Chapters 3,4, and 5
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Introduced Species
species brought unnaturally into an environment by humans and can destabilize ecosystems
ex rats brought by ship, cats brought to catch rates, and then cats destroyed habitat and killed eggs and young of native birds
Avian Malaria
killed native birds at lower elevations
global warming has allowed it to thrive at higher elevations and decimate more of the bird population
Natural Selection
traits that enhance survival and reproduction will dominate
Darwin + Wallace discover natural selection as the mechanism of evolution
Adaptations are characteristics that lead to beeter reporductive success over generations
often caused by mutations which are accidental changes in DNA
Sexual Reproduction leads to variation
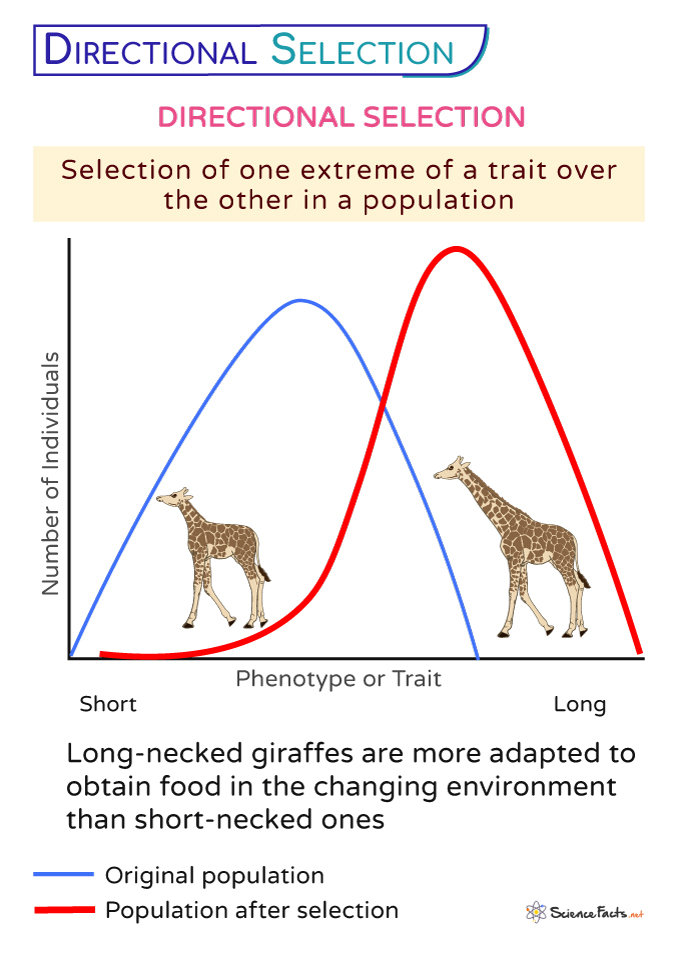
Directional Selection
drives a feature in one direction
Convergent vs. Divergent Evolution
Convergent: unrelated species may acquire similar traits due to pressures of natural selection in similar environments
Divergent: closely related species diverge in appearance due to pressures of natural selection, resulting in a variety of features froma. single ancestor
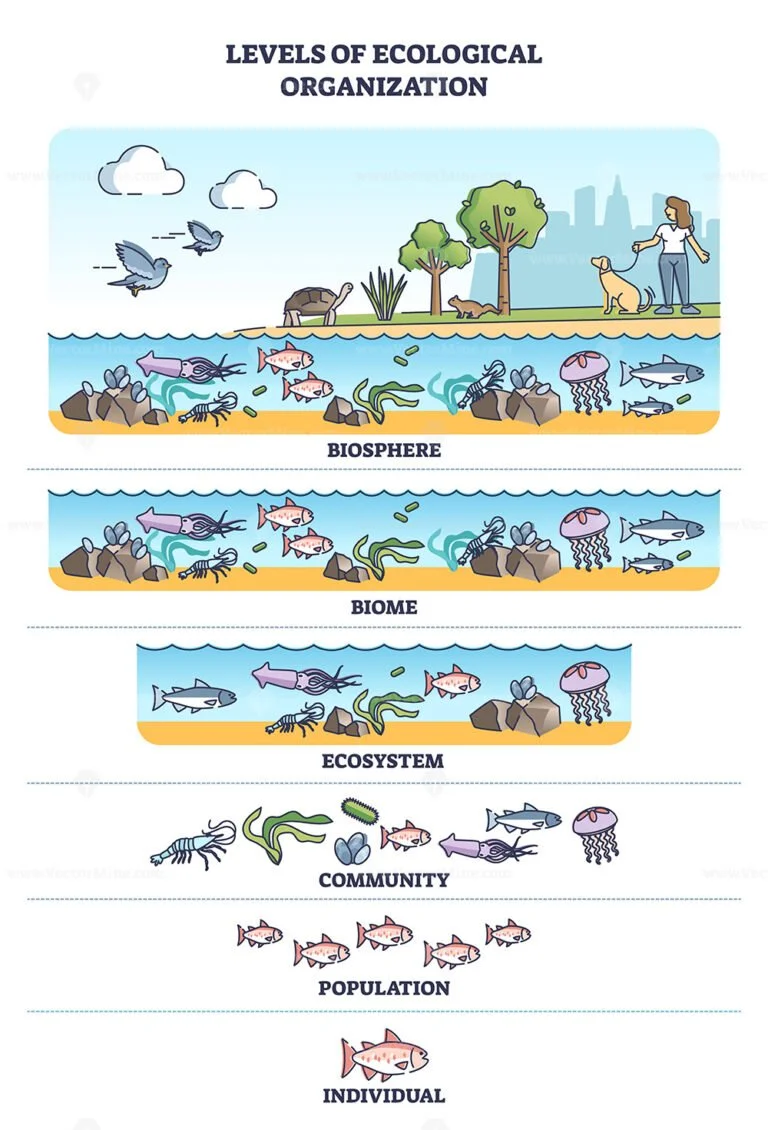
Levels of organization
Speciation
process by which new species are generated
Allopatric: species in different population are physically separated and have different mutations with no gene flow, overtime they are so different that they are unable to breed
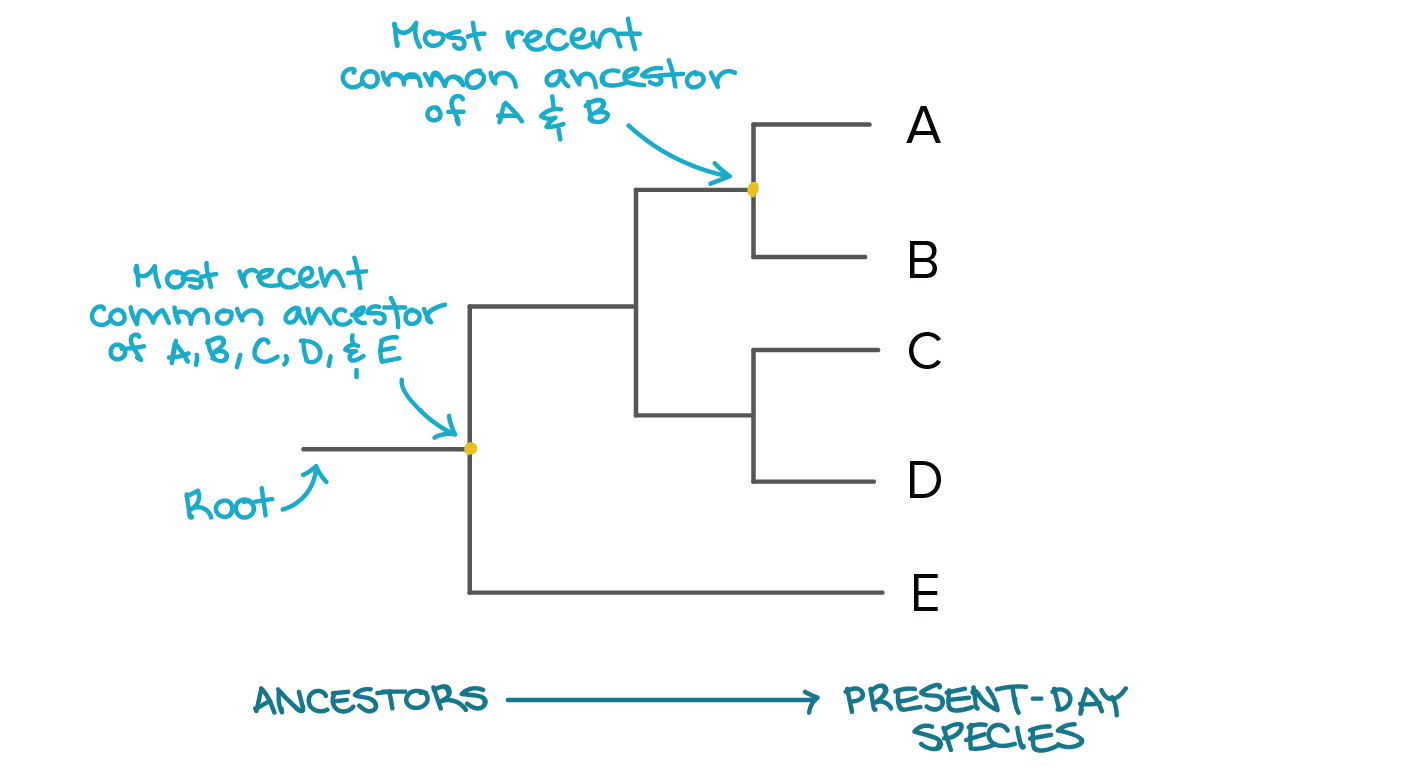
Phylogenetic Trees
diagrams that show relationships in divergence
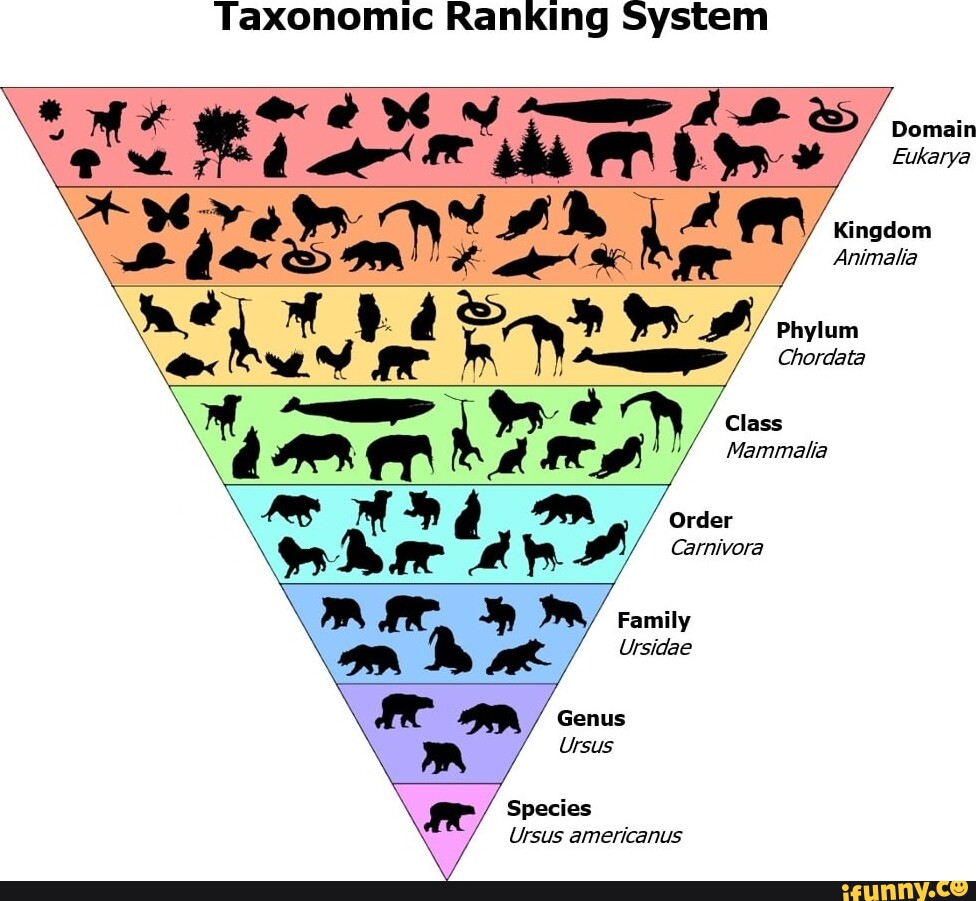
Taxonomic Classification
Extinction
the disappearance of a species from earth permanently
# of species in existence = speciation - extinction
factors that cause extinction:
sever climate/topographic changes
invasive species
Most Vulnerable
bottleneck: small population
Endemic species: only occur in one region
Mass Extinction
a lot of species die out compared to the background extinction rate which is a constant rate of extinction as part of evolution
Cretaceous-Tertiary (KT) event: asteroid impact that killed dinosaurs
End-Permian Extinction
Humans are causing the 6th mass extinction due to resource depletion, growing development, and introduction of non-native species
Niches
organisms thrive in specific habitats and roles that match their trates (habitat selection)
fill a specific niche in their community
narrow niche = specialist
broad niche = generalist
Fundamental Niche: full niche of species
Realized Niche: portion of niche that is actually fulfilled
Characteristics that help predict population dynamics
Population Size
Population Density
Population Distribution
Random
Uniform
Clumped
Sex Ratio
Age Structure/Distribution
Birth and Death Rates
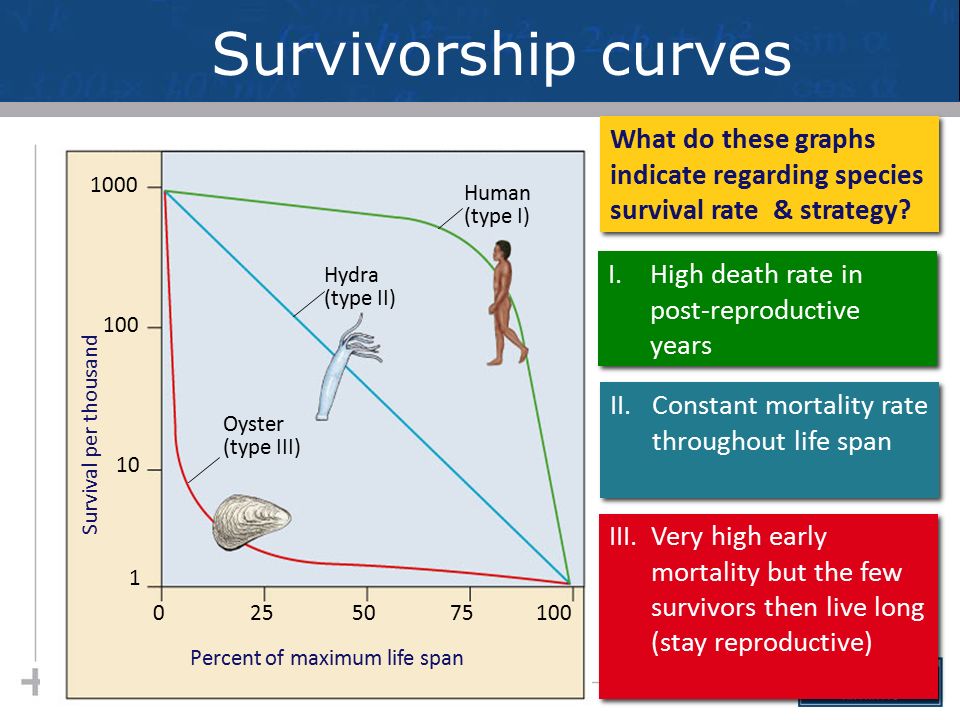
Survivorship Curves
Type I: higher death at older age (humans)
Type II: equal rates of death at all ages (birds)
Type III: highest death rate at young ages (toads)
Factors in growth
growth is exponential until a constraint is meant: typically only when conditions are ideal or a species is introduced to a new environment with abundant resources
carrying capacity (k value)
logistic growth curve
overshoot: when pop goes over carrying capacity
Biotic Potential
K-selected: low biotic potential, longer gestational period, higher survival rates, stabilize close to carrying capacity, larger animals
R-Selected: high biotic potential, short gestational period, population size fluctuates/often is below carrying capacity, low parental care, smaller
Competition
when organisms seek the same shared resource
intraspecific: between members of the same species
interspecific: between members of different species
Competitive Exclusion Principle
two species w/ exactly the same requirements cannot coexist in exactly the same habitat
either one species excludes the other or they find species coexistence where neither fully excludes the other
species change their behavior to minimize competition
causes resource partisioning and character displacement
Exploitive Interactions
Predation
drives cyclical population dynamics
Parasitism
insects that parasitize other insects = parasitoids
parasites that caust disease = pathogen
Herbivory
Mutualism
2+ species benefit from interacting
physically close association = symbiosis (i.e.e algae and fungi => Lichen)
Pollination
Producers/Autotrophs
first trophic level that produces its own energy
photo/chemosynthesis
Consumers
Eat other organisms
Primary Consumer: eats producers and are usually herbivores
Secondary Consumers: eat primary consumer
Tertiary Consumers: eat secondary consumers and are usually carnivores
Detritivores/Decomposers
consume non-living organic matter
Detritivores: scavenge the waste products + dead bodies of other in the community (i.e. soil insects)
Decomposers: break down litter + non-living matter into smaller pieces that can be taken up by plants
enhance soil nutrients
Keystone Species
species that have wide reaching impacts far out of proportion to its abundance - often high on the food chain
trophic cascade = effect of one species on an ecosystem as a whole
can also be caused by ecosystem engineers
Disturbance
an event that affects environmental conditions
commmunities can
resist change = resistance
change in response but return to original state after = resilience
If disturbance eliminates all or most of a community, the area will undergo succession
Primary Succession
occurs when there is practically no vegetation or soil life left
begins w/ pioneer species that is well adapted for colonization
lichens colonize bare rock and secrete acid that breaks down the rock surface eventually forming soil
plants and insects come and provide more nutrient
larger plants and animals establish themselves
Climax community stay until another disturbance
Secondary Succession
when disturbance does not destroy all living things in the soil, what is left of previous community helps shape the process
Phase (Regime) Shift
overall character of the community changes
human activity can cause this: novel/non-analog communities
Feedback Loops
system output serves as input
negative: output from system moving in one direction causes the system to move the other direction
positive: increased output = increased input = even more increased output etc.
moves toward extreme
i.e. glaciers melting not being able to reflect sunlight so they get hotter and melt more
Emergent Properties
characteristics not evident in the components alone
System interactions
Main systems: lithosphere (rock and sediment), atmosphere (air), hydrosphere (water), and Biosphere (organisms+abiotic parts of environment)
Energy moves in one direction
Matter is recycled
ecotones = transitional zones between two ecosystems
Primary Production
autotrophs convert solar energy to chemical energy
total amount of energy produced = gross primary production
net primary production = gross production - respiration (energy used for cellular respiration by the plant)
rate at which energy is converted to biomass = productivity / net primary productivity
eaten by heterotrophs, some is used to generate biomass which becomes secondary production
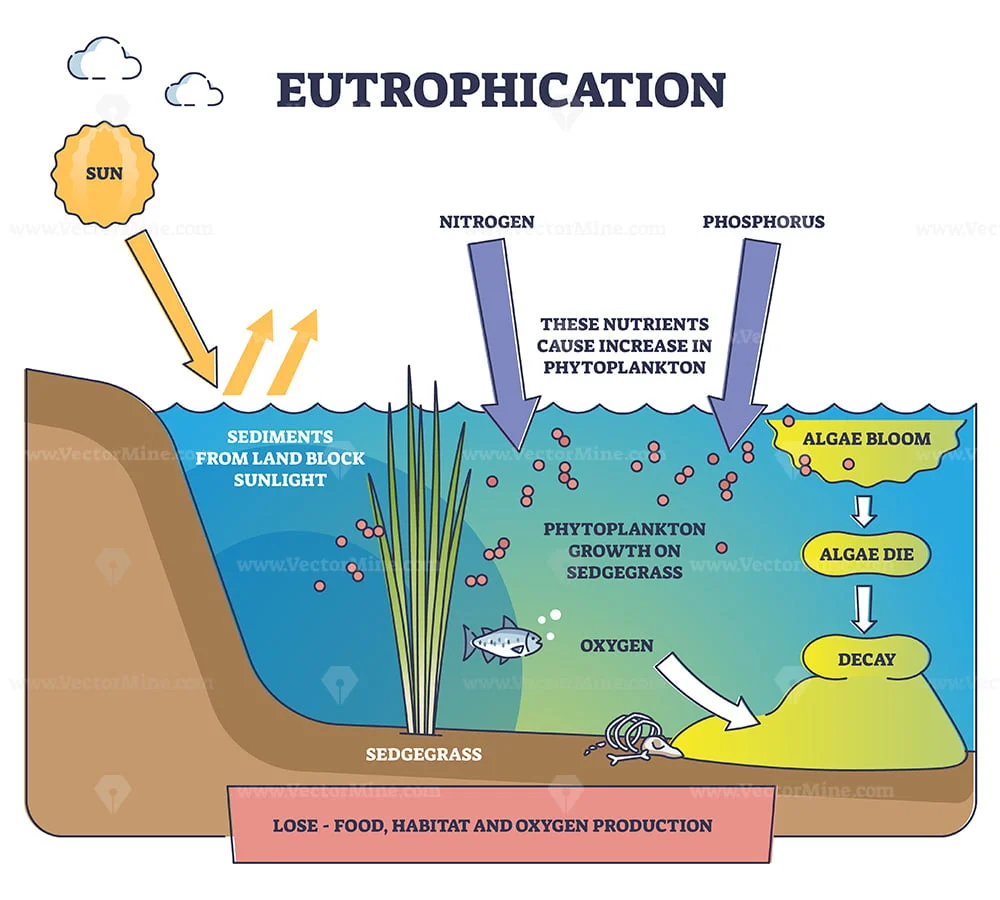
Eutrophication
super bloom of algae due to nitrogen and phosphorus increase from runoff causes decomposers to over-consume oxygen and creates a dead zone
Nutrients
macronutrients: required in large amounts
micronutrients: needed in smaller amounts
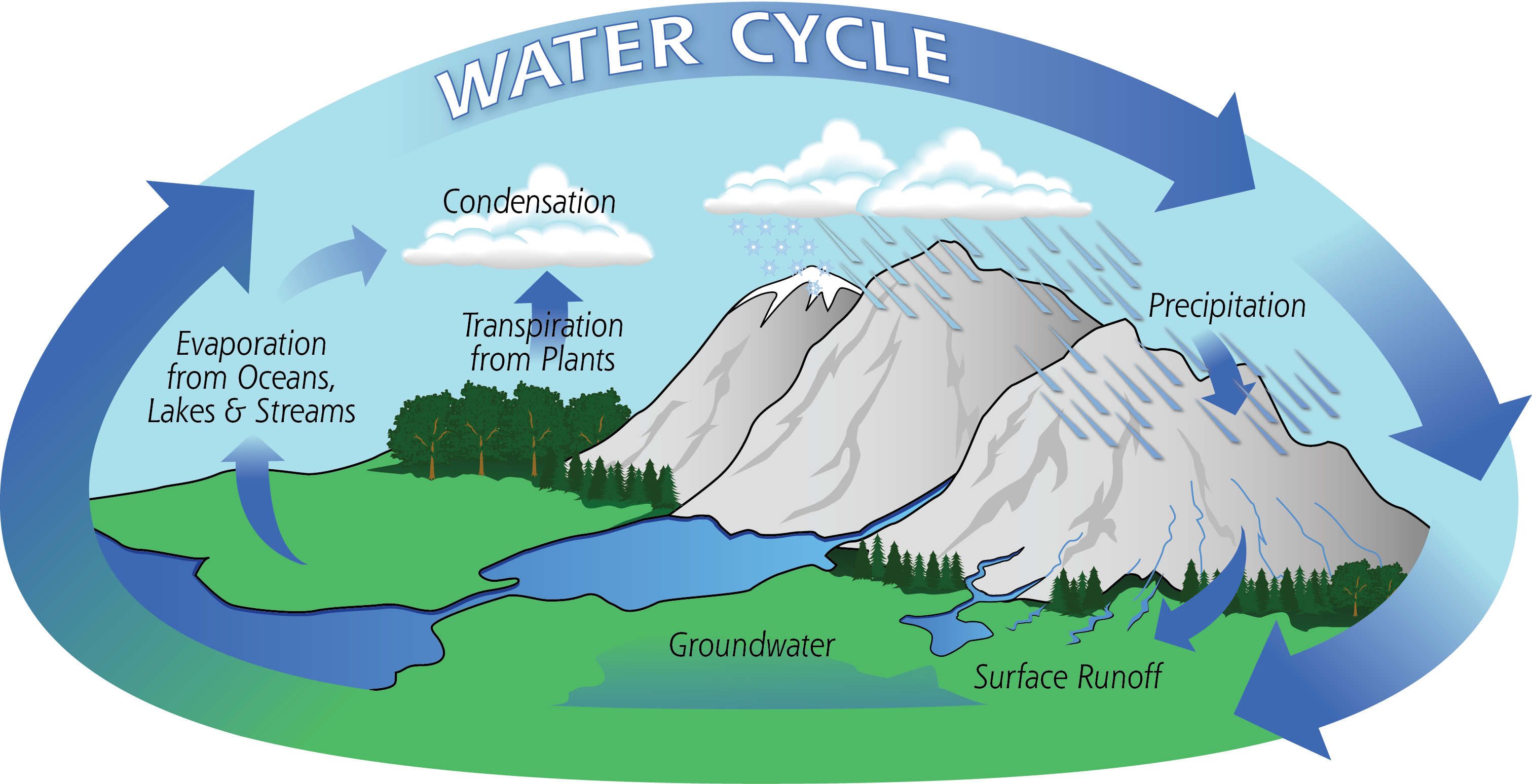
Hydrologic Cycle
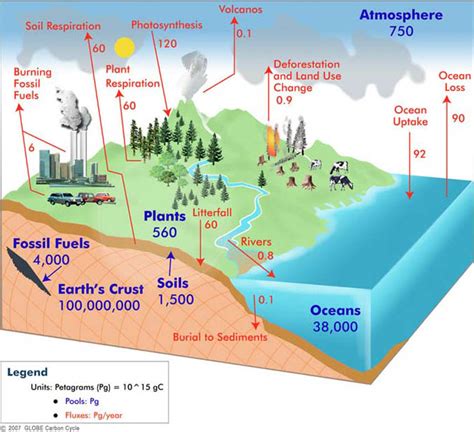
Carbon Cycle
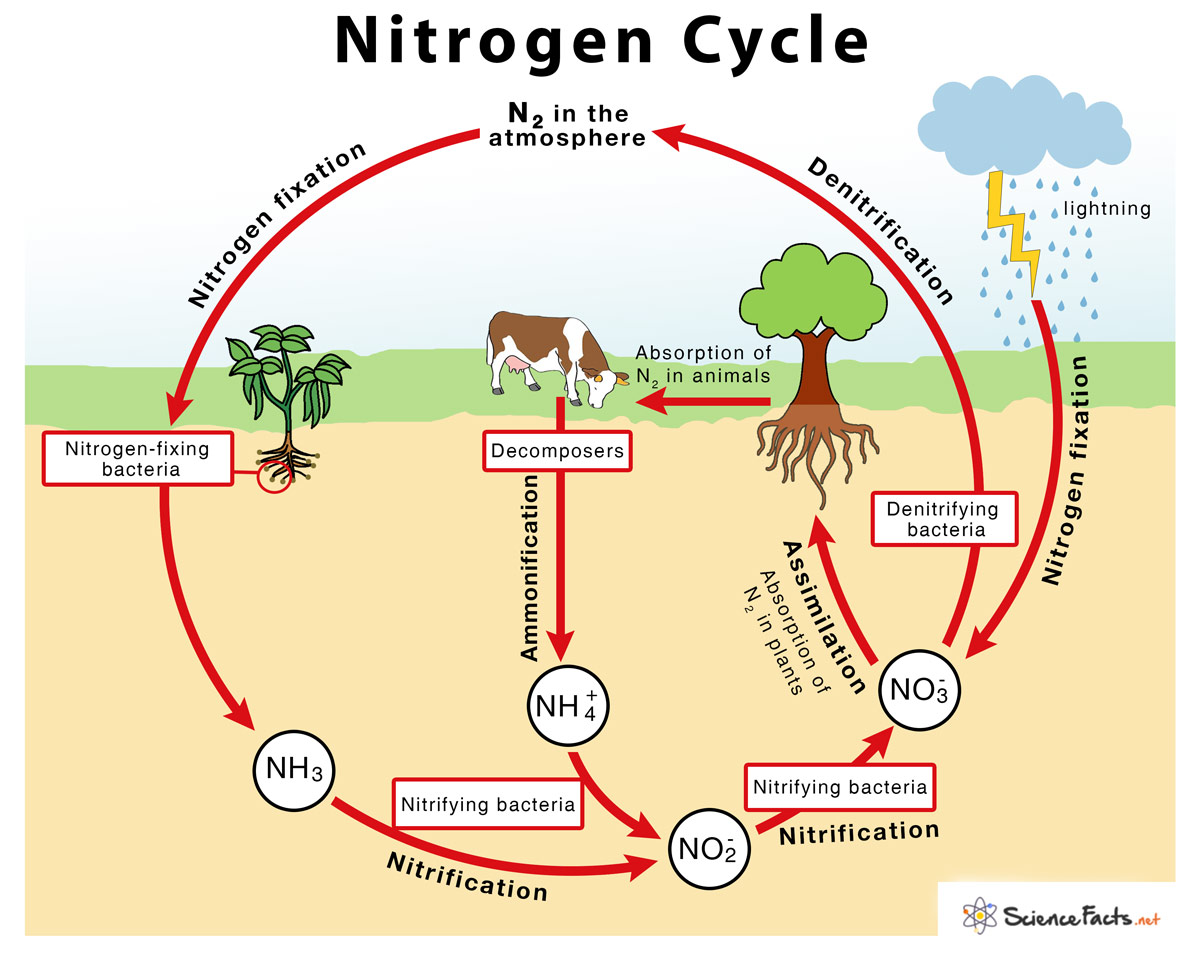
Nitrogen Cycle