Wallace Dental Assisting Midterm
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
What are the phases mouth opening and movement of the TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint)
Jaw open = Hinge
Jaw wide open = Glide and Hinge movement
Which of the following is the second phase in mouth opening of the TMJ
Glide
What are sharp containers
A “trash can” for contaminated needles, scalpel blades, orthodontic wires or endodontic instruments
What are the qualities that make a sharp container
All the answers are correct
Who is responsible for laundering contaminated PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
The employer or laundry service
What is the space between the teeth and the inner mucosal lining
Oral vestibule
What nerve is the primary source of innervation in the oral cavity
Trigeminal nerve (5th cranial nerve)
What bone forms the cheekbones
Zygomatic bone
What are some materials that surface barriers are made of
All the answers are correct
What are most surface barriers made of
Plastic
What are critical instruments
Instruments that touch bone or penetrate soft tissue
What are examples of critical instruments
Forceps
Scalpels
Bone Chisels
Scalers
Burs
What are semi-critical instruments
Instruments that touch the mucous membranes but won't touch bone or penetrate soft tissue
What are examples of semi-critical instruments
Mouth mirrors
High volume evacuator (HVE) tips
Rubber dam forceps
X-ray film holders
Amalgam carriers
What are noncritical instruments
Instruments that make contact only with intact skin
What are examples of noncritical instruments
Position Indicator Device (PID) of the X-ray
Lead apron
Curing lights
What kind of instruments should be heat sterilized
Both critical and semi-critical
What instruments do not need to be heat sterilized (disinfestation/basic cleaning is sufficient enough)
noncritical
What are the four types of tissue that make up the teeth
Enamel
Dentin
Pulp
Cementation
What part of the tooth does the enamel make up
Anatomic crown
Is enamel the hardest material in the body
Yes! (Lara yes)
What tissue makes up the main portion of the tooth function
Dentin
What is the pulp of a tooth
Contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue
What is the purpose of the cementum
To protect the root of the tooth AND join the enamel of the CEJ (cementoenamel junction)
What tissues make up the periodontium
Cementum
Alveolar Bone
Periodontal ligament
IN THIS EXACT ORDER
What teeth make up anterior teeth
Incisors and canines
What are the tooth numbers for anterior teeth
#6 - 11 and #22 - 27
What teeth makes up the posterior teeth
Premolars and molars
What are the tooth numbers for posterior teeth
#1 - 5, #12 - 16 and #17 - 21, #28 - 32
What are the reasons why instruments are wrapped/packaged before sterilization
All the answers are correct
What is the work pattern to sterilizing instruments
Dirty
Clean
Contaminated
Pre-Clean
Storage
What are the seven steps for instrument processing
Transport
Cleaning
Packaging
Sterilization
Storage
Delivery
Quality Assurance Program
What is a soft tissue exam
A complete examination involving the:
Lymph Nodes
Neck
Cheeks
Lips
Mucosa
Palate
Tonsil Area
Tongue
Floor of the mouth
What is a oral cavity exam
Examination of the teeth and mouth
What is an extra-oral exam
An examination of large areas of the jaw or skull
What is a dental exam
Gathering and recording specific components of:
Head and neck examination
Soft tissue examination
Examination of the teeth AND periodontal tissue
Diagnostic radiographic and imaging
Impressions to create a diagnostic cast/model
Photographs
(All the previous exams combined)
What is detection
Discovers problems/imperfections via explorer
What is palpation
The examiner’s hands are used to examine texture, size, and consistency of hard and soft tissue in the mouth for any abnormalities (via fingers)
What is probing
he examination of the gum pockets around the teeth using a thin, calibrated instrument called a periodontal probe to measure the depth of the pockets and assess gum health (via periodontal probe)
What is the only way to determine that sterilization has occurred
Biological monitoring (spore testing) is the only approved way to confirm whether sterilization has occurred
What is a sub-supine position
The patient’s head is lower than the feet
What is an upright position
90 degrees (or a right angle/sitting in a chair normally)
What is a supine position
The chair back is lowered until the patient is almost lying down
What is an elevated position
The patient is standing (literally standing straight)
What determines the position of the dental chair
Specific dental procedure '
Area of the mouth
What is done in the reception area of the dental clinic
Patients are received, pleasantly greeted, and feel welcomed at the dental office
Patients “wait” for their scheduled appointment
What is done in the dental lab
Used to pour impressions
Prepare study models
Polish removable items (like dentures or space maintainers)
What is done in the general office of a dental clinic
Aka business office
Hub for management of the business side of dentistry
Scheduling area
Financial and insurance arrangements
Patient record storage
What is done in the dental operatory of a dental clinic
Also known as treatment rooms
Heart of the clinical area
Where patients receive treatment (or operate on)
Who developed the standard classification system used to describe the location of decay
G.V Black (aka father of modern dentistry)
What color indicates that a dental treatment has been treated
Blue or black ink
What color represents indicates that dental needs to be completed in future dental appointments
Red ink
What critical information is needed before providing dental treatment
Comprehensive medical and dental history
What is necessary when recording vital signs
Sphygmomanometer
Thermometer
Stethoscope
How is the mouth mirror and explorer delivered to the dentist
Two hand exchange
What hand is used to retrieve dental instruments from a dental tray
Left hand (if I am working with a right handed dentist aka also me)
What is an HVE and what is it used for
High-volume evacuator
Basically a suction that sucks out saliva, blood, water, and debris
Why is a rubber dam isolation most commonly used for
Isolating teeth that needs to be worked on
Most common for root canals
What follows examination instruments on the tray setup?
Hand (Manual Cutting Instrument)/Tooth Prep Instruments
What follows hand (manual) cutting instruments on the tray setup.
Restorative instruments
What follows restorative instruments on the tray set up.
Accessory instruments/items
Why are mouth mirrors used?
Retracting of the mouth
Reflecting light
Enhanced visibility
Magnifies hard to reach area views
Illumination
What are prophy angles (also called prophylaxis angle)
An attachment used for coronal polishing procedures
What is a prophy angle attached to
Low-speed dental handpiece or slow handpiece
Why is dental radiography used in a dental office
Detects dental decay in early stages
Identifies bone loss in early stages
Locates abnormality in surrounding hard and soft tissues
Evaluates growth and development
Documents the condition of a patient at a specific time
Obtains info during a dental procedure
What are some ways operators can protect themselves from radiation exposure
Radiation monitoring
Personnel monitoring
Equipment monitoring
What is an example of personnel monitoring for radiation exposure
Film badge (pocket dosimeter) which measures the amount of occupational exposure
What proper equipment is used to prevent occupational exposure to radiation
All the answers are correct
Radiopaque images appear as
White/light gray
Radiolucent images appear as
Black
What are examples of radiopaque images in a radiograph
Metal
Enamel
Dense bone
What are examples of radiolucent images in a radiograph
Airspace
Soft tissues
Dental pulp
Black areas of a radiograph are usually
Airspace
White areas of a radiograph are usually
All the answers are correct
Gray areas of a radiograph are usually
Soft tissue
What is density of a radiograph
The overall blackness of darkness of a film
What are some factors that could affect the density of a radiograph
Amount of radiation reaching the film
Distance from x-ray tube to the patient (length of the PID)
Processing of dental film using conventional film
Patient’s body size
What is contrast of a radiograph
Images on the radiograph that appear in ranges of black, white, and gray
What are examples of contrast imaging
Radiopaque images
Radiolucent images
What agency requires a written privacy policy
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
What is topical anesthesia
local numbing method that deadens nerve endings on the skin's surface by applying a gel, cream, spray, or other form of anesthetic directly to the area
What is local anesthesia
a medication that temporarily blocks pain in a small, specific area of the body by preventing nerves from sending pain signals to the brain
What is infiltration anesthesia
Injects anesthetic solution into the tissue near the apices of the tooth being treated
(smaller surface area)
What is block anesthesia
Injects anesthetic near a larger terminal nerve area, numbing a larger surface area
(larger surface area)
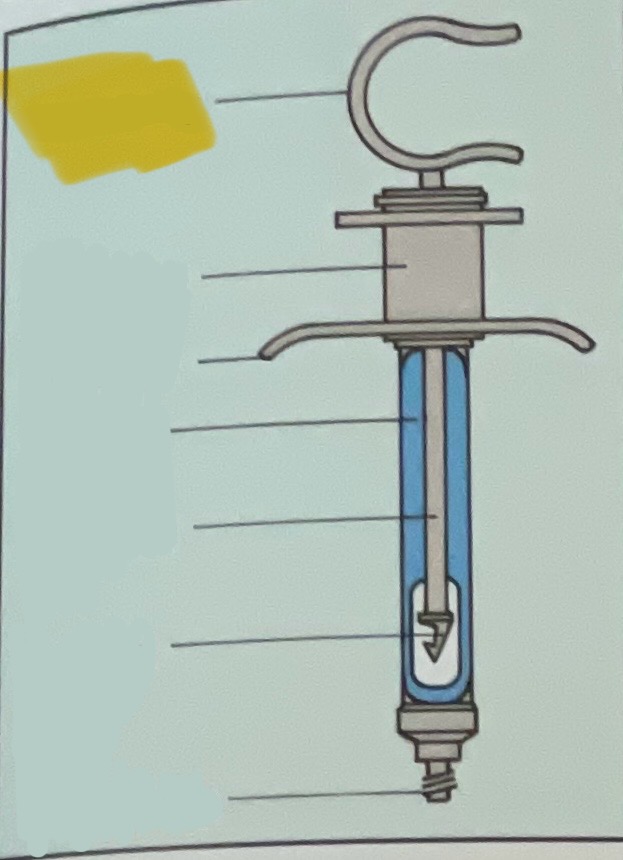
Thumb ring
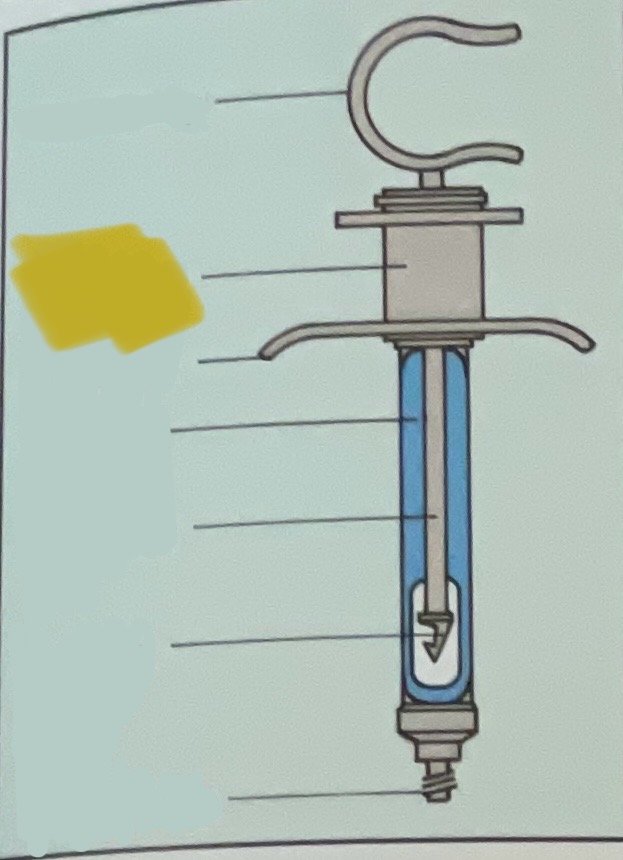
Finger grip
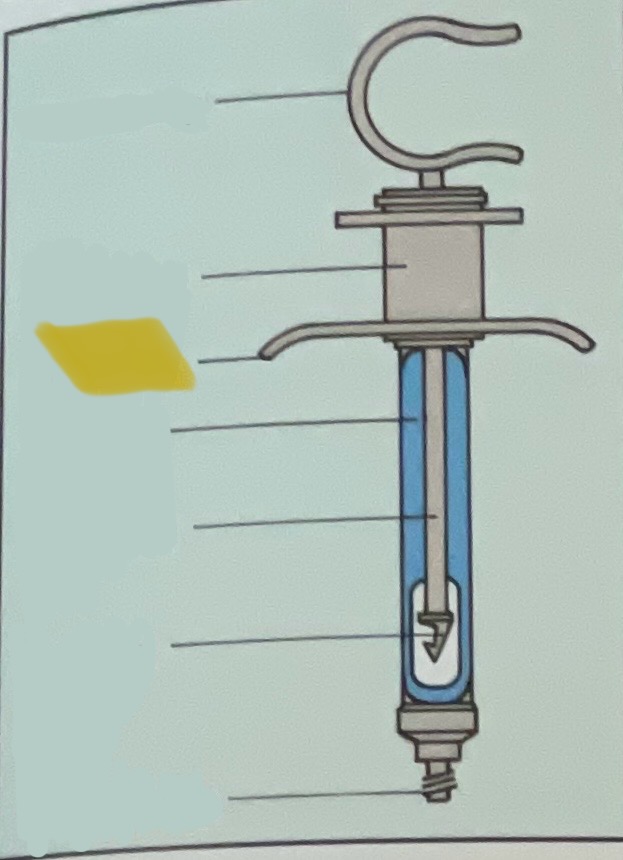
Finger bar
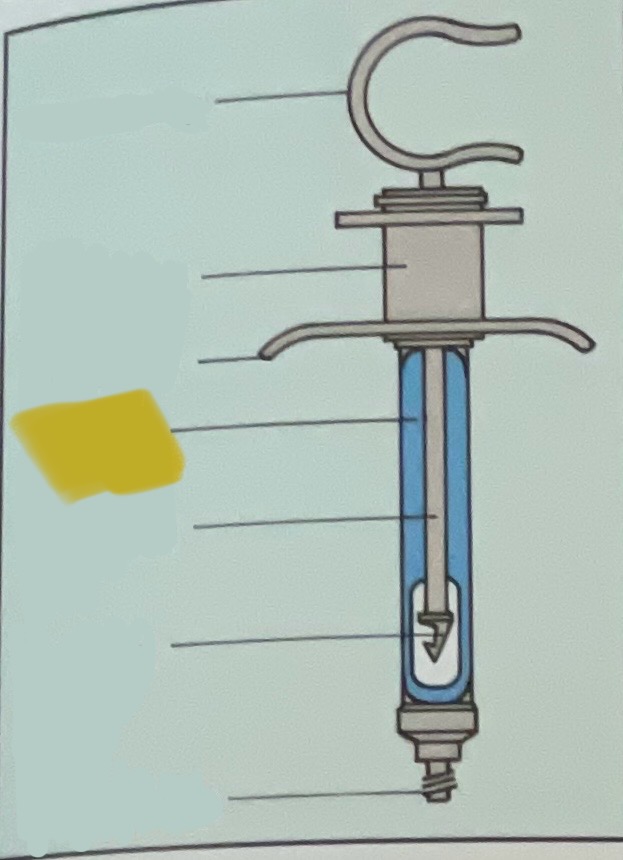
Barrel of syringe
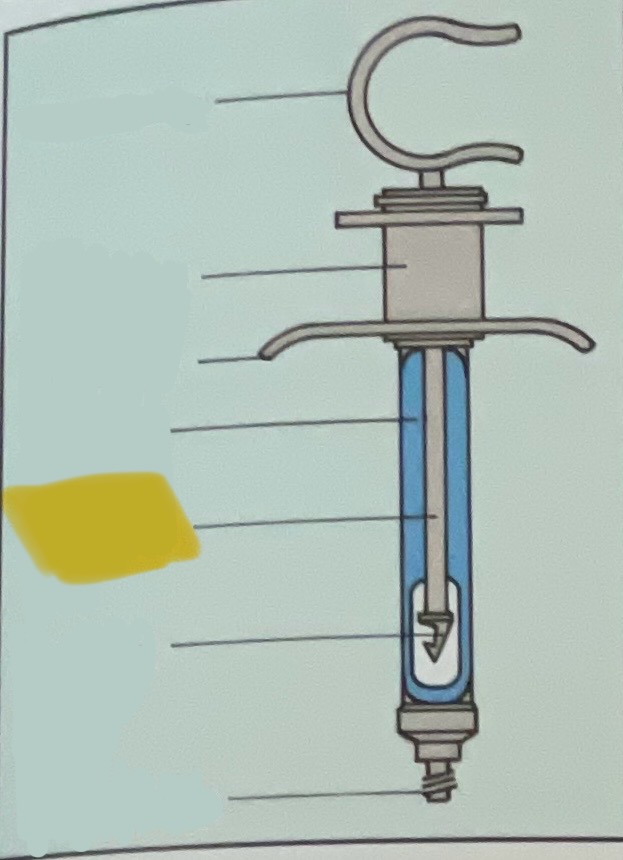
Piston rod
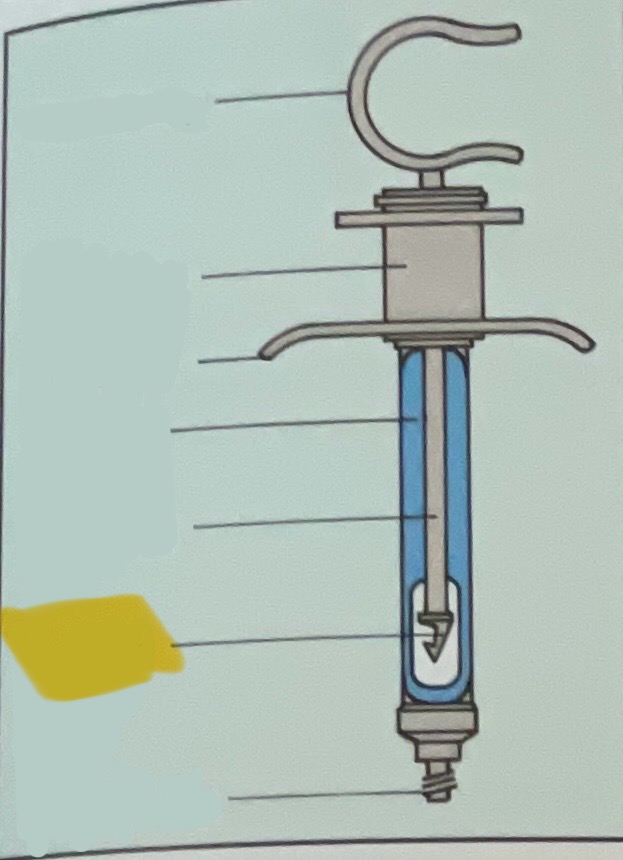
Harpoon
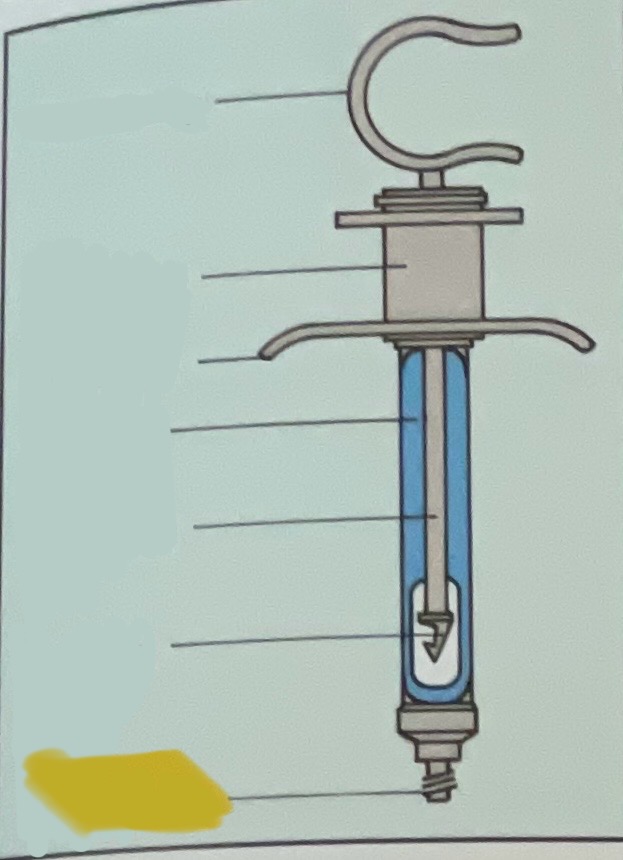
Threaded tip
What is the first step in loading an anesthetic syringe
Holding the syringe, use the thumb ring to pull back the plunger AND with the other hand, load the anesthetic cartiridge into the syringe
What is the second step in loading an anesthetic syringe
Release the thumb ring and allow the harpoon to engage into the stopper, AND to ensure that the cartridge is in place, shake the syringe
What is the third step in loading an anesthetic syringe
Screw the needle into position on the syringe, AND make sure that it is not in sight of the patient
What does it feel like to have nitrous-oxide in your body
Aka laughing gas (inhaled through the nose)
Patient will feel relaxed and help eliminate fear
Mildly sedative
What drug is most frequently used in an medical emergency
Oxygen (O2)
When should a lead apron and thyroid collar be used
During dental x-rays (or any situation involving high radiation exposure)
What is a lead collimator
Used for x-ray machines
Restricts/controls the size and shape of the x-ray beam as it leaves the tube head
What are potential hazards to radiation exposure
Tissue damage
Biologic effects
Ionization
Cumulative effects
Acute and chronic radiation exposure
Genetic and somatic effects
Critical organs
How to store a lead apron
Hanging them on a wall mounted rack (or regular rack meant for lead aprons)