Pulm E2- Pulm Circulation Disorders
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what is a pulmonary embolism?
obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by material that originated elsewhere in the body;
most commonly arises from thrombus in deep venous system of lower extremities
PE is more common in ____
males
what is Virchow’s triad?
hypercoagulability, venous stasis, endothelial injury
what is the pathophysiology of a PE?
thrombus travels to pulm vasculature → obstruction → inc in pulm vasc resistance → pulm HTN → RV failure
inc dead space → impaired gas exchange → inc CO2 → hyperventilation / tachypnea
inflame response secondary to chemical mediators released by thrombus → bronchoconstriction of small airways, vasoconstriction, surfactant dysfunction and atelectasis, V/Q mismatch = hypoxemia
pulm infarction if smaller peripheral vessels occluded
what are the classifications of a PE?
Hemodynamically unstable: hypotension (SBP < 90 or DBP drop 40); more likely to die from obstructive shock (ex RVHF)
hemodynamically stable: ranges from mild sx to asx; mild hypotension that resolves w/ fluids
what are risk factors for PE?
genetics (thrombophilia, factor V leiden, prothrombin gene mutation, protein C or S def, hyperhomocysteinemia)
prolonged immobilization
recent ortho surgery
malignancy
indwelling venous catheter
obesity
pregnancy
smoking
hormone replacement therapy
what are sx of a PE?
dyspnea- typically acute and severe
pleuritic chest pain
cough ± hemoptysis
presyncope or syncope
less common: arrhythmias, sudden cardiac arrest, syncope, dizziness, hemodynamic collapse
what are you looking for on a physical exam of a PE?
tachypnea, tachycardia
hypoxia
signs of DVT- unilateral calf swelling/erythema and homan’s sign
signs of pulm HTN
signs of RV failure
what labs to order for PE?
ABG: hypoxemia, resp alkalosis w/ hypocapnia
CBC: WBC normal or elevated
CMP: renal function and electrolytes
Cardiac Enzymes BNP & Trop: elevated, assoc w/ inc RV afterload, prognostic not diagnostic
D-Dimer: not useful for confirmation; high neg predictive value w/ low pos predictive value
what imaging studies can be ordered for PE?
EKG: tachycardia MC, nonspecific ST and T wave inversion, S1Q3T3 rare
CXR: typically normal; hampton’s hump, westermarks sign
venus Doppler u/s to evaluate LE DVT
lung scintigraphy/ VQ scan: when CTA is contraindicated and in pregnancy
CT pulm angiography: gold standard; contraindicated in iodine contrast allergy and renal insufficiency
catheter based pulmonary angiography: invasive and expensive; rarely used
what imaging study is the gold standard for PE?
CT pulmonary angiography
what is the diagnostic test of choice for a PE in pregnancy?
lung scintigraphy / V/Q scan
what is hamptons hump?
rare; wedge shaped, pleura based triangular opacity w/ an apex pointing toward the hilus
pathognomic for PE
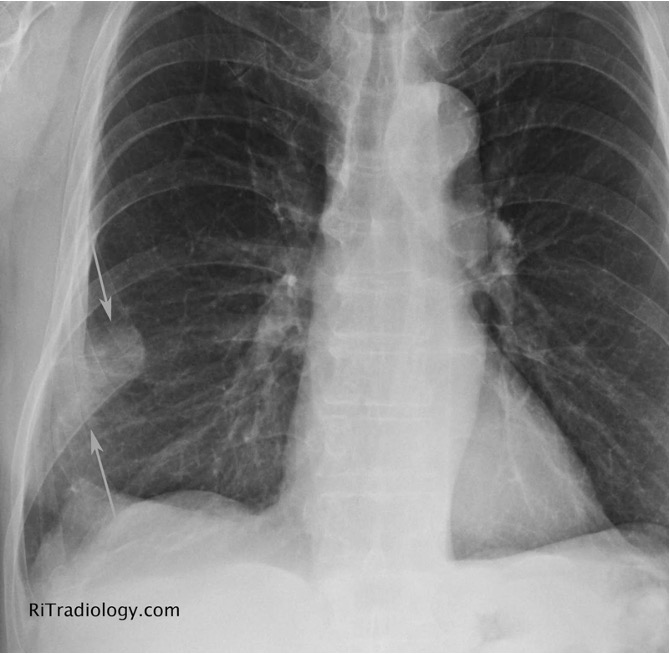
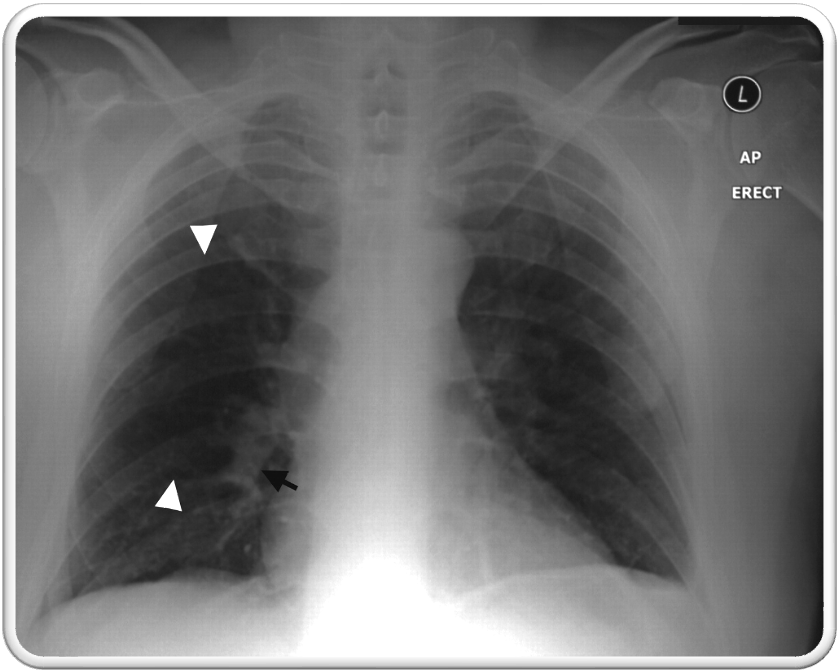
what is westermarks sign?
rare; sharp cut off of pulmonary vessels w/ distal hypo perfusion in a segmental distribution w/in the lung
pathognomic for PE
what is used for risk stratification and clinical decision criteria to esteem the probability for acute PE?
wells / modified wells critera
what is well’s criteria?
S&S of DVT → 3
PE is likely #1 dx → 3
HR > 100 → 1.5
immobilization ≥3 days or surgery is past 4 wks → 1.5
PMHx PE or DVT → 1.5
hemoptysis → 1
malignancy w/ tx w/in 6 mos or palliative → 1
what criteria is used to determine if a low risk pt warrants further evaluation for PE?
pulmonary embolism rule out criteria (PERC)
what is PERC?
age < 50
HR < 100
SaO2 ≥ 95%
no hemoptysis
no estrogen use
no surgery/trauma requiring hospitalization w/in 4 wks
no prior VTE
no unilateral leg swelling
low risk pts only, if any criteria is positive → can’t r/p PE
if score 0 → <2% chance of PE
what is the clinical prediction tool to determine pre test probability of a PE based on risk factors and clinical findings and has a greater degree of standardization?
geneva score
what is Geneva score?
age > 65 → 1
previous DVT or PE → 3
surgery or LE fracture in previous wk → 2
active cancer → 2
unilateral LE pain → 3
hemoptysis → 2
HR 75-94 → 3
HR ≥ 95 → 5
pain on leg palpation or unilateral edema → 4
0-3 pts: low prob; 4-10 pts: intermediate prob; ≥ 11 pts: high prob
How would this PE be classified?
SBP < 90 or drop of ≥40 in > 15 min
possible RV dysfunction w/ progression to obstructive shock
death often occurring in first 2 hrs
hemodynamically unstable
How would this PE be classified?
stable BP
mildly sx or asx
hemodynamically stable
what is tx for a hemodynamically stable PE?
supplemental O2
peripheral IV access (± IVFs)
empiric anticoagulation
LMWH: Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
unfractionated heparin → preferred in severe renal failure
if anticoagulation contraindicated → IVC filter
what is an inferior vena cava filter?
blocks path of LE venous emboli from entering pulm circulation
indications:
pts w/ VTE who have absolute contraindication to anticoagulants
recurrent VTE and PE
retrievable filters preferred
what is tx for hemodynamically unstable PE?
low bleed risk w/ no contraindications → thrombolytics (tPA) [preferred w/in 48 hrs sx onset]
if thrombolytics contraindicated
surgical embolecteomy
percutaneous catheter directed therapy
ECMO
surgical embolectomy → required cardiopulmonary bypass
catheter directed therapy
what are thrombolytics (tPA)?
able to rapidly dissolve embolic burden and improve cardiorespiratory hemodynamics
MOA: activates plasminogen to plasmic which accelerates lysis of thromboemboli
potential comp → hemorrhage
ex: ateplase (activase)
what are absolute contraindications to tPA?
any prior intracranial hemorrhage
known intracranial malformation or neoplasm
ischemic stroke < 3 mo
suspected dissection
recent surgery
recent head trauma
bleeding diathesis
what are relative contraindications to tPA?
age > 75
current anticoagulants
pregnancy
CPR > 10 min
recent internal bleed 2-4 wks
uncontrolled HTN (180/110)
remote ischemic stroke
major surgery w/in 3 wks
what is a surgical embolectomy?
invasive procedure to remove clot; requires cardiopulmonary bypass
indications:
hemodynamically unstable pt
when thrombolysis contraindicated or failed
potential comps → perforation of pulm artery, cardiac arrest, bleeding
what is catheter directed therapy?
infuse thrombolytics directly into pulm artery
clot removal via u/s assisted thrombolysis, suction embolectomy, or thrombus fragmentation
success rate 87%
possible comp → perforating pulm arteries leading to massive hemorrhage or cardiac tamponade
what is venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-A ECMO)?
advanced form of life support used in pts w/ severe respiratory or cardiac failure when conventional tx has failed
can be used for pts w/ massive PE in which thrombolytics are contraindicated
what should all PE patients receive to prevent recurrence?
≥3 mos of anticoagulant tx (up to a year if PE unprovoked or persistent risk factors)
preferred: oral factor Xa inhibitors
Apixaban (Eliquis)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
severe renal insuf: warfarin; monitor PT/INR (goal 2-3)
alt:
LMWH (Lovenox)
Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
what is pulmonary HTN?
elevated pulmonary arterial pressures
inc in mPAP ≥ 20 at rest
pulm cap wedge pressure > 15
MC in women
what are the most frequent causes of pulmonary HTN (PH)?
left heart disease and lung disease
what is group 1 pulmonary arterial HTN?
idiopathic PAH (MC)
inc vascular resistance and blood vessel narrowing w/in pulm vasculature; unknown cause
heritable PAH aka familial or genetic PAH
uncommon; possible molecular/genetic causes
assoc w/ chronic conditions
CT dz, congenital heart dz, chronic liver dz, HIV, drugs, toxins
what is group 2 PH?
d/t left heart disease; assoc w/ impaired exercise activity and reduced survival
what is group 3 PH?
d/t chronic lung dz or hypoxemia; ex- COPD, interstitial lung dz
what is group 4 PH?
d/t pulm artery obstructions; ex- PE
what is group 5 PH?
d/t unclear multifactorial mechanisms; ex- sarcoidosis, sickle cell anemia, thyroid disorders, etc
what is the pathophysiology of group 1 and 2 PH?
inc vascular resistance and blood vessel narrowing occur w/in pulm vasculature
PAH: molecular/genetic changes → hypertrophy of smooth muscle, endothelial cells, adventitia → restricted flow through pulm arts → inc vascular resistance → RV inc filling and SV → inc pulm art pressure
LHD: inc in LA/LV filling pressure → dec compliance of pulm arts promoting stiff pulm vasculature
what are ssx of PH?
progressively worsening dyspnea - typically starts w/ exertion
dull retrosternal CP
dizzy/syncope
fatigue
nonproductive cough
peripheral edema
partner syndrome- compression of recurrent laryngeal n. by enlarged pulm artery
what are PE findings of PH?
dyspnea
sx of RHF
JVD
loud P2
R murmurs (tricuspid regurg)
hepatomegaly
peripheral edema
ascites
what is diagnostic workup for PH?
blood tests: not useful
normal-elevated BNP → marker for RV dysfunciton
normal-elevated LFTs → high hepatic venous pressure
PFTS: assess for obstructive or restrictive lung dz
CXR: eval for cardiomegaly, inc RV size or pulm vascular congestion
ECG: eval sx of LHD, LVH, RAD, RVH, RBBB, etc (normal does not exclude dx)
TTE: noninvasive screening test of choice
pulm art systolic pressure > 40
mPAP of 25
right heart catheterization: measurement of mPAP & PCWP
mPAP > 25 w/ PCWP > 15 = left heard dz
vent/perfusion scintigraphy
high res CT: provide clues of classification and prognostic info
what is the gold standard to confirm dx of PH?
right heart catheterization
what is the goal of tx for PH?
prevent progression and tx underlying dz if present
what are all possible tx for PH?
based on sx and severity
pulm rehab and active physiotherapy
supplemental O2 for hypoxia
diuretics for volume overload
tx for anemia
vasodilators
endothelin receptor antags (ERA) → ambrisentan, bosentan, macitentan
PDE5 inhibitor (PDE5I) → sildenafil, tadalafil
prostacyclin analogue → epoprostenol
guanylate cyclase stimulant (sGC) → riociguat
digoxin: slow vent rate for atrial tachyarrhythmia
CCB: lower PAP and vasc resistance for pts w/ positive vasoreactivity during right heart cath (Nifedipine, diltiazem, amlodipine)
what are pros and cons of epoprostenol (flolan)
Pros:
inc surfactant production
improve V/Q mismatch
reduce pulm vasc resistance
improve RV performance
Cons:
inhibit plt function
short half life- avoid circuit interruptions
what is tx for low or intermediate risk PH (class II-III)?
combo tx ERA and PDE5I
alt: PDE5I and sGC stimulant
what is tx for high risk PH (class IV)?
Trimble combo ERA, PDE5I, and IV prostacyclin analog
what is another name for cor pulmonale?
pulmonary heart
what is cor pulmonale?
alteration in structure and function of RV caused by dz of lung or pulmonary vasculature (PH common link)
what are possible causes of cor pulmonale?
COPD, massive PE (MC acute), PH, interstitial lung dz
what is the MC cause of acute cor pulmonale?
massive PE
what is the pathophysiology of cor pulmonale?
inc PAP → inc RV afterload → RV dilatation and inc RV EDP
RV pressure and volume overload → septal displacement towards LV → dec LV filling volume → dec CO
what are sx of cor pulmonale?
dyspnea on exertion- MC
fatigue / lethargy
exertional syncope
exertional CP
chronic productive cough
what are PE findings of cor pulmonale?
tachypnea
JVD
cyanosis
hepatomegaly
ascites
palpable left parasternal lift
loud S2
systolic murmur of tricuspid regurg
what is the diagnostic workup for cor pulmonale?
CXR: enlarged pulm artery, cardiomegaly
EKG: RAD, RVH, tachyarrhythmias
TTE: RVH, sx of PH
ABG
PFT and 6 minute walk test: assess severity
R heart catheterization: evidence of RV dysfunction w/o LV dysfunction, assess PH severity
Labs:
H/H: eval for polycythemia
ANA: screen for collagen vascular dz
coagulation studies
BNP
what is the gold standard for diagnosis or cor pulmonale?
right heart catheterization
what is the goal of treatment of cor pulmonale?
improve oxygenation and RV function; inc RV contractility and dec pulm vasoconstriction
what is tx for cor pulmonale?
O2 therapy: relieve hypoxemia pulm vasoconstriction
diuretics: dec RV filling volume (caution- can cause hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis)
CCB: lowers pulm pressures
pulm vasodilators: support RV function via dec PVR
prostacyclin analogues- epoprostenol
ERA- bosentan
PDE5I- sildenafil