Section 3: Glycogen Synthesis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What does UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase activate
It activates glucosyl units
takes glucose and activates it
What does glycogen synthase extend
Extends glycogen chains
we need to have an existing glycogen primer to synthesize
What does glycogen branching enzyme transfer
Transfers seven-residue glycogen segments
Glycogen Synthesis & Degradation image
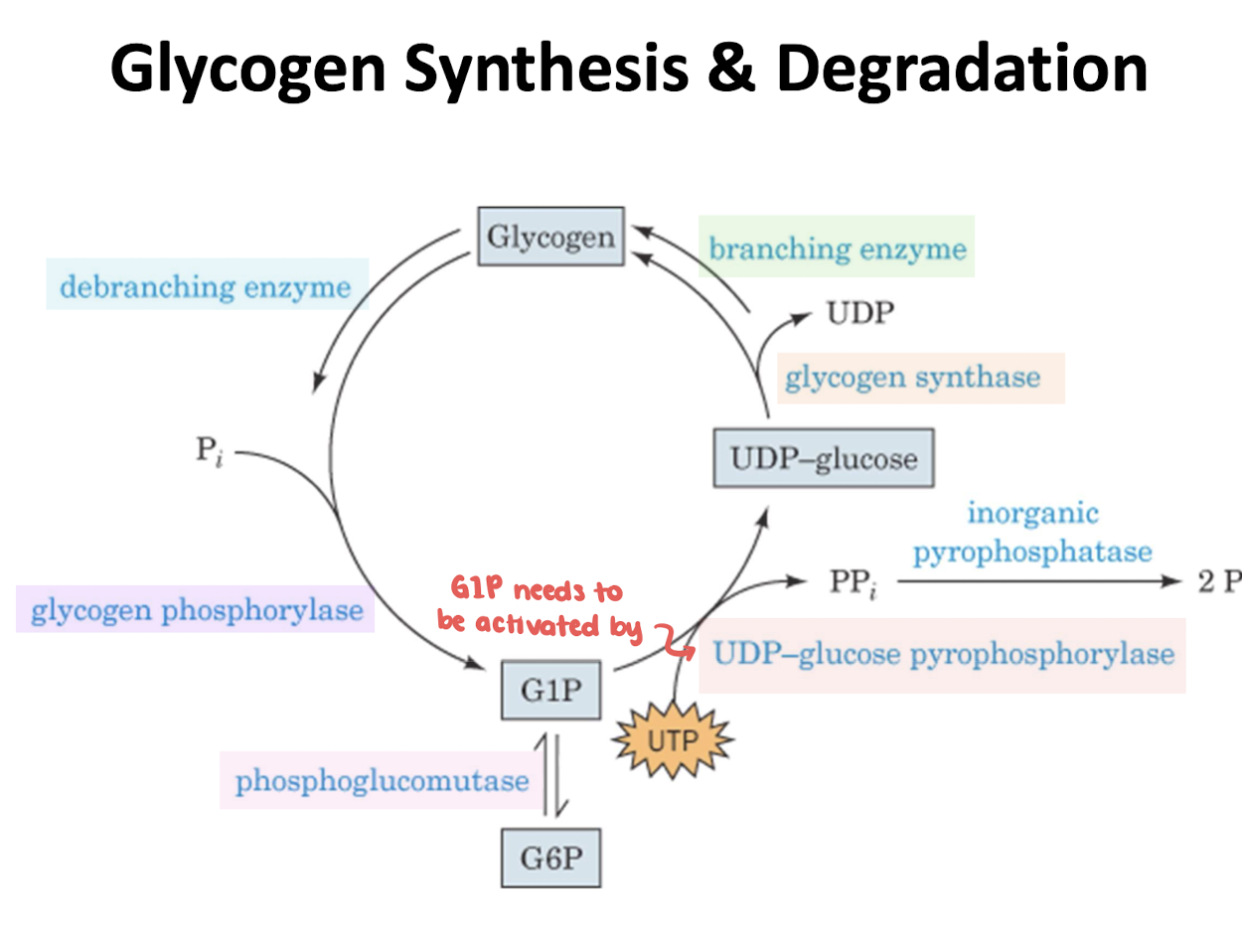
Is glycogen synthesis from G1P thermodynamically favorable or nonfavorable
Thermodynamically unfavorable
What are three enzymes that participate in glycogen synthesis
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
glycogen synthase
glycogen branching enzyme
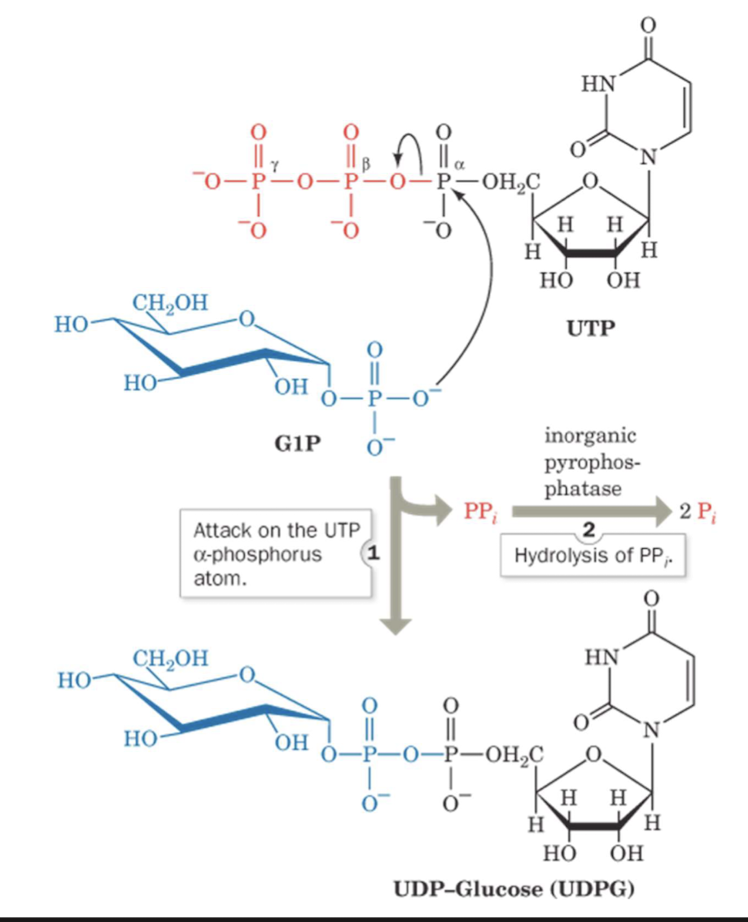
Describe UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase function
It activates glucosyl units
Uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG)
UDPG is “activated” compound
it can donate a glucosyl unit to the growing glycogen chain
Formation of UDPG itself has ‘∆G˚’ = 0
What makes UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase exergonic
Subsequent exergonic hydrolysis of PPi by inorganic pyrophosphatase makes the overall reaction exergonic
What is the overall equation for UDP-glucose pryophosphorylase
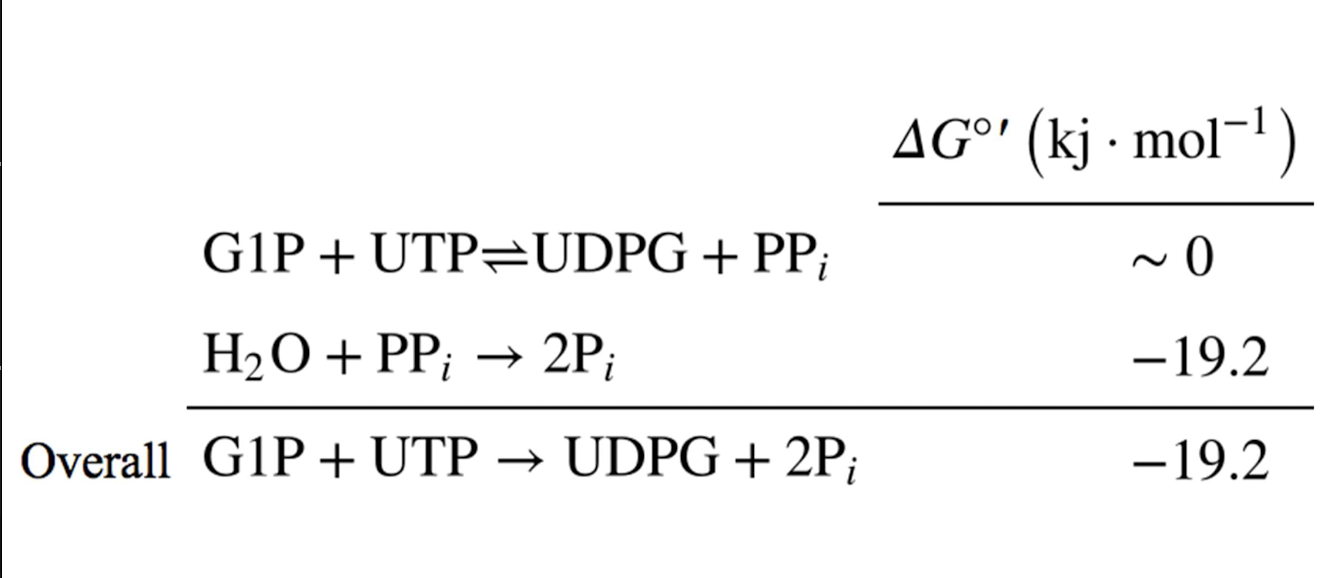
UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase reaction
Describe glycogen synthase function
Extends glycogen chains
It transfers glucosyl unit of UDPG to C4-OH group on one of glycogen’s non-reducing ends to form an α(1→4) glycosidic bond
The ‘∆G˚’ for the glycogen synthase reaction is -13.4 kJ • mol-1
Glycogen synthase reaction
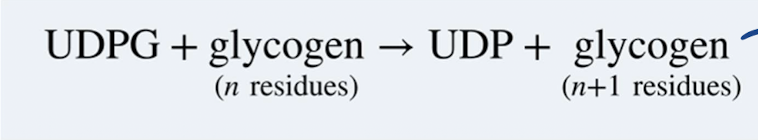
Is glycogen synthase spontaneous or nonspontanoues
Spontaneoues
Describe how glycogen synthesis has an energetic price
We have to put in energy that comes from UTP
UTP is the energy we require to activate our glucose unit before we can incorporate it into our glycogen
1 UTP is cleaved to UDP for each glucose residue incorporated into glycogen
UTP is replenished using ATP as substrate through a phosphoryl-transfer reaction mediated by nucleoside diphosphate kinase
UTP consumption is energetically equivalent to ATP consumption
Can glycogen synthase simply link 2 glycose residues together ?
NO! it can ONLY extend already existing α(1→4)-linked glucan chain
What is the 1st step in glycogen synthesis
Glycogenin acts as glycosyltransferase
— it attaches glucose residue donated by UDPG to OH group of its Tyr 194
What is the importance of glycogenin
Glycogenin is responsible for building up initial glycogen
Glycogenin extends the glucose chain by up to 7 additional UDPG-donated glucose residues
Formation a glycogen “primer”
W/ a primer, only then do we see the activity of our glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase commence is extending the primer
Each glycogen molecule associated w/ …
1 molecule glycogenin
Responsible for initial glycogen primer composed up to 6 glucose subunits
1 molecule glycogen synthase
adds on to the primer
Describe the function of glycogen branching enzyme
Transfers 7-residue glycogen segments
glycogen synthase generates only α-amylose
This would only allow to release one glucose molecule at a time
Branching by amylo-(1,4→1,6)-transglycosylase (branching enzyme) distinct from glycogen debranching enzyme
A branch is created byy transferring a 7-residue segment from chain end to C6-OH grpup of a glucose residue on the same or another glycogen chain
Each transferred segment must come from a chain of at least 11 residues
How many residues are between 2 branches
4 resiudes
Branching pattern of glycogen has been optimized by evolution for the …
… efficient storage and mobilization of glucose