Myeloid cells
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the cellular components that make up the myeloid cells?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, macrophages, and NK cells (participate in innate response)
What are some characteristics of neutrophils?
defend against bacteria and fungi
localized inflammation prolonged through cytokines
contains granules with enzymes
usually the first leukocyte to arrive at site of injury
move through blood vessels (diapedesis)
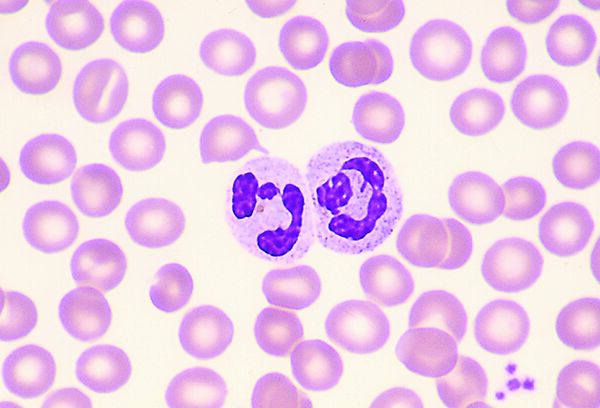
What does a neutrophil look like?
Cytoplasm contains purple granules, nucleus is banded or segmented
What are some characteristics of eosinophils?
inc. during allergies and parasitic infections
usually suppress excess inflammation
contains granules
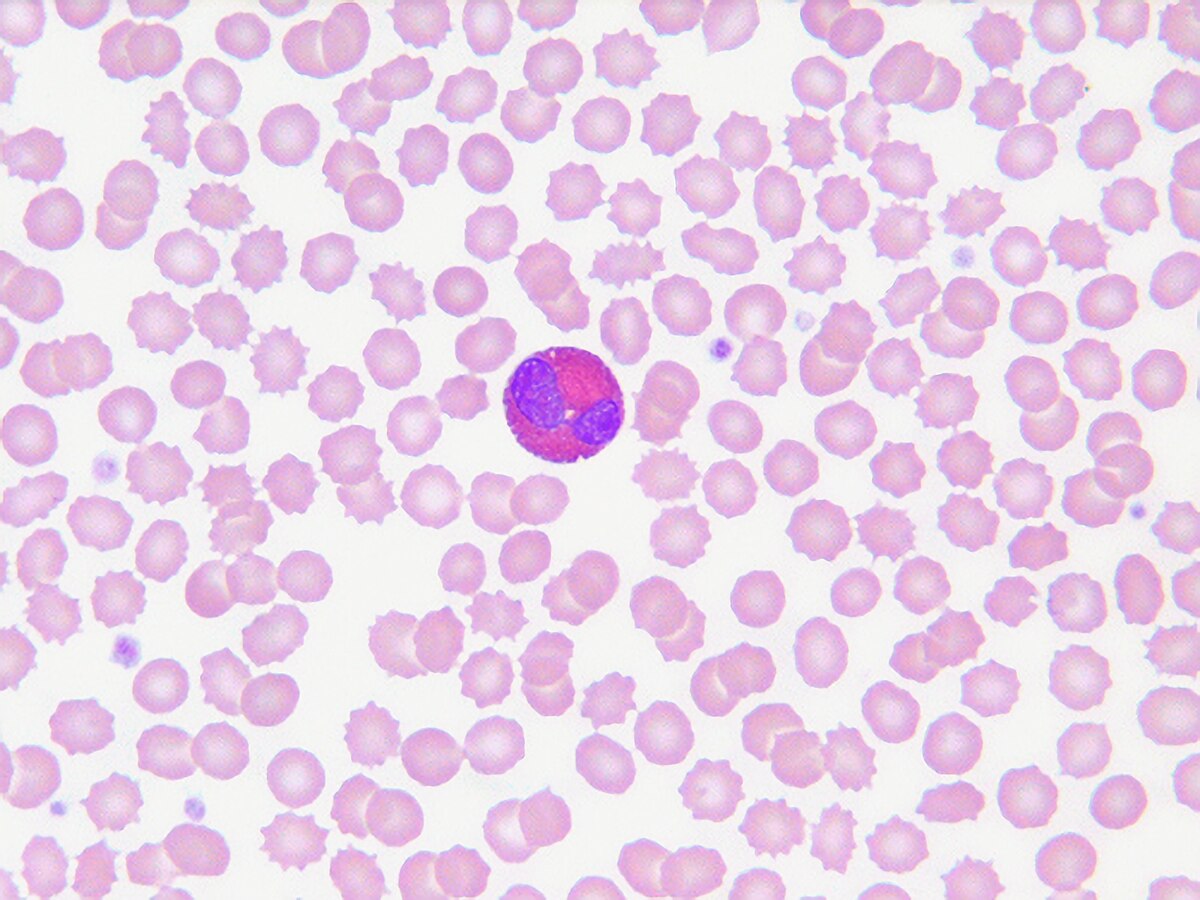
What does an eosinophil look like?
Pinker granules within cytoplasm, bigger than the ones in neutrophils
What are some characteristics of basophils?
regulate acute hypersensitivity (IgE binds to mast cells!)
granulated with heparin and histamine that:
inc. vascular permeability
muscle spasms
vasodilation
vast amounts are produced during anaphylactic shock
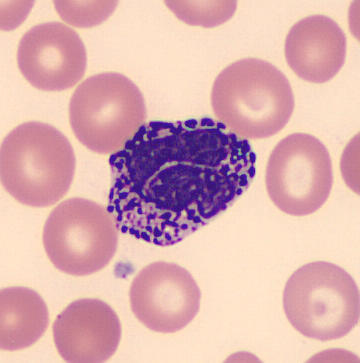
What do basophils look like?
Very dark purple granules
What are some characteristics of monocytes and macrophages?
ingest and kill intracellular and extracellular pathogens
proteolytic enzymes on their surface suppress tumor growth
present antigens to the adaptive immune system
secrete cytokines
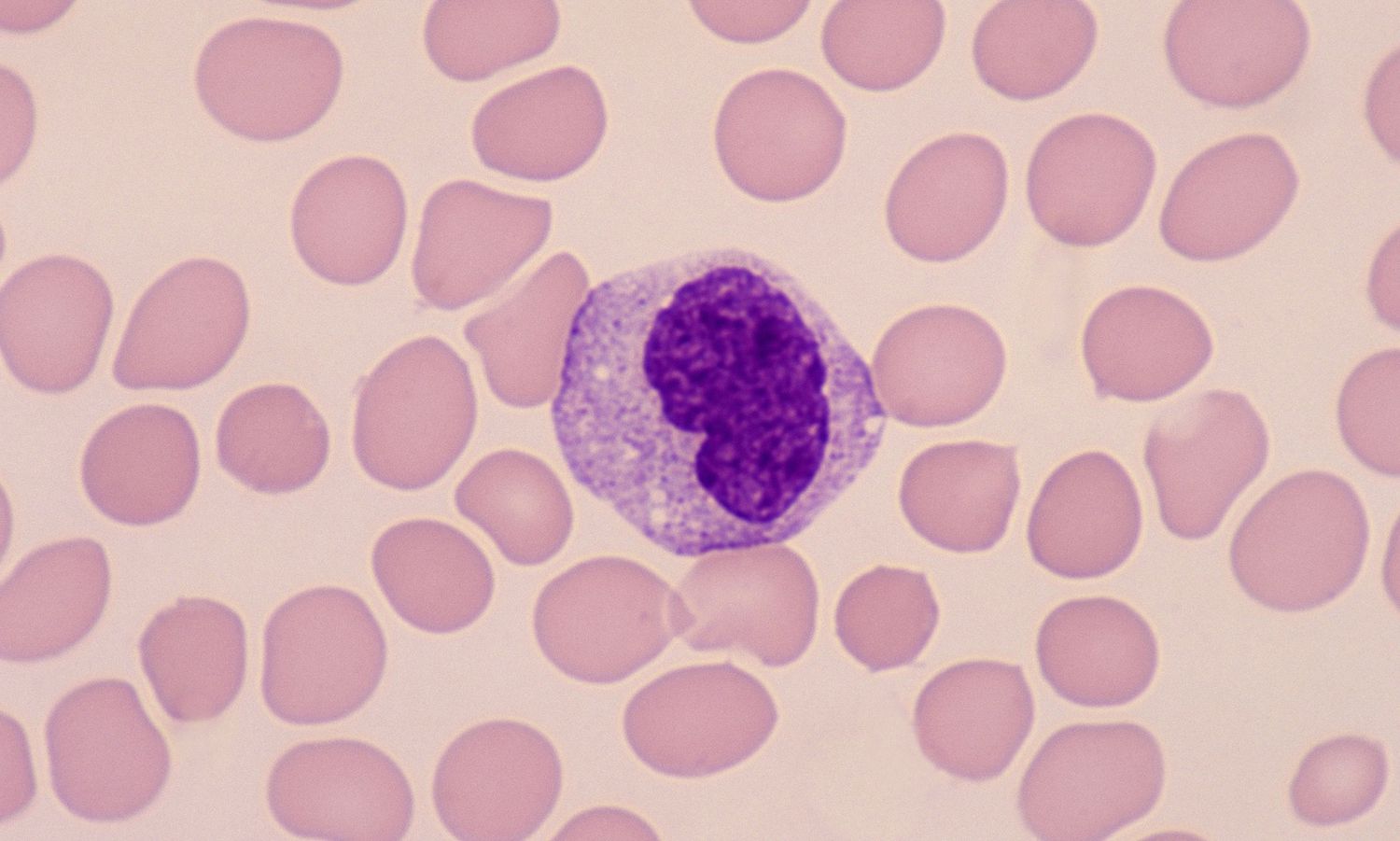
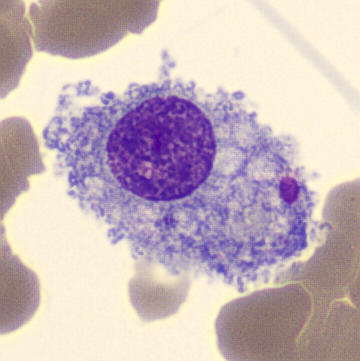
What does a monocyte look like?
a bi-lobed nucleus with purple cytoplasm
What does an activated monocyte, or macrophage, look like?
Lighter blue cytoplasm with vacuoles touching the nucleus (engulfment of material)
List the steps of phagocytosis.
Chemotaxis towards microbe
Ingestion of microbe
Engulfment into a phagosome within the cell
Fusion of a lysosome with the phagosome, producing a phagolysosome
digestion of the contents via enzymes
Residual body formation housing undigested material
Discharge from the cell