Comprehensive Skin Disorders & Infections: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is the primary function of the skin?
Acts as the first line of defense, prevents fluid loss, controls body temperature, and synthesizes vitamin D.
What are the three main layers of the skin?
Epidermis, Dermis, and Subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis).
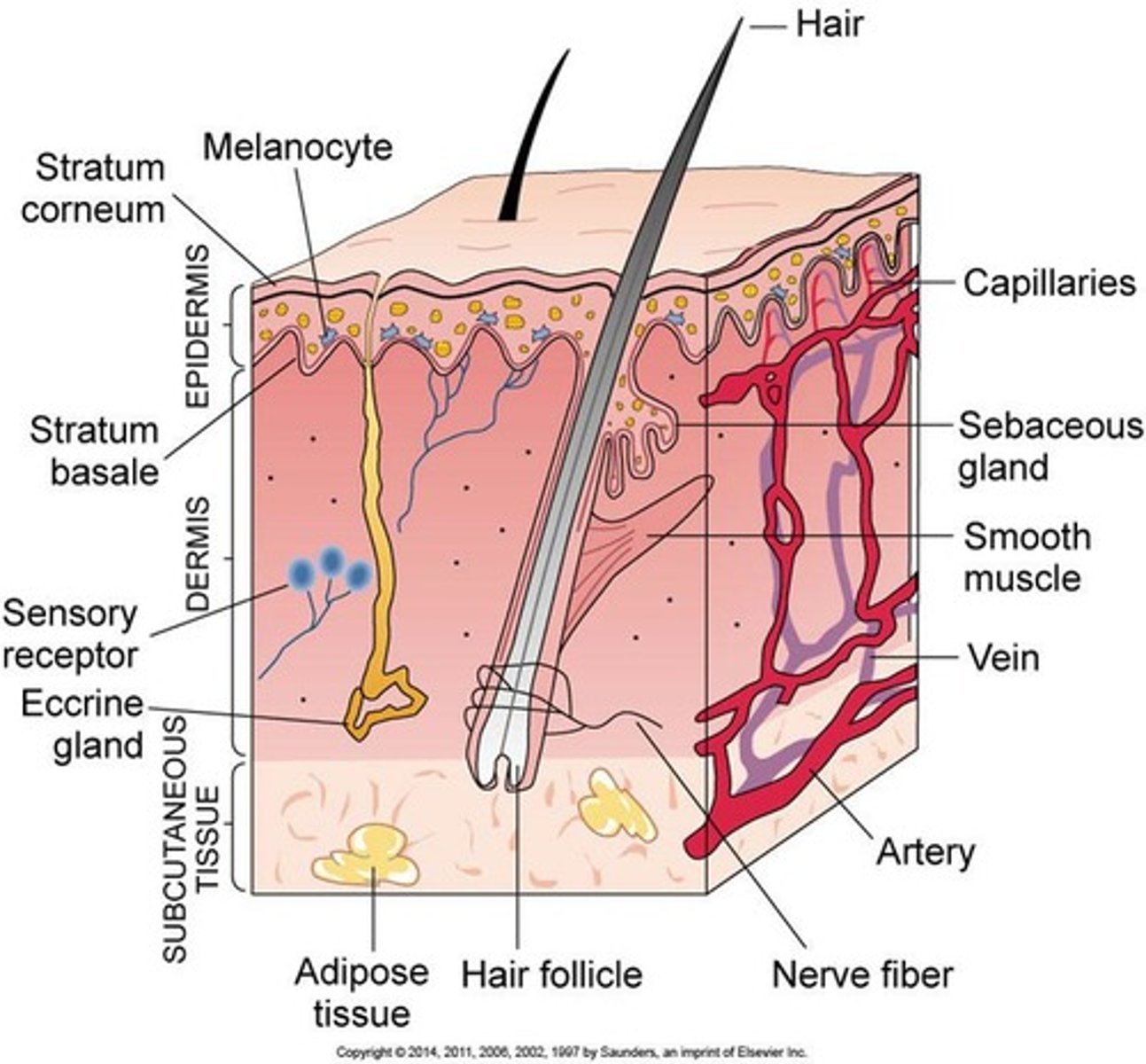
Which layer of the epidermis is responsible for mitotic activity?
Stratum basale.
What begins in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis?
Keratin formation.
What is the role of the dermis?
Contains connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and sensory receptors for pressure, touch, pain, heat, and cold.
What are the appendages of the skin?
Hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands.
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
Produce sebum, with secretion increasing at puberty.
What is albinism?
A condition characterized by a lack of melanin production.
What is vitiligo?
A condition that causes small areas of hypopigmentation.
What is the significance of skin lesions?
Their physical appearance is necessary for diagnosis and may indicate systemic disorders or localized factors.
What is pruritus and what can cause it?
Itching associated with allergic responses, chemical irritation, or infestations by parasites.
What is contact dermatitis?
An inflammatory reaction caused by exposure to an allergen or irritant.
What are the signs of allergic dermatitis?
Pruritic, erythematous, and edematous areas often covered with small vesicles.
What is urticaria (hives)?
A type I hypersensitivity reaction characterized by raised, itchy lesions.
What is atopic dermatitis (eczema)?
A chronic inflammatory skin condition often associated with allergic rhinitis and asthma.
What are common treatments for atopic dermatitis?
Elimination of aggravating agents, topical glucocorticoids, and antihistamines.
What is seborrheic dermatitis?
A chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting areas with active sebaceous glands.
What is psoriasis?
A chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by silvery plaques and increased keratinocyte proliferation.
What are the signs of pemphigus?
Blisters in the oral mucosa and skin that are painful but not pruritic.
What is scleroderma?
An autoimmune disease that causes thickening of the skin and can affect internal organs.
What is cellulitis?
An infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, usually caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus.
What are common signs of cellulitis?
Redness, swelling, pain, and possible red streaks along lymph vessels.
What is the treatment for bacterial skin infections?
Systemic antibiotics are often required.
What is the role of culture and staining in diagnosing skin lesions?
To identify bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections.
What triggers the release of histamine in urticaria?
An IgE-mediated response to allergens.
What are the characteristics of chronic urticaria?
Lasts more than 6 weeks and is not mediated by IgE.
What is the primary treatment for severe urticaria?
Corticosteroids, especially when airway inflammation is present.
What is the common appearance of psoriasis?
Silvery plaques with an erythematous base and possible joint involvement.
What are the potential complications of atopic dermatitis?
Secondary infections due to scratching.
What is folliculitis?
An infection that begins at hair follicles.
What are common areas affected by skin infections?
Face, neck, legs, axillae, and back.
What is a furuncle?
A painful nodule that develops into a large abscess.
What is a carbuncle?
A collection of furuncles that coalesce to form a large infected mass.
What are the signs of a skin abscess?
Firm, red lesions that produce large amounts of purulent exudate (pus).
What is the treatment for a skin abscess?
Warm compresses, analgesics, and surgical drainage if necessary.
What is impetigo?
A common infection in infants and children caused by S. aureus and group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
What are the signs and symptoms of impetigo?
Small red vesicles that enlarge, rupture, and form yellowish-brown crusts.
How is impetigo treated?
Topical antibiotics in early stages and systemic antibiotics for extensive lesions.
What is acute necrotizing fasciitis?
A severe infection causing inflammation and tissue necrosis, usually caused by group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus.
What are systemic manifestations of acute necrotizing fasciitis?
Fever, tachycardia, hypotension, mental confusion, and possible organ failure.
What is the treatment for acute necrotizing fasciitis?
Aggressive antimicrobial therapy, fluid replacement, and excision of infected tissue.
What causes leprosy?
Mycobacterium leprae.
What are the clinical signs of leprosy?
Flat lesions, nerve damage, and potential loss of limbs.
What is varicella-zoster virus (VZV) commonly known as?
Chickenpox.
What are the initial symptoms of chickenpox?
Fever, fatigue, runny nose, headache, cough, and sore throat.
How does chickenpox spread?
Via respiratory droplets or direct contact with blister fluid.
What is herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) associated with?
Cold sores.
What is the primary symptom of herpes simplex infections?
Painful vesicles that rupture and crust over.
What virus causes warts?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) types 1-4.
What is tinea capitis?
An infection of the scalp, common in school-age children.
What is tinea pedis commonly known as?
Athlete's foot.
What is the treatment for tinea infections?
Topical antifungal medications or oral antifungal medications for severe cases.
What is scabies?
An infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei that causes intense itching.
What are the types of lice affecting humans?
Pediculus humanus corporis (body louse), Pediculus humanus capitis (head louse), and Pediculus humanus pubis (pubic louse).
What do female lice do after mating?
They lay eggs (nits) on hair shafts.
What are seborrheic keratoses?
Benign lesions associated with aging or skin damage, appearing as oval elevations that may be smooth or rough.
What is actinic keratosis?
A skin lesion caused by sun exposure, appearing as a pigmented, scaly patch that may develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
What are warning signs of skin cancer?
A sore that does not heal, changes in lesions, new moles, and skin lesions that bleed or itch.
What are guidelines to reduce the risk of skin cancers?
Limit sun exposure, wear protective clothing, stay in shade, use sunscreen, and protect children from sun damage.
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
A painless malignant tumor of the epidermis, often found on sun-exposed skin, with an excellent prognosis if treated early.
What is malignant melanoma?
A highly metastatic skin cancer that develops from melanocytes or a nevus, characterized by multicolored lesions with irregular borders.
What are the classifications of burns?
Superficial (first-degree), partial-thickness (second-degree), and full-thickness (third and fourth-degree) burns.
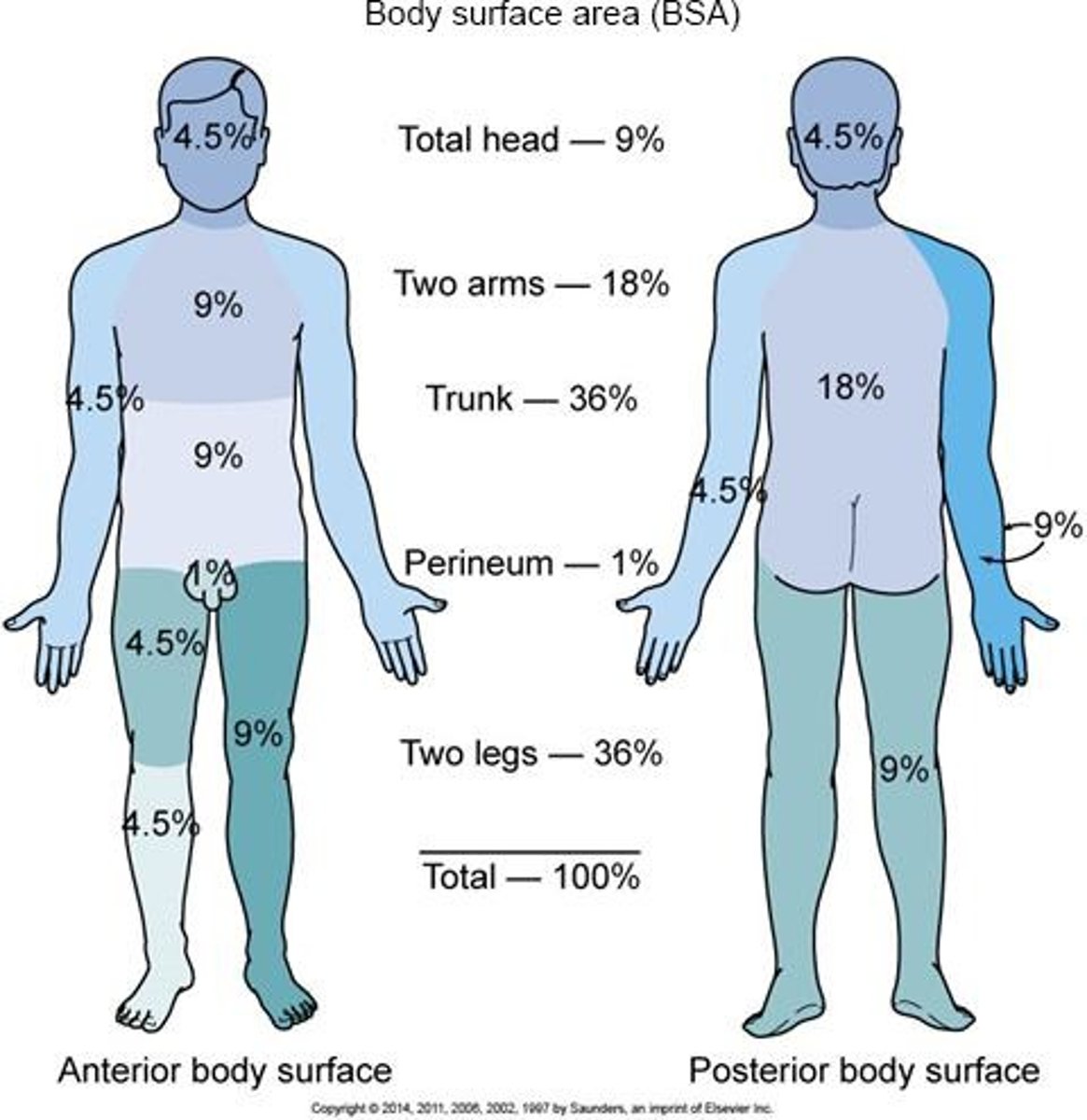
What is the Rule of Nines used for?
To assess the total body surface area affected by burns.
What are the effects of burn injury?
Dehydration, edema, shock, respiratory problems, pain, infection, and hypermetabolism during healing.
What is the healing process for burns?
Requires immediate wound covering to prevent infection, can be prolonged, and may involve scar tissue development.
How does burn injury affect children?
It can compromise their growth and metabolic needs, requiring additional surgeries or grafts.
What is hypermetabolism in burn healing?
An increased metabolic rate that occurs during the healing period after a burn injury.
What is the role of physiotherapy in burn recovery?
To help with rehabilitation and to manage scar tissue development.
What are excoriations in the context of lice infestations?
Skin abrasions resulting from scratching due to itching caused by lice bites.
What is the prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma if treated early?
Excellent, especially if the lesion is removed in a reasonable time.
What are the characteristics of malignant melanoma?
It often appears as a rapidly growing, multicolored lesion that may bleed and change in shape, color, or texture.
What is the significance of nits in lice infestations?
Nits are the eggs laid by female lice, indicating an active infestation.