Mdoule 2: CPI Overview
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Chemical Process Industry
chemical reactions; extraction, separation, purification; preparation of specifically formulated mixtures
Heavy Chemicals
Those dealt in large quantity normally crude or less purified chemicals
Fine Chemicals
Those that are completely purified substances and produced in limited quantity
Organic Compound
includes nucleic acids, fats, sugars, proteins, enzymes, and hydrocarbon fuels (w/ C-H bo
Inorganic Compound
includes salts, metals, and other elemental compounds (w/o C-H bonding)
Natural Compound
Available in nature
Synthetic Products
Man-made compounds
Catalyst
increases or decreases the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the process. If consumed then it should regenerate at the end of the process.
Bulk Drug
the active substance used in a drug formulation. It becomes an active ingredient of the finished dosage form of the drug
Resin
natural or synthetic compound which begins in a highly viscous state and hardness with treatment
Pigments
defined as coloring agents that are practically insoluble in the application medium
Dyes
defined as coloring agents that are practically soluble in the application medium
Solvent
A liquid in which substances (or solutes) are dissolved to form a solution
Miscellaneous
All other compounds which do not cover in above class
Samahan sa Pilipinas ng mga Industriyang Kimika
SPIK
Chemical Industries Association of the Philippines
English of SPIK
Philippine Chemical Industry
the branch of the manufacturing sector that converts various materials into useful and profitable products via chemical reactions and process
Basic Chemicals, Chemical Products, Rubber Products, Plastic Products
Sectors of Chemical Industries in the Philippines (4)
Intermediates; Base Materials
Chemical process industries procures raw materials from natural environments to convert them into -, which subsequently serve as - - to every other kind of industry
Lithosphere
coal, natural gas, and petroleum
Earth’s Crust (Lithosphere)
mineral ores, carbon, hydrocarbons
Ocean Water (Hydrosphere)
1.5 x 10^21 L contains about 3.5 percent by mass dissolved material
Seawater (Hydrosphere)
Good source of sodium chloride, magnesium, and bromine
Air (Atmosphere)
N2, O2, Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe
Earth’s Atmosphere
5 x 10^15 tons; unlimited
Vegetation and Animals (Biosphere)
agro-based industries
Natural Products (Biosphere)
oils, fats, waxes, resins, sugar, natural fibers, and leathers
Chemical Process
consists of a combination of chemical reactions such as calcination, ion exchange, electrolysis, oxidation, hydration, and operations based on physical phenomena such as evaporation, crystallization, distillation, and extraction
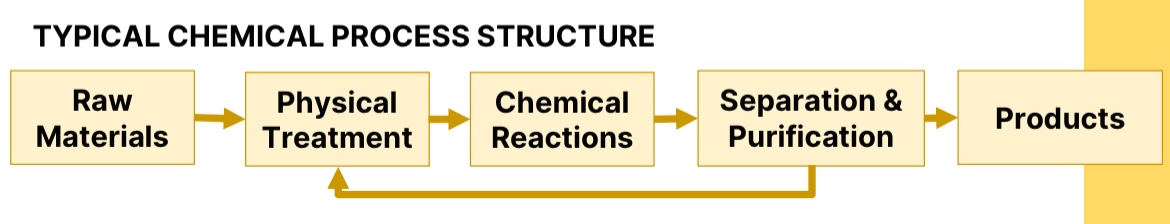
Typical Chemical Process Structure
Chemical Reaction
a process that always results in the inter conversion of chemical substances
Process Engineering
often the synonym for chemical engineering and focuses on the design, operation, and maintenance of chemical and material manufacturing processes
Product Engineering
process of designing and developing a device, assembly, or system such that it can be produced as an item for sale through some production manufacturing process
Batch Processing
This involves the processing of bulk material in batches through each step of the desired process. Used for small-scale production
Continuous Processing
This processing involves moving one work unit at a time between each step of the process with no breaks in time; volume remains constant
Batch Process
Medicine
Continuous Process
Ammonia
Unit Process
commercialization of a chemical reaction under such conditions as to be economically profitable; chemical transformations or conversions
Unit Operations
Based on fundamental laws and physiochemical principles. Design, material of construction and operation; and calculation of various physical parameters (mass flow, heat flow, mass balance, power and force, etc.); Physical Change

Unit Processes
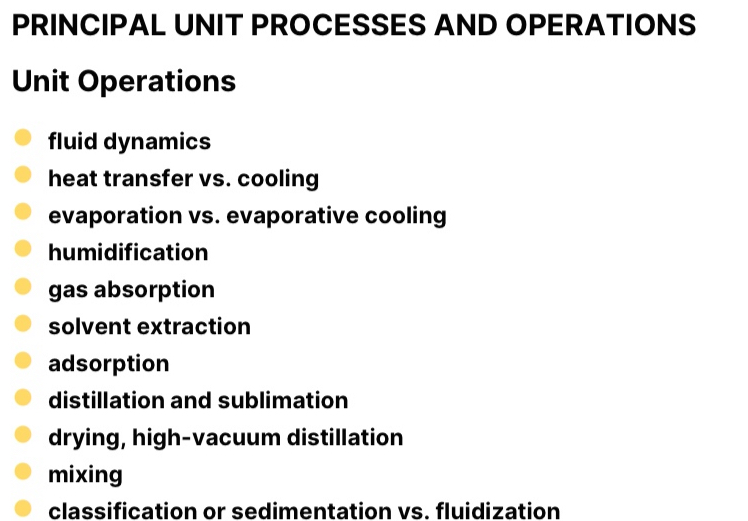
Unit Operations
Block Diagram
Units as Blocks
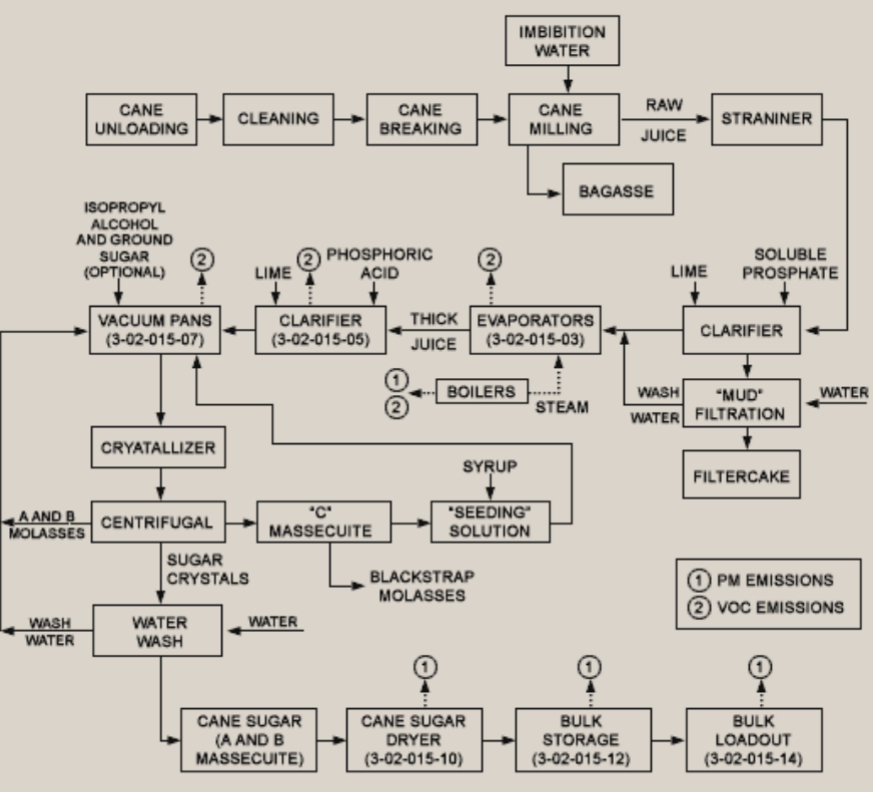
Process Flow Diagram
Detailed Schematic Units
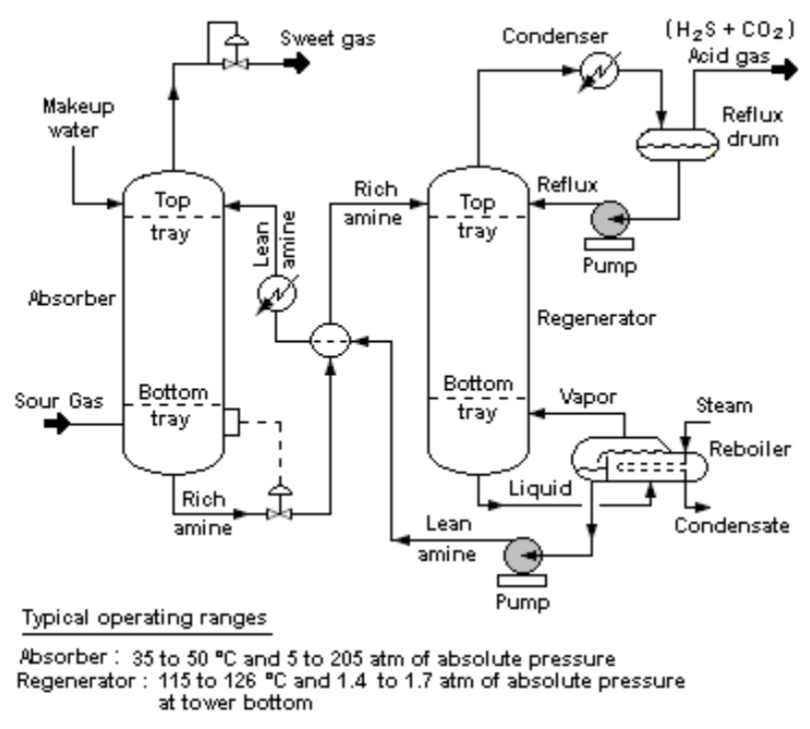
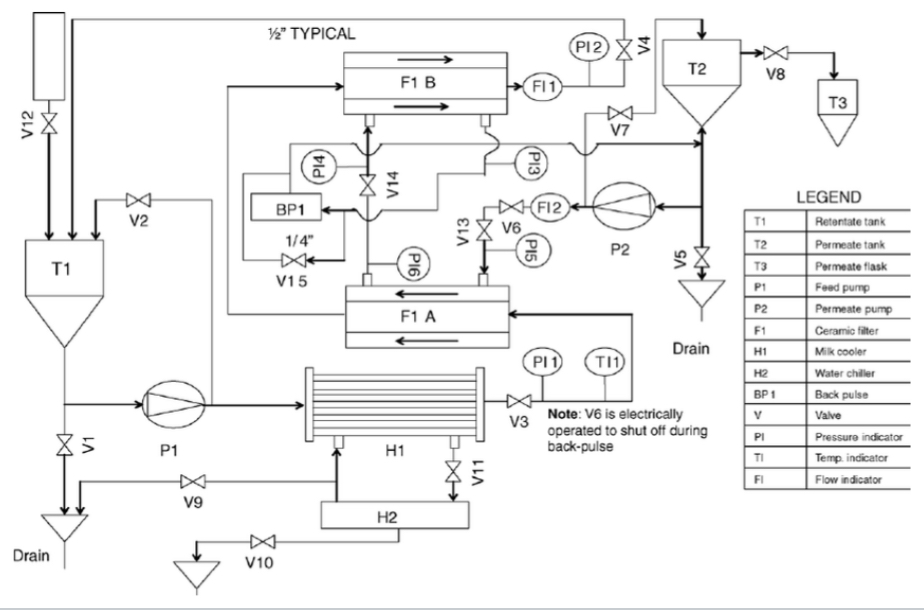
Process & Instrumentation Diagram
Block Diagram
Schematic Flow Diagram; shows what is to be done rather than how it is to be done
Process Flow Diagram
System Flow Diagram (SFD) or Flowsheet; describes the general flow of plant processes and equipment;
Process & Instrumentation Diagram
Process and Instrumentation Diagram; Graphical representation of equipment, piping, and instrumentation; w/ minor details such as piping details and designations; used by technicians
LEARN FD SY
LEARN FD SY
parameter being controlled/measured
P&ID: first letter
type of control device being used
P&ID: second letter
loop it represents
the number (logical numerator)