Unit 2 - People in Buisness
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The "what you should know" sections
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Why people work (motivations to work)
Money
Essential income: Money earned to live on
Disposable income: Money earned to spend on luxuries after essential income has been spent on living expenses
Security
Financial security to pay for the goods and services they need now and in the future without worrying about running out
Belonging
Form friendships and have a peer group to share ideas with at work
Personal development
New skills at work or the opportunity to prove themselves by taking on extra responsibilities or through promotion
Recognition
Receive positive feedback from managers => raise self-esteem
The benefits of a well-motivated workforce
Labour productivity
Employees motivated => work harder => increased output => lowers cost of producing goods => increase profit from selling those goods
Reduced absenteeism
Employees happy at work => less likely to take time off for no reason
High level of attendance => more productive
Labour turnover (number of people who leave the organisation in one year)
Employees unhappy at work => leave to find better job => business will have to pay recruitment costs to replace them
Business reputation
Motivated employees => good employer reputation to business => attracts better employees (more productive and need less training, highly skilled employees) => new ideas for the business
Improved workforce relations
Motivated employees => less likely to cause industrial acton
Industrial action causes major problems for business:
Slowing down production => dissatisfied customers =>loss of potential customers to competitors
Maslow’s hierarchy (the concept of human needs)
Believed people are motivation by having their needs met
People start at the bottom of the hierarchy and as each need is met, they move onto the next level
Can help managers provide the right conditions for the needs of their employees to be met
(Most important to least important)
Physiological needs (food, water, clothing, shelter)
Anything needed for survival or to function in daily life
Safety and security needs (job security, security guards, health and safety laws)
Anything that provides physical safety or security
Social needs
Anything that allows ppl to mix, socialise, form friendships and find acceptance
Esteem needs
Anything that allows people to find respect and achievement through the recognition of others
Self-actualisation
Anything that allows someone to fulfil their full potential through the achievement of their personal goals
Benefits:
Simple and easy to understand bc most people can relate to it
Can be applied to a wide range of industries bc most employees wamt similar things
Limitations:
Assumes all needs have to be met in this order (which isn’t always true)
cultural differences between countries => affects the needs of employees
Taylor’s theory
Taylor broke up production into small, simple tasks by using division of labour and had individual employees specialise in those roles (scientific management)
Develop a science for each element of work (understanding the best way for the worker to work productively and efficiently)
Scientifically select, train, teach and develop the worker
Cooperate with the worker
Divide the work and responsibility
He measured their productivity and noticed employees’ output increased when they were offered pay and their output fell when their pay was reduced
Employees are only motivated by money
Benefits:
Reduces the cost of production bc the fixed costs are spread over a wider number of units produced (the more employees output, the less productions costs)
Employees will be motivated to work harder if they feel they can get higher levels of pay
Fewer resources are wasted because employees make fewer mistakes (since their pay is based on output)
Limitations:
Assumes all employees are only motivated by money which isn’t always true
If the employee’s output isn’t measurable, it’s difficult to see if increased pay is motivating them
Sometimes the process of breaking up the job into specialised tasks can become repetitive and boring
Herzberg’s theory
All factors linked to a motivated workforce could be split into 2 groups:
Hygiene factors: factors that will demotivate if they’re not present or taken away but don’t increase motivation if they’re increased
Ex.) Pay, working conditions, supervision, relationships with co-workers, fringe conditions (benefits that employees receive in addition to their salary, such as a company car or access to childcare)
Motivational factors: factors that improve motivation if they are improved or increased
Ex.) Meaningful or challenging work, responsibility, potential for promotion or advancement, good quality training, recognition or achievement
Benefits:
More flexible than Taylorism bc a wider range of factors is considered
Relatively simple to understand => easy for managers to use
Recognises for different people are motivated by different factors
Limitations:
Assumes people aren’t motivated by money which isn’t always true
Doesn’t take into account how the factors that motivate employees can change overtime
Assumes all employees are ambitious for promotion or self-improvement which isn’t always true
1. **Wage:** amount of money to employees based on the amount of work produced
1. **Time-based rates:** a fixed amount of money for each hour they work
2. **Piece-rate system:** paid based on how many units of output they produced
2. **Salary:** a fixed amount of money that is paid to an employee every year, usually split up and paid each month
3. **Bonus:** an amount of money paid to an employee in addition to their wage or salary, usually as a reward for good performance
4. **Commission:** a payment given to __salespeople__, where they receive a percentage of the value of the goods they sell
5. **Profit sharing:** where employees receive an additional payment to their wage or salary when the business they are working for makes a profit
* Don’t involve a cash payment to the employee but in other forms
* Free accommodation/food
* Company car
* Extra holiday time
* Pension schemes
* Healthcare schemes/free health insurance
* Discounts on the products the business sells
* Comfortable or relaxing environments in which to take breaks
* Free training or professional development
* Free access to childcare facilities
* **Benefits:**
* If a business offers more perks => attract more highly skilled employees
* Employees who are given health-related benefits are less likely to take time off
* **Limitations:**
* Offering these benefits generates additional business costs that will not be covered
* The time spent organising the perks could be spent increasing output or productivity => creating an opportunity cost
1. ^^**Job enrichment**^^
1. Employees are given a wider range of tasks at different levels which offer more challenges and usually more responsibility
2. ^^**Job rotation**^^
1. Employees are moved from one task or duty to another for a short period of time to give them more experience and variety in their work
3. ^^**Job enlargement**^^
1. Employees are given a wider range of tasks to complete at the same level of work/Employees are given more variety by expanding the types of work they have to complete
4. ^^**Teamwork**^^
1. Businesses organise employee into teams and give them responsibility for completing a particular task
2. Sometimes done under instruction or close super vision ^^**(working groups)**^^ or done unsupervised ^^**(autonomous working groups)**^^
5. ^^**Training**^^
1. Businesses provide opportunities for their employees to learn new skills
2. Employees may be motivated by the possibility of career development and promotion
6. ^^**Opportunities for promotion**^^
1. Motivates employees by making them feel that their efforts have been recognised and that their work adds value to the business
* **Benefits:**
* Reduces boredom
* Encourages employees to develop new skills => more flexible
* **Limitations:**
* Only works in short term bc of repetitiveness
* Some employees may not want to change jobs/duties
* ^^**Job enlargement**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Gives workforce a variety of skills => more flexible
* Lowers total wage costs for business bc employees handle a wider range of tasks
* **Limitations:**
* Increased costs for business bc employees may require additional training or development
* Employees will have to adjust to their new role => reduced productivity in short term
* ^^**Job enrichment**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Provides employees with work that develops their skills and interests => improved self-esteem
* Reduces the rate of labour turnover and absenteeism (bc of more responsibility and doing more things => not boring)
* **Limitations:**
* Not all employees are interested in developing or moving to the next stage
* Difficult to make jobs more challenges (especially jobs that use highly technical machinery => requires training and experience)
* **Benefits:**
* Encourages employees to mix socially and form friendship groups (=> fulfils Maslow’s hierarchy of needs => more motivation)
* Encourages employees to share ideas and experiences => improves efficiency
* **Limitations:**
* Could result in conflict between team members
* Could allow employees to resist any changes that managers want to implement (especially for autonomous working groups that have more freedom and responsibility for their actions)
* ^^**Opportunities for promotion**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Allows the employees to develop and learn new skills => flexbility
* If employees are interested in promotion, their self-esteem needs will be met
* **Limitations:**
* Only a limited number of promotion opportunities available
* Giving promotions => higher wage costs for the business (bc higher positions mean higher salaries/wages)
* Assumes that all employees are motivated by responsibility which isn’t always true
* **Benefits:**
* More efficient for business bc employees are only paid for the time spent working
* Lowers business costs bc paying for wages is usually cheaper than paying salaries
* **Limitations:**
* Employees may worry about losing their jobs if their output falls
* Employees may reduce the quality of their output to try to produce goods faster (especially for piece-rate)
* ^^**Salary**^^
* **Benefits:**
* More security for employees (less likely to face dismissal or redundancy)
* Easier for businesses to work out what the salary costs will be and plan for them bc it’s a fixed amount
* **Limitations:**
* Employees receiving fixed pay => lose incentive of earning money by producing more output
* Employees often work longer hours than wage workers bc the nature of their work is harder and more complex
* ^^**Bonus**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Employees work harder to earn bonus bc the bonus is linked to the employee output
* If a business has a reputation for rewarding good performance => attract highly skilled employees in the future
* **Limitations:**
* Sometimes businesses can set unrealistic targets to achieve a bonus
* If employees are given a fixed time to receive a bonus, motivation may fall once the target has been achieved (since afterwards there is no motivating factor anymore)
* ^^**Commission**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Employees more motivated to sell bc their pay is linked to their productivity
* Easier for managers to assess the performance of salespeople bc their pay can be used to measure and compare their performance
* **Limitations:**
* Salespeople may feel like they’ll lose their jobs if their sales are too low
* Salespeople may be encouraged to use aggressive sales methods to get customers to buy => damage the brand
* ^^**Profit-sharing schemes**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Employees more willing to accept managers’ decision because they’re aiming to improve their standard of living
* If a business offers a profit-sharing scheme => attract highly skilled employees
* **Limitations:**
* Profit to shareholders is reduced
* Employees may be demotivated when they see the scheme as unfair bc the profits are distributed equally rather than based on effort or contribution
1. ^^**The cost to the business (costs, time, productivity)**^^
1. Additional payments made to employees in the form of financial motivators and some non-financial motivators will increase costs for businesses like in training
2. Others, such as job design, have indirect costs in terms of lost productivity
2. ^^**Type of job role**^^
3. ^^**The employees**^^
1. Employees are individuals => motivated by different things
2. ^^Best to consider several different alternatives^^
4. ^^**The impact on efficiency**^^
1. Businesses need to consider whether the short-term loss of efficiency or the short-term costs will be offset by the long-term gains in productivity or revenue
5. ^^**External pressures**^^
1. The different stakeholders external of the business can affect the motivation strategy the business chooses
* ^^**Flat:**^^ short chain of command and few levels of hierarchy, sometimes wide span of control
* **Benefits:**
1. Easier to communicate as the chain of command is shorter => fewer mistakes
2. Employees are given more responsibility => improve motivation
* **Limitations**
1. Possibility of mistakes are employees are unsupervised and working independently
2. Less chance of promotion
* ^^**Tall:**^^ long chain of command and several levels of hierarchy
* **Benefits:**
1. More managers => supervising workforce easier
2. Employees may be motivated by the chance of promotion
* **Limitations**
1. More difficult communication bc of longer chain of command
2. More managers’ salaries have to be paid which tend to be higher
1. ^^**Levels of hierarchy:**^^ Each level represents a level of management
2. ^^**Chain of command:**^^ the route by which authority is passed down an organisation from the most senior manager to those with no subordinates through **delegation**
1. ^^**Short & Long**^^
3. ^^**Span of control:**^^ the number of subordinates a manager will supervise directly
1. ^^**Narrow**^^
* **Benefits:**
1. Less need for training as employees are more closely supervised
2. Closer supervision => less waste and higher quality of work
* **Limitations:**
1. Communication & decision-making is often slower bc more managers are involved
2. More expensive bc a greater number or managers are required
2. ^^**Wide**^^
* **Benefits:**
1. Fewer managers/supervisors => less expensive
2. Less supervision => improve employees’ motivation
* **Limitations:**
1. Fewer managers and supervisors => fewer opportunities for promotion
2. Less control over subordinates’ work => more mistakes and wasted resources
1. ^^**Directors:**^^ highest ranking managers
* In limited companies, they are employees who employed by the chief executive and voted in by the shareholders. In private limited companies, they may be the owners or shareholders of the business
* **Duties:**
* Lead the business
* Decide on the strategy of the business
* Set the objectives that must be met to achieve the strategy
* Meet with the shareholders at the AGM (for public limited companies)
* Plan for the future growth of the business
* Manage employees in their own span of control
2. ^^**Managers:**^^ responsible for the day-to-day running of a functional area, department or possibly a whole section of the business
* They are specialists who ensure that the objectives of the business are met
* **Duties:**
* Achieve the objectives or targets set by senior management
* Manage and motivate employees in their span of control
* Deal with any problems
* Provide directors with information to develop strategies for the future
3. ^^**Supervisors:**^^ responsible for monitoring the work of subordinates
* Their role is to monitor and check the work of individuals and assign tasks based on the instructions given to them by managers (delegation)
* **Duties:**
* Receive instructions or targets from management
* Ensure that employees complete the work they are given and the targets are achieved
4. ^^**Other employees:**^^ not involved in the main activities of a business but work in areas providing support
* Ex.) administrators, IT support, cleaners, maintenance, and security staff
* **Duties:**
* Complete roles that support the production of goods and services
* Work towards targets set by management
1. ^^**Planning**^^ (looking at the current position of the business and identifying where it wants to be, then developing a strategy for how that is going to be achieved)
2. ^^**Coordinating**^^ (the process of bringing resources together to enable the business to produce goods and services)
* In particular, the business’s human resources need to be brought together, instructed correctly and monitored in the most motivating way possible
3. ^^**Organising**^^ (managers making sure they use their time effectively to complete their work and organising the resources of the business as efficiently as possible to keep costs low)
4. ^^**Commanding**^^ (having the respect of their workforce => able to direct the staff on how they are expected to perform while maintaining staff motivation)
5. ^^**Controlling**^^ (making sure that all employees are working hard and all tasks are completed on time and are of high quality)
* ^^**The correlation between trust and control**^^
* __The positive correlation:__ If a manager trusts their subordinates, then they are likely to delegate tasks to them, giving up some of their control
* __The negative correlation__ is between the level of control they have in their employees and how much managers are prepared to delegate
* **Benefits:**
* Reduces management stress and workload
* Allows senior management to focus on key tasks
* Subordinates are empowered and motivated
* **Limitations:**
* There are some situations where managers cannot/should not delegate responsibility
* Dependent on the quality/experience of subordinates
* Harder in a small firm
* May increase workload and stress of subordinates
1. ^^**Autocratic:**^^ leaders make all the decisions and don’t involved the employees
* Communication is one-way and delegation is not used
* Common in emergency situations where a fast decision is often needed (ex. fire service & military)
2. ^^**Democratic:**^^ leaders involved employees in decision-making
* Communication is two-way and delegation is sued
* Managers encourage employees to share ideas
3. ^^**Laissez-faire:**^^ managers allow employees complete freedom in how they complete the tasks
* Managers set the tasks and deadlines but completely delegate the process of completing the task to the employees and don’t get involved
* **Advantages:**
1. Employees may feel secure bc they don’t need to think for themselves
2. Fast decision-making
3. Good in crisis or emergency situations
* **Disadvantages:**
1. Demotivating bc employees are not given the chance to express their ideas, making them feel unimportant
2. Could lead to staff wanting to leave the company if they feel they can’t make suggestions
^^**Democratic leadership:**^^
* **Advantages:**
1. Employees may feel more motivated bc their ideas are being listened to
2. More efficient as specific skills and experiences are being used => more cost-efficient than the managers’ own ideas
3. Managers may be able to use their time more effectively bc they can delegate some of the tasks
* **Disadvantages:**
1. Could result in no decision being reached if there is too much conflict with employees
2. Can be demotivating if the manager takes credit for the employees’ ideas
3. Decision-making will take longer => inefficiency
^^**Laissez-faire leadership:**^^
* **Advantages:**
1. May create motivated employees who can make their own decisions
2. Allows the workforce to approach the tasks in their own way =>more innovation & new ideas
3. Promotes trust in the workforce => more efficient leadership
* **Disadvantages:**
1. Lower productivity bc employees have no supervision
2. Poorer quality bc there is less supervision (mistakes are less likely to be picked up)
3. employees may not have sufficient knowledge to manage their tasks efficiently
* Usually represents employees within the same industry and employees can choose to become a members
* By forming a trade union, the members/employees can increase their power by working as a group with ^^**collective bargaining**^^ (bargaining with management for better pay or working conditions)
* Resolves conflicts between managers and employees by acting as a ‘neutral third party’ and to help the employees and managers to reach a final decision (process called ^^**arbitration**^^)
* ^^**The effects:**^^
* **Positive:**
* Having access to collective bargaining => motivate employees (bc they have more job security if they’re apart of a group) => more productivity
* Employees would be motivated by having their social needs met (Maslow’s hierarchy of needs) (bc by being a member of a union, employees can become part of a peer group which would allow the sharing of ideas)
* As being a union member gives employees greater job security, it can lower labour turnover => reduce labour and recruitment costs in the long-term
* **Negative:**
* Trade unions have more power to demand higher wages => pushing costs up for businesses => force businesses to lose profits or raise prices
* Industrial action can generate bad publicity
* If there is a dispute, union members may stop producing goods => lowering output => limiting the amount of goods and services available to customers => makes business seem less competitive
* **Benefits:**
* Cheaper since there are no costs involved in advertising
* Managers already know the skills of the employees
* Can save time as external recruitment can take several weeks
* Employees are motivated by the possibility of promotion
^^**External recruitment:** employees are employed from outside the business to fill a vacancy^^
* **Benefits:**
* Attract potentially stronger selection of candidates
* Candidates can bring in fresh new ideas
* Doesn’t create vacancies that need to be filled in other parts of the business
* Doesn’t create conflict (internal candidates don’t become demotivated if not chosen)
1. **Vacancy is identified**
* ^^**Job analysis:**^^ the process of identifying a vacancy and the duties involved
2. **Skills needed are identified**
* **Job design:** the process of identifying the skills, qualities and roles needed to complete a job
3. **Job description is produced**
* ^^**Job description:**^^ a document listing the roles and duties of an employee
4. **Job specification is produced**
* ^^**Job specification:**^^ a document listing the skills, qualities and qualifications an employee is expected to have (aka **person specification**)
5. **Job is advertised**
* The advert often includes a summary of the main duties and responsibilities, as well as the key skills and qualifications needed
6. **Applications are received and shortlist is created**
* ^^**Shortlisting:**^^ the process of a business identifying which potential employees (candidates) it wants to put forward for selection
7. **Selection takes place**
* ^^**Selection:**^^ the process of choosing the most suitable candidate for a job
1. ^^**Interview**^^ (either be one-to-one or involve a panel of several people)
2. Job-related tasks (candidates completing one of the duties that they would.be expected to complete in the job)
3. ^^**Psychometric tests**^^ (tests of language, math, logic to assess how likely it is that a candidate will learn and develop new skills in the workplace)
4. Presentation (candidates are asked to give a presentation to assess their understanding of the job and their communication skills)
8. **Vacancy is filled**
1. **Cost**
* Business will want to employ the best candidate while keeping costs low
* If the candidate has more experience, they can command a higher salary => higher costs
* If the candidate has no experience, it might require training => increase costs in the long term
2. **Skills and experience**
* Candidates with more experience and skills are more expensive in the short term but can lead to greater efficiencies for the business => long term: higher output & possibly cost savings in the future
3. **The job roles**
* Some jobs require a detailed knowledge of the business => internal candidates would be more suitable
* Other job roles might require specific skills => require external recruitment
* **Benefits:**
* More motivated or less tired than full-time employees => more productive
* Attract greater variety of part-time staff => increases the skills and experience of the workforce
* Average cost of a part-time employee is lower than a full-time employee
* Employees are more flexible => easier for business to cover busy periods or meet increased demands
^^**Full-time employees:** an employee who works, on average, 35 hours (or more) per week^^
* **Benefits:**
* Likely to become more familiar with the business => more productive
* More likely to be loyal to the business => less costs bc business doesn’t need to hire more people in the future
* Fewer employees are needed => costs of hiring and training are lower
* Communication is easier bc they spend more time in the business and will likely receive the information
* **Benefits:**
* Employees understand the requirements of the job and the business => improved efficiency
* Employees feel settled into the organisation quicker => reduced labour turnover
* **Limitations:**
* (Short term) Employees spending time in training => not producing goods or services => output is reduced
* (Long term) Employees are being trained by staff who may pass bad habits onto them => efficiency & quality problems
* ^^**Work shadowing:**^^ employees observe and learn from a more experience member of staff
* ^^**In-situ training:**^^ employees complete their tasks under the supervision of a trainer
* ^^**Computer-based training:**^^ software is used to teach specific skills to employees in the workplace
* **Benefits:**
* Employees are working throughout the training programme => no loss in productivity
* Employees are trained by existing members of staff => fewer costs
* **Limitations:**
* New employees not fully learnt the skills required => less productive
* Training is dependent on the level of instructions given by other employees which may not always be of high quality
* **Benefits:**
* Employees are trained by experts who are familiar with the most efficient and modern industry methods => increases productivity
* Current employees are not required to teach trainees => doesn’t limit productivity
* **Limitations:**
* External businesses are involved => higher costs
* Employees don’t get hands-on experience within their workplace => fewer practical skills being learnt
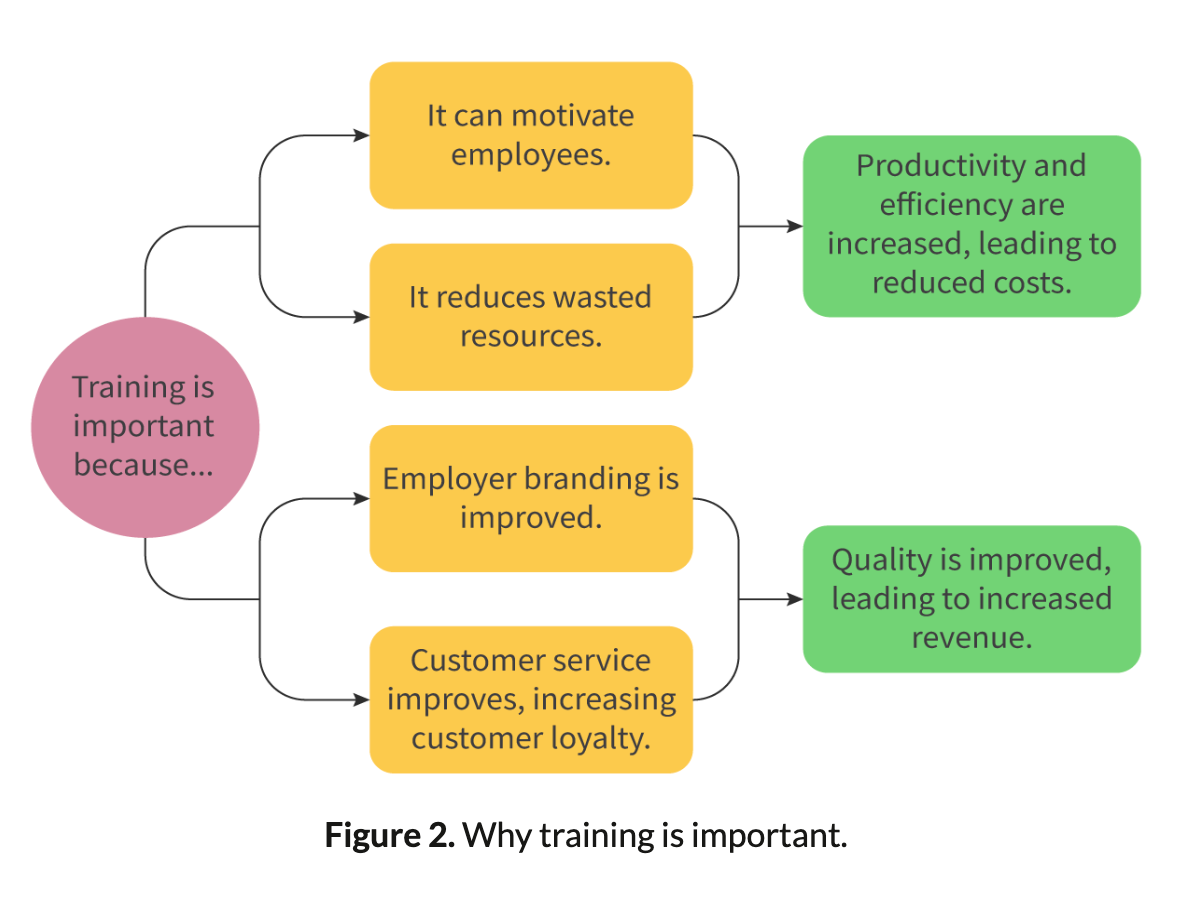
1. **Upskilling the workforce**
* New skills => improve quality of finished products and increase their added value
2. **Improving employee efficiency**
* Employees develop their job-related skills => fewer wasted resources
3. **Improving employer branding**
* Employees are attracted to businesses with good training programmes
4. **Increasing employee motivation**
* Employees are likely to be more motivated if they feel appreciated and valued by the business
1. *Resignation*
* *The employee volunteers to leave the organisation, usually to go to another job*
2. *Retirement*
* *Employees leave the business after they’ve reached a certain age*
3. ^^**Redundancy**^^
* ^^Employees are asked to leave to __save costs or improve the productivity__^^
* As a result the employee is paid some form of compensation (redundancy pay) after employee leaves as the job doesn’t exist
4. ^^**Dismissal**^^
* ^^The employee is asked to leave because their __behaviour is unreasonable/they cannot do the job__^^
1. **Improve efficiency**
* Owners might want to reduce the number of layers of the organisational hierarchy in order to increase the speed of decision making
2. **Closure**
* Either the whole business closes (for example, due to bankruptcy) or the manager closes part of the business to save costs
3. **Automation**
* Managers decide to replace people with machinery to reduce costs or improve efficiency
4. **External events**
* Changes in the external environmental can force the business to make people redundant (for example, a downturn in the economy)
* **Impact on employees:**
* Provides job security
* If employer fails to deliver part of the contract, such as holiday benefits, the employees can sue using a grievance procedure
* **Impact on employers:**
* Improve job security lowers labour turnover => reduces recruitment costs
* If employee doesn’t fulfil part of their contract, the employer can legally dismiss them => productivity is not negatively impacted
* ^^**Unfair dismissal (when the business asks the employee to leave but the conditions for this is unfair)**^^
* **Impact on employees:**
* If an employees is dismissed unfairly, they can take their employer to an industrial tribunal and may receive compensation
* If employees don’t need to worry about an unfair dismissal => more secure & motivated
* **Impact on employers:**
* If an employer is taken to an industrial tribunal => high compensation costs & damage employer branding
* Employers have to keep more detailed and accurate records of employee performance => lowering managers’ efficiency
* ^^**Discrimination (the process of treating one individual or individuals less favourably than others based on a characteristic or difference that’s perceived as negative)**^^
* **Impact on employees:**
* Employees must receive equal treatment and equal pay
* Employees would be recruited based on their merits, not on discrimination => increases motivation
* **Impact on employers:**
* Equal pay may mean the employer has to increase wages => higher costs
* As employers recruit based on merit => employer branding increases
* Includes the provision of safety equipment, protection from dangerous machinery, suitable hours of work and hygienic conditions
* **Impacts on employees:**
* A safe & clean environment => motivating for employees
* Employees will require additional training for any extra safety features they’re expected to know about
* **Impacts on employers:**
* A safe & clean environment => attract higher skilled employees
* Extra safety equipment => additional capital investment + increased costs
* ^^**Minimum wages (protections to make sure employees could afford to live on these wages, improving their standard of living)**^^
* **Impact on employees:**
* Low-paid employees will earn more money => have more disposable income and a higher standard of living
* Some employees might campaign to close the wage gap => trade union activity
* **Impact on employers:**
* A set minimum wage will increase the wage costs for the business => forces business to raise prices
* Businesses will try to retain staff to minimise costs
* Employees are kept informed about decisions that are made or changes that are happening => employee motivation improves bc they’re taken into consideration
* Enables faster decision making + improves customer service => business more competitive bc they’re able to react to the market faster => increases market share
* **Benefits:**
* Quick & easy to write and send
* The sender can add a "‘read receipt’ to the email so they know when the receiver has read it
* **Limitations:**
* Some people may not check their emails on a regular basis => not respond quickly
* Can be used too often and ignored
^^**Fax (written → electronic)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Quick and easy to send a paper copy of a document
* Very fast
* **Limitations:**
* Not all businesses have a fax machine
* Faxes can be unreliable (i.e. problems with the phone line)
* Often replaced by email
^^**Report (document, written)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Specific to the research topic
* Format is often easy to read and understand
* **Limitations:**
* Time-consuming to research and write
* Often contains a lot of information that is difficult to summarise
^^**Letter (written)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Important way to passing information onto staff and customers
* Copies of the same letter can be sent to multiple people => saves time
* **Limitations:**
* May contain errors => be used against the business
* Not guarantee the stakeholder has read it
* **Benefits:**
* Allows people to discuss their concerns and opinions and ideas
* Decisions can be made very quickly
* **Limitations:**
* Could be dominated by some people => others’ opinions may not be heard
* Can be time-consuming and not always lead to an outcome
^^**Advertisement (visual, electronic)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Can be creative and fun => improves brand image
* Can attract new customers
* Useful for recruiting staff
* Using the right media can catch stakeholders’ attention quickly
* **Limitations:**
* Expensive
* May not be actioned by some stakeholders
* People may see the advertisement but not pay attention to it
^^**Video (call) (visual, electronic)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Direct and almost as effective as face-to-face communication
* Cheap to use
* **Limitations:**
* Time zones will be different => issues with planning
* Requires good quality technology which isn’t always available
^^**Social media (electronic)**^^
* **Benefits:**
* Can be seen as innovative
* Quick, efficient and specific
* Can be accessed by many people quickly
* Can create a positive brand image
* **Limitations:**
* An age gap (older generations are less likely to use social media so the business is less likely to reach these stakeholders)
* Requires internet access which in some areas is not always possible
1. Urgency
2. Cost
3. Complexity of message
4. Available technology
5. Need for feedback
1. Message could be received in the receiver’s **second language**
1. Business could translate the message using a specialist agency or automated translation software if the message is communicated electronically
2. Message could be t**oo long**
1. Message should be brief as possible or broken up into several shorter messages
3. Receiver may not understand the message bc of **complex or technical language & use of jargon**
1. The sender should ensure that the message uses language that is simple and easy to understand
2. The sender should allow opportunity for feedback and for the receiver to ask questions
4. **Noises** can prevent the sender or receiver from understanding the message
1. The message needs to be transmitted in a quiet environment or a written format should be used
5. There may be **long distance** between sender and receiver which causes problems with face-to-face communication
1. Electronic forms of communication (such as video calls) can make it easier to communicate over long distances
2. Planning for time zones should be taken into account
1. If there is a **poor relationship between the manager and employee**, there may be **no trust** and the employee may not believe what is being communicated to them + they may not fully listen to the message
1. Management need to change their style or take action to build trust and show that they are listening to the employee
2. **Management may choose a medium they’re comfortable with but the employees may not be familiar with** (i.e. technology)
1. Regular updates and training need to be offered to employees
2. A range of different methods should be used
3. If the organisational structure is too complex, the __**message will have to go through too many people**__ => change message or distort message before it reaches the receiver
1. The management could consider using delayering or delegation to ensure that the message is passed through fewer people