transfers (week 7)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Definition of Transfer
Safe movement of a person from one surface, location, or position to another
Independent 06
pt can perform the transfer/gt without any verbal or manual assistance
Modified Independent
pt can perform an activity without physical assistance from you but requires an assistive device or adaptive equipment (ie. walker, bed rail, grab bars, furniture)
05-Setup or clean-up assistance
pt needs someone else to set up or clean-up an activity but does not need any asst physically
Supervision
pt can perform the task without set-up, cues, or physical assistance; however, pt is not independent or safe doing the task alone
standby assist
pt needs verbal cues and/or instructions in order to complete a task but does not need any physical assistance from you to be safe and efficient; you need to be close but not touching the pt (book says tactile cues also but I don’t agree)
04-Supervision or touching asst
you give vc and/or touching (CGA) in order for pt to complete the task
CGA
you are making contact with the pt by holding onto the gait belt or the pt but does not need more help than a touch or close guarding
GG codes
06-Independent
05-Setup or clean-up asst
04-Supervision or touching asst
03-Partial/mod asst
02-Substantial/max asst
01-Dependent
Levels of Assistance
Minimal asst
03-Moderate asst or Partial asst
02-Maximum asst or Substantial asst
01-Dependent (Total) asst
Minimal asst
pt performs 75% or more of the activity (you are doing 25 % of the work)
03-Moderate asst or Partial asst
pt performs 50-74% of the activity (you are doing less than half the work)
02-Maximum asst or Substantial asst
pt performs 25-49% of the activity (you are doing almost all the work; more than half)
01-Dependent (Total) asst
pt is not able to assist with the activity at all (you are doing ALL the work) and/or you need additional assist from someone else or equipment to complete the task
Required Documentation
Amount of assistance required
Amount of time to complete transfer
Amount of people to complete transfer
Level of safety demonstrated
Weight bearing status
Level of consistency of performance
Equipment or devices used
gait belt
An adjustable belt or strap that is secured around a person’s waist and is used to protect and control the person
´Used to increase pt safety during mobility and with balance activities
´May be used to prevent falls but also to lower pt to the ground slowly to avoid injury
´Should be used with ALL pts in the hospital and long term care settings
´Used often in Rehab setting
´Used rarely in OP and HH settings
when to use gait belt
Applied in sitting position
Applied around the pt’s waist and adjusted snuggly
May need to be tightened once standing due to slipping down
In some instances, the belt may be secured around the chest
Therapist’s hand holds from under the belt
For bariatric pts, 2 belts may need to be joined prior to putting on pt.
gait belt and falling
A fall is considered to be the pt’s knees touching the floor even though you descend slowly with a soft landing
The belt can be used to slowly lower someone to the ground instead of holding them up
If you have a bariatric pt, you will NOT be able to hold them up and will HAVE to lower them to the floor
Preparation for Transfers
Proper footwear (shoes with rubber soles, socks with grips on the bottom)
Safety or gt belt
Be alert to the unexpected
Apply the gt belt from in front or slightly from the side of the pt
Secure gait belt, bedrail, or other protective devices
Instruct the pt to push up from what they are sitting on when coming to std and to reach back for chair/bed before sitting on it; Do NOT allow pt to put their arms around your neck
Environment free of unnecessary equipment
before the transfer
Analyze transfer into component parts
Prepare the environment
Prepare patient
Prepare yourself and other persons involved
Analyze transfer into component parts
position of equipment- make sure pt’s assistive device is within reach and the correct heighth
pt’s ability to use the equipment
position of patient’s body – poor balance, hemiplegia
movements required – pt’s ability to assist
Prepare the environment
position chair perpendicular to the bed so that pt will be moving towards his strong side during transfer
lock the wheels if applicable
Prepare patient
tell the pt the plan
what they need to do
apply proper footwear
apply the gait belt
Prepare yourself and other persons involved
decide who will be the leader if more than 1 person is helping and give the instructions
Sit to Stand
Move forward in chair positioning COG near BOS
Position feet (stronger leg in back)
Lean forward
Use arms simultaneously to push up from what the patient is sitting on-----“Nose over toes”
Stand up
Reverse process for stand to sit
During the Transfer
Be alert to devices or external factors that may interfere (curtains, IV poles, catheters)
Stabilize patient’s knees, pelvis, and upper thorax for control
Remain close to and guard patient properly
Use proper body mechanics
Use concise statements while guiding the patient and others through the transfer
Conditions Requiring Special Precautions
Total hip replacement
Low back trauma or discomfort
Spinal cord injury
Burns
Hemiplegia
Total hip replacement
usually avoid hip adduction, flexion more than 90 degrees, internal rotation
usually for 3 months but depends on physician
Low back trauma or discomfort
avoid lumbar rotation, trunk side bending, and trunk flexion)
acronym is no BLT w/pickles (no bending, lifting, twisting, or pulling)
usually avoid any lifting more than 10 lbs
no pulling
“logrolling” technique
“hooklying” position
Spinal cord injury
if acute, may have an external appliance (brace or halo device) and/or an internal fixation ( bone graft, metal rods or wires)
if an old injury, prone to osteoporosis (esp. long bones and vertebra)
avoid distraction and rotational forces
protective positioning in side-lying or sitting
prone to syncope when transferring from supine to sitting due to orthostatic hypotension
Autonomic dysreflexia
Burns
avoid creating shear forces across the burn, graft site, or area where the graft was taken due to impaired healing
ensure that you lift the burned area when moving to avoid shearing
Hemiplegia
avoid pulling the affected limbs when moving the patient due to tendency to have shoulder subluxation
pain/discomfort when rolling or lying on the affected shoulder
Weight Bearing Status
Non–weight bearing (NWB)
Partial weight bearing (PWB)
Toe-touch weight bearing (TTWB)
Full weight bearing (FWB)
Weight bearing as tolerated (WBAT)
Different types of transfers
sit pivot
stand pivot
recumbent
sit pivot
pt remains in a sitting or squatting position during the transfer
Independent
Assisted
Dependent
stand pivot
pt remains upright during transfer
Independent
Assisted
Dependent
recumbent
pt is lying down during transfer
Dependent
Transfer Activities
Bed <-> chair
Two-person dependent: bed<->chair, chair <-> floor
Three-person dependent: bed <-> stretcher
Wheelchair/chair <-> floor
Standing dependent pivot from bed to wheelchair
Diagnosis specific such as total hip replacement, hemiplegia, weight bearing restriction, spinal cord injury (SCI)
Bariatric – using a draw sheet and doing a 2 man pivot
Sliding board
Mechanical lift
Bed <-> chair
Position chair so that the patient is moving towards their strong side
Have patient move to edge of the bed
Ensure proper foot wear
Apply gait belt
Instruct patient to push up using arms and non-affected leg
Instruct patient to pivot so that buttocks moves toward chair and to sit on the chair
Instruct patient to scoot back in the chair and assist if needed
Position patient for comfort
Reverse procedure for going back to bed
Transfer for a patient with a THR
Follow the steps for bed <->chair transfers but add the following:
Instruct patient to move to edge of bed using noninvolved (unaffected) extremities and assist with moving the involved (affected) limb
Follow specific hip replacement guidelines as involved lower extremity is moved off the bed and positioned with feet on the floor
Push up from bed with hands, stand, and grasp hand grips of walker
Transfer for a patient with back pain
Follow the steps for bed <->chair transfers but add the following:
Lift one leg up at a time to get feet flat on bed
Log roll to sidelying then sit up on edge of bed (assist when needed)
Push up from bed with arms, stand, and grasp hand grips on assistive device if used
Transfer Equipment and Devices
Transfer board
Hydraulic or pneumatic lift
Electric hoist
Bedrail
Over-the-bed or trapeze bar
sliding boards
Used to do a lateral transfer from one fairly even surface to another
Bridges the gap btn two surfaces
Used when a pt is unable to bear weight on LEs or too weak to stand on legs
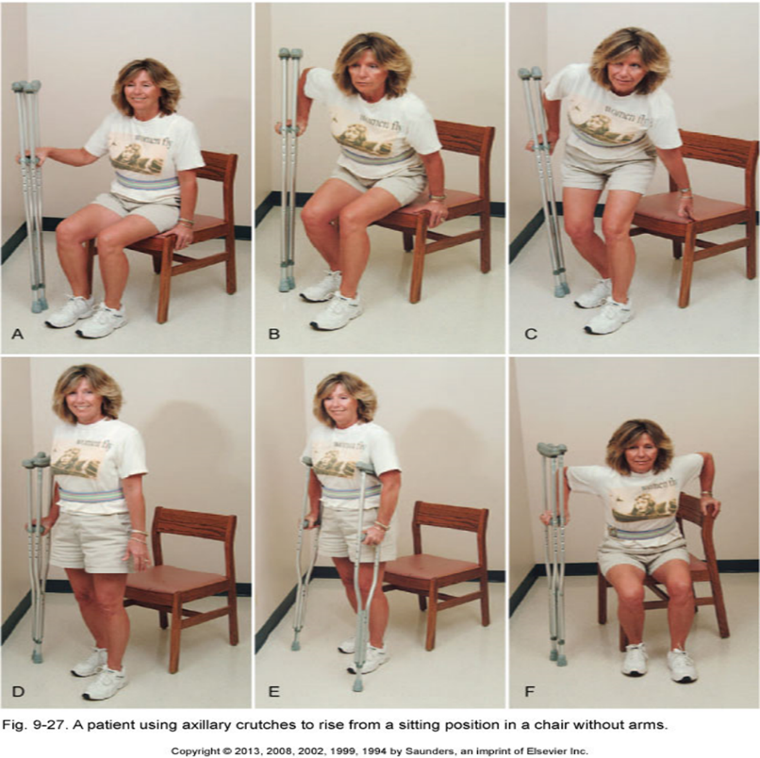
sit to stand with crutches
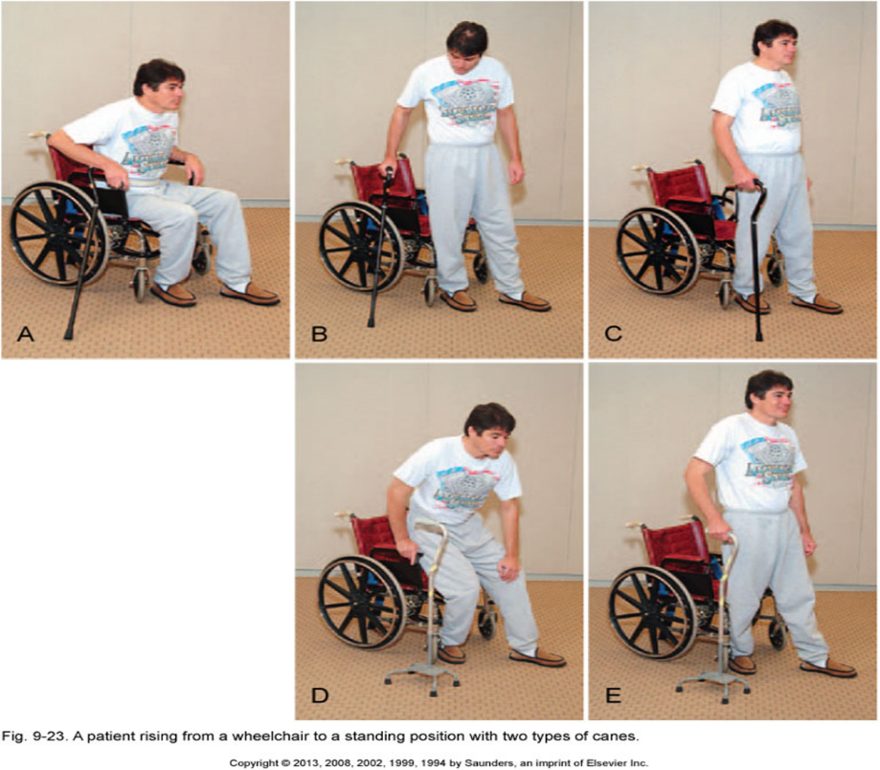
sit to stand with a cane