Bio A-Level PPQs
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Describe the role of a ribosome in the production of a polypeptide. Do not include transcription in your answer. [3]
- mRNA binds to ribosome
- Idea of two codons
- (Allows) tRNA with anticodons to bind
- (Catalyses) formation of peptide bond between amino acids
- Moves along (mRNA to the next codon)
Describe the structure of glycogen. [2]
- Polysaccharide/polymer of a-glucose
- (Joined by) glycosidic bonds
OR branched structure
Suggest how glycogen acts as a source of energy. [2]
- Hydrolysed (to glucose)
- Glucose used in respiration
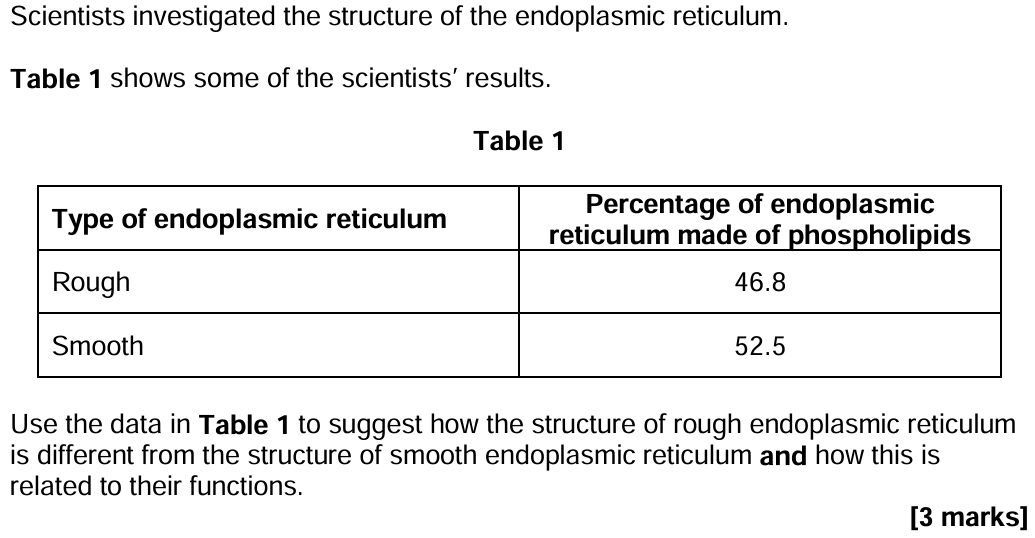
Suggest and explain two ways the cell-surface membranes of cells lining uterus may be adapted to allow rapid transport of nutrients. [2]
- Membrane folded so large surface area
OR
Membrane has larger surface area for (fast) diffusion - Large number of protein channels/carriers for active transport
- Large number of protein carriers for active transport
- Larger number of protein (channels/carriers) for co-transport

- Co-transport
- Uses ATP
- Sodium ion and proton bind to protein
- Protein changes shape (to move sodium ion and/or proton across membrane)
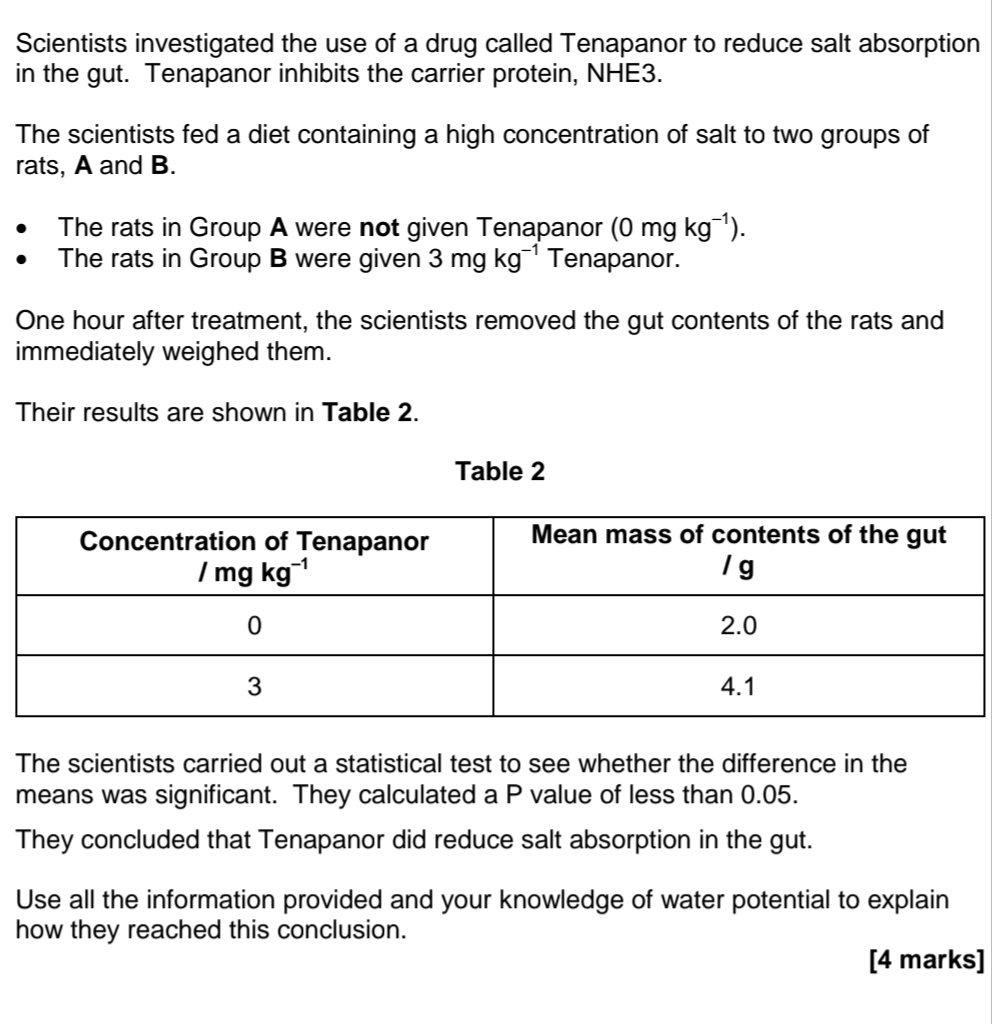
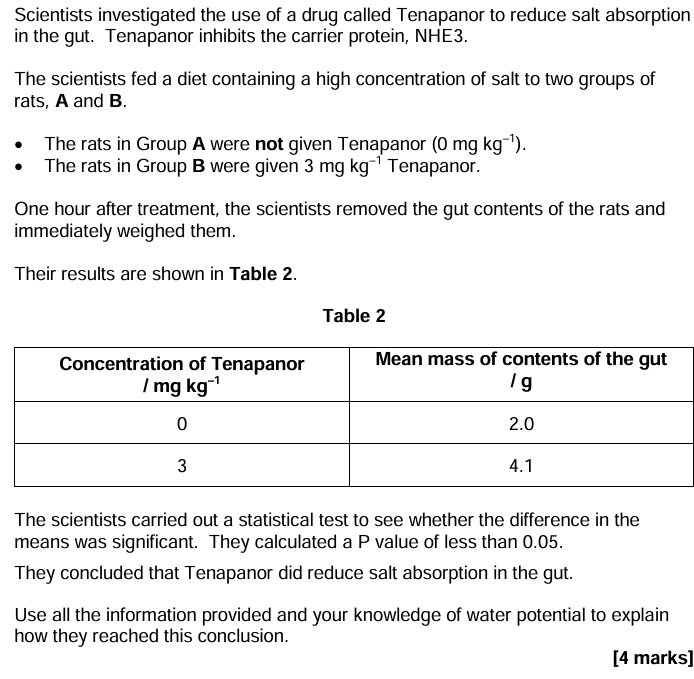
- Tenapanor/Group B causes significant increase
- Less than 0.05 probabilty that results are due to chance
- (More salt in gut) reduces water potential in gut (contents)
- (so) less water absorbed out of gut (contents) by osmosis
OR water moves into gut (contents) by osmosis
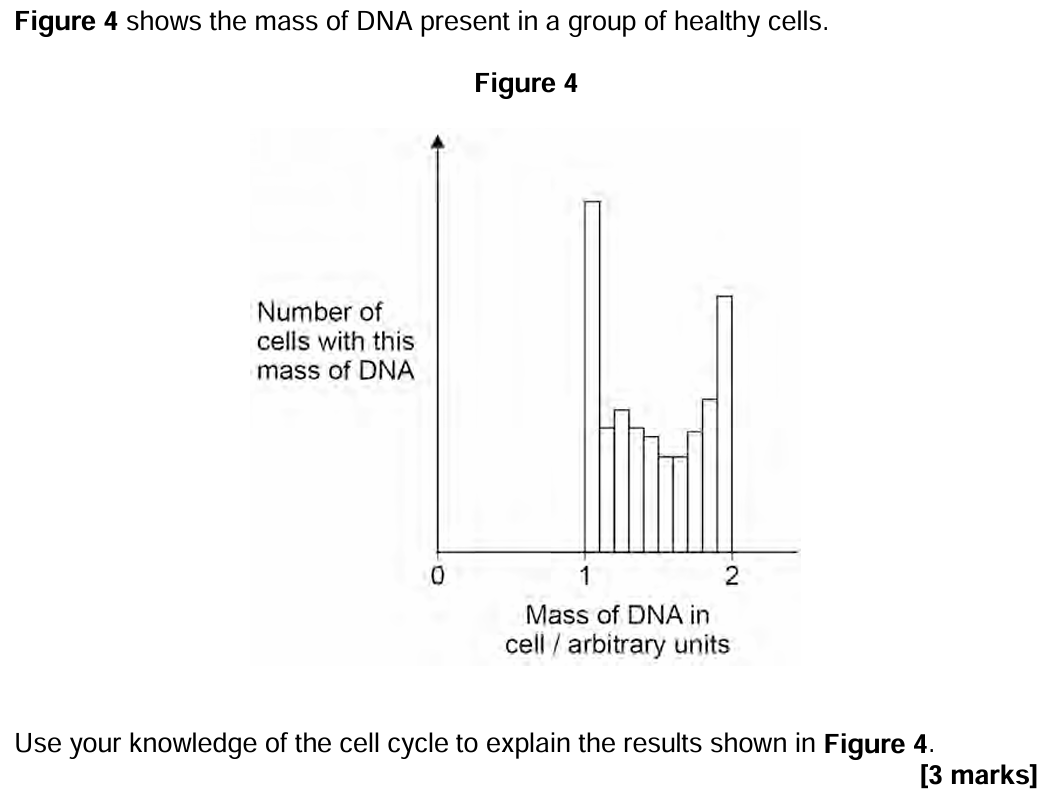
Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in xylem. [5]
- Water lost from leaf via transpiration / Water evaporates from leaves
- Lowers water potential of mesophyll/leaf cells
- Water pulled up xylem (creating tension)
- Water molecules cohere/'stick' together by H bonds
- (forming continuous) water column
- Adhesion of water to walls of xylem
Student wants to determine rate of water loss per mm2 of surface area of the leaves of a shoot (in a potometer).
Outline a method to find this rate. Assume that all water loss from shoot is from the leaves. [3]
- Method for measuring surface area of (all) leaves e.g. draw around each leaf on graph paper and count squares
- Of both sides of (each) leaf
- Divide rate of water loss by total surface area of leaves
Rate of water movement through shoot in potometer may not be same as movement through shoot of whole plant.
Suggest one reason why. [1]
Plant has roots
OR
Xylem cells very narrow
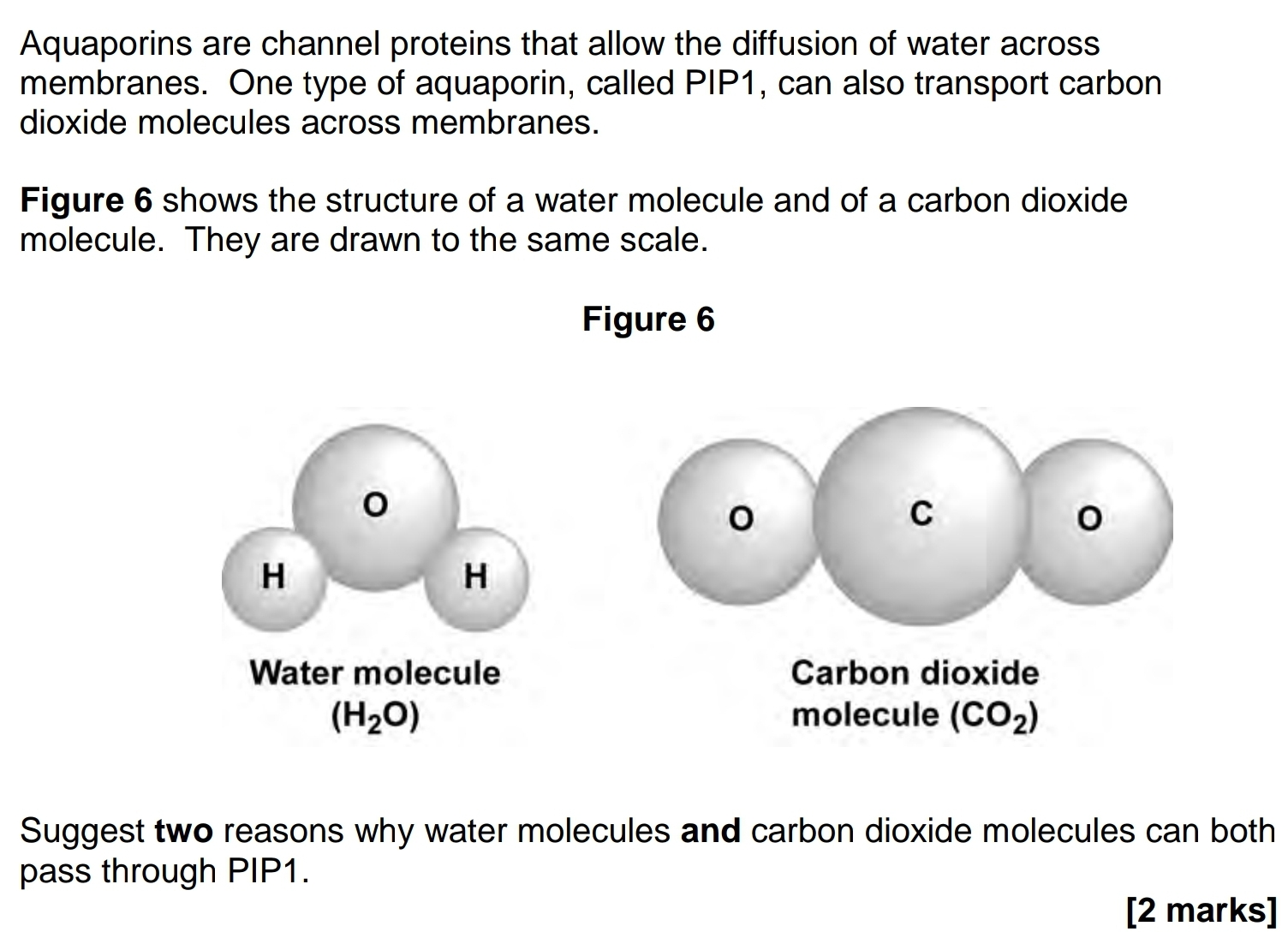
- Both small/similar size
- Have similar shape

- Single-stranded RNA complementary (base sequence) to PIP1 mRNA
- Binds to mRNA (of PIP1)/leads to destruction of mRNA
- Prevents/reduces translation (of PIP1)
- Reduces photosynthesis that uses water
Transgenic poplar trees (with inhibited PIP1 production) still produce some PIP1, why? [1]
Not all mRNA destroyed/disabled
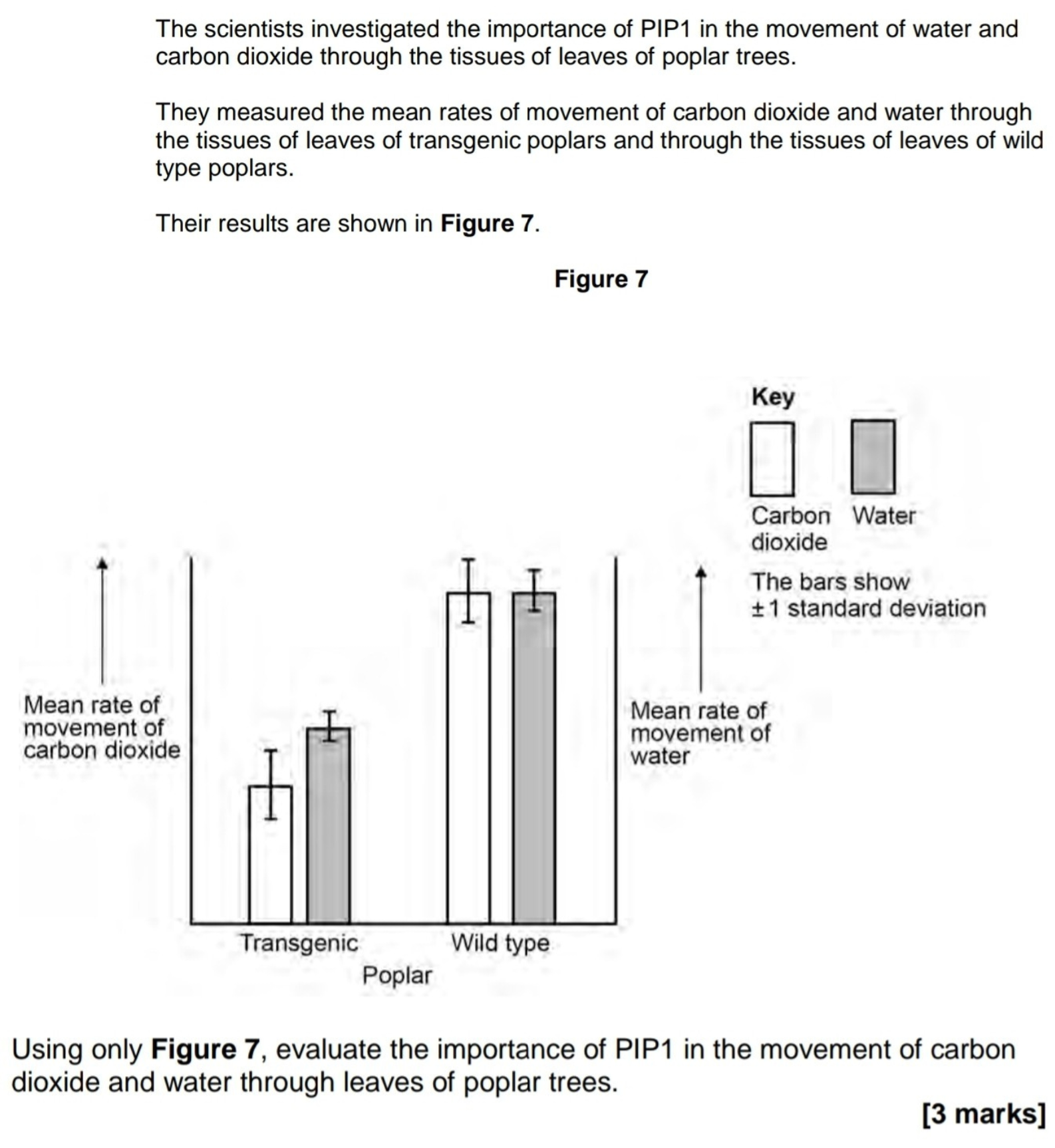
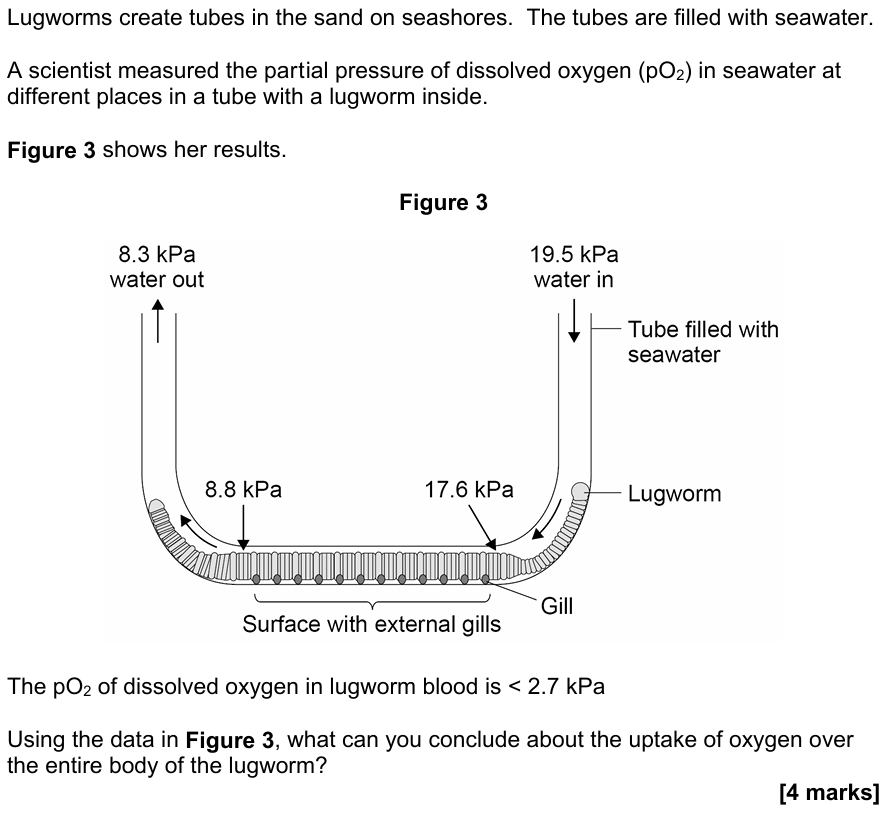
- Loss of PIP reduces water and carbon dioxide movement
- Differences significant because SDs don't overlap
OR
Need stats test to see if differences significant - Greater effect on carbon dioxide transport
- Not all movement through PIP (so there's still some water and carbon dioxide movement)



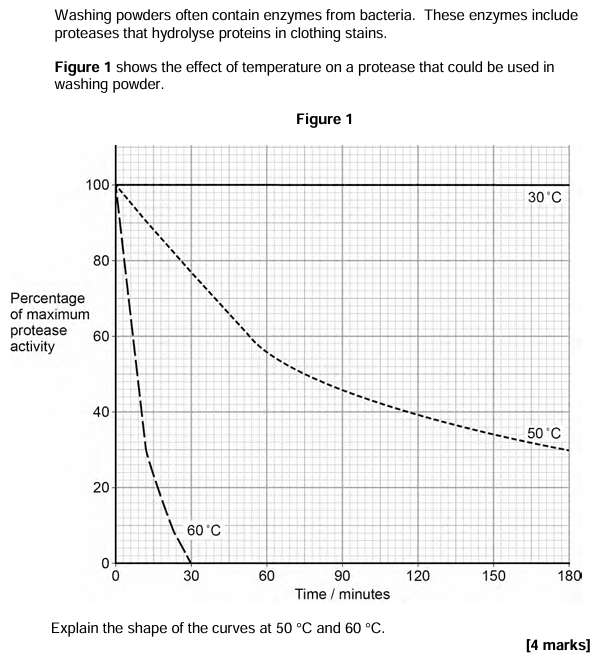

















Lignin is a polymer found in the walls of xylem vessels in plants.
Lignin keeps the xylem vessel open as a continuous tube.
Explain the importance of the xylem being kept open as a continuous tube. [3 marks]
(Allows unbroken) water column
OR (So) no barrier to (water) movementCohesion from H bonds between (all) water (molecules)
OR cohesion from (polar) attraction between (all) water (molecules)Evaporation/transpiration creates tension (in column)
OR Water moves from xylem (into cells) creates tension
OR (To) pull up water creates tension (in xylem);
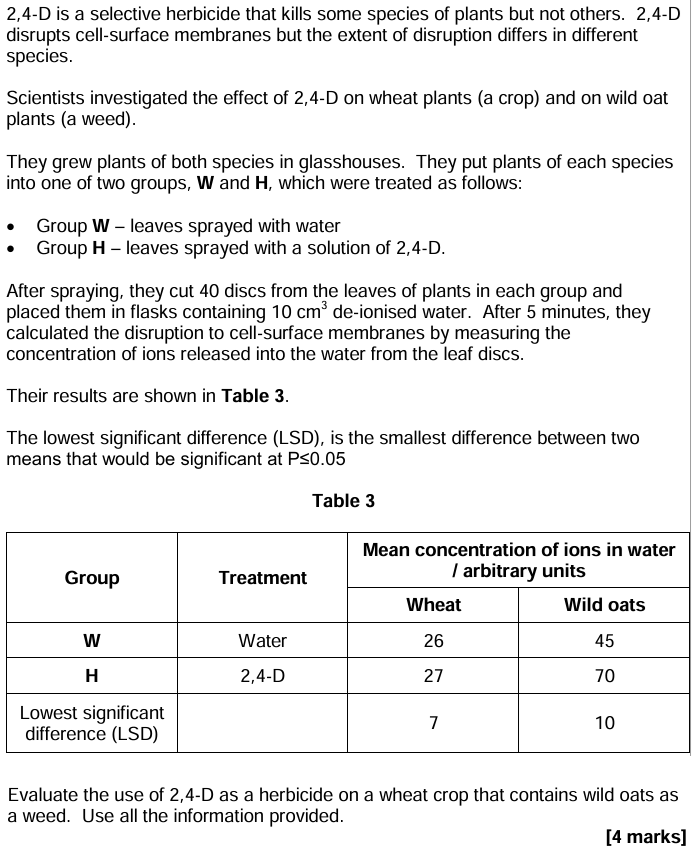
A student investigated the use of cinnamon oil as an antimicrobial substance.
She investigated the effect of cinnamon oil on the growth of five different bacterial cultures grown on agar plates.
The student added 100 mm3 of each bacterial culture from its glass bottle onto a separate agar plate.
She spread each bacterial culture evenly over the agar using a spreader.
Describe the aseptic techniques she should use. [3 marks]
Wash hands with soap
OR Disinfect surfacesUse sterile pipette/syringe (to transfer bacteria)
(Remove bottle lid and) flame neck of bottle
Lift lid of (agar) plate at an angle
Work close to upward air movement
Use sterile spreader
Place pipette/spreader into disinfectant (immediately after use);
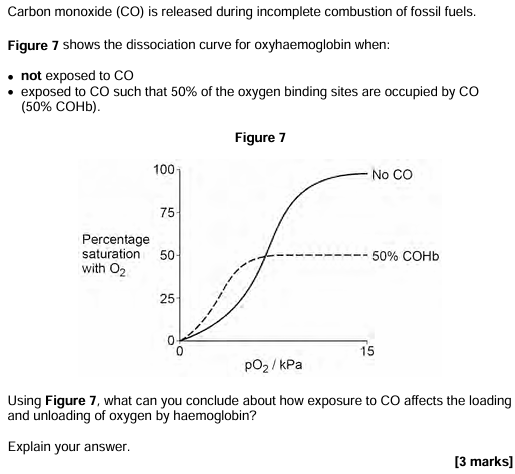

MiTMAB acts as a non-competitive inhibitor of an enzyme called dynamin.
Suggest how MiTMAB can cause dynamin to become inactive. [3 marks]
(MiTMAB) binds (to dynamin) other than the active site
Changes the shape of (dynamin) active site
Not complementary so substrate does not bind
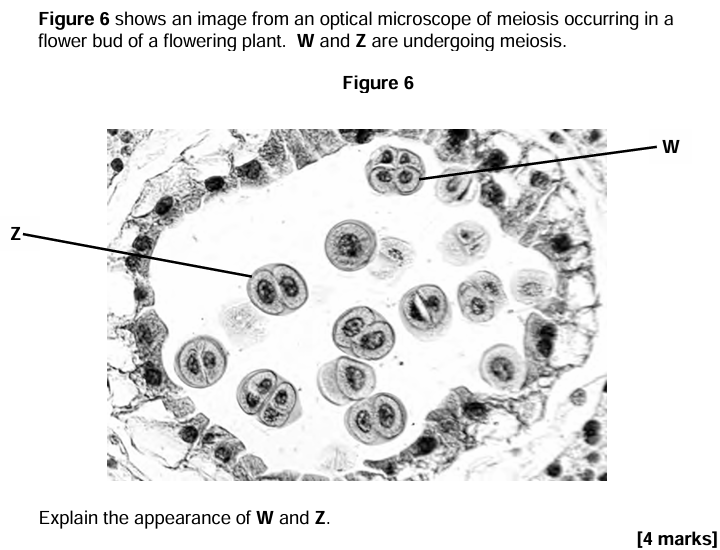
This question is about the genetic code.
Define universal, non-overlapping and degenerate. [3 marks]
(Universal) The same codon/triplet always codes for the same amino acid
(Non-overlapping) Codons/triplets do not overlap
OR Each base is only part of one triplet(Degenerate) More than one triplet codes for each amino acid
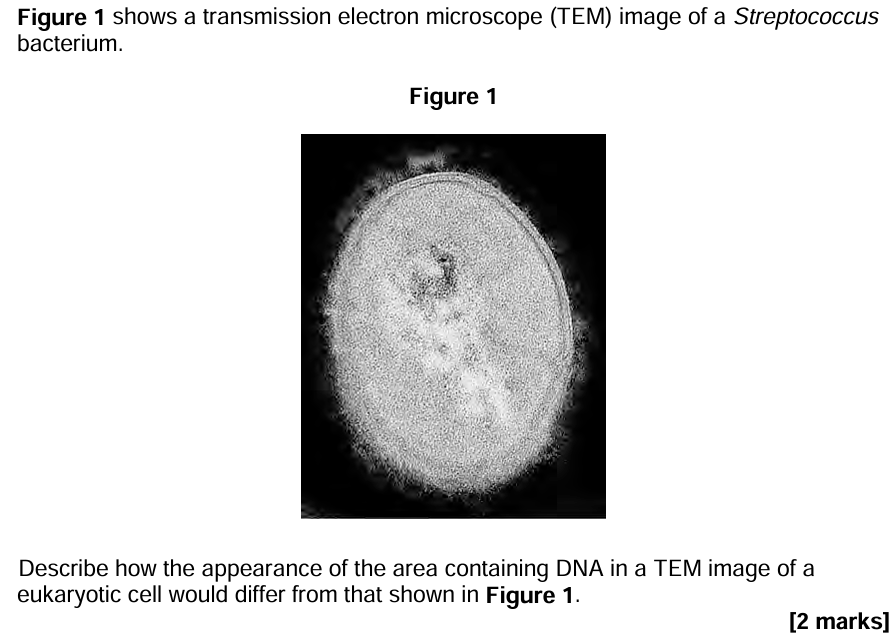
Nucleus
Nucleolus/nucleoli
OR Nuclear membrane/envelopeMitochondria/chloroplast contain DNA

(Thicker capsule so phagocytes) less likely to bind to murein (in cell wall)
OR (Thicker capsule so phagocytes) less likely to be stimulated by murein (in cell wall)Reduced phagocytosis so more bacterial growth / division / binary fission
Explain why phospholipids can form a bilayer but triglycerides cannot. [3 marks]
Phospholipid both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
OR Phospholipid polarTriglycerides only hydrophobic
OR Fatty acid/triglyceride is non-polarHydrophilic/phosphate group attracts water (to either side of bilayer)
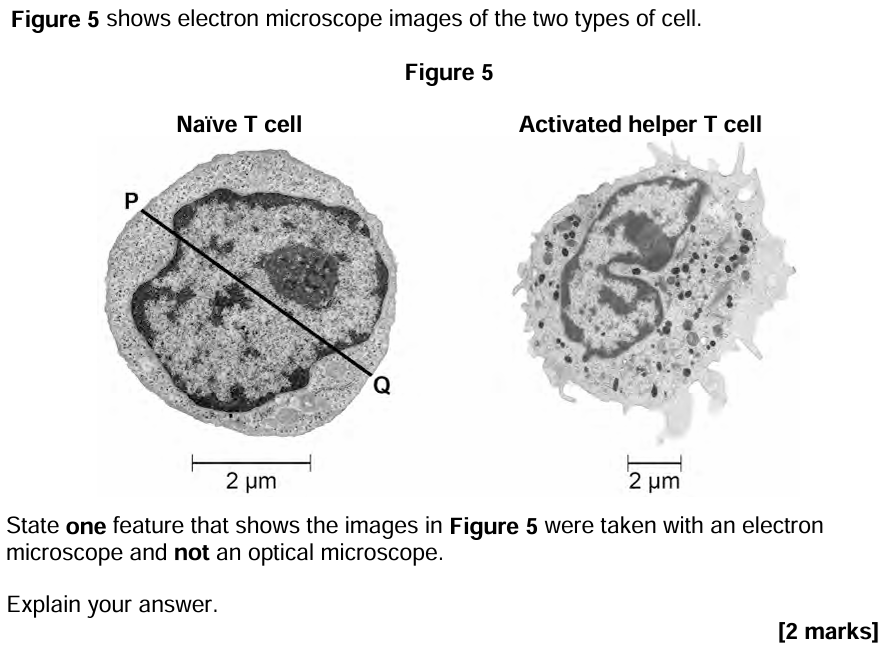
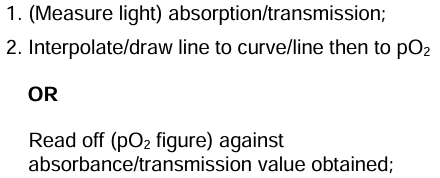
Nuclear membrane /nucleolus /vesicles/ lysosomes/ribosomes distinct/visible
EM has greater resolution
The DNA-replication enzymes of a human cell make copies of the human papilloma virus genome.
Name two enzymes that are involved in replicating the DNA of the human papilloma virus and describe their roles in the replication process. [3 marks]
(DNA) helicase and (DNA) polymerase
(Helicase) breaks hydrogen bonds (to unwind DNA)
(Polymerase) condensation reactions to join (adjacent) nucleotides
OR (Polymerase) forms phosphodiester bonds between (adjacent) nucleotides
A student prepared a plant root to observe cells undergoing mitosis.
He put the root in a small bottle of hydrochloric acid in a 40 °C water bath.
Why did he put the plant root in acid? [1 mark]
To break down cell wall
OR To stop mitosis/cell division/cell cycle
State two precautions required when working with hydrochloric acid. [2 marks]
Eye protection
Gloves
Add water to spills (immediately)
Do not pour away down sink;
During exercise, there is a significant increase in the glucose uptake by muscle cells.
Give two reasons why glucose uptake by muscle cells increases significantly during exercise.
Explain your answers. [4 marks]
Increased respiration
To provide more ATP for muscle contraction
(More glucose being used so) concentration gradient for glucose
OR Increased numbers of glucose transporter proteins in the membrane(Glucose enters by) facilitated diffusion