Cellular Respirations/ATP/Anaerobic Respirations Study Guide
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
glycolysis
2 ATP molecules are used at the start of glycolysis to get the process started. High-energy electrons are passed to the electron carrier NAD+ forming two molecules of NADH. 4 ATP are synthesized during glycolysis for a net gain of 2 ATP.
Krebs Cycle (citric acid)
Pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis enters mitochondria. Pyruvic acid molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and acetyl-CoA molecules. Acetyl-CoA combines with a 4-carbon compound, producing a 6-carbon molecule—citric acid. Energy released by the breaking and rearranging of carbon bonds is captured in ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces four types of products:
•high-energy electron carriers (NADH and FADH2)
•carbon dioxide
•2 ATP molecules (per glucose molecule)
•the 4-carbon molecule needed to start the cycle again
Cellular Respirations Equation
Glucose + Oxygen —> Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (36-38)
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP)
Where does CO2 come from?
CO2 is produced during the Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
The electron carriers produced during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle bring high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor. The passing of electrons through the electron transport chain causes H+ ions to build up in th intermembrane space, making it positively charged relative to the matrix. The charge difference across the membrane forces H+ ions through channels in enzymes known as ATP synthases. As the ATP synthases spin, a phosphate group is added to ADP, generating ATP.
How much ATP does Cellular Respirations generate?
36 ATP
Fermentation
releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP without
oxygen. Cells convert NADH to the electron carrier NAD+. This allows glycolysis to produce a steady stream of ATP (anaerobic)
Lactic Acid Fermentation
lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid that occurs in most organisms, including humans, used to produce beverages such as buttermilk and foods such as cheese, yogurt, and pickles, causes burning in the muscles
Alcoholic Fermentation
produces ethyl alcohol, NAD+ and carbon dioxide occurs in yeast and a few other microorganisms, produces alcoholic beverages and causes bread dough to rise
What does our body use for short, quick bursts of energy?
the body uses ATP already in muscles as well as ATP made by lactic acid fermentation
What does our body use for exercise longer than 90 seconds?
cellular respiration is the only way to continue generating a supply of ATP.
Where does glycolysis occur?
in the cytoplasm
What is produced from glycolysis?
A NET gain of 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate molecules.
Where does the Krebs Cycle occur?
In the Mitochondria
What is produced from the Krebs Cycle?
CO2, 2 ATP, NADH and FADH2
Where is the electron transport chain?
In the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is produced from the electron transport chain?
H2O and 32 ATP
When does Lactic acid Fermentation occur?
It occurs during anaerobic respiration when oxygen is limited, such as during intense exercise. 2 ATP produced
Pyruvate + NADH -> Lactic acid + NAD+
When does alcoholic fermentation occur?
It occurs during anaerobic conditions, in yeast and some bacteria, producing ethanol (alcohol) and carbon dioxide along with 2 ATP.
Pyruvate + NADH → Alcohol + CO2 + NAD+
aerobic
needs oxygen
anaerobic
does not require oxygen
Fermentation is
anaerobic
Lactic acid example
yogurt
Alcoholic fermentation example
bread
What are 2 disadvantages to Fermantation?
It doesn't produce a lot of ATP and it produces a toxic byproduct.
Photosynthesis equation
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light Energy → Glucose + Oxygen.
What type of activities do muscles use Carbs for?
Energy during high-intensity exercise - sprinting
What type of activities do muscles use Fats for?
Energy during prolonged, low-intensity exercise - running a marathon
How long does it take for carbs to convert into usable energy?
Generally within 15-60 minutes after consumption, converts quickly
How long does it take for fats to convert into usable energy?
Generally takes several hours following consumption, as they convert more slowly than carbohydrates.
There is less energy contained in 1 gram
Carbohydrate
There is more energy contained in 1 gram
fats
Carbs produce less …
ATP because they use less oxygen compared to fats
Glycolysis provides the pyruvic acid molecules used in fermentation
True
Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue by providing the NAD+ needed to accept high-energy electrons
True
Fermentation is a anaerobic process
True
Fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm
true
Alcoholic fermentation gives off carbon Dioxide and is used in making bread
true
Most organisms perform fermentation using a chemical reactions that converts pyruvic acid to lactic acid
true
Fermentation function
Produce ATP without oxygen
Cellular respiration
Produce ATP with oxygen
What causes humans to become lactic acid fermenters?
due to anaerobic conditions during intense exercise, leading to insufficient oxygen for aerobic respiration
Where does the energy used to make ADP into ATP come from?
The breakdown of glucose through cellular respiration. Energy is stored in the bonds of bio-molecules like carbs and lipids
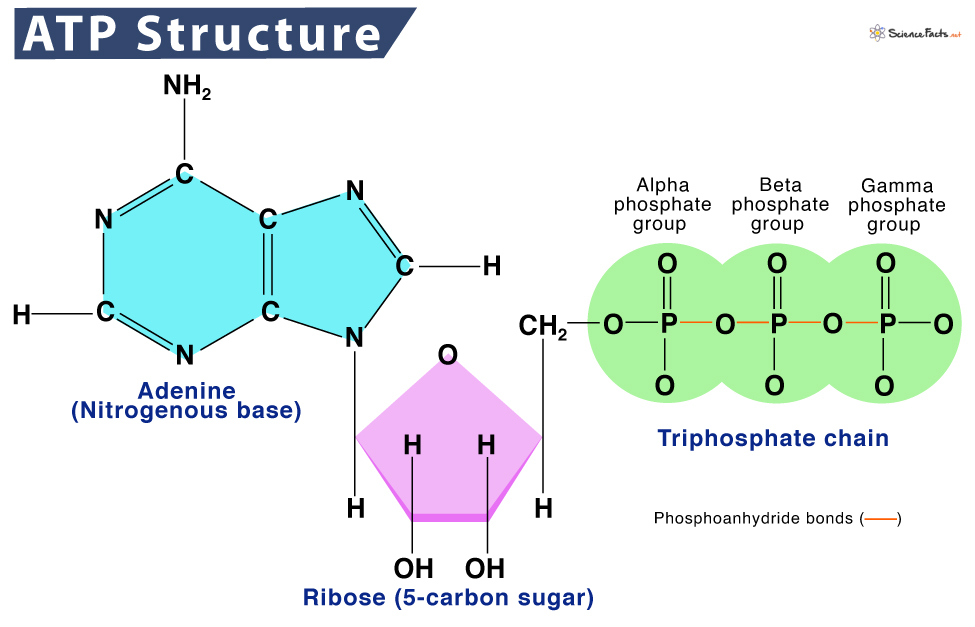
ATP structure
adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups linked by high-energy bonds.
Ribose is a
carbohydrate or sugar
When joining adenine to ribose you have to take out what?
Hydroxide and Hydrogen which form a water molecule H2O
What is required for the chemical combination of adenine ribose and 3 phosphates?
energy
When you change ATP to ADP what is released?
A phosphate group and energy
When you change ADP to ATP what is used and released?
A phosphate group and energy is used
Energy can be
recycled
Phosphates in ATP are joined by what?
high-energy bonds