mol bio exam 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
initiation of DNA transcription
TFIID binds TATA with help of TBP
TFIIB binds to position RNA Pol II
RNA Pol II, TFIIH, and TFIIE bind
TFIIH unwinds DNA and phosphorylates Ser 5
everything disassociates and elongation begins
pausing transcription
after 30-50 BP synth, Ser2 phosph
elongation transcription
bc Ser 2 phosph, RNA pol begins work
termination
cstf and cspf move fromm RNA pol —> RNA
cleave and terminate seq via PAP and poly A BP
exonuc runs bc 5’ not capped and dislodges RNA Pol II
parts of a transcription factor
proteins that directly bind to a specific DNA seq through DNA binding domain
activation domain regulates level of transcription by recruiting RNA Pol II or transcriptional cofactors
cobinding
intermediary facilitates binding of TFs
co-occupancy
rapid alternating
heterodimers
bind together
cooperative binding
binding of one facilitates binding of the other
chromatin mediated tf interactions
pioneer TFs remove/ displace nucleosomes
nucleosomes block TF binding
TF binding mediates DNA bending
enhanceosome model
everything matters: loc,spacing
billboard model
flexible
DNA methyltransferase
methylates cytosine to 5-methyl cytosine
often at CpG sites
Dnmt 3a/3b vs Dnmt 1
denovo vs maintenance methylation
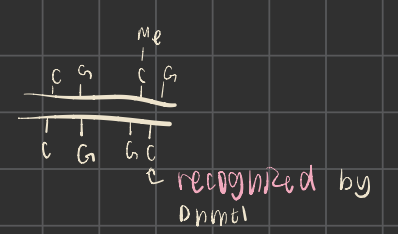
demethylation
no direct mechanism
TET oxidizes 5mC —> adds OH to Me to prevent maintenance methylation
thymine DNA glycosylase excises the incorrect base via base excision repair
methylation
highly methylated at repetitive elements, intergenic DNA
prevent TF binding
attract MeCPs —> trigger heterochromatin
recruit transcriptional repressors
chromatin spreading
writer makes mark
reader reads it and binds to nucleosome —> recruits writer
how is chr spreading prevented
reverted by eraser
boundary elements prevent spreading: nuclear pores, insulators, enzyme diffusion
chromatin remodeling
nucleosome sliding allows access of transcription machinery to DNA
chromatin remodeling complex will slide histones
histone chaperone removes histones
histone replacement will replace w easier to move histones
histone modifying enzymes can add acetylation/ methylate differently to open up heterochr
insulators
insulator proteins bound to insulator DNA regions prevent heterochr spread and bring enh close to promoter via DNA looping
CTCF = insulator in humans
can form homodimers and multidimers
peaks will be inside facultative chr. peaks, showing that spreading stops
can isolate active regions from repressed
variegation
position of gene relative to heterochr alters expression
when heterochr shifts closer to gene, it increases variegation
PCR experiment
amplify DNA and visualize it
must use a specific primer (forward and reverse)
mutant —> no product or change in size
doesn’t evaluate expression well
illumina
goal: amplifies DNA + seq it
makes copies in cluster
seq w/ specific or non-spec primers
ChIP-seq
goal: identify DNA bound by DNA binding molecule (ChIP-qPCR is used for TF binding to specific DNA seq and ChIP seq is for TF binding to all bound DNA seq)
interpretation: intersection between pos and neg site = TF binding site
procedure
cross link bound proteins to DNA
isolate chromatin and shear DNA
precipitate chr. w protein spec antibody
reverse cross link and digest protein
ligate p1 and p2 adaptors to construct frag library
illumina seq
RNA Seq
goal: method to quantify RNA
interpretation: compare infected reads to control reads
PCA: similarities cluster and differences are far apart
volcano plot shows up and downregulation
process:
make cDNAs from mRNA w reverse transcriptase
shatter into fragments
map reads
bisulfite seq
goal: evaluate methylation
interpretation: methylated C remain as C
process:
treatment of DNA converts unmethylated C—> U
PCR/sanger or illumina seq
uracil will dilute out to thymine over time w pcr