AE 279 Energy and Environment Midterm 3.1, 3.2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a conduit and what are some examples?
A conduit refers to a channel or pipe through which a fluid or energy flow is directed, often with the purpose of maintaining a specific temperature or energy transfer.
Examples include pipes, ducts, nozzles, diffusers, valves, one side of a heat exchanger, etc.
True or False. A decrease in the mechanical energy of the flow is accompanied by an increase in the fluid’s thermal energy.
True!
What is a heat exchanger?
It is used to intentionally transfer heat from a higher T fluid to a lower T fluid while keeping the fluids separate. The HT occurs across the heat exchanger surface.
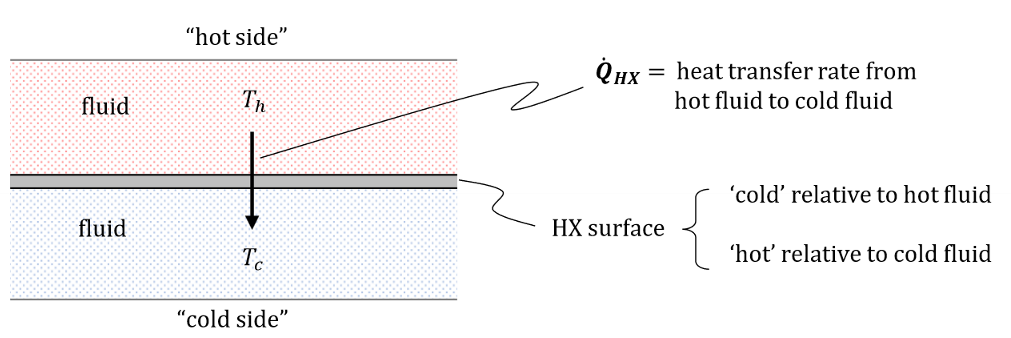
Define refrigeration.
Refrigeration is the traditional term for the process f moving heat from a lower T location to a higher T location.
What is a vapour compression refrigeratio cycle?
A vapor compression refrigeration cycle is a thermodynamic process used to transfer heat from a low-temperature space to a higher-temperature space, essentially creating a cooling effect. This is referrd to as a means fo refrigeration even though it is often used for heating.
What is a refrigerator? What is a heat pump?
Refrigerator if its purpose is to cool.
Heat pump if its purpose is to heat.
What is a coefficient of performance? COP?
COP is a measure of efficiency (ie beneft/cost)
What is a simple vapour compression refrigeration cycle?
A simple vapor-compression refrigeration cycle is a process that uses a refrigerant to transfer heat from a low-temperature area to a high-temperature area, cooling the low-temperature area.
It involves four main components: two heat exchangers (evaporator and condenser) and two components causing △P and △v (compressor and expander)
The system creates the conditions that allow heat to be absorbed from a colder location and released to a warmer location.
What is a compressor?
Recieves low P and T (high v) and compresses it to a higher P and T (lower v)
What is a expander?
High P liquid refrigerant (on edge of vapour dome is allowed to expand (increase v) as it emerges from the expander restriction. Its thermodynamic state drops into the vapour dome. The fluid flows out as a saturated mixture at low P and T.
What is a evaporator?
Heat is transferred from th eheat source to a refrigerant. Refrigerant h increases and saturated liquid evaproates (ie boils to a vopir) .
What is a condenser?
Heat transferred from refrigerant to sink. Refrigerant h decreases and it condenses.