6.1 risk factors +diagnosis + treatment
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Recent or prolonged antibiotic therapy (especially clindamycin, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems)
Broad‑spectrum antibiotics suppress normal gut flora, removing the microbial “shield” that normally keeps C. difficile in check, and allowing its spores to germinate and multiply.
Age ≥ 65 years
Older adults have naturally less diverse gut microbiota and weaker immune responses, making them more prone to colonisation and severe disease.
Hospitalisation or long‑term care facility stay -
High environmental contamination with C. difficile spores and frequent antibiotic use in these settings increase both exposure and susceptibility.
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or H₂‑blocker use
Gastric acid suppression may let more spores survive passage through the stomach and reach the colon; PPIs are most strongly linked.
Immunosuppression (e.g., corticosteroids, chemotherapy, HIV infection, organ transplant drugs) -
Impaired innate and adaptive immunity reduces the body’s ability to control C. difficile growth and toxin effects.
Gastrointestinal surgery or manipulation (including feeding tubes, colectomy, or endoscopic procedures) -
Surgical stress and altered gut motility disrupt the microbiome and mucosal barriers, raising infection risk.
Previous C. difficile infection -
Prior disease indicates residual spores or an already disrupted microbiome, so recurrence risk is high—about 20–25 % after a first episode.
diagnosis
patients with type 6/7 stool should submit a stool sample for testing
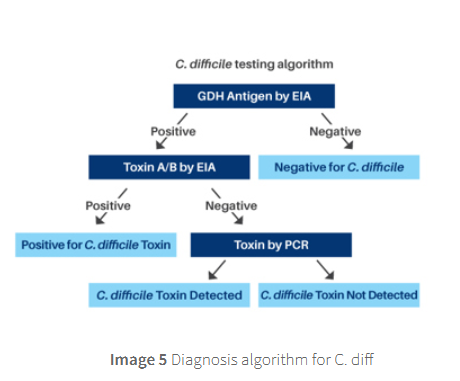
Diagnosis is based on a two‑step test:
glutamate‑dehydrogenase (GDH) or
nucleic‐acid amplification test (NAAT) to screen for the organism → followed by an immunoassay for free toxins (toxin testing) to confirm active disease.
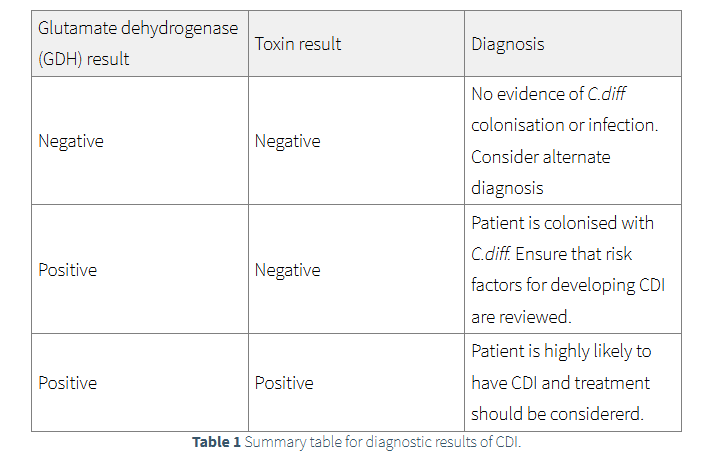
The test for GDH will show if the patient is colonised with C.diff. If the test is negative there is no presence of C.diff and
therefore the patient should not be treated for CDI. An alternative diagnosis should be investigated.
Patients who are GDH positive will then be investigated for toxin A/B through enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Positive results indicate presence of C.diff toxin and treatment is recommended.
Negative toxin EIA and PCR results indicate that CDI is unlikely,
however due to the test not being 100% sensitive treatment of CDI may be recommended and alternative diagnosis considered.
sensitivity
sensitivity refers to the tests ability to correctly identify individuals who have the disease, true positive
treatment
Do NOT recommend loperamide in patients with C.diff or other infectious related diarrhoea.
Use of loperamide can potentially worsen the illness.
While it may reduce the number of bowel movements, it can also prolong the infection and increase the risk of complications like toxic megacolon.
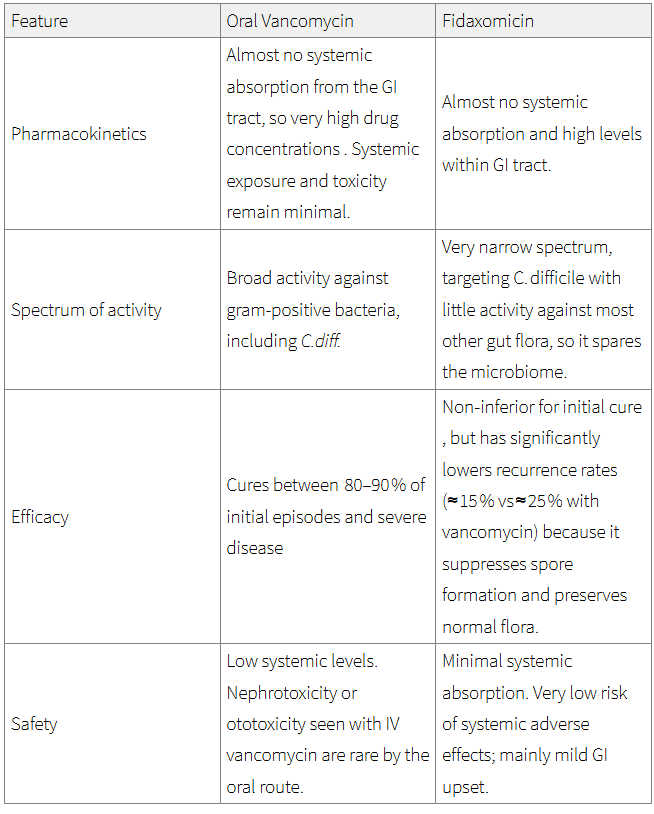
First line - First episode of mild, moderate or severe.
Oral Vancomycin 125 mg four times daily (QDS) for ten days.
Second line - If vancomycin unsuitable or ineffective, or second episode of CDI occurs within 12 week of initial symptom resolution.
Oral Fidaxomicin 200 mg twice daily (BD) for ten days.
Life-threatening CDI
Oral Vancomycin 500mg four times daily (QDS) for 10 days PLUS Intravenous metronidazole 500mg three times daily (TDS) for 10 days.
watch video too