FRSC Quiz 4 (serology, dna, paint metal and soil)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What’s the most common type of paint that comes into the lab?
Automotive paint
Automotive paint layers
Electrocoat primer
Primer surfaces
Base coat/color coat
Clear coat
How is soil analysis useful
Helps create a link between a suspect and a crime or a crime scene and another location
Color, texture, and mineral composition are compared using microscopy, spectroscopy, and chemical analysis
Preliminary examinations
Visual and microscopic observation: examiners look for obvious foreign material and characteristics such as color/texture for clues on its origin
Laboratory examination
particle size analysis
Sieve separates soil into dif grain ranges to determine particle size distribution
Microscopic examination
Microscope used to analyze the mineral content, composition, and structure of soil particles
Density gradient tests
Density gradient created in a. Liquid and soil sample is added to see how it separates into dif layers, revealing its density profile
Laboratory analysis
Chemical tests
Ignition and heat tests
Evidence
Serology
Scientific study/diagnostic examination of blood serum, especially in regards to the response of the immune system to pathogens or introduced substances
When was the first successful blood transfusion
1665 → bw dogs
What happens when a blood transfusion fails
Instant death ! Transfused blood will coagulate in the recipient
Blood def.
Mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances
What is the fluid portion of blood
plasma
Primarily water and accounts for 50% of blood content
What are the solid material suspended in the plasma
Mostly cells,
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Erthyrocytes
Red blood cells
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Platelets
Cells that bind together when vessels are damaged
Antigens
Proteins on the surface of red blood cells that stimulate the body to produce antibodies and are responsible for blood typing
Antibodies
Proteins that destroy/inactivate a specific antigen
Type A Blood - what antibodies, antigens and compatible types
Anti B antibodies
A antigens on the surface
Compatible with type A and O
Type B Blood - what antibodies, antigens and compatible types
Anti A antibodies
B antigens on surface
Compatible with type B and O
Type AB Blood - what antibodies, antigens and compatible types
No antibodies
A and B antigens on the surface
Compatible with A, B, AB, and O (AB POS is UNIVERSAL RECIPIENT)
Type O Blood - what antibodies, antigens and compatible types
Anti A and Anti B antibodies
No antigens
Compatible with Type O (UNIVERSAL DONOR)
Blood clots
Form when protein Fibrin traps and entangles red/white blood cells, platelets and solids
What remains after blood clot is removed
Serum → yellowish liquid of plasma without fibrinogen
Rhesus factor/Rh factor
Inherited protein found on the surface of the red blood cells
if ur blood type is pos, blood cells have Rh protein.
If blood type is neg, then blood cells don’t have the protein
Immunoassay
Tests to measure the presence and/or concentration of analyze
Ex. Covid test and pregnancy tests
Analyte
Molecule detected by immunoassay
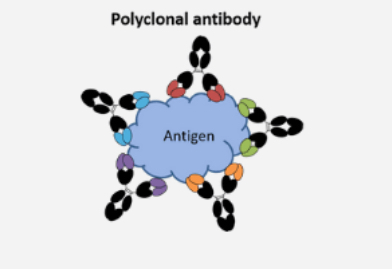
Polyclonal antibody
cheap to produce
Mixed population of antibodies
May bind to dif. Areas of the target molecule
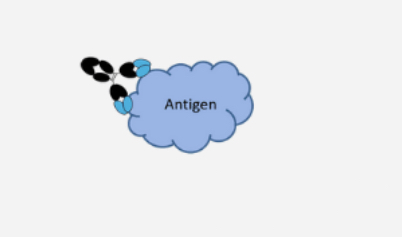
Monoclonal antibody
expensive to produce
Single antibody species
Will only bind single specific site
May only recognize a particular protein form
How are polyclonal antibodies made
Using different immune cells. They have the affinity for the same antigen but dif epitopes
How are monoclonal antibodies are made
using identical immune cells that are all clones of a specific parent cell
What’s the best way to detect/indicate presence of blood at a crime scene
Preliminary color test
Kastle-Meyer (phenolphthalein) Test
based on the observation that blood hemoglobin possesses peroxidase-like activity
Phenolphthalein reagent and hydrogen peroxide are mixed together and the hemoglobin causes the formation of a deep pink color
Not specific to blood, some vegetation will turn pink as well (potatoes and horseradish)
Peroxidase
Enzymes that accelerate the oxidation of several classes of organic compounds by peroxides
Luminol
Contains hydrogen peroxide, which combines with the iron in the blood to produce oxygen
Oxygen and luminol react and form a luminescent compound
Requires COMPLETE DARKNESS for max effectiveness
Blood, bleach, feces, urine, and horseradish, all trigger luminols chemiluminescence
Bluestar
Easier to mix and extremely sensitive to blood +doesnt require complete darkness for visualization
Does luminol or bluestar effect the sample?
No ! It doesn’t interfere with subsequent DNA testing which is important because evidence wont get destroyed before it gets to another discipline
Genes
unit of inheritance consisting of a DNA segment located on a chromosome
Chromosome
Threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells carrying genetic information in the form of genes
How many chromosomes in human cells
46 total, 23 from mom/egg and 23 from dad/sperm
How many mL is normal ejaculate And how much spermatozoa in each mL
2.5-6 milliliters
100 mil spermatozoa in each mL
Acid phosphates
Enzyme secreted by phosphate gland
Concentration of this enzyme is 400x greater in seminal fluid than any other bodily fluid
What’s significant about spermatozoa
It’s only found in sperm, so it’s prescience can unequivocally identify sperm
Seminal fluid with no sperm can happen however if a person has had a vasectomy or if they have a really low sperm count
What nucleotides + pairs are in DNA
Adenine + Thymine
Guanine + Cytosine
Summarize DNA Replication
DNA double helix strand unravels
Double helix is recreated as nucleotides are added led according to complementary base pairing
Now u have two identical copies of DNA
How is DNA replication important in forensics
PCR → polymerase chain reaction
Small/broken bits of DNA found in evidence are copied in order to increase the sample size
Short tandem repeats
Areas on the chromosome that contain short repeating sequences within the DNA molecule
They’re basically just fillers that have no effect on outward appearance or genetic function
What was used before PCR
RFLP → restriction fragment length polymorphism
It was laborious and expensive so it was short lived