14- Ecology
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
a ______ is a group of organisms that are able to interbreed and make viable, fertile offspring
species
to be considered a species, offspring must have the capacity to ______
reproduce
an organism's ______ is the type of place an organism lives in
habitat
habitats includes all other organisms, as well as the _____ and _____ aspects of the environment
physical; chemical
a _____ is a group of organisms of a specific species that live in a given location
population
(ex. all of the koi fish living in a pond)
what is the definition of an ecological community?
all of the populations living in a certain area where the different species interact
an ______ is an ecological community (biotic), plus the abiotic factors populations interact with
ecosystem
______ factors are the nonliving elements in an ecosystem
abiotic
what are some examples of abiotic factors?
temperature, sunlight, water levels... anything nonliving
______ factors are the living elements in an ecosystem
biotic
what are some examples of biotic factors?
plants, animals, microorganisms... anything living
density dependent ecological factors are dependent on the population density and become more significant as the population density ______ (increases/decreases)
increases
diseases and resource competition are examples of density _____ factors
dependent
density _____ factors exert their effects regardless of the population density
independent
weather and climate are examples of density _____ factors
independent
the biosphere is a combination of all the _____ on Earth
ecosystems
the _____ encompasses interactions between ecosystems, and with the lithosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere
biosphere
an organism's ______ describes all the biotic and abiotic resources it uses
niche
an organism's ______ niche describes the environment where an organism truly lives
realized (niche)
an organism's ______ niche refers to the full range of environmental conditions where an organism could theoretically survive
fundamental (niche)
which type of niche are organisms restricted to due to competition?
their realized niche
Gause's law is also known as the ______ principle
competitive exclusion
the ______ states that 2 species are not able to occupy the same niche while also maintaining their population levels
competitive exclusion principle (Gause's law)
_____ allows 2 species to coexist, despite the fact that they seem to compete for resources
resource partitioning
resource partitioning occurs when species use different means to obtain the _____ resource, or they seek out _____ resources
same; slightly different
how might niche overlap be minimized/potential competition be avoided?
by having chance genetic mutations/variations which result in phenotypic characteristics that allow for the pursuit of different types of resources (as compared to a similar species)
describe the phenomenon of character displacement:
it is the phenomenon of chance genetic mutations/variations occurring, which result in unique phenotypic characteristics that allow for the pursuit of different types of resources (as compared to similar species). These characteristics lead to niche overlap being minimized and potential competition between those species being avoided. Because of this decreased competition, the unique individuals experience greater reproductive success, and this results in a higher prevalence of organisms with the advantageous, unique characteristic.
what is a common example that demonstrates character displacement?
the beak variations of Galapagos finches, which allows them to eat different types of seeds
during the process of ______, a population evolves into more than 1 distinct species
speciation
______ speciation refers to a speciation event that occurs as a result of naturally occurring evolution
natural
In contrast to natural speciation, artificial speciation is a result of artificial, intentional methods such as _____
selective breeding
a method where only organisms with a given phenotypic trait are chosen for reproduction is called ______
selective breeding
what are the 2 types of biological interactions (as they relate to time)?
short-term; long term
competition, where 2 species compete for the same resource(s), is an example of a ______ biological interaction
short-term
symbiosis is an example of a ______ biological interaction
long-term
the 4 types of competition are: ______, ______, ______, and ______
exploitation; interference; intraspecific; apparent
______ competition is indirect, and it occurs when a common resource is depleted
exploitation
Lions and cheetahs hunt for a common resource - the gazelle. If cheetahs are more successful and eat all the gazelles, the lions will suffer from depletion of this food resource. What type of competition is this scenario referring to?
exploitation competition

______ competition is a type of competition in which the physical establishment of other individuals who compete for a mutual resource is directly prevented
interference
Allelopathy is the production of biochemicals by an organism that influences the growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms. It is a form of ______ competition
interference
______ competition is a type of competition that occurs between members of the same species
intraspecific
two rabbits competing for carrots is an example of ______ competition
intraspecific
______ competition occurs when one predator preys on two species
apparent
(ex. owl preys on spiders and beetles)

______ refers to a close, long-term biological interaction between 2 organisms in their environment. This interaction could be necessary for the survival of the organism(s)
symbiosis
(symbiosis = "living together")
3 different types of ecological symbiosis are: ______, ______, and ______
mutualism; commensalism; parasitism
______ is a type of symbiosis that occurs when both organisms benefit from the other's presence
mutualism

______ is a type of symbiosis that occurs when one organism benefits and the other organism is neither helped nor harmed by the other's behavior
commensalism

______ is a type of symbiosis that occurs when one organism benefits at the other organism's expense
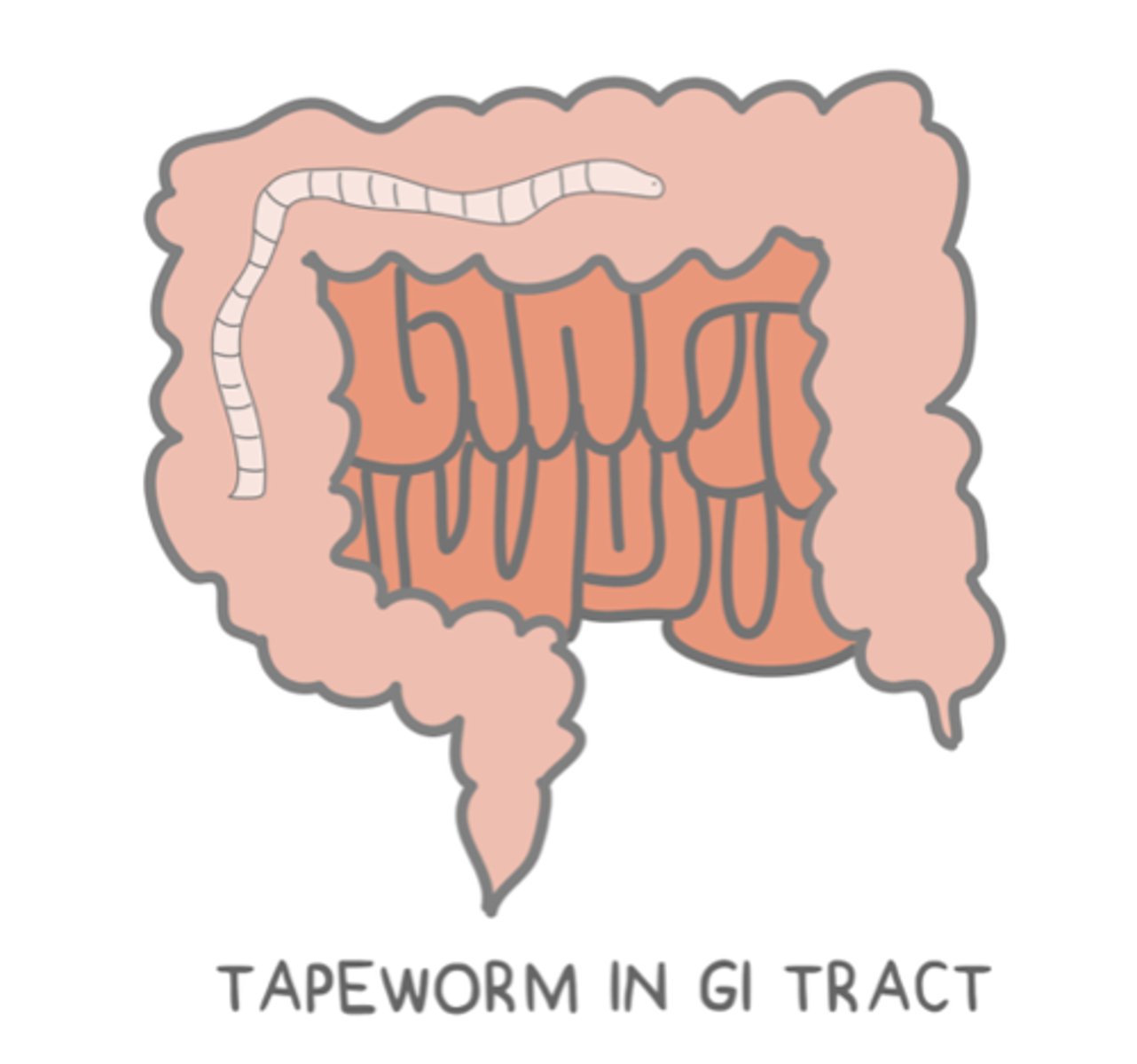
parasitism
(an example is a tapeworm in the gastrointestinal tract of a human. The parasitic tapeworm obtains shelter and food that passes through the GI tract, but the human is unable to absorb all of the nutrients from their food)
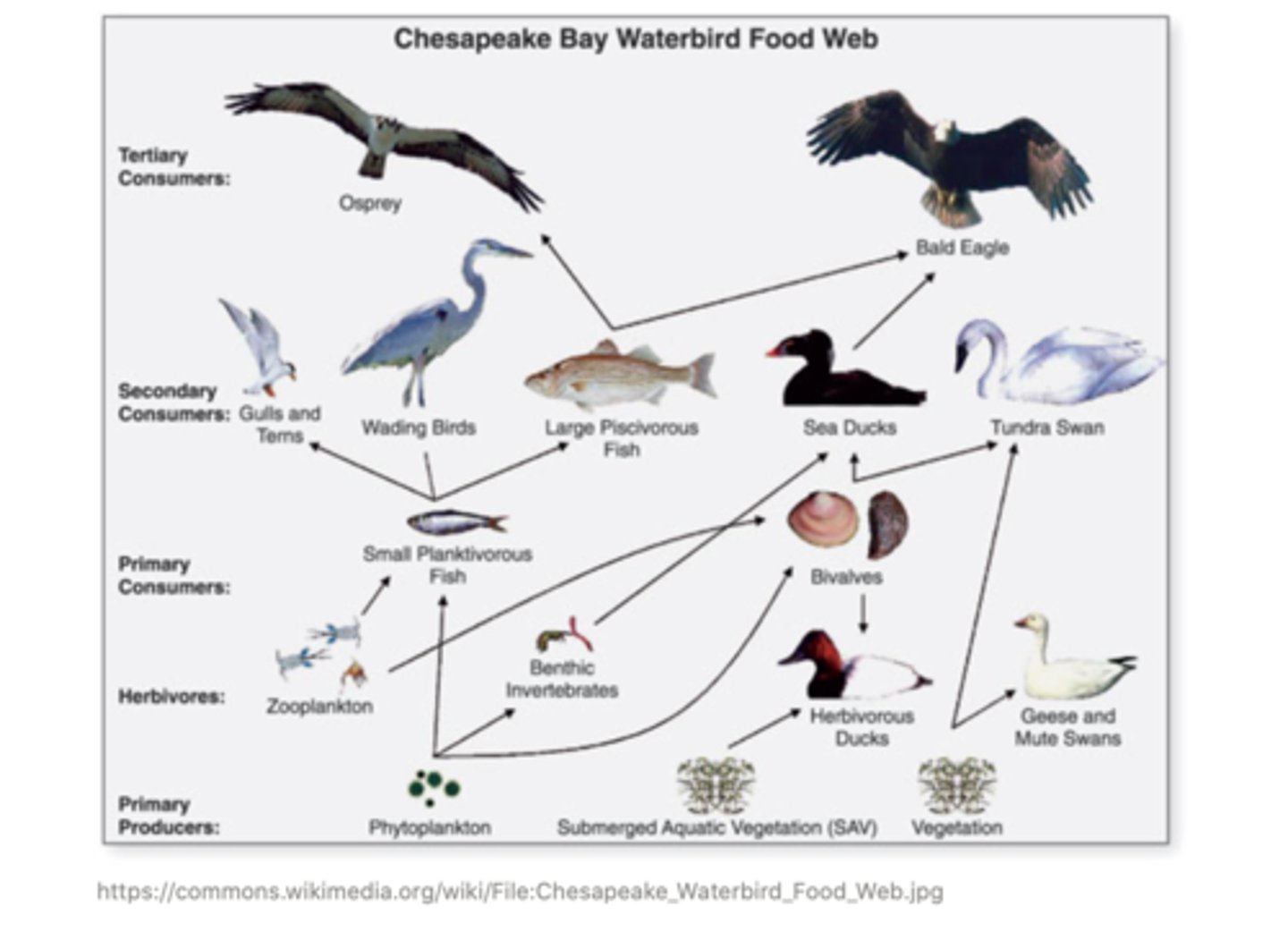
a ______ is a linear depiction of what eats what
food chain
a _____ depicts the interconnections between food chains within a community
food web
(expanded version of a food chain)
the term ______ refers to an organism's position within a food chain/web
trophic level
a ______ is an organism that is able to produce energy (organic compounds) through sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and other inorganic substances in its environment
autotroph
a ______ is an organism that must ingest organic compounds to generate energy and survive
heterotroph
_____ is the relationship between the predator (hunter) and the prey (hunted)
predation
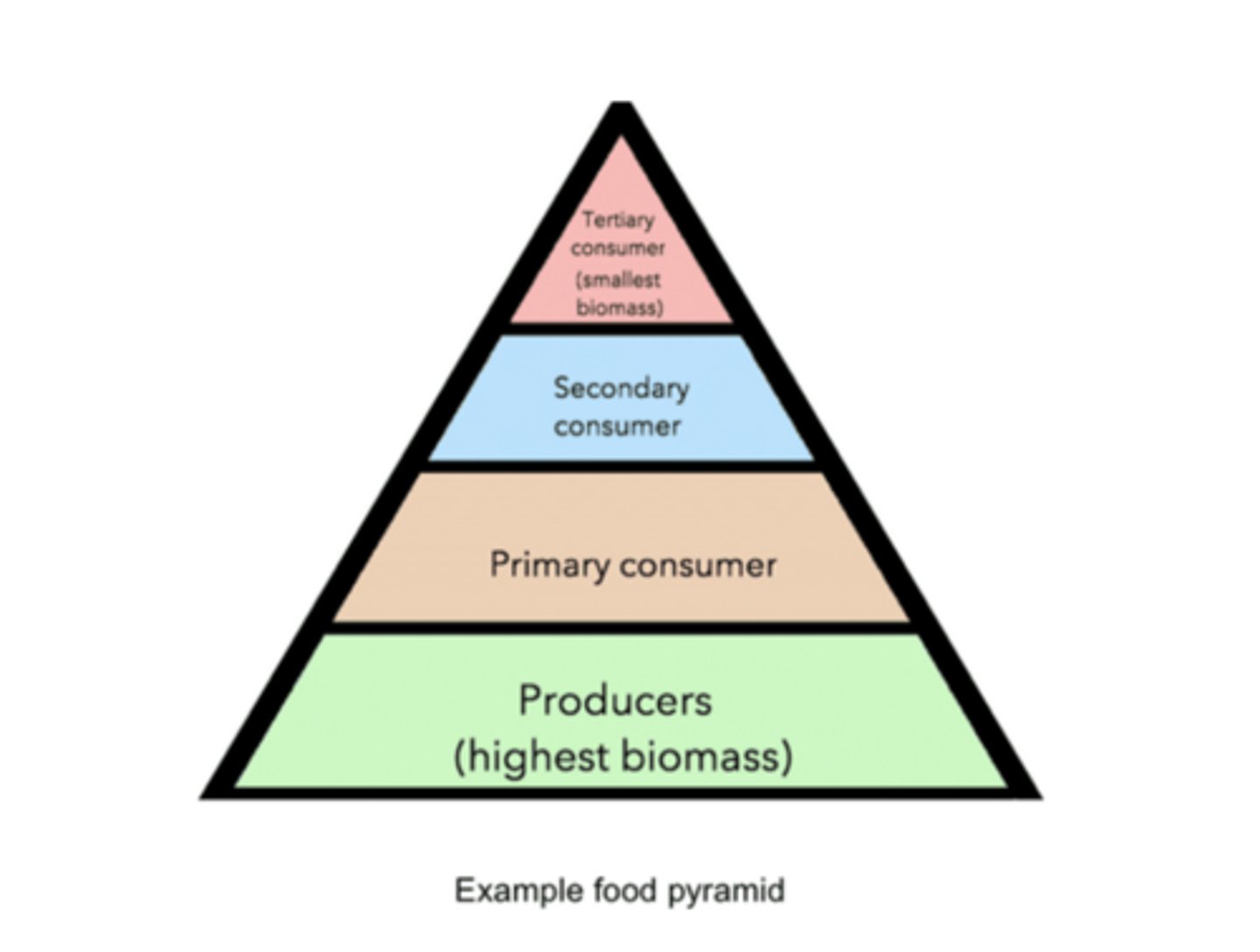
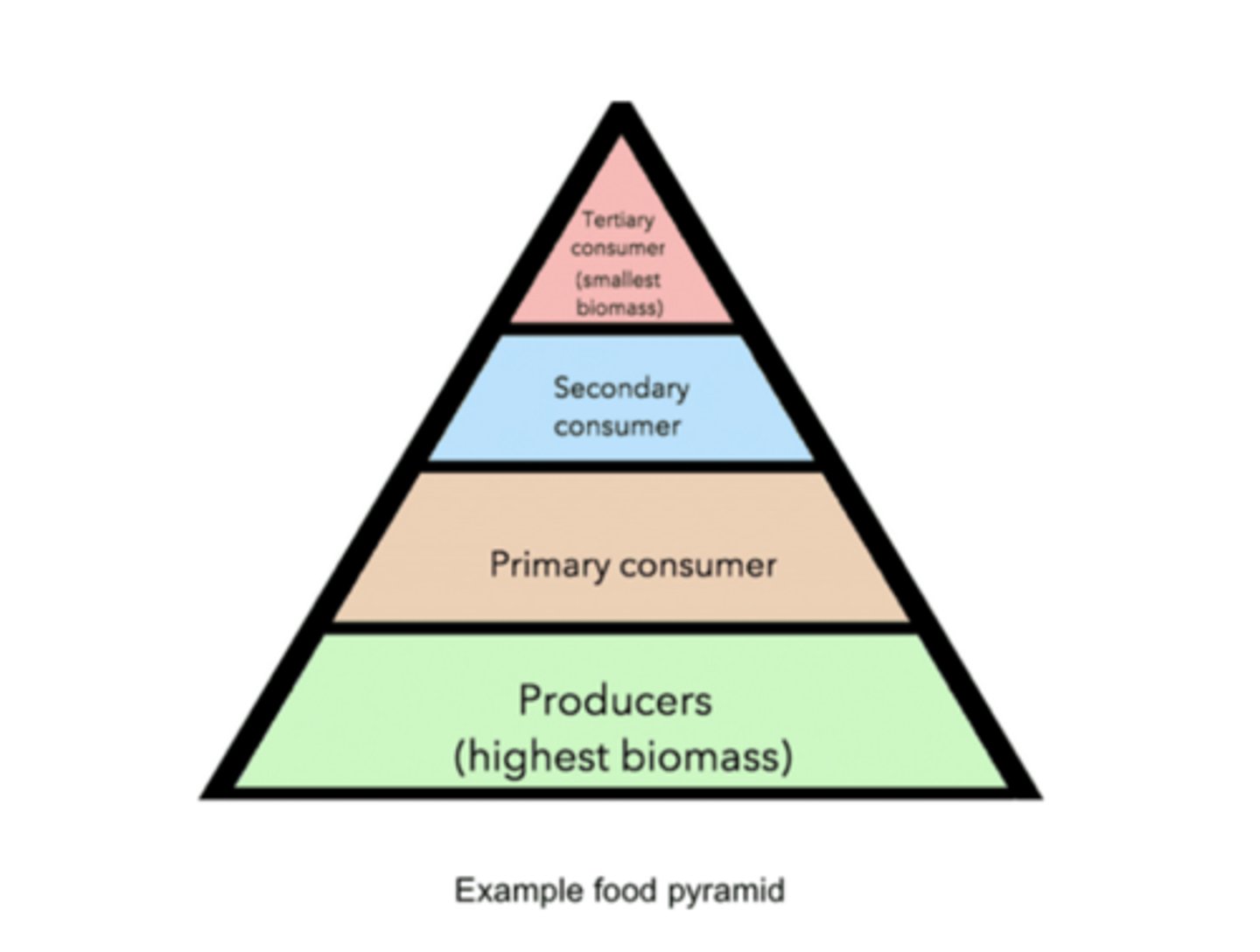
______ are located at the lowest trophic level
primary producers
most commonly, primary producers are usually _____ (autotrophs/heterotrophs)
autotrophs
primary producers (autotrophs) tend to undergo photosynthesis to generate the _____ of an ecosystem
biomass
______ is the total mass of living organisms in an area or ecosystem
biomass
primary consumers are organisms that solely consume ______, and they tend to be ______
primary producers; herbivores
______ are located 1 trophic level higher than primary producers
primary consumers
a ______ is an organism that derives its energy from plant matter
herbivore
_____ consumers prey on primary consumers
secondary
______ are located 1 trophic level higher than primary consumers
secondary consumers
secondary consumers are also known as primary _____
carnivores
a ______ is an organism that eats animal tissues
carnivore ("meat eater")
a ______ is an organism that consumes both plant and animal material to survive
omnivore
_____ prey on secondary consumers
tertiary consumers
______ are located 1 trophic level higher than secondary consumers
tertiary consumers
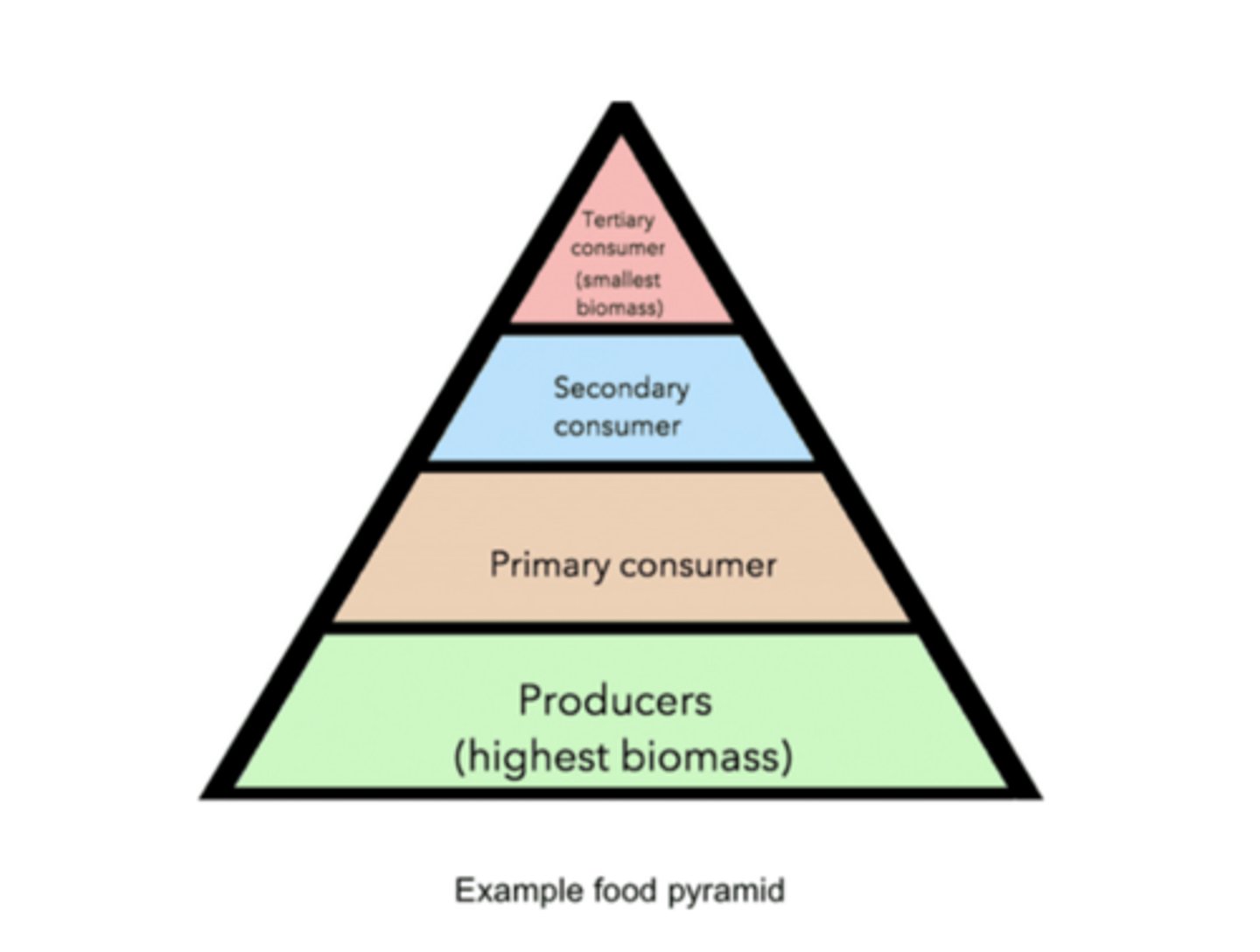
tertiary consumers are also known as secondary ______
carnivores
the predator at the top of the food chain is called an ______
apex predator
does a food chain/web need to extend beyond a tertiary consumer?
no - the apex predator could theoretically be a secondary consumer just as easily as it could be a quaternary consumer
what percentage of energy is lost when moving from a lower to higher trophic level?
about 90%
(only ~10% of the energy stored in one trophic level can be converted to organic tissue in the next trophic level)
the most biomass is stored at the _____ trophic levels, while the least biomass is stored at the _____ trophic levels
lowest; highest
______ are animals that consume other dead animals (and sometimes dead plant matter)
scavengers (ex: vultures)
scavenging is done by both _____ and _____
carnivores; herbivores
______ are organisms that are involved in the breakdown and recycling of dead plant and animal material
decomposers
decomposers are broken down into three classes: ______, ______, and ______
saprophytes; fungi; detritivores
_____ are plants, fungi, and microorganisms that consume dead or decaying organic materials for survival
saprophytes
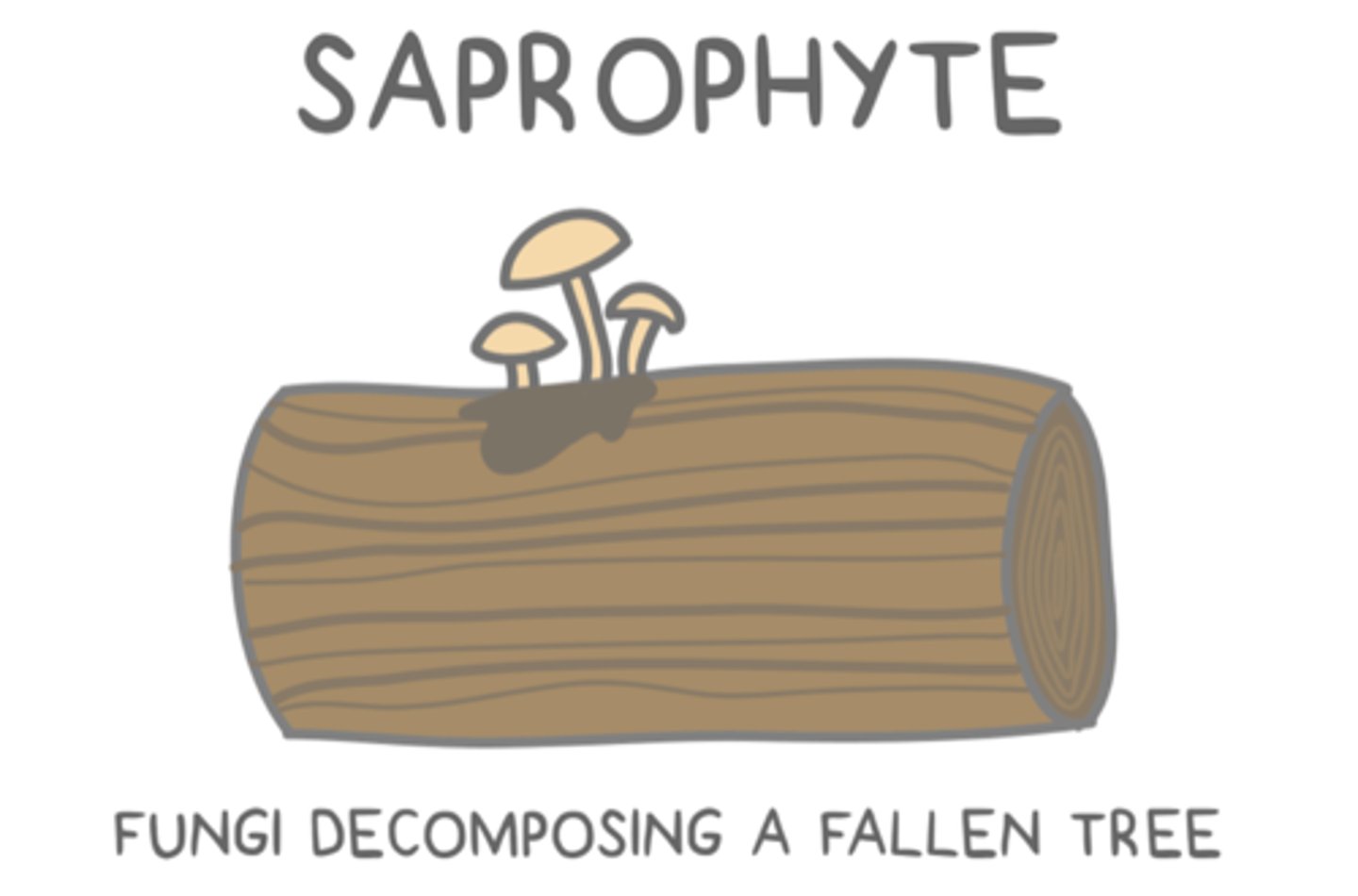
in many ecosystems, ______ are the most important decomposers
fungi (bacteria are also important)
when decomposers break down the dead or decaying matter, it becomes a component of ______
detritus
______ is a combination of feces and decomposing organic matter
detritus
______ do not break down organic matter; rather, they consume detritus, which helps expose additional organic matter for decomposition by fungi/bacteria
detritivores

worms and slugs are examples of ______
detritivores

______ species (also called an introduced species) is a species that lives outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there by human activity, either deliberately or accidentally.
non-native
the impact of non-native species is highly ______
variable
(Some have a substantial negative effect on the local ecosystem (ex. invasive species), while others may have no negative effect or only minor impact.)
There are two types of non-native species: ______ and _______
naturalized species; exotic species
a key characteristic of a ______ species is that if it becomes sufficiently abundant, they have the potential to have adverse effects on native plants and animals
naturalized
the ______ is a species' ability to undergo its highest possible birth rate and lowest possible death rate, resulting in a maximal population growth
biotic potential
biotic potential occurs when environmental conditions are _____ for that species
ideal
the ______ is the maximum population size (number of organisms of a given species) that an ecosystem can sustain
carrying capacity
______-selected species undergo long gestation periods to produce few, large offspring that take a relatively long time to mature
K (also called K-strategists)
______-selected species provide significant parental investment and support, therefore a high percentage of the offspring survive to reproductive age
K
a ______ percentage of offspring survive to reproductive age in K-selected species
high
survival of K-selected species is demonstrated by a _____ survivorship curve
type I
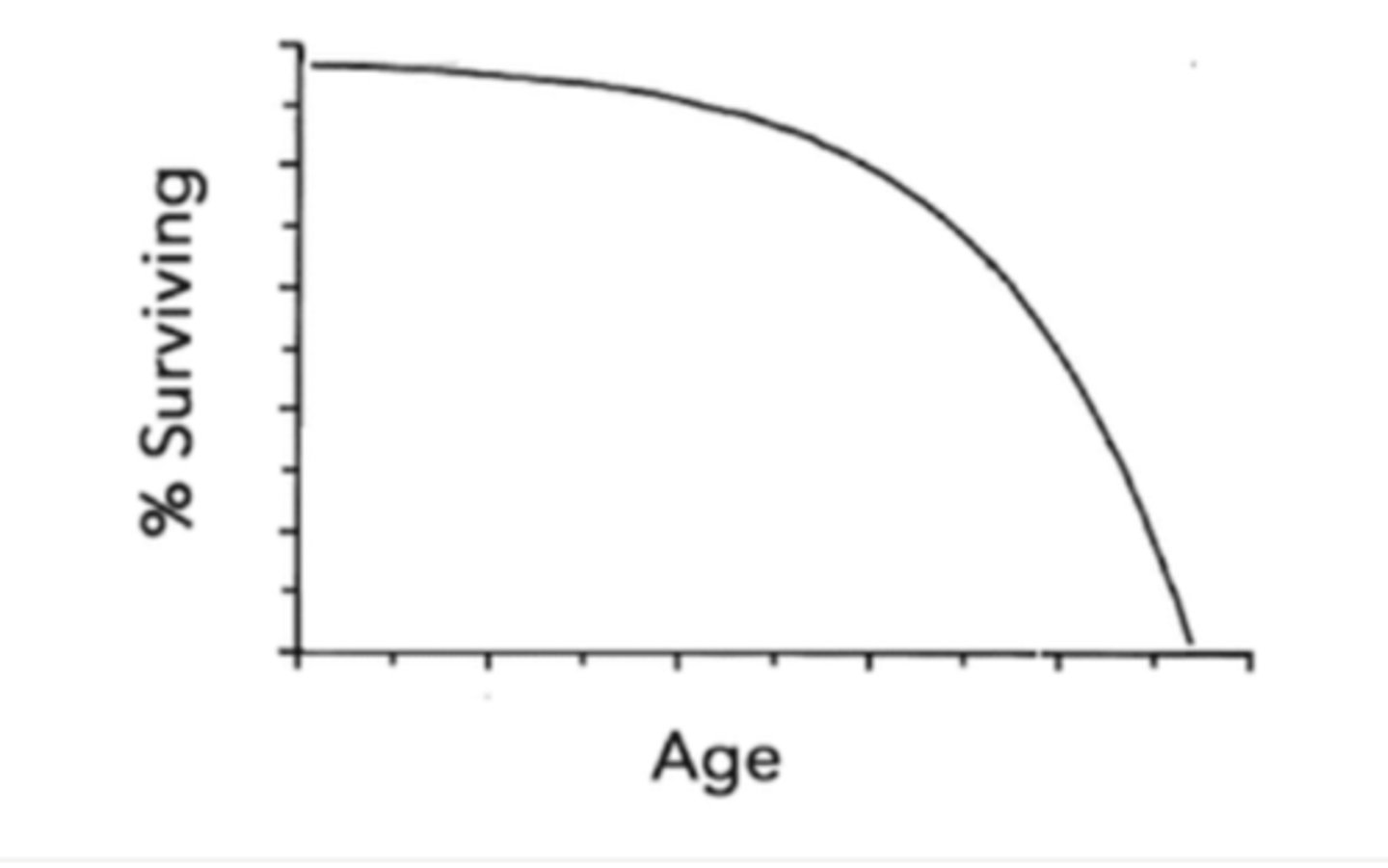
describe a type 1 survivorship curve:
high rate of survival during early and middle age, with mortality increasing during old age
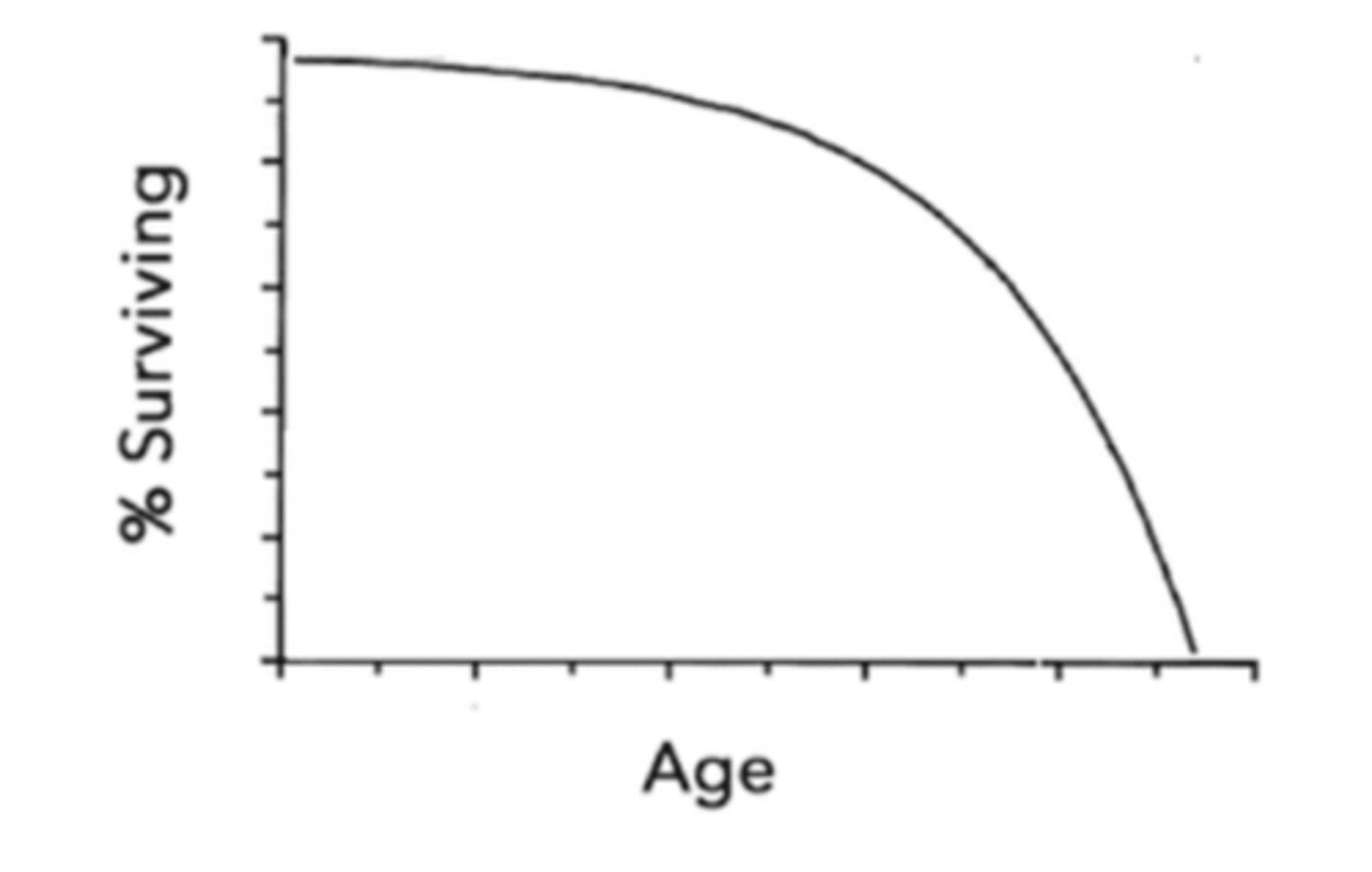
______-selected species produce abundant, small offspring that mature quickly
R (also called r-strategists)
______-selected species provide little to no parental investment/support
R
a ______ percentage of offspring survive to reproductive age in R-selected species
low
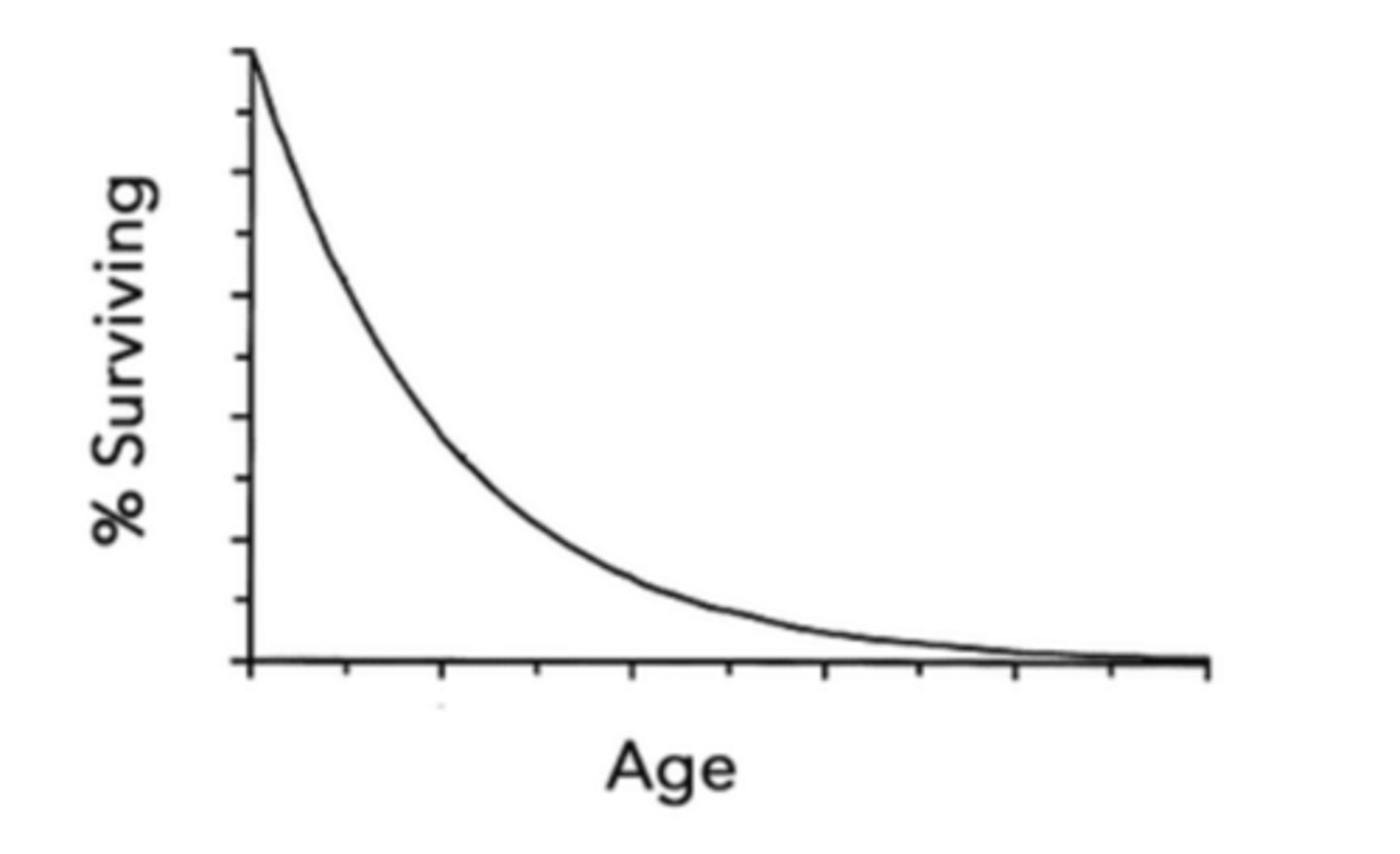
survival of R-selected species is demonstrated by a ______ survivorship curve
type III
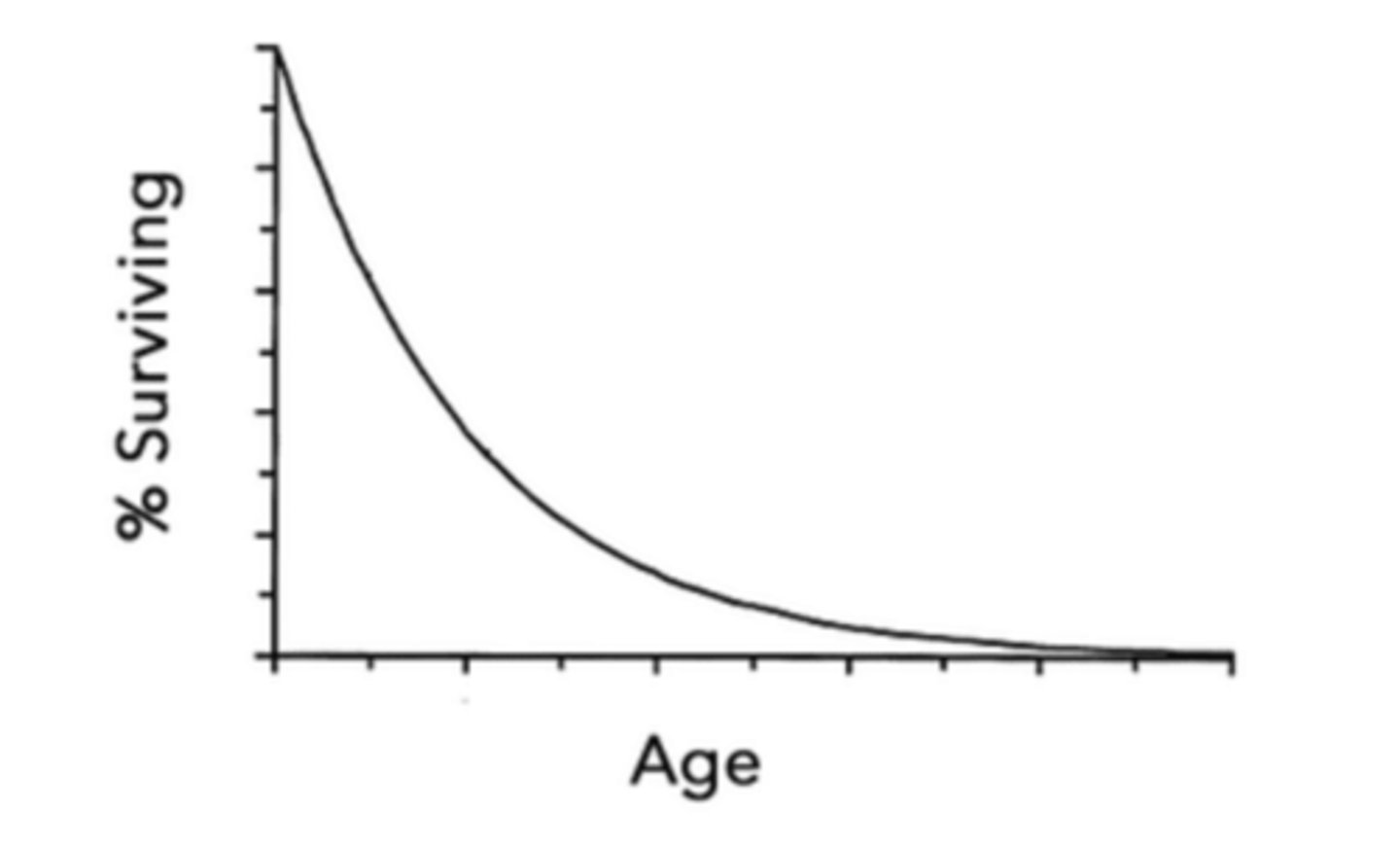
describe a type III survivorship curve:
survival undergoes exponential decay with respect to age