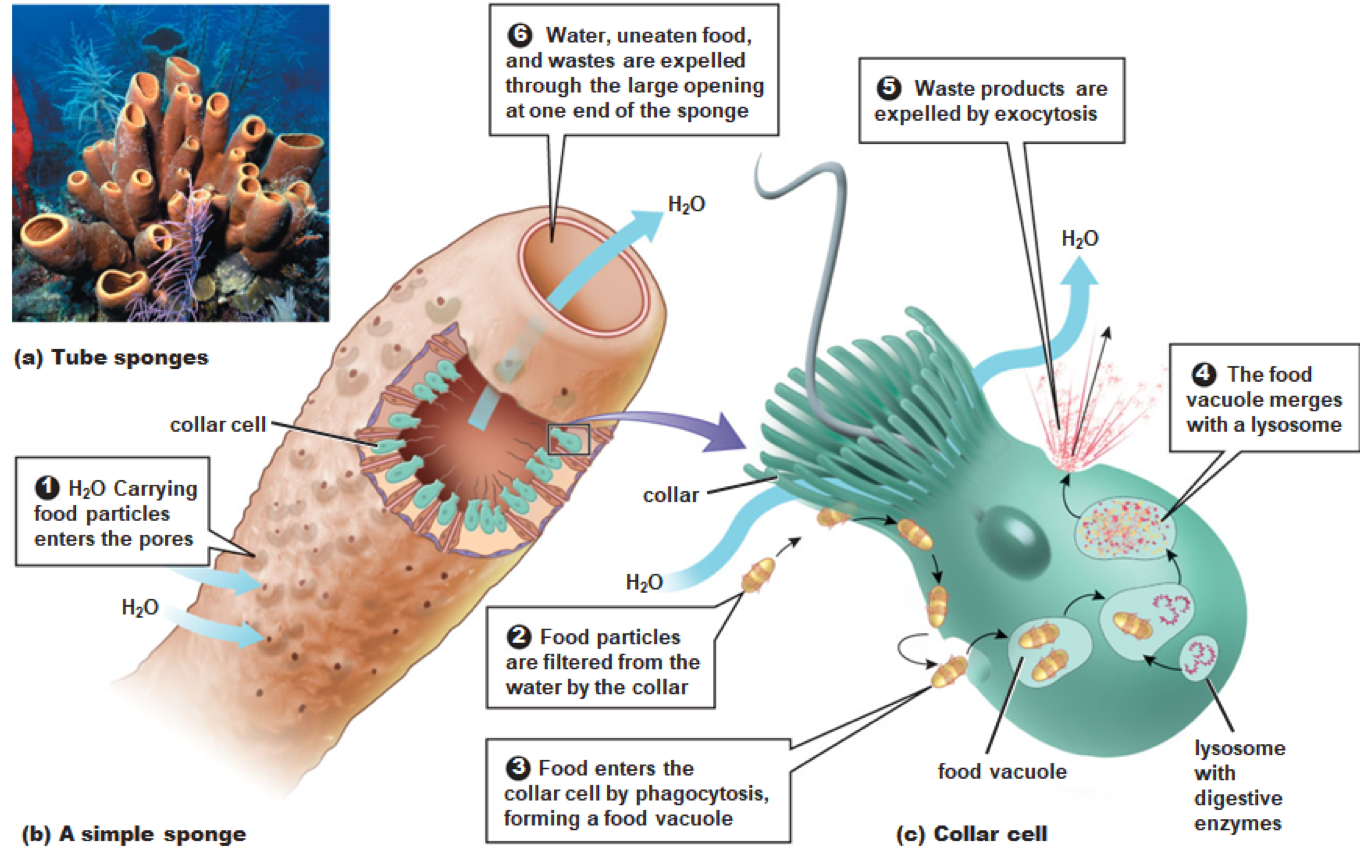
73
New cards
one opening
The simplest digestive system is a chamber with _____
74
New cards
extracellular digestion
___ is when food is broken down by enzymes outside the cells
75
New cards
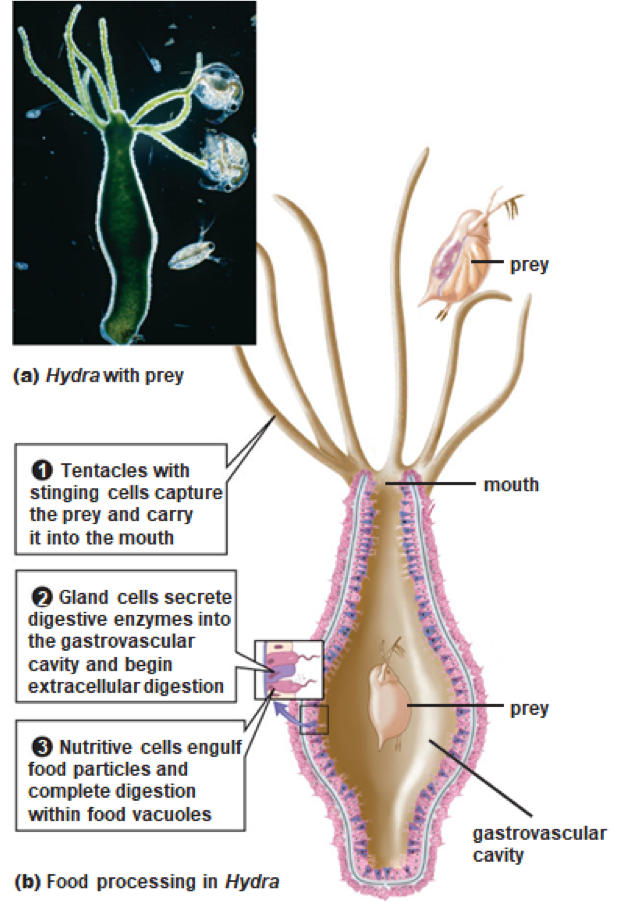
the cnidarians (aquatic invertebrate animal) such as sea anemones, Hydra, and sea jellies
A sac with one opening is the simplest digestive system, and is found in:
76
New cards
gastrovascular cavity
cnidarians (aquatic invertebrate animal) have a _________ with a single opening at one end that acts as both a mouth and an anus
77
New cards
extracellular digestion: tentacles capture food--> Cells lining the gastrovascular cavity release enzymes--> these cells absorb the food--> Expel wastes thru mouth
Explain the digestion of aquatic cnidarians (invertebrate animal)
78
New cards
79
New cards
tubular
Most animals have____ digestive systems with specialized compartments
80
New cards
invertebrate animals
mouth; anus
grind up, enzymatically break down, absorb nutrients, and expel the wastes through the anus
mouth; anus
grind up, enzymatically break down, absorb nutrients, and expel the wastes through the anus
Tubular Digestion system:
In most____
begin___, end____
Specialized regions within the tube--
In most____
begin___, end____
Specialized regions within the tube--
81
New cards
A Tubular Digestion system
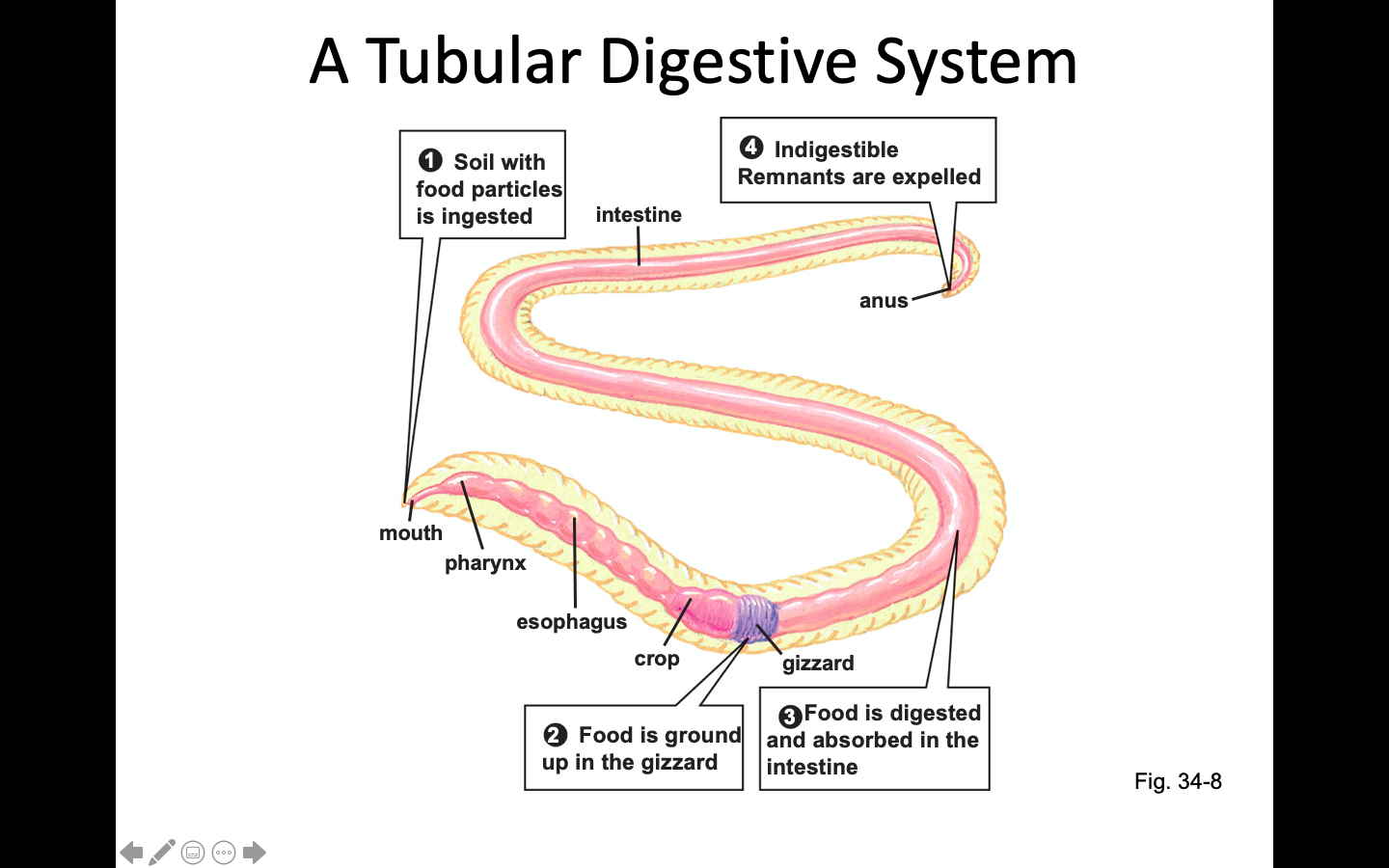
What type of Digestion system does the earthworm have?
82
New cards
Tubular Digestion system: burrows & soil passes thru the esophagus--> the crop (expandable sac) for storage--> gizzard to grinding--> intestine, enzymes break down--> Body absorbs--> wastes expelled
Explain an earthworms Digestion system:
83
New cards
What mode of digestion do worms use?
84
New cards
Carnivores-- eat other animals
Herbivores-- eat only plants
Omnivores-- eat both animals and plants
Herbivores-- eat only plants
Omnivores-- eat both animals and plants
Different animals have radically different diets:
85
New cards
tiger Carnivores
rabbit Herbivores
human Omnivores
rabbit Herbivores
human Omnivores
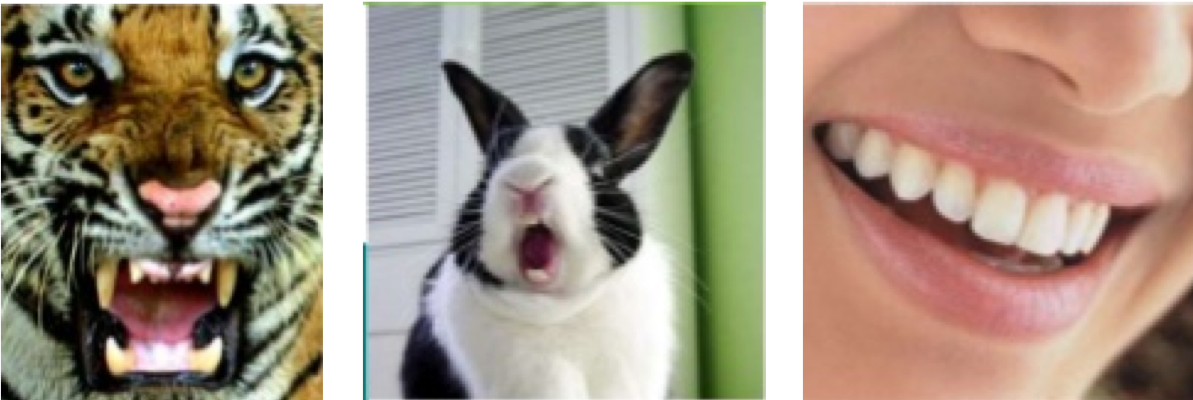

86
New cards
Incisors are used for biting
Canines are used for tearing
Premolars are used for grinding
Molars are used for crushing and chewing
Canines are used for tearing
Premolars are used for grinding
Molars are used for crushing and chewing
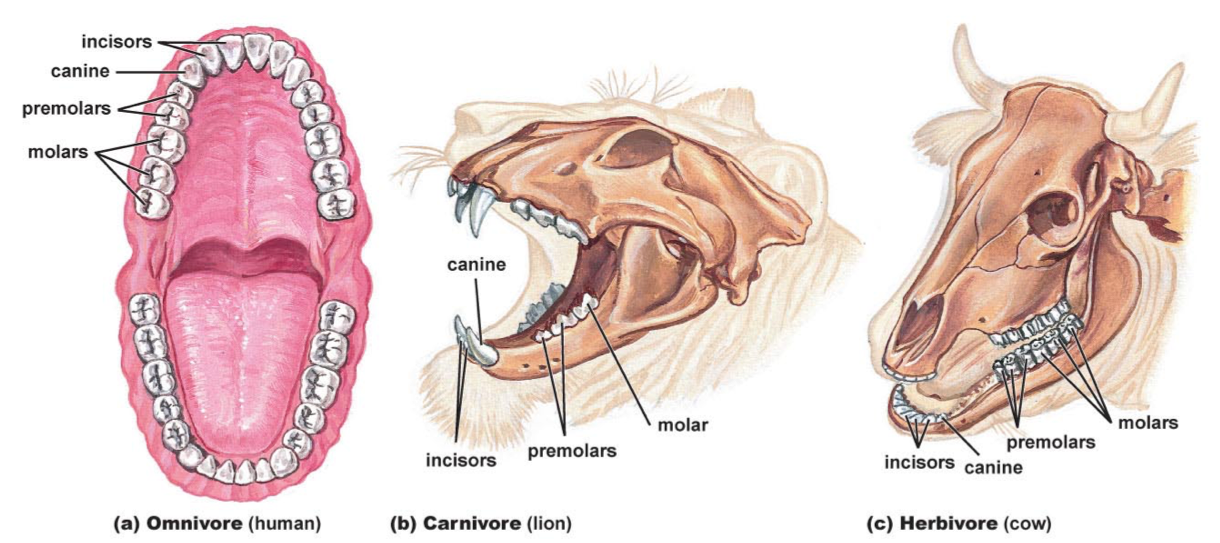
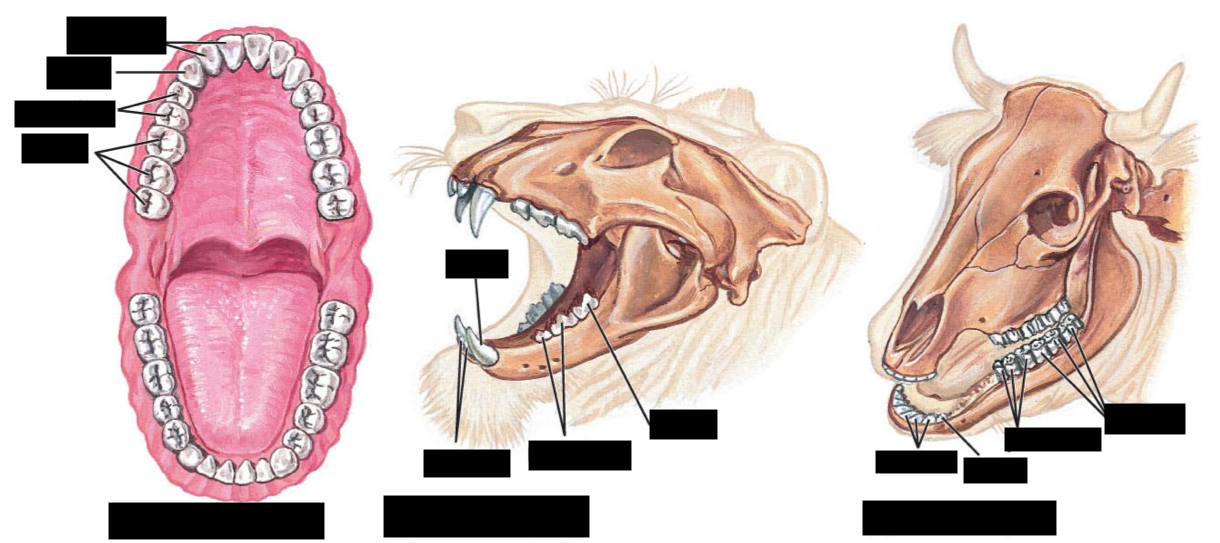
Different teeth:
87
New cards
lion
cow
cow
88
New cards
--thin, flat incisors for shearing off food, small canines, and large premolars and molars for crushing and grinding
--enlarged canines for stabbing and tearing flesh, and molars and premolars with sharp edges for shearing through tendon and bone
--reduced canines but large incisors for snipping plants, and big, flattened premolars and molars for grinding up plant material
--enlarged canines for stabbing and tearing flesh, and molars and premolars with sharp edges for shearing through tendon and bone
--reduced canines but large incisors for snipping plants, and big, flattened premolars and molars for grinding up plant material
Teeth
omnivores--
Carnivores---
Herbivores--
omnivores--
Carnivores---
Herbivores--
89
New cards
Bird’s stomachs grind food
--lack teeth and swallow food whole
--lack teeth and swallow food whole
What will a bird's stomach do?
90
New cards
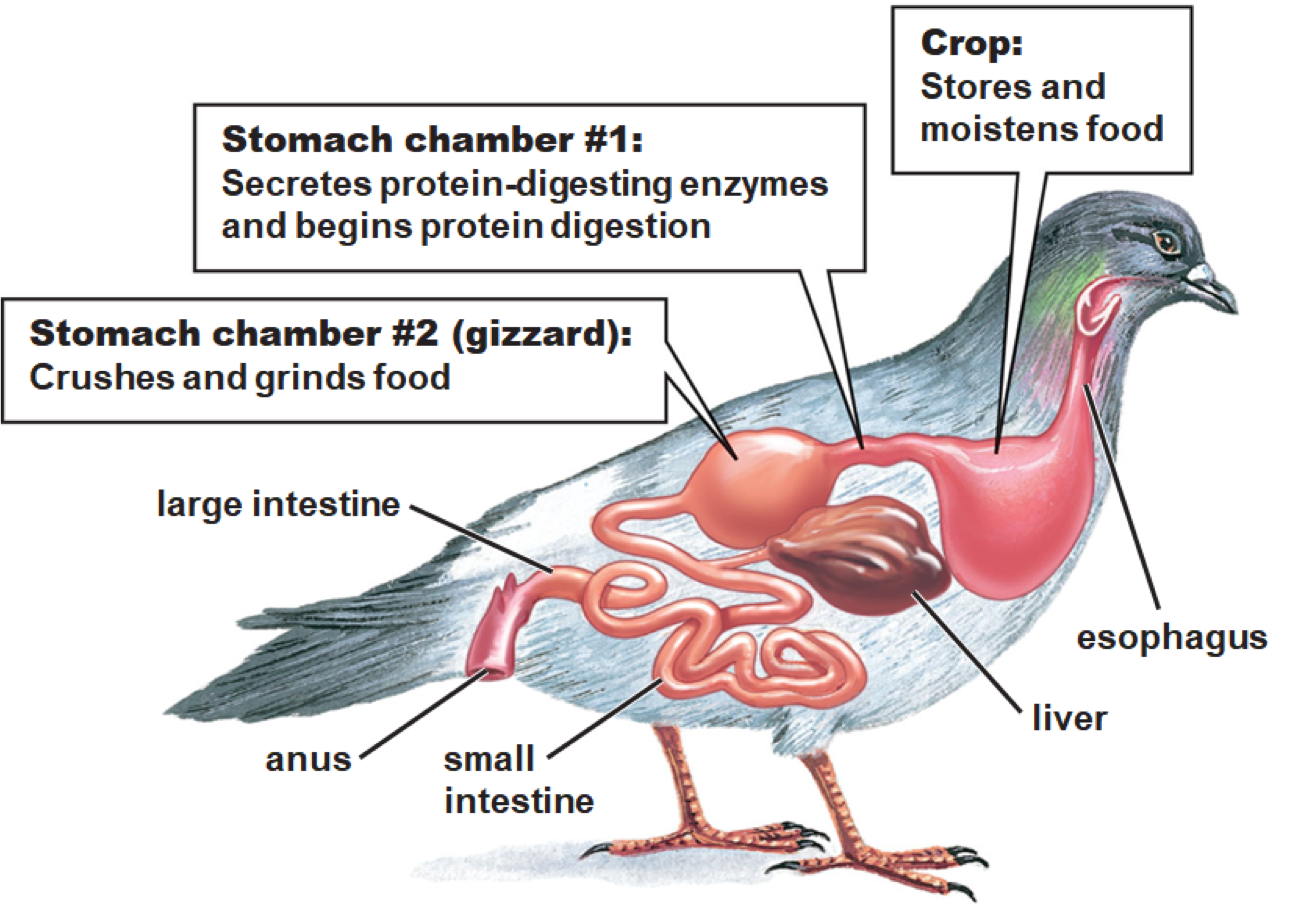
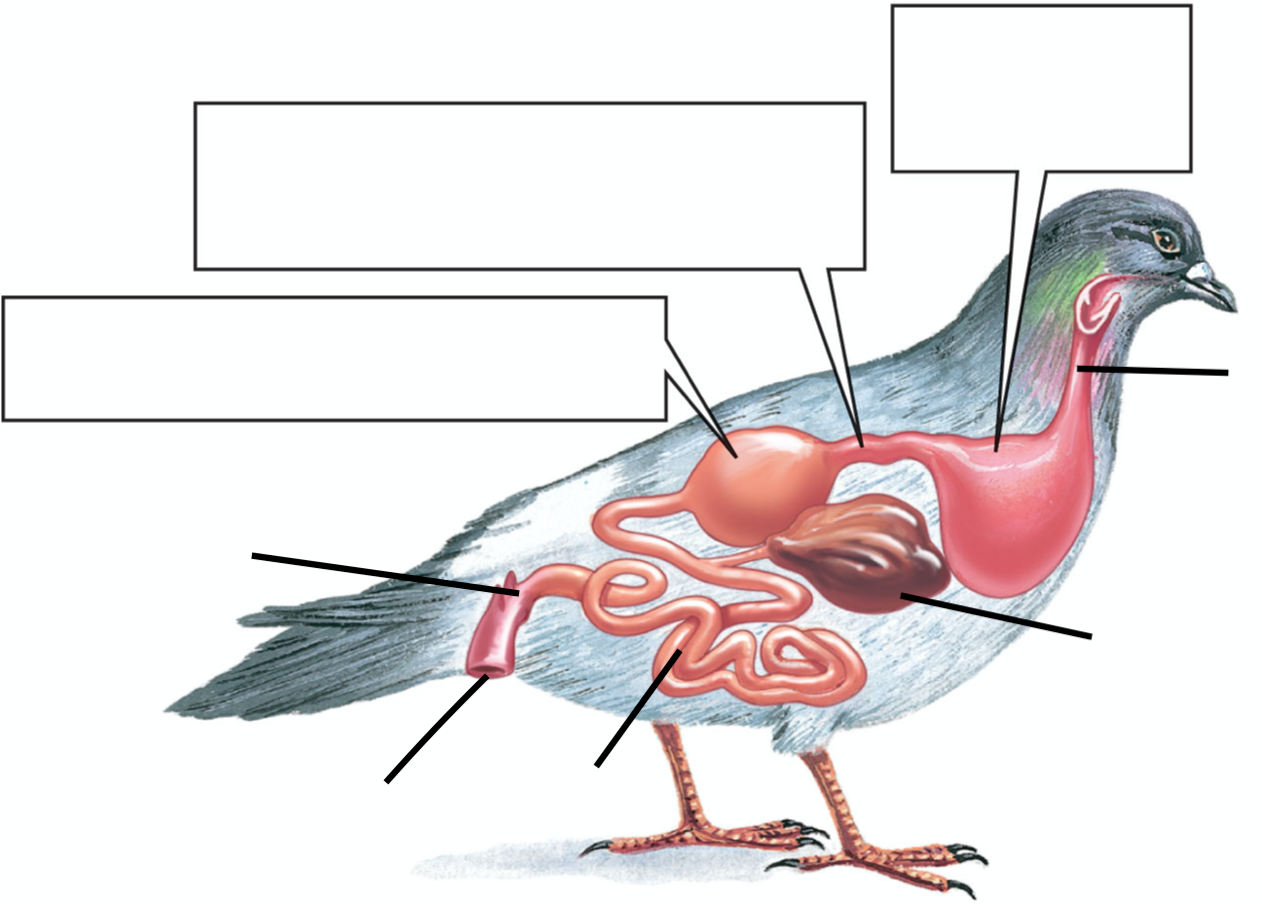
Swallow food whole--> esophagus--> crop, stores and moistens--> stomach-- 1st chamber, enzymes; 2nd chamber, grinding--> Gizzard, more grinding--> small intestines, digested more and absorbed--> Expelled
Explain digestion system of a bird:
91
New cards
92
New cards
Ruminant
cellulose
cellulose
______ herbivores, such as cows, are able to break down___
93
New cards
Rumen
Reticulum
Omasum
Abomasum
Small intestine
Reticulum
Omasum
Abomasum
Small intestine
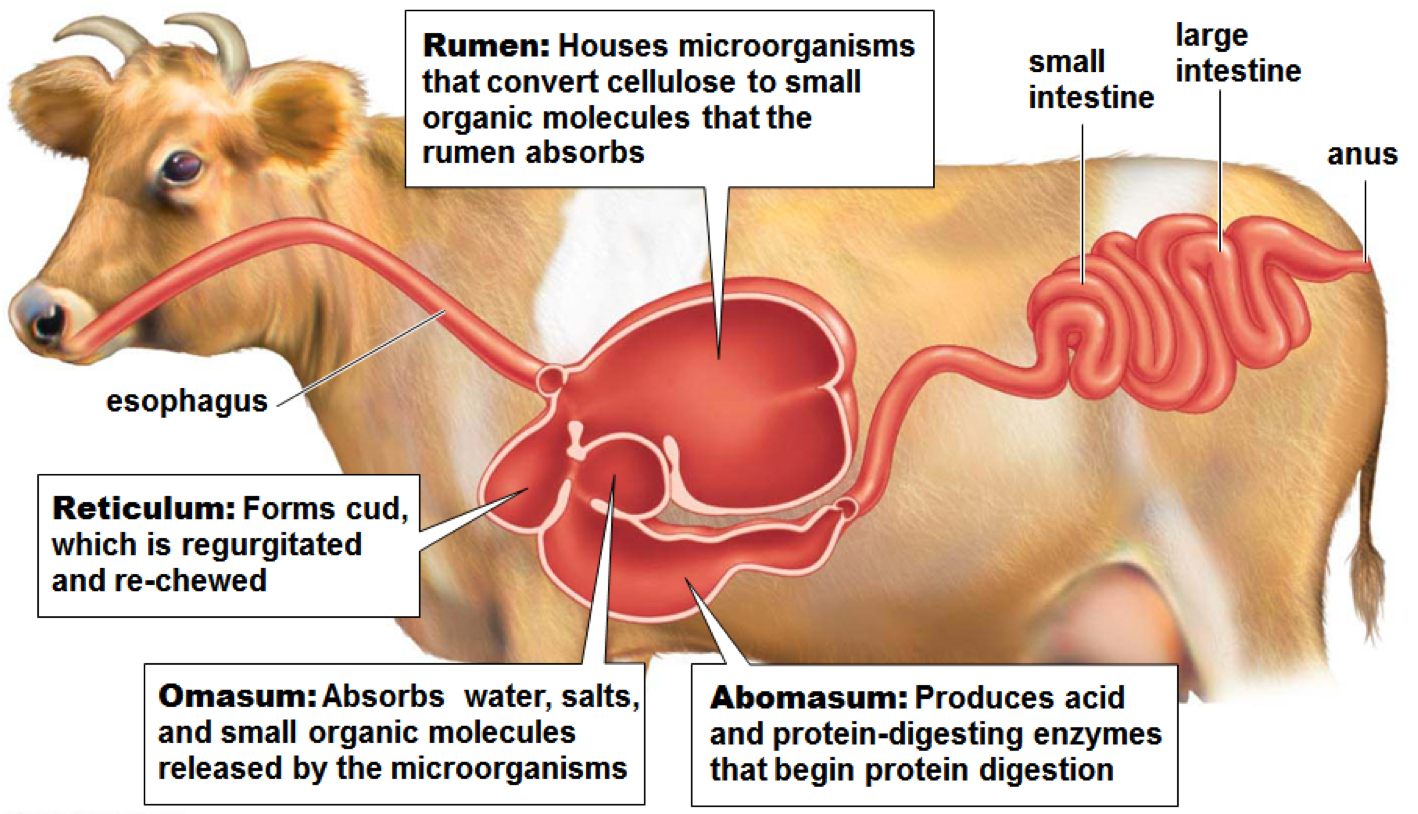
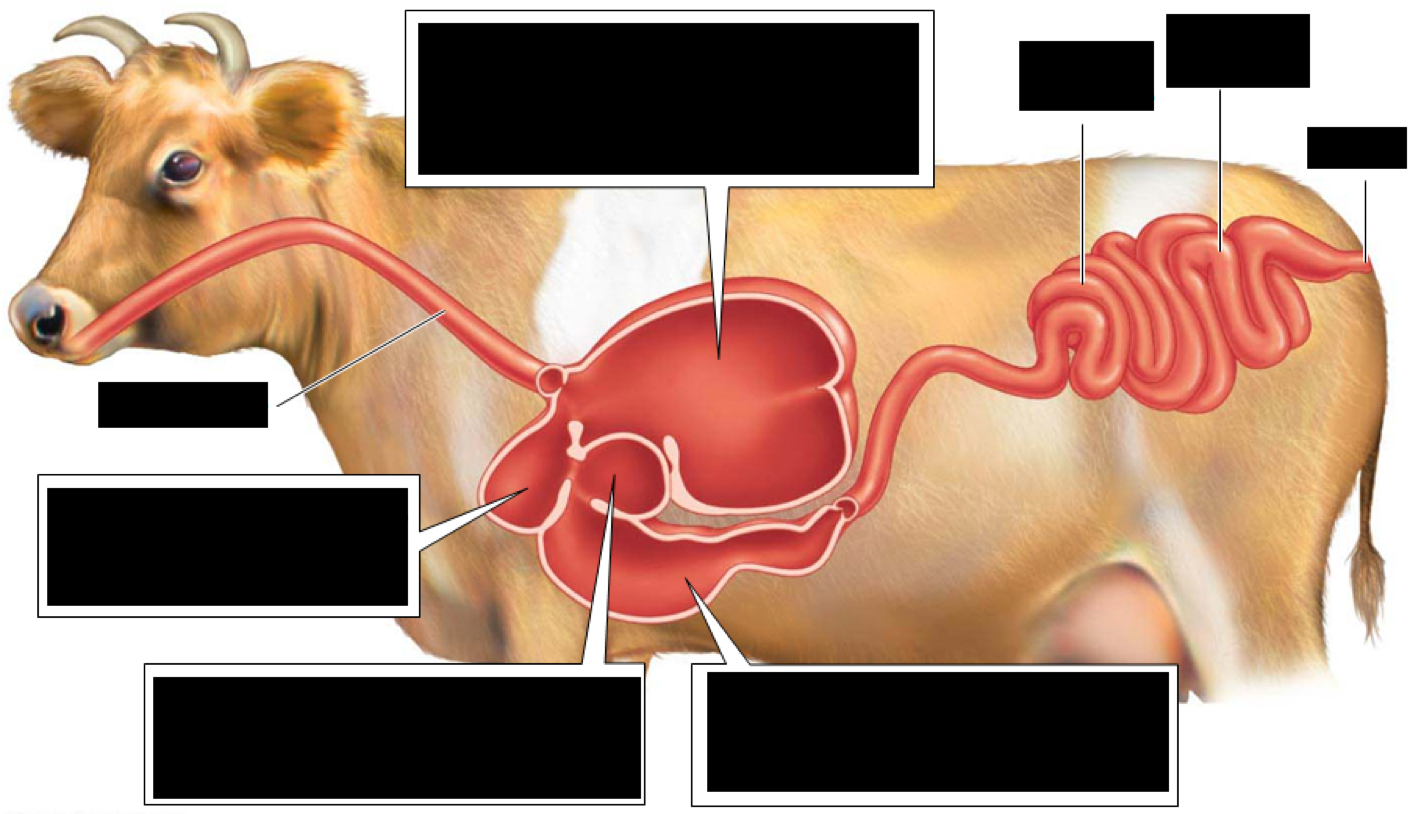
Ruminants have multiple stomach chambers that contribute to the digestion of plant cellulose
---_____: houses bacteria, break down and then ferment cellulose and other carbohydrates
---_____: cud is regurgitated, chewed, and swallowed back into the rumen
---____: water, salts, and some small organic molecules are absorbed
---____: acid and protein-digesting enzymes begin protein digestion
---____: majority of the nutrients are absorbed
---_____: houses bacteria, break down and then ferment cellulose and other carbohydrates
---_____: cud is regurgitated, chewed, and swallowed back into the rumen
---____: water, salts, and some small organic molecules are absorbed
---____: acid and protein-digesting enzymes begin protein digestion
---____: majority of the nutrients are absorbed
94
New cards
The ruminant digestive system
95
New cards
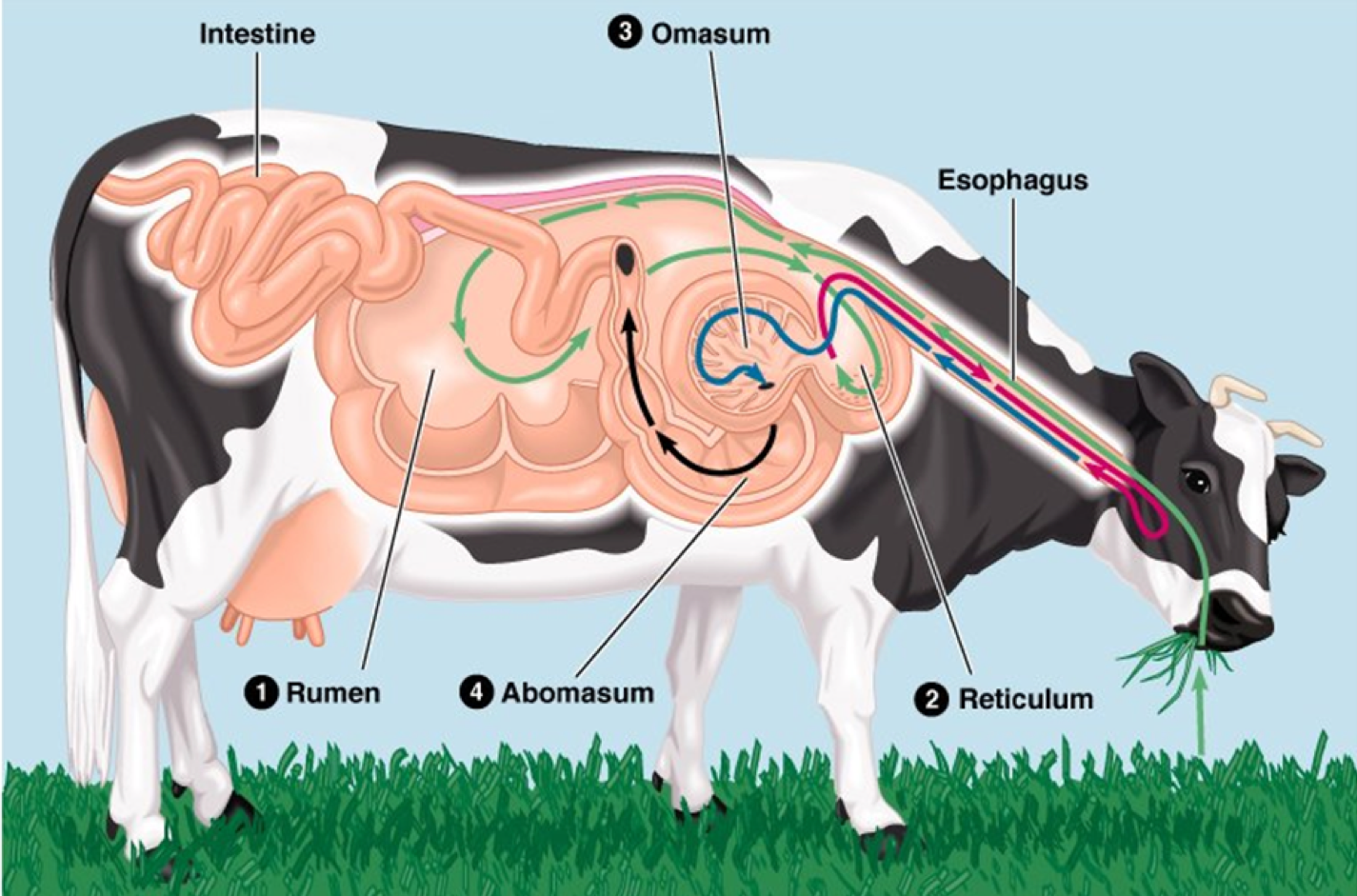
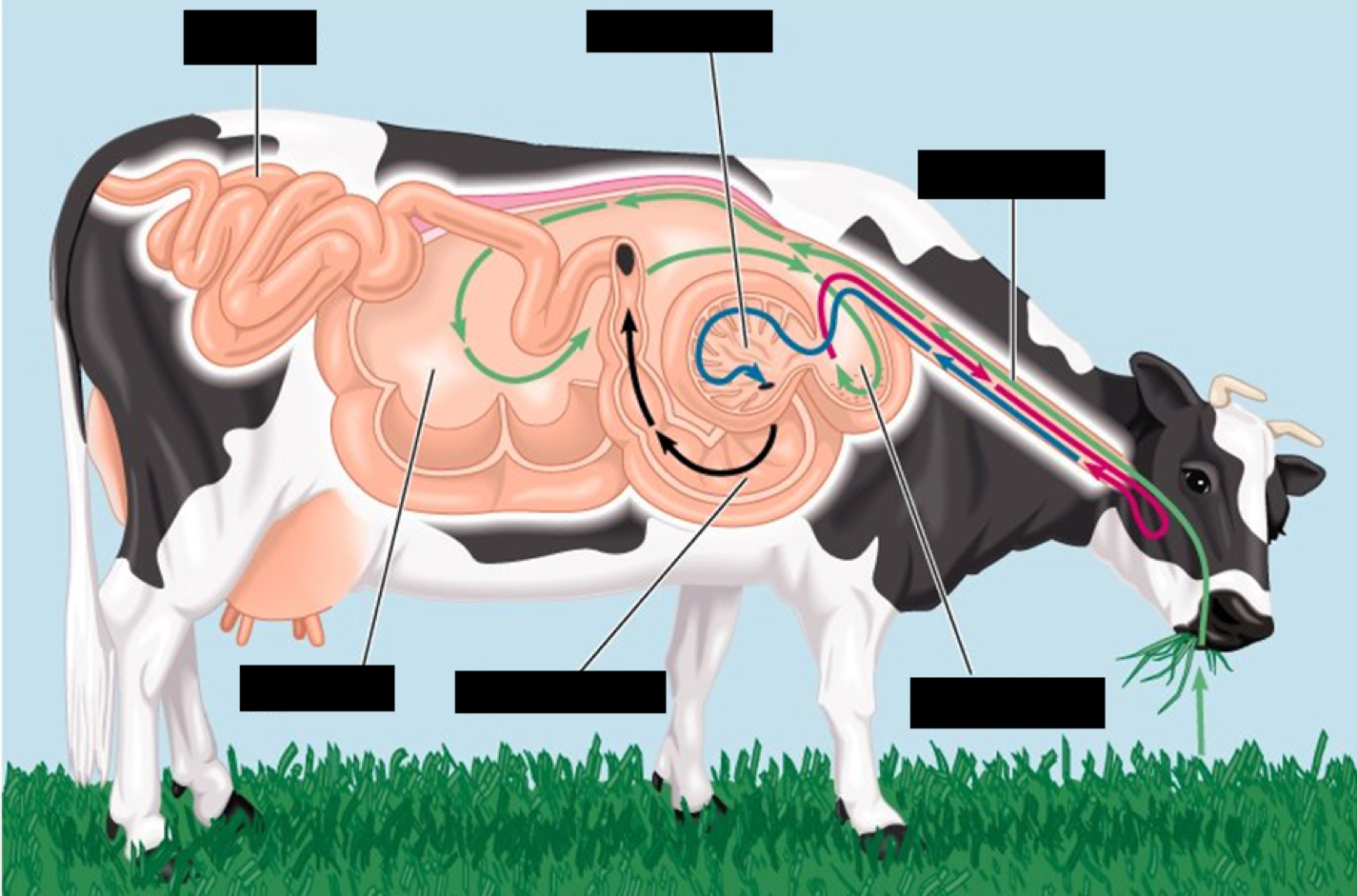
Mouth--> Esophagus--> Rumen--> Reticulum--> Esophagus--> mouth--> Esophagus--> Reticulum--> Omasum--> Abomasum--> Intestine
96
New cards
diet
--Because cell walls are difficult to digest, herbivore intestines are long --more time for nutrient absorption
--Carnivore intestines are relatively short --Proteins are easy
--Because cell walls are difficult to digest, herbivore intestines are long --more time for nutrient absorption
--Carnivore intestines are relatively short --Proteins are easy
Small intestine length is correlated with ____
Explain how this relates to herbivores vs carnivores~~
Explain how this relates to herbivores vs carnivores~~
97
New cards
In frog development, the herbivorous tadpole has a long small intestine, but the carnivorous frog intestine shortens to one-third its tadpole length
How can frogs relate to intestine length?
98
New cards
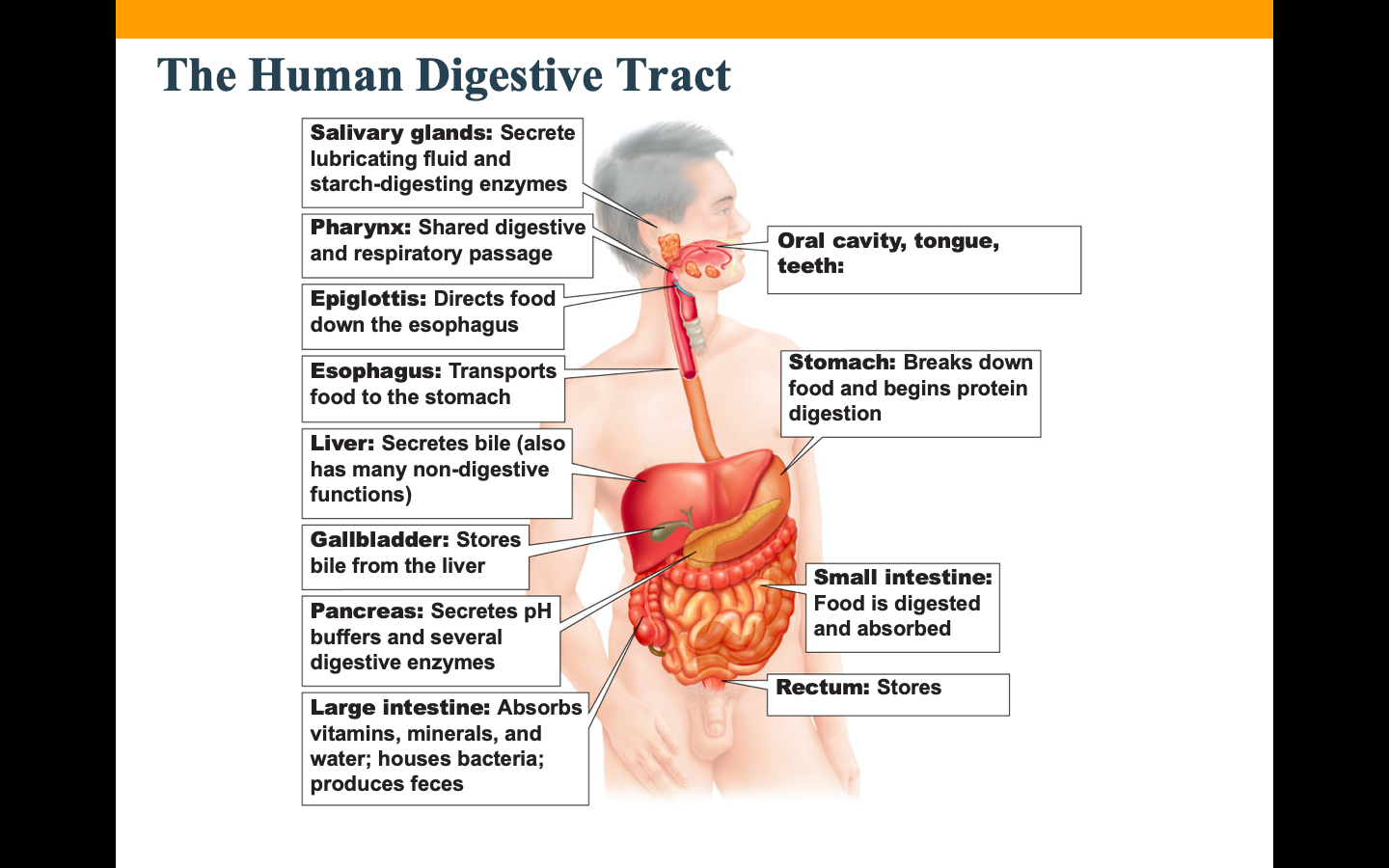
99
New cards
in the mouth
chewing= Mechanical
saliva= chemical
chewing= Mechanical
saliva= chemical
Where do Mechanical and chemical digestion begin?
give examples
give examples
100
New cards
amylase; breaks down starches into sugars
guard against infection
lubricates
dissolves
guard against infection
lubricates
dissolves
The functions of saliva include:
--Saliva contains______, which~
--It contains bacteria-killing enzymes and antibodies to~
--It_____ food to ease with swallowing
--It___ some molecules and exposes them to taste buds on tongue, which helps to identify the type and quality of food
--Saliva contains______, which~
--It contains bacteria-killing enzymes and antibodies to~
--It_____ food to ease with swallowing
--It___ some molecules and exposes them to taste buds on tongue, which helps to identify the type and quality of food