Option G - Urban Environments
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Site
The actual physical location of a settlement (e.g. land, water supply, soil)
Situation
The location of a settlement in relation to other places (e.g. nearby rivers, trade routes)
Isolated dwelling
An individual household where no services are available and the resident travel to local villages for low order goods
Hamlet
A very small group of houses with few or no services (10-100 people)
Village
A small settlement with limited services (<10,000 people)
Town
A larger settlement with a range of services (<100,000 people)
City
A major settlement with extensive services, infrastructure or official city status (>100,000 people)
Conurbation
A continuous urban area formed by the merging of towns and cities
Metropolis
A large urban agglomeration (>1 million)
Millionaire city
A city with over 1 million people
Megacity
A city with over 10 million people
Megalopolis
A chain of connected cities and conurbations that form one massive urban area
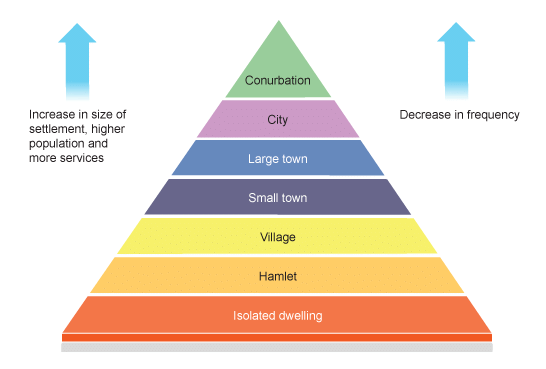
Settlement Hierarchy
The ranking of settlements based on size, population, and the range of services they provide
Threshold
Minimum demand/sales a business needs to stay in operation
Suburbanization
Outward growth of towns and cities to engulf surrounding villages and rural areas
Gentrification
The process of wealthier people moving into a poorer urban area, improving housing and services, which often leads to the displacement of lower-income residents
Counter-urbanization
A process involving the movement of population away from larger urban areas to smaller urban areas
Urban renewal
The redevelopment of run-down areas in a city, involving new buildings, infrastructure, and public spaces to revitalize the area
Urban circular city
A sustainable city in which there are recycling, reuse, and reeducation or resources, renewable form of energy, and measures taken to reduce the ecological footprint
Urban sprawl
The rapid expansion of the geographic extent of cities/towns, often characterized by low-density housing and increased reliance on private cars for transportation
Nodality
The degree of connectedness a location has in relation to transport communications
Sphere of influence
The total area from which people are willing to travel to an urban function
Bid rent
The value of land for different purposes (e.g. commercial, residential)
Peak land value intersection
The region within a settlement with the greatest land value and commerce
Industrialization
The growth of manufacturing and industry in a region, often leading to urban growth, job creation, and infrastructure development
Deindustrialization
The decline of manufacturing industries, usually in HICs, leading to job losses, economic change, and sometimes urban decline
Positive segregation
Where groups of people of the same ethnicity chose to group close together, often for support or to be close to facilities
Negative segregation
When groups of people are forced to live in close proximity due to being excluded from other areas, often due to cost or red lining
Urban growth
The increase in the number of people living in urban areas
Urbanization
The increase in the % (or proportion) of a population living in an urban area
Centripetal population movement
The movement of people towards the city from the countryside
Natural increase
Birth rate is higher than death rate
Centrifugal movement
The outward population movement away from the center of a city
Urban Heat Island Effect
When urban areas are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas due to human activities and built surfaces (like concrete and asphalt) that absorb and retain heat