Physiology of circulation and pathophysiology of hypertension
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:35 PM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
Aorta and large conduit arteries
- transports blood to tissues
- under high pressure ( 100 mmHg)
- low resistance
- under high pressure ( 100 mmHg)
- low resistance
2
New cards
Small arteries and arterioles
- control blood flow to tissue via vasoconstriction and vasodilation
- major site of vascular resistance
- site of action for anti-hypertensive drugs
- major site of vascular resistance
- site of action for anti-hypertensive drugs
3
New cards
Capillaries
- site for nutrient and gas exchange between blood and tissues
4
New cards
Venous system
- returns blood to heart
- under low pressure
- under low pressure
5
New cards
What is the function of the arterial system?
- deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues
6
New cards
What is the function of he venous system?
- remove carbon dioxide and waste from the tissues
7
New cards
What are the functions of the circulatory system?
- deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues
- remove carbon dioxide and waste from tissues
- transport: hormones= control ; wbcs: defense ;
- distribute heat: temperature regulation
- remove carbon dioxide and waste from tissues
- transport: hormones= control ; wbcs: defense ;
- distribute heat: temperature regulation
8
New cards
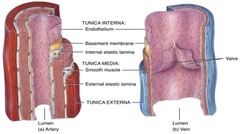
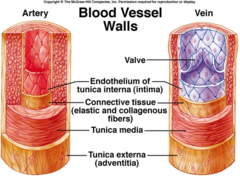
What is the tunica intima?
-inner layer of blood vessel, endothelium
9
New cards
True/False: The smooth muscle cells are circular
- True
10
New cards
What is the tunica media?
-layer of smooth muscle cells that contract and alter vessel diameter
- sympathetic nerve fibers cause vasoconstriction and vasodilation to regulate blood pressure
- sympathetic nerve fibers cause vasoconstriction and vasodilation to regulate blood pressure
11
New cards
What is the tunica externa?
-Outermost, collagen and elastic fibers.
12
New cards
Which ions and how would they contribute to smooth muscle contraction?
- Influx of calcium ions causes depolarization which leads to contraction
- Influx of sodium ions causes depolarization which causes contraction
- Efflux of chlorine ions causes depolarization which causes contraction
- Influx of sodium ions causes depolarization which causes contraction
- Efflux of chlorine ions causes depolarization which causes contraction
13
New cards
What is the mean pressure of the capillaries?
- 17 mmHg
14
New cards
Which ions and how do they lead to smooth muscle relaxation?
- an efflux of potassium ions causes hyperpolarization which leads to relaxation of the smooth muscle
15
New cards
What is blood flow?
- the quantity of blood that passes a given point in the circulation in a given period of time
16
New cards
Which cell type is organized circularly around blood vessels?
- smooth muscles
17
New cards
True/False: endothelial cells contract
- False: the endothelial cells do not contract only smooth muscle cells contract
18
New cards
If a person has anemia what happens to their blood flow?
- They will have less red blood cells which leads to less viscosity and will cause their blood flow to be faster
19
New cards
If you increase the diameter of the blood vessels what happens to the blood flow?
- the blood flow will increase
20
New cards
What happens to the blood flow with an increase in the radius of the blood vessel/
- the blood flow will be increased
21
New cards
What happens to the baroreceptors when a person has low blood pressure?
- the baroreceptors are inhibited, so their is an increase in vasomotor activity to increase the heart rate , increase the CO , and increase the resistance
22
New cards
What happens to the baroreceptors if a persons blood pressure is high?
- baroreceptors inhibit the vasomotor center activity
23
New cards
True/False: an increase in vessel length leads to a decrease in blood flow
- True
24
New cards
Laminar flow
- velocity of flow in the center of the vessel is far greater than that at the outer edges
25
New cards
Turbulent flow
- disordered flow caused by fast flow rate, obstruction in the vessel, sharp turn in the vessel, or passing over a rough surface
- increases resistance
- increases resistance
26
New cards
Blood flow formula
F= change in pressure/resistance

27
New cards
Total peripheral resistance/ systemic vascular resistance
- the resistance of the entire systemic circulation
28
New cards
True/False: Blood flow is equivalent to cardiac output for the entire vascular system
- True
29
New cards
What are the factors regulating vascular resistance and blood flow?
- vessel diameter
- hematocrit and blood viscosity
- pressure
- hematocrit and blood viscosity
- pressure
30
New cards
True/ False: blood flow is extremely sensitive to vessel diameter changes
- True
31
New cards
What is the relationship between blood flow and hematocrit/blood viscosity
- if there is an increase in hematocrit leads to increase in blood viscosity which increases the vascular resistance and decreases blood flow
32
New cards
Blood flow autoregulation
- a local adaptive mechanism used by tissues in our body to maintain constant perfusion despite fluctuations in arterial pressure
- occurs between 70-175 mmHg
- occurs between 70-175 mmHg
33
New cards
What is autoregulation of blood flow?
- local regulation of blood flow assures tissues receive the nutrients they need and assures that pressure spikes do not affect nutrient distribution
34
New cards
What are the acute local control of blood flow mechanisms?
- metabolic theory ( vasodilator theory, oxygen lack theory)
- myogenic theory
- myogenic theory
35
New cards
What are the long term local control of blood flow mechanisms?
- angiogenesis ( increased vascularity, collateral vessels
36
New cards
Metabolic theory ( vasodilator theory)
- the greater the rate of metabolism or the lower the availability of oxygen/nutrients, the greater to formation of vasodilators by tissues
- increase tissue metabolism/ decrease oxygen deliver- decrease oxygen/ nutrients in tissue- release of vasodilators ( adenosine, ATP and ADP, CO2, histamine, K+, H+) - decreased arteriole resistance ( vasodilation) - increase in blood flow
- increase tissue metabolism/ decrease oxygen deliver- decrease oxygen/ nutrients in tissue- release of vasodilators ( adenosine, ATP and ADP, CO2, histamine, K+, H+) - decreased arteriole resistance ( vasodilation) - increase in blood flow
37
New cards
Metabolic theory ( oxygen lack theory)
- in the absence of oxygen or other nutrients required for contraction, vascular smooth muscle will relax causing vasodilation of metarterioles and precapillary sphincters
- increase tissue metabolism or decreased oxygen in blood - decreased oxygen or nutrients in vessels - reduction in vascular smooth muscle contraction ( vasodilation) - opening of metarterioles and precapillary sphincters - increase in blood flow
- increase tissue metabolism or decreased oxygen in blood - decreased oxygen or nutrients in vessels - reduction in vascular smooth muscle contraction ( vasodilation) - opening of metarterioles and precapillary sphincters - increase in blood flow
38
New cards
Myogenic theory
- an increase in intraluminal pressure stimulates vasoconstriction of small arteries and arterioles
- caused by smooth muscle cells
- maintains constant blood flow
- caused by smooth muscle cells
- maintains constant blood flow
39
New cards
Where is pathological alterations of myogenic tone seen?
- in stroke, hypertension, and diabetes
40
New cards
Mechanism of myogenic response
- increased intraluminal pressure= activates stretch sensors =smooth muscle cell depolarization= calcium channel activation = calcium ion influx and rise in calcium ion concentration =vasoconstriction = reduction of blood flow
- decreased intraluminal pressure = stretch sensors are activated = smooth muscle cell depolarization = calcium ion channel activation = influx of calcium ions and rise in calcium ion concentration= vasodilation = increase in blood flow
- decreased intraluminal pressure = stretch sensors are activated = smooth muscle cell depolarization = calcium ion channel activation = influx of calcium ions and rise in calcium ion concentration= vasodilation = increase in blood flow
41
New cards
Which things mediate endothelium dependent vasodilation?
- NO
- PGI2
- SKCa and IKCaK+ channel
- PGI2
- SKCa and IKCaK+ channel
42
New cards
Which things mediate endothelial dependent vasoconstriction?
- Superoxide
- ET1
- TxA2
- ET1
- TxA2
43
New cards
What is angiogenesis?
- formation of new blood vessels
44
New cards
What are collateral vessels?
- formation of alternate flow pathways
45
New cards
What can lead to hypertension?
- sympathetic overdrive and stress
46
New cards
What is the sympathetic innervation of the systemic circulation?
- sympathetic nerve fibers innervate all vessel except capillaries and precapillary sphincters and some metarterioles
- innervation of small arteries and arterioles allow sympathetic nerve to increase vascular resistance
- large veins and heart
- innervation of small arteries and arterioles allow sympathetic nerve to increase vascular resistance
- large veins and heart
47
New cards
Vasoconstrictor area
- neurons from this area excite preganglionic vasoconstrictor neurons in the SNA; CNS ischemic response
48
New cards
Vasodilator area
- neurons project upward and inhibit the vasoconstrictor area
49
New cards
Sensory area ( lower pons and medulla)
- receive signals from the circulatory system and output signals control vasodilator and vasoconstrictor areas
50
New cards
Heart control area of vasomotor center
- sympathetic control through the vasoconstrictor area; parasympathetic control through the cardioinhibitory area
51
New cards
True/False: Higher nervous system control can excite or inhibit the vasomotor center
- True
52
New cards
What is the baroreceptor reflex?
- senses changes in the blood pressure and sends signal to CNS which initiates appropriate response to maintain nearly constant blood pressure
- maintains MAP : 85-11 mmHg
-
- maintains MAP : 85-11 mmHg
-
53
New cards
True/False: baroreceptors stay the same during hypertension
- false: they reset in hypertension
54
New cards
chemoreceptor reflexes
- sense lack of oxygen , carbon dioxide excess or hydrogen ion excess and stimulates the vasomotor center
55
New cards
What pressure are chemoreceptors stimulated?
- at 80 mmHg
56
New cards
True/False: There is an enhanced chemoreceptor drive in hypertension
- True
57
New cards
When is the CNS ischemic response activated?
- it is activated when pressure fall below 60 mmHg with greatest activation at 15- 20 mmHg
58
New cards
How does NO relaxes the blood vessel?
-NO -> GC -> cGMP -> PKG -> MLCP activation -> relaxation
59
New cards
What contributes to hypertension?
- vasoconstriction
60
New cards
What is one of the most powerful activators of the sympathetic vasoconstrictor systems?
- CNS ischemic response
61
New cards
What is CNS ischemic response?
- when their is a reduced cerebral blood flow - excess CO2 buildup which stimulates the vasomotor center - which increases arterial pressure
62
New cards
Endothelial 1 pathway
-ET-1/TXA2/PGH2 -> Gq11 -> PLC-> IP3 -> Ca2+ rise -> Ca2+-CaM -> MLCK -> contraction
63
New cards
Which neurotransmitters are vasoconstrictors?
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine
-Vasopressin
-Endothelin
- Epinephrine
-Vasopressin
-Endothelin
64
New cards
What are hormones/neurotransmitters considered vasodilators?
- prostaglandins
- nitric oxide
- nitric oxide
65
New cards
Which alpha receptor inhibits renin release in the kidney?
- alpha 2
66
New cards
Which alpha receptor inhibits NE release in the brain?
- alpha 2
67
New cards
Which beta receptor causes cardiac stimulation by increasing heart rate, force of contraction and conduction velocity in the heart?
- beta 1
68
New cards
Which beta receptors cause renin release in the kidneys?
- beta 1
69
New cards
Which beta receptor causes smooth muscle relaxation causing vasodilation and bronchodilation in the blood vessels?
- beta 2
70
New cards
Which alpha receptors causes vasoconstriction of the blood vessels and increase resistance?
- alpha 1
71
New cards
True/False: The beta 1 receptors cause increase in stroke volume and heart rate during cardiac stimulation
- True
72
New cards
How does the alpha 1 receptors cause vasoconstriction in the blood vessels of the smooth muscles?
- alpha 1 is coupled to the Gq protein which binds to PLC - PLC increases IP3 which stimulates and increase Ca2+ which causes vasoconstriction
73
New cards
How does the beta 2 receptors?
- Beta 2 is coupled to Gs which stimulates release of cAMP which stimulates PKA and PKA inhibits myosin light chain kinase - which inhibits phosphates from binding to myosin which causes relaxation ( vasodilation)
74
New cards
How does the alpha 2 receptor cause vasodilation in the brain?
- NE is inhibited which decreases sympathetic activity which causes vasodilation
75
New cards
True/False: An increase in SA and AV node firing cause an increase in chronotropic effect ( increase heart rate)
- True
76
New cards
What happens to arterial pressure when blood volume increases?
- arterial pressure increases
77
New cards
What happens to the kidney when their is an increase in arterial pressure?
- causes the kidney to lose Na+ and water which returns extracellular fluid volume to normal
78
New cards
pressure diuresis
- increased pressure causes excretion of water
79
New cards
Pressure naturiuresis
- increased pressure causes excretion of salt
80
New cards
True/False: In the kidneys an increased blood volume = increase blood pressure = increased sodium excretion
- True
81
New cards
What does the Renin- Angiotensin- Aldosterone System ( RAAS) do to the kidney?
- increase water and sodium retention and increase vasoconstriction
82
New cards
What binds to AT1 ( Gq) receptors on the vascular smooth muscles and causes vasoconstriction?
- Ang II